Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2015 Nov;7(6):557-564. 10.4168/aair.2015.7.6.557.
Toxoplasma gondii Infection Suppresses House Dust Mite Extract-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in NC/Nga Mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Malaria & Parasitic Disease, Korea National Institute of Health, Cheongwon-gun, Chungbuk, Korea. ondalgl@korea.kr
- KMID: 2130262
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2015.7.6.557
Abstract
- PURPOSE
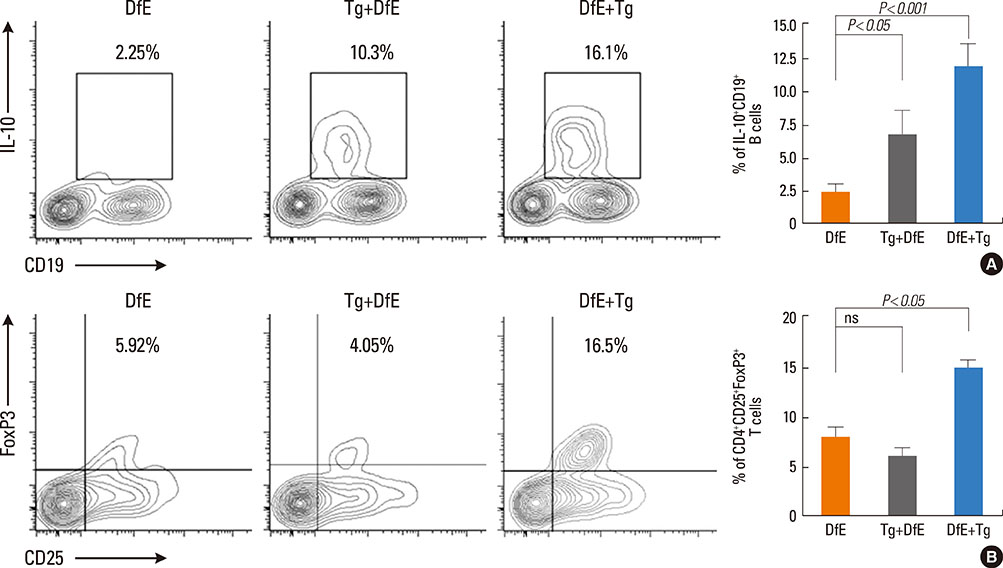
Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii) is an obligate intracellular protozoan parasite that infects humans and animals via congenital or postnatal routes, and it is found worldwide. Modulation of the immune system by parasite infection is proposed to suppress allergic inflammation. Growing evidences have shown that interleukin (IL)-10-producing regulatory B cells (B(regs)) and CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells (T(regs)) induced by parasite infection play a critical role in allergic or autoimmune diseases because these cells regulate negatively cellular immune responses and inflammation. Currently, the role of IL-10-producing regulatory B cells in host immune response during T. gondii infection is unknown. In this study, we investigate whether T. gondii infection can suppress the development of unrelated atopic dermatitis (AD)-like lesions.
METHODS
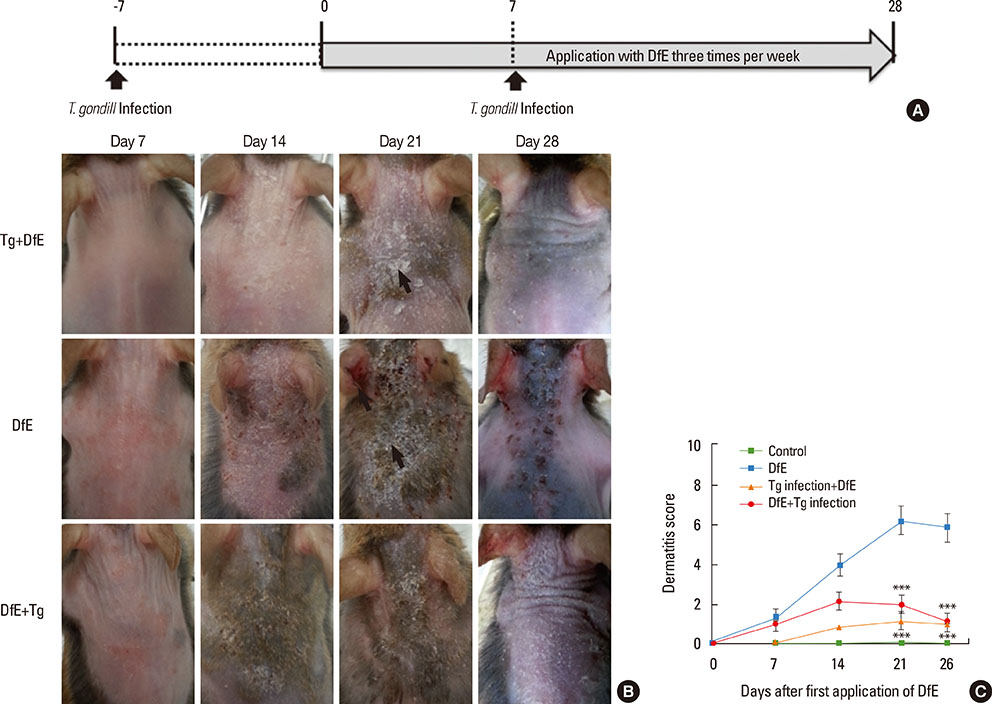
AD is a chronically relapsing inflammatory skin disease accompanied by severe itching; for this, we used NC/Nga mice, a well-known experimental model of systemic AD. Repeated exposure to Dermatophagoides farinae crude extract (DfE), known as a major environmental allergen, evokes AD-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice under specific pathogen-free conditions. NC/Nga mice were intraperitoneally infected with 10 cysts of T. gondii.
RESULTS
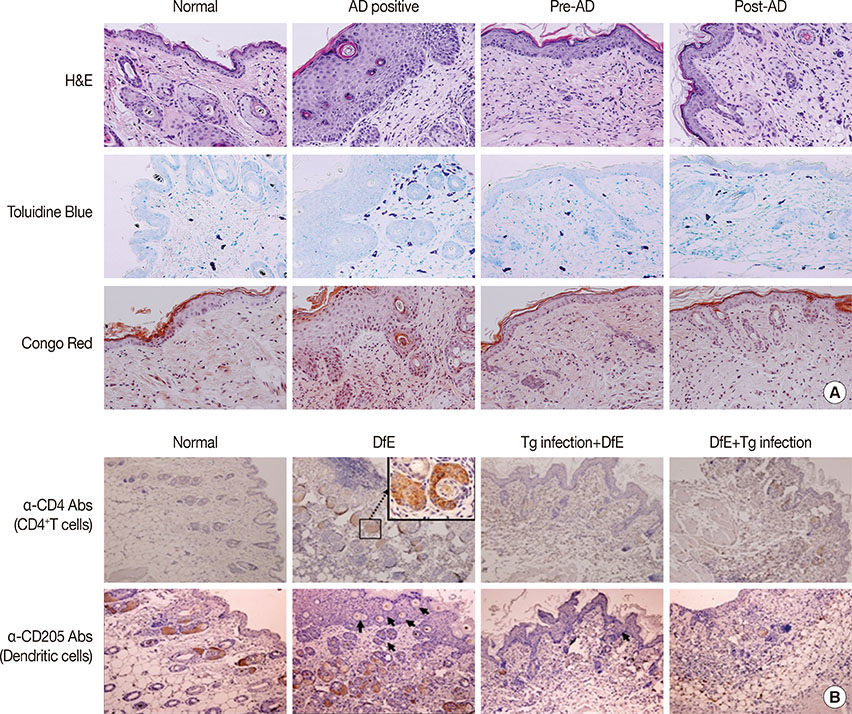
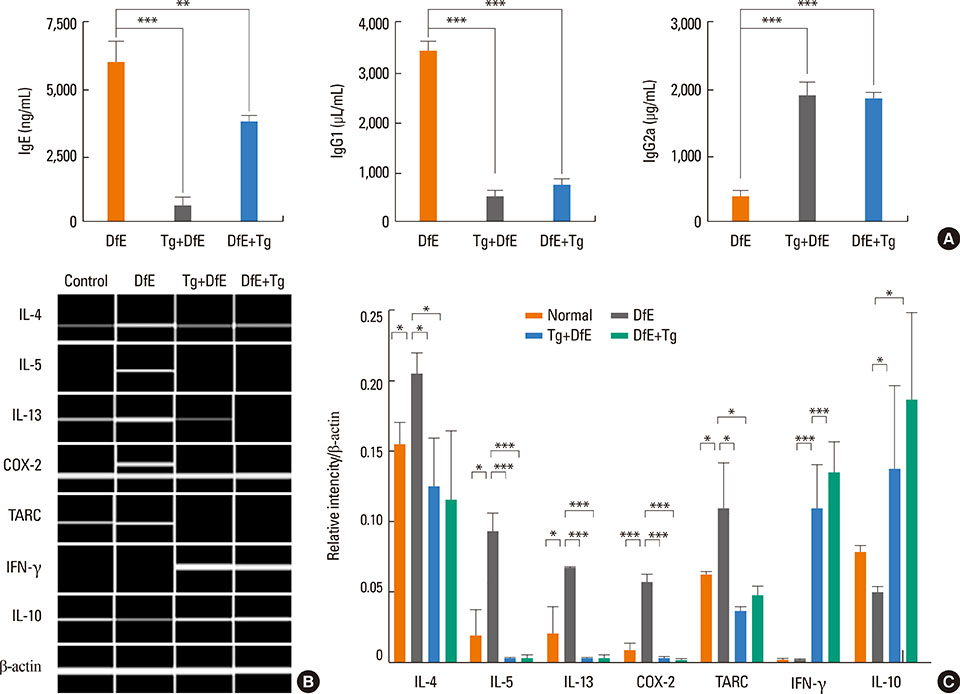
T. gondii infection significantly ameliorated AD-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. The subpopulation of B(regs) and T(regs) in the AD mice was expanded in the course of T. gondii infection. In addition, T. gondii infection inhibited Th2 and enhanced Th1 immune response in the DfE-treated AD mice.
CONCLUSIONS
We have experimentally demonstrated for the first time that T. gondii infection ameliorated AD-like skin lesions in a mouse model of AD. Our study could in part explain the mechanisms of how parasite infection prevents the development of allergic disorder. Therefore, these immunemechanisms induced by T. gondii infection may be beneficial for the host in terms of reduced risk of allergic immune reactions.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Asher MI, Montefort S, Björkstén B, Lai CK, Strachan DP, Weiland SK, et al. Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC Phases One and Three repeat multicountry cross-sectional surveys. Lancet. 2006; 368:733–743.2. Ring J, Krämer U, Schäfer T, Behrendt H. Why are allergies increasing? Curr Opin Immunol. 2001; 13:701–708.3. Wills-Karp M, Santeliz J, Karp CL. The germless theory of allergic disease: revisiting the hygiene hypothesis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2001; 1:69–75.4. Gereda JE, Leung DY, Thatayatikom A, Streib JE, Price MR, Klinnert MD, et al. Relation between house-dust endotoxin exposure, type 1 T-cell development, and allergen sensitisation in infants at high risk of asthma. Lancet. 2000; 355:1680–1683.5. Garn H, Renz H. Epidemiological and immunological evidence for the hygiene hypothesis. Immunobiology. 2007; 212:441–452.6. Amu S, Saunders SP, Kronenberg M, Mangan NE, Atzberger A, Fallon PG. Regulatory B cells prevent and reverse allergic airway inflammation via FoxP3-positive T regulatory cells in a murine model. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:1114–1124.e8.7. Jeong YI, Kim SH, Ju JW, Cho SH, Lee WJ, Park JW, et al. Clonorchis sinensis-derived total protein attenuates airway inflammation in murine asthma model by inducing regulatory T cells and modulating dendritic cell functions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011; 407:793–800.8. Jeong YI, Kim YJ, Ju JW, Hong SH, Lee MR, Cho SH, et al. Identification of anti-allergic effect of Clonorchis sinensis-derived protein venom allergen-like proteins (CsVAL). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014; 445:549–555.9. Ronet C, Hauyon-La Torre Y, Revaz-Breton M, Mastelic B, Tacchini-Cottier F, Louis J, et al. Regulatory B cells shape the development of Th2 immune responses in BALB/c mice infected with Leishmania major through IL-10 production. J Immunol. 2010; 184:886–894.10. Wilson MS, Taylor MD, Balic A, Finney CA, Lamb JR, Maizels RM. Suppression of allergic airway inflammation by helminth-induced regulatory T cells. J Exp Med. 2005; 202:1199–1212.11. Kishi C, Amano H, Suzue K, Ishikawa O. Plasmodium berghei infection ameliorates atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. Allergy. 2014; 69:1412–1419.12. Zaccone P, Fehervari Z, Phillips JM, Dunne DW, Cooke A. Parasitic worms and inflammatory diseases. Parasite Immunol. 2006; 28:515–523.13. Hussaarts L, van der Vlugt LE, Yazdanbakhsh M, Smits HH. Regulatory B-cell induction by helminths: implications for allergic disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 128:733–739.14. Taylor MD, van der Werf N, Maizels RM. T cells in helminth infection: the regulators and the regulated. Trends Immunol. 2012; 33:181–189.15. Gordon S, Martinez FO. Alternative activation of macrophages: mechanism and functions. Immunity. 2010; 32:593–604.16. Mizoguchi A, Mizoguchi E, Takedatsu H, Blumberg RS, Bhan AK. Chronic intestinal inflammatory condition generates IL-10-producing regulatory B cell subset characterized by CD1d upregulation. Immunity. 2002; 16:219–230.17. Fillatreau S, Sweenie CH, McGeachy MJ, Gray D, Anderton SM. B cells regulate autoimmunity by provision of IL-10. Nat Immunol. 2002; 3:944–950.18. Lund FE. Cytokine-producing B lymphocytes-key regulators of immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 2008; 20:332–338.19. Lee MK, Lee WY, Yong SJ, Shin KC, Lee SN, Lee SJ, et al. A case of autoimmune progesterone dermatitis misdiagnosed as allergic contact dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2011; 3:141–144.20. Noh G, Lee JH. Regulatory B cells and allergic diseases. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2011; 3:168–177.21. Jeong YI, Hong SH, Cho SH, Lee WJ, Lee SE. Induction of IL-10-producing CD1d(high)CD5+ regulatory B cells following Babesia microti-infection. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e46553.22. Wilson MS, Taylor MD, O'Gorman MT, Balic A, Barr TA, Filbey K, et al. Helminth-induced CD19+CD23hi B cells modulate experimental allergic and autoimmune inflammation. Eur J Immunol. 2010; 40:1682–1696.23. Lee JC, Hayman E, Pegram HJ, Santos E, Heller G, Sadelain M, et al. In vivo inhibition of human CD19-targeted effector T cells by natural T regulatory cells in a xenotransplant murine model of B cell malignancy. Cancer Res. 2011; 71:2871–2881.24. Velavan TP, Ojurongbe O. Regulatory T cells and parasites. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011; 2011:520940.25. Elmore SA, Jones JL, Conrad PA, Patton S, Lindsay DS, Dubey JP. Toxoplasma gondii: epidemiology, feline clinical aspects, and prevention. Trends Parasitol. 2010; 26:190–196.26. Mangan NE, Fallon RE, Smith P, van Rooijen N, McKenzie AN, Fallon PG. Helminth infection protects mice from anaphylaxis via IL-10-producing B cells. J Immunol. 2004; 173:6346–6356.27. Smits HH, Hammad H, van Nimwegen M, Soullie T, Willart MA, Lievers E, et al. Protective effect of Schistosoma mansoni infection on allergic airway inflammation depends on the intensity and chronicity of infection. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 120:932–940.28. Girgis NM, Gundra UM, Loke P. Immune regulation during helminth infections. PLoS Pathog. 2013; 9:e1003250.29. Fenoy I, Giovannoni M, Batalla E, Martin V, Frank FM, Piazzon I, et al. Toxoplasma gondii infection blocks the development of allergic airway inflammation in BALB/c mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009; 155:275–284.30. Matsuoka H, Maki N, Yoshida S, Arai M, Wang J, Oikawa Y, et al. A mouse model of the atopic eczema/dermatitis syndrome by repeated application of a crude extract of house-dust mite Dermatophagoides farinae. Allergy. 2003; 58:139–145.31. Oshio T, Sasaki Y, Funakoshi-Tago M, Aizu-Yokota E, Sonoda Y, Matsuoka H, et al. Dermatophagoides farinae extract induces severe atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice, which is effectively suppressed by the administration of tacrolimus ointment. Int Immunopharmacol. 2009; 9:403–411.32. Matsui K, Nishikawa A. Percutaneous application of peptidoglycan from Staphylococcus aureus induces an increase in mast cell numbers in the dermis of mice. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005; 35:382–387.33. Matsuda H, Watanabe N, Geba GP, Sperl J, Tsudzuki M, Hiroi J, et al. Development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesion with IgE hyperproduction in NC/Nga mice. Int Immunol. 1997; 9:461–466.34. Hirata H, Arima M, Cheng G, Honda K, Fukushima F, Yoshida N, et al. Production of TARC and MDC by naive T cells in asthmatic patients. J Clin Immunol. 2003; 23:34–45.35. Jahnz-Rozyk K, Targowski T, Paluchowska E, Owczarek W, Kucharczyk A. Serum thymus and activation-regulated chemokine, macrophage-derived chemokine and eotaxin as markers of severity of atopic dermatitis. Allergy. 2005; 60:685–688.36. Correale J, Farez M, Razzitte G. Helminth infections associated with multiple sclerosis induce regulatory B cells. Ann Neurol. 2008; 64:187–199.37. Yanaba K, Bouaziz JD, Haas KM, Poe JC, Fujimoto M, Tedder TF. A regulatory B cell subset with a unique CD1dhiCD5+ phenotype controls T cell-dependent inflammatory responses. Immunity. 2008; 28:639–650.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of the presentation of atopic dermatitis induced by trinitrochlorobenzene and house dust mite in NC/Nga mice
- Patch test and Specific IgE Concentration with House Dust Mite Antigens in Atopic Dermatitis Patients
- Correlation between House Dust Mite Allergen Concentrations in Scalp Dander and Clinical Severity of Atopic Dermatitis in Children
- Developing an Atopic Dermatitis Model and the Effects of Actinidia Extract on Dermatitis in NC/Nga Mice
- Two Cases of Atopic Dermatitis Improved by Combination Treatment of Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy and Histamine-Immunoglobulin Complex