J Adv Prosthodont.
2011 Sep;3(3):152-160. 10.4047/jap.2011.3.3.152.
Effects of the immobilization of heparin and rhPDGF-BB to titanium surfaces for the enhancement of osteoblastic functions and anti-inflammation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Pusan National University, Yangsan, Korea.
- 2Department of Prosthodontics, Institute for Clinical Dental Research, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea. swshin@korea.ac.kr
- 3Department of Orthopedic Surgery & Rare Diseases Institute, Korea University Medical Center, Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2118125
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2011.3.3.152
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was to investigate the effects of recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor (rhPDGF-BB) and heparin to titanium surfaces for enhancement of osteoblastic functions and inhibition of inflammation activity.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
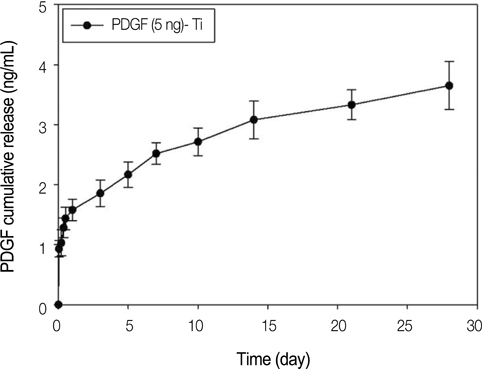
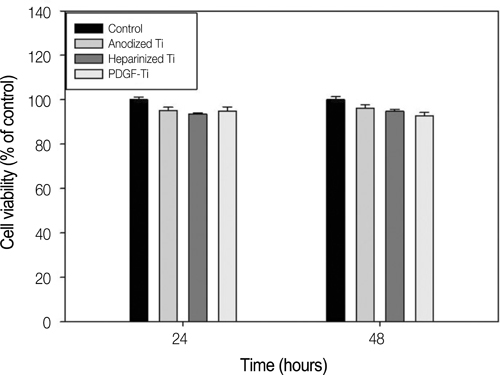
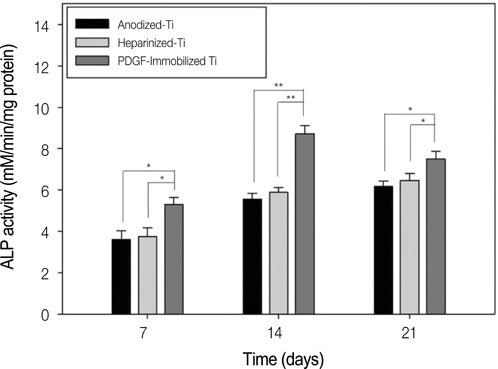
The anodized titanium discs, not coated with any material, were used as a control group. In heparinized- Ti group, dopamine was anchored to the surface of Ti substrates, and coated with heparin. In PDGF-Ti group, rhPDGF-BB was immobilized onto heparinized Ti surface. The surface morphologies were investigated by the scanning electron microscope in each group. The release kinetics of rhPDGF-BB were analyzed, and cytotoxicity tests for each group were conducted. The biocompatibilities were characterized by measuring cell proliferation, alkaline phosphatase activity, and calcium deposition using MG-63 cells. Statistical comparisons were carried out by one-way ANOVA tests. Differences were considered statistically significant at *P<.05 and **P<.001.
RESULTS
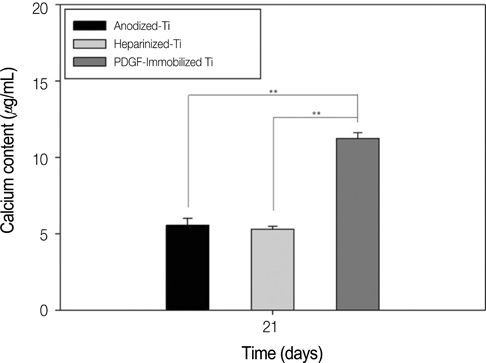
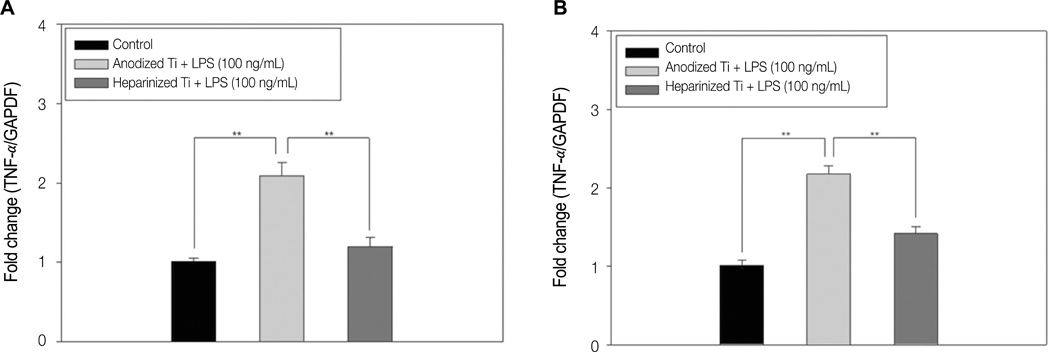
The combination of rhPDGF-BB and heparin stimulated alkaline phosphatase activity and OCN mRNA expression in osteoblastic cells (*P<.05 and **P<.001). MG-63 cells grown on PDGF-Ti had significantly higher amounts of calcium deposition than those grown on anodized Ti (**P<.001). Heparinized Ti was more anti-inflammatory compared to anodized Ti, when exposed to lipopolysaccharide using the transcript levels of TNF-alpha and IL-6 of proinflammatory cytokine (*P<.05 and **P<.001).
CONCLUSION
The result of this study demonstrated that the incorporation of rhPDGF-BB and heparin onto Ti surface enhanced osteoblastic functions and inhibited inflammation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Alkaline Phosphatase
Calcium
Cell Proliferation
Dopamine
Electrons
Heparin
Humans
Immobilization
Inflammation
Interleukin-6
Kinetics
Osteoblasts
Platelet-Derived Growth Factor
Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-sis
RNA, Messenger
Titanium
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Alkaline Phosphatase
Calcium
Dopamine
Heparin
Interleukin-6
Platelet-Derived Growth Factor
Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-sis
RNA, Messenger
Titanium
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Combined effects of rhBMP-2 and rhVEGF coated onto implants on osseointegration: pilot study
Jung-Bo Huh, Mi-Jung Yun, Chang-Mo Jeong, Sang-Wan Shin, Young-Chan Jeon
J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2013;51(2):82-89. doi: 10.4047/jkap.2013.51.2.82.
Reference
-
1. Rezania A, Healy KE. The effect of peptide surface density on mineralization of a matrix deposited by osteogenic cells. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000. 52:595–600.2. Bab I, Chorev M. Osteogenic growth peptide: from concept to drug design. Biopolymers. 2002. 66:33–48.3. Giannobile WV. Periodontal tissue engineering by growth factors. Bone. 1996. 19:23S–37S.4. Park YJ, Ku Y, Chung CP, Lee SJ. Controlled release of platelet-derived growth factor from porous poly(L-lactide) membranes for guided tissue regeneration. J Control Release. 1998. 51:201–211.5. Camelo M, Nevins ML, Schenk RK, Lynch SE, Nevins M. Periodontal regeneration in human Class II furcations using purified recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor-BB (rhPDGF-BB) with bone allograft. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2003. 23:213–225.6. Nevins ML, Camelo M, Lynch SE, Schenk RK, Nevins M. Evaluation of periodontal regeneration following grafting intrabony defects with bio-oss collagen: a human histologic report. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2003. 23:9–17.7. Nevins M, Camelo M, Nevins ML, Schenk RK, Lynch SE. Periodontal regeneration in humans using recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor-BB (rhPDGF-BB) and allogenic bone. J Periodontol. 2003. 74:1282–1292.8. Nevins M, Giannobile WV, McGuire MK, Kao RT, Mellonig JT, Hinrichs JE, McAllister BS, Murphy KS, McClain PK, Nevins ML, Paquette DW, Han TJ, Reddy MS, Lavin PT, Genco RJ, Lynch SE. Platelet-derived growth factor stimulates bone fill and rate of attachment level gain: results of a large multicenter randomized controlled trial. J Periodontol. 2005. 76:2205–2215.9. Lynch SE, de Castilla GR, Williams RC, Kiritsy CP, Howell TH, Reddy MS, Antoniades HN. The effects of short-term application of a combination of platelet-derived and insulin-like growth factors on periodontal wound healing. J Periodontol. 1991. 62:458–467.10. Lynch SE, Williams RC, Polson AM, Howell TH, Reddy MS, Zappa UE, Antoniades HN. A combination of platelet-derived and insulin-like growth factors enhances periodontal regeneration. J Clin Periodontol. 1989. 16:545–548.11. Bolander ME. Regulation of fracture repair by growth factors. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1992. 200:165–170.12. Andrew JG, Hoyland JA, Freemont AJ, Marsh DR. Platelet-derived growth factor expression in normally healing human fractures. Bone. 1995. 16:455–460.13. Fujii H, Kitazawa R, Maeda S, Mizuno K, Kitazawa S. Expression of platelet-derived growth factor proteins and their receptor alpha and beta mRNAs during fracture healing in the normal mouse. Histochem Cell Biol. 1999. 112:131–138.14. Nash TJ, Howlett CR, Martin C, Steele J, Johnson KA, Hicklin DJ. Effect of platelet-derived growth factor on tibial osteotomies in rabbits. Bone. 1994. 15:203–208.15. Mitlak BH, Finkelman RD, Hill EL, Li J, Martin B, Smith T, D'Andrea M, Antoniades HN, Lynch SE. The effect of systemically administered PDGF-BB on the rodent skeleton. J Bone Miner Res. 1996. 11:238–247.16. Sasisekharan R, Ernst S, Venkataraman G. On the regulation of fibroblast growth factor activity by heparin-like glycosaminoglycans. Angiogenesis. 1997. 1:45–54.17. Perets A, Baruch Y, Weisbuch F, Shoshany G, Neufeld G, Cohen S. Enhancing the vascularization of three-dimensional porous alginate scaffolds by incorporating controlled release basic fibroblast growth factor microspheres. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2003. 65:489–497.18. Ishibe T, Goto T, Kodama T, Miyazaki T, Kobayashi S, Takahashi T. Bone formation on apatite-coated titanium with incorporated BMP-2/heparin in vivo. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009. 108:867–875.19. Young E. The anti-inflammatory effects of heparin and related compounds. Thromb Res. 2008. 122:743–752.20. von Walter M, Herren C, Gensior TJ, Steffens GC, Hermanns-Sachweh B, Jahnen-Dechent W, Rüger M, Erli HJ. Biomimetic modification of the TiO2/glass composite Ecopore with heparinized collagen and the osteoinductive factor BMP-2. Acta Biomater. 2008. 4:997–1004.21. Kodama T, Goto T, Miyazaki T, Takahashi T. Bone formation on apatite-coated titanium incorporated with bone morphogenetic protein and heparin. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2008. 23:1013–1019.22. Kim SE, Song SH, Yun YP, Choi BJ, Kwon IK, Bae MS, Moon HJ, Kwon YD. The effect of immobilization of heparin and bone morphogenic protein-2 (BMP-2) to titanium surfaces on inflammation and osteoblast function. Biomaterials. 2011. 32:366–373.23. Clark AE, Hench LL, Paschall HA. The influence of surface chemistry on implant interface histology: a theoretical basis for implant materials selection. J Biomed Mater Res. 1976. 10:161–174.24. Puleo DA, Nanci A. Understanding and controlling the bone-implant interface. Biomaterials. 1999. 20:2311–2321.25. De Giglio E, Sabbatini L, Colucci S, Zambonin G. Synthesis, analytical characterization, and osteoblast adhesion properties on RGD-grafted polypyrrole coatings on titanium substrates. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2000. 11:1073–1083.26. Tosatti S, De Paul SM, Askendal A, Vande Vondele S, Hubbell JA, Tengvall P, Textor M. Peptide functionalized poly(L-lysine)-g-poly(ethylene glycol) on titanium: resistance to protein adsorption in full heparinized human blood plasma. Biomaterials. 2003. 24:4949–4958.27. Damsky CH. Extracellular matrix-integrin interactions in osteoblast function and tissue remodeling. Bone. 1999. 25:95–96.28. Turksen K, Bhargava U, Moe HK, Aubin JE. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies recognizing rat bone-associated molecules in vitro and in vivo. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992. 40:1339–1352.29. van den Beucken JJ, Walboomers XF, Boerman OC, Vos MR, Sommerdijk NA, Hayakawa T, Fukushima T, Okahata Y, Nolte RJ, Jansen JA. Functionalization of multilayered DNA-coatings with bone morphogenetic protein 2. J Control Release. 2006. 113:63–72.30. Hochart H, Jenkins PV, Smith OP, White B. Low molecular weight and unfractionated heparins induce a downregulation of inflammation: decreased levels of proinflammatory cytokines and nuclear factor-kappaB in LPS-stimulated human monocytes. Br J Haematol. 2006. 133:62–67.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of RHPDGF-BB and RhBMP-2 on Osseointegration of Titanium Implants at Periimplant Bone Defects Grafted with Hydroxyapatite: Micro-Ct and Histologic Analysis
- Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB-Immobilized Asymmetrically Porous Membrane for Enhanced Rotator Cuff Tendon Healing
- The effect of immobilization of heparin and bone morphogenic protein-2 to bovine bone substitute on osteoblast-like cell's function
- Anti-Oral Microbial Activity and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Rosmarinic Acid in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated MC3T3-E1 Osteoblastic Cells on a Titanium Surface
- Comparison of alkaline phosphatase activity of MC3T3-E1 cells cultured on different Ti surfaces: modified sandblasted with large grit and acid-etched (MSLA), laser-treated, and laser and acid-treated Ti surfaces