J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2005 Sep;12(3):164-173. 10.4184/jkss.2005.12.3.164.
Tissue Engineered Intervertebral Disc by Atelocollagen Scaffolds and Growth Factors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hwanlee@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Medical Engineering, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Brain Korea 21 Project Team for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1941681
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2005.12.3.164
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: In vitro experimental study.
OBJECTIVES
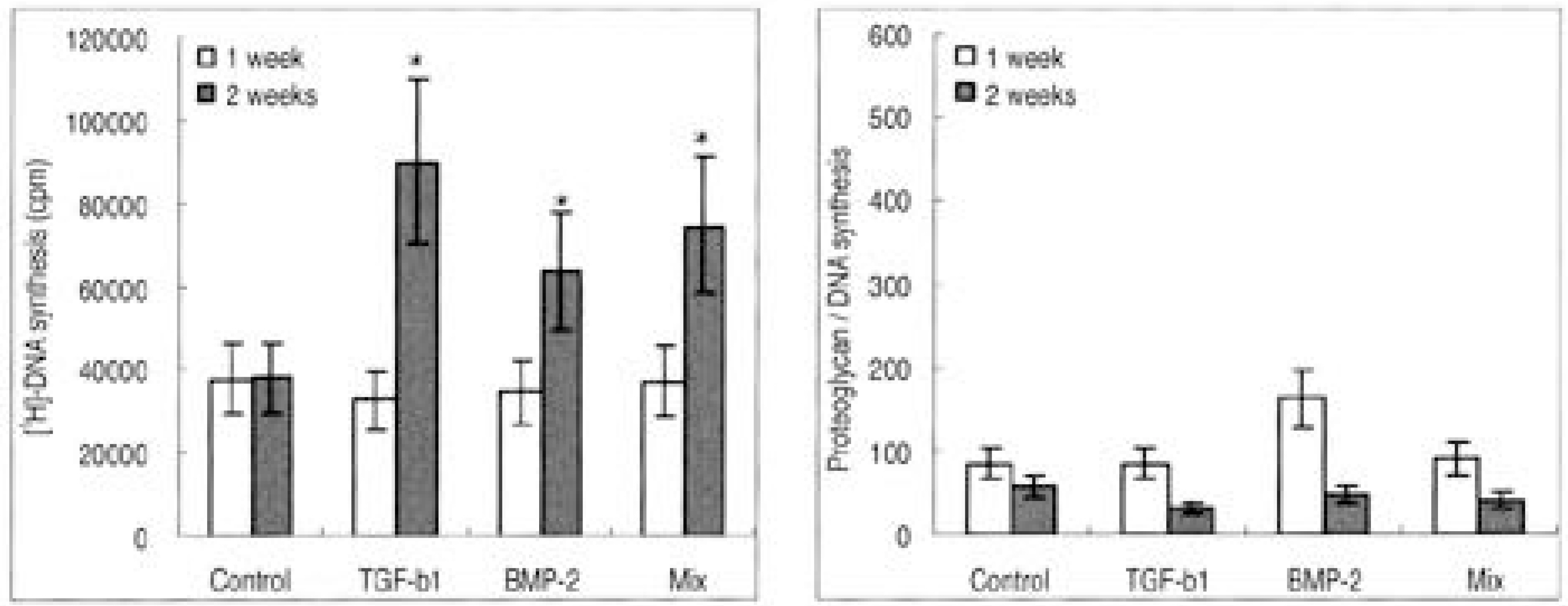
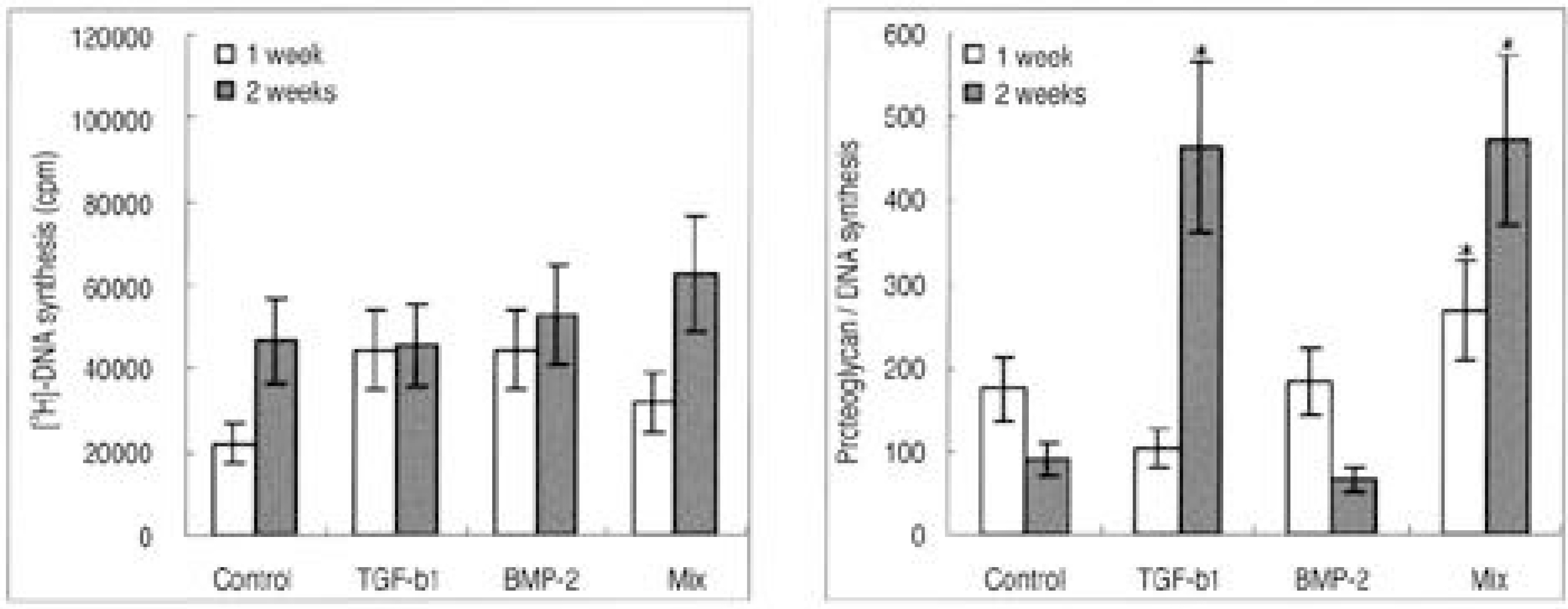
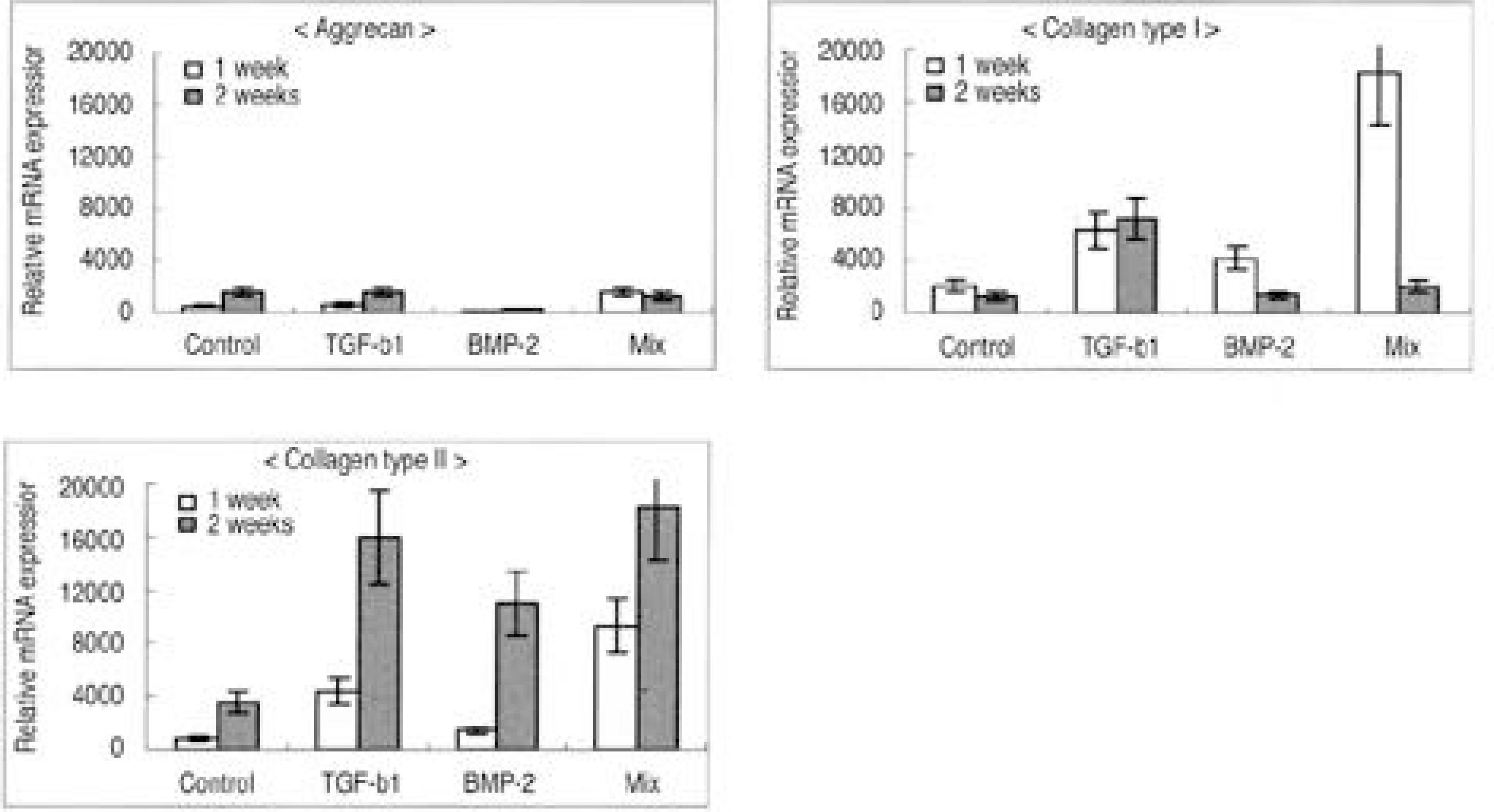
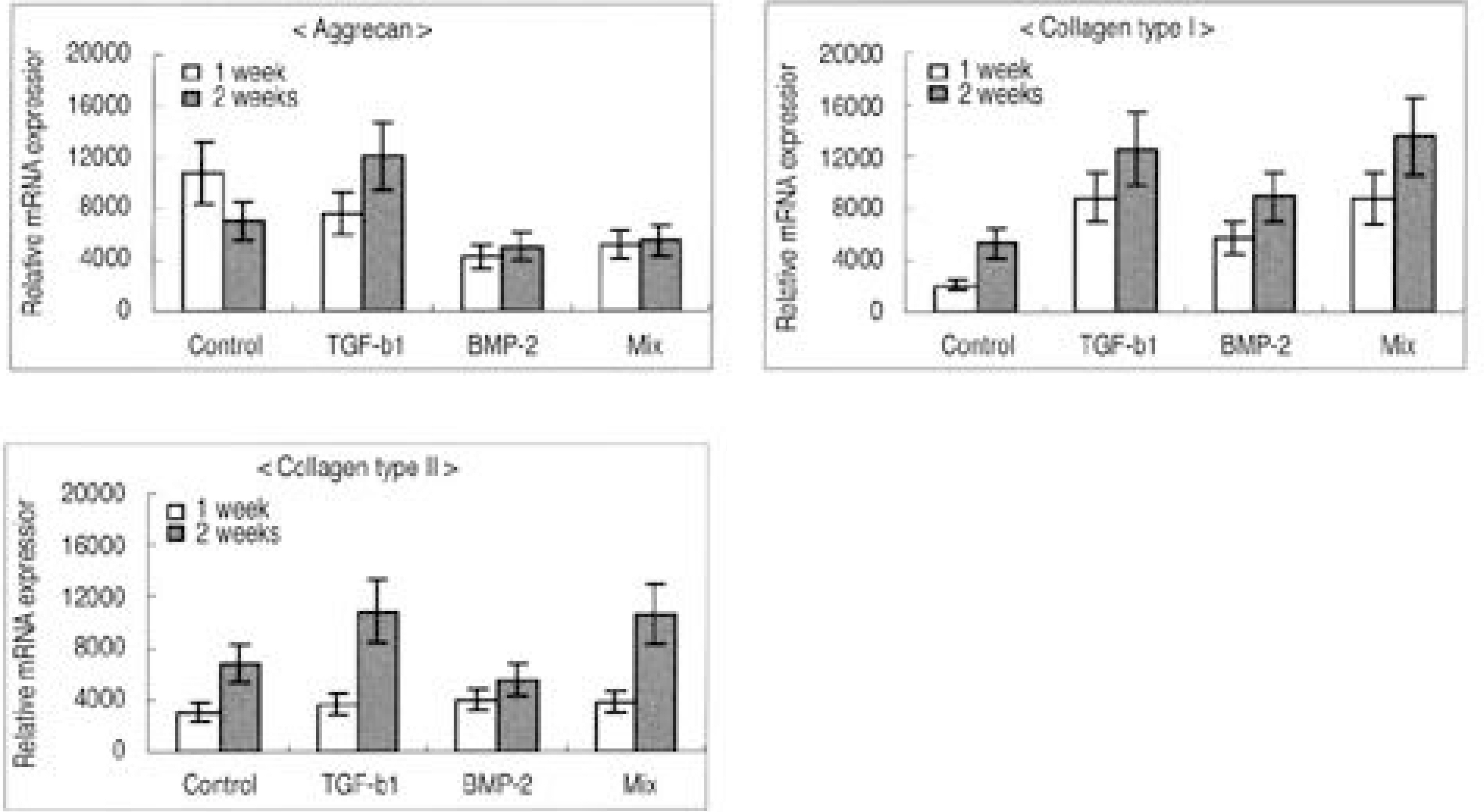
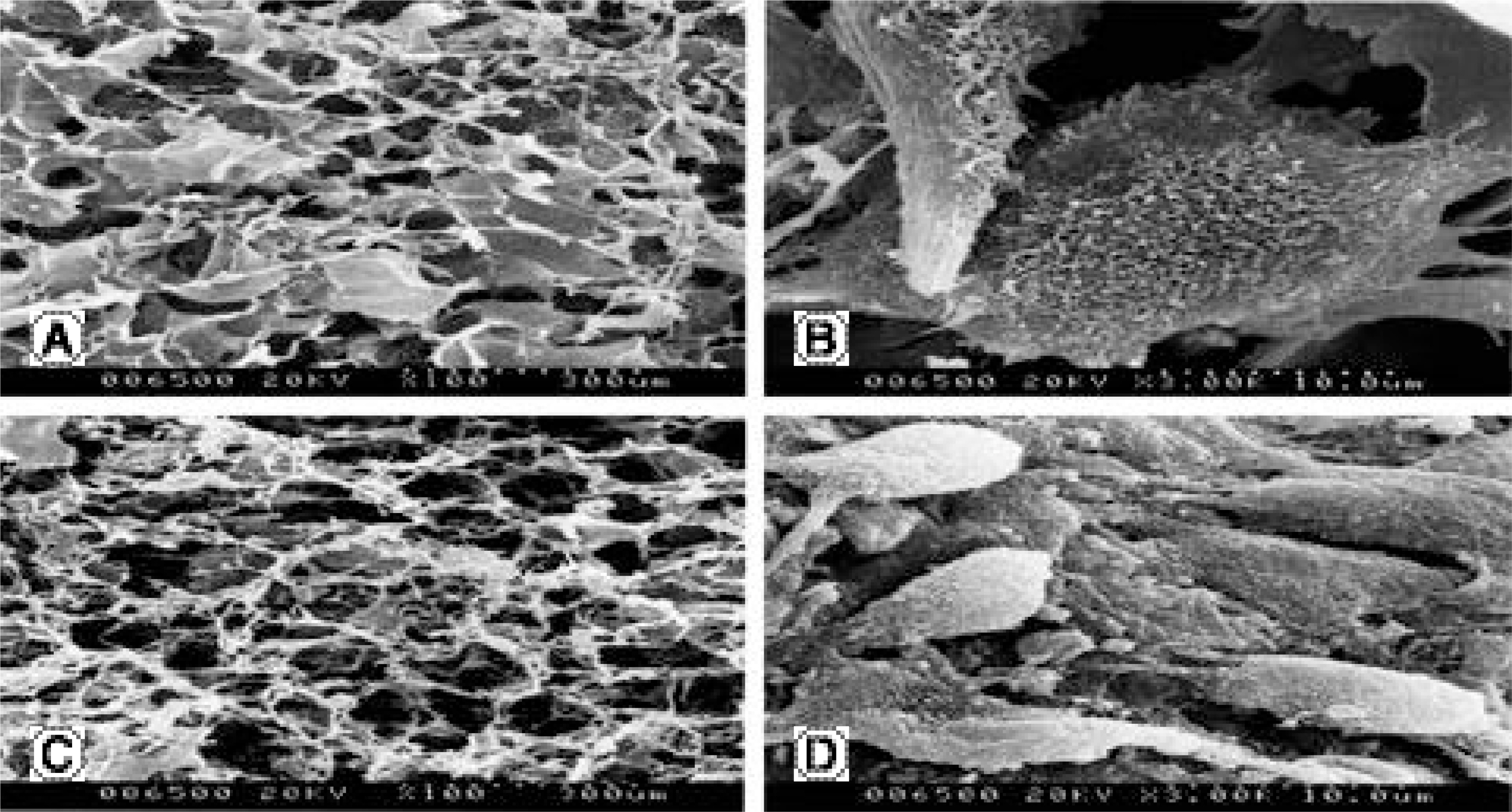
To examine the cellular proliferation, synthetic activity and phenotypical expression of intervertebral disc (IVD) cells seeded on types I and II atelocollagen scaffolds, with the stimulation of TGF-beta1 and BMP-2. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Recently, tissue engineering is regarded as a new experimental technique for the biological treatment of degenerative IVD diseases, and has been highlighted as a promising technique for the regeneration of tissues and organs in the human body. Research on cell transplantation in artificial scaffolds has provided that the conditions for tissue engineering have to be equilibrated, including the cell viability and proliferation, maintenance of characteristic phenotype, suitable scaffolds in organisms and biologically stimulated growth factor. MATERIAL AND METHOD: Lumbar IVD cells were harvested from 10 New Zealand white rabbits, with the nucleus pulposus cells isolated by sequential enzymatic digestion. Each of 1% types I and II atelocollagen dispersions were poured into a 96-well plate (diameter 5 mm), frozen at -70 degrees C, and then lyophilized at -50 degrees C. Fabricated porous collagen matrices were made using the cross-linking method. Cell suspensions were imbibed by surface tension into a scaffold consisting of atelocollagen. The cell cultured scaffolds were then treated with TGF-beta1 (10 ng/ml) or BMP-2 (100 ng/ml) or both. After 1 and 2 week culture periods, the DNA synthesis was measured by [3H] thymidine incorporation, and newly synthesized proteoglycan by incorporation of [35S] sulphate. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reactions for the mRNA expressions of type I and II collagen, aggrecan and osteocalcin were performed. The inner morphology of the scaffolds was determined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
RESULTS
The IVD cultures in collagen type II with TGF-beta1 demonstrated an increase in proteoglycan synthesis and up regulation of aggrecan and types I and II collagen mRNA expressions compared to the control. IVD cultures in the type I atelocollagen scaffold with growth factors exhibited an increase in DNA synthesis and up regulation of the type II atelocollagen mRNA expression. With all combinations of growth factor, the IVD cultures in types I and II atelocollagen scaffolds showed no up regulation of the osteocalcin mRNA expression. Furthermore, there was no synergistic effect of TGF-beta1 and BMP-2 in the matrix synthesis or for the mRNA expression of the matrix components.
CONCLUSIONS
Nucleus pulposus cells from rabbit were viable in atelocollagen types I and II atelocollagen scaffolds. The type I atelocollagen scaffold was suitable for cell proliferation, but the type II atelocollagen scaffold was more suitable for extracellular matrix synthesis. The IVD cells in both scaffolds were biologically responsive to growth factors. Taken together, nucleus pulposus cells in atelocollagen scaffolds, with anabolic growth factors, provide a mechanism for tissue engineering of IVD cells.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aggrecans
Cell Proliferation
Cell Survival
Cell Transplantation
Collagen
Collagen Type II
Digestion
DNA
Extracellular Matrix
Human Body
Intercellular Signaling Peptides and Proteins*
Intervertebral Disc*
Microscopy, Electron, Scanning
Osteocalcin
Phenotype
Proteoglycans
Rabbits
Regeneration
RNA, Messenger
Surface Tension
Suspensions
Thymidine
Tissue Engineering
Transforming Growth Factor beta1
Transplants
Up-Regulation
Aggrecans
Collagen
Collagen Type II
DNA
Intercellular Signaling Peptides and Proteins
Osteocalcin
Proteoglycans
RNA, Messenger
Suspensions
Thymidine
Transforming Growth Factor beta1
Figure
Reference
-
1). Adams P, Muir H. Qualitative changes with age of pro -teoglycans of human lumbar discs. Ann rheum Dis. 1976; 35:289–296.2). Benoist M. Natural history of the aging spine. Eur Spine J. 2003; 12:S86–S89.
Article3). Friberg S, Hirsch C. Anatomical and clinical studies on lumbar disc degeneration. Acta Orthop Scand. 1949; 19:222–242.
Article4). Guiot BH, Fessler RG. Molecular biology of degenerative disc disease. Neurosurgery. 2000; 47:1034–1040.
Article5). Lipson SJ, Muir H. Experimental intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Rheum. 1981; 24:12–21.6). Lyons G, Eisenstein SM, Sweet MB. Biochemical changes in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981; 673:443–453.
Article7). Prescher A. Anatomy and pathology of the aging spine. Eur J Radiol. 1998; 27:181–195.
Article8). Gruber HE, Hanley EN. Recent advances in disc cell biology. Spine. 2003; 28:186–193.
Article9). Mochida J. New strategies for disc repair: novel preclinical trials. J Orthop Sci. 2005; 10:112–118.
Article10). Alini M, Li W, Markovic P, Aebi M, Spiro RC, Rough-ley PJ. The potential and limitations of a cell-seeded col -lagen/hyaluronan scaffold to engineer an intervertebral disc-like matrix. Spine. 2003; 28:446–454.11). An HS, Thonar EJ, Masuda K. Biological repair of intervertebral disc. Spine. 2003; 28:S86–S92.
Article12). Vacanti JP, Langer R, Upton J, Marler JJ. Transplantation of cells in matrices for tissue regeneration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1998; 33:165–182.13). Zeltinger J, Sherwood JK, Graham DA, Mueller R, Griffith LG. Effect of pore size and void fraction on cellular adhesion, proliferation, and matrix deposition. Tissue Eng. 2001; 7:557–572.
Article14). Grunder T, Gaissmaier C, Fritz J, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-2 enhances the expression of type II collagen and aggrecan in chondrocytes embedded in alginate beads. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2004; 12:559–567.15). Kim SE, Park JH, Cho YW, et al. Porous chitosan scaffold containing microspheres loaded with transforming growth factor-β1: implications for cartilage tissue engineering. J Control Release. 2003; 91:365–374.
Article16). Moon SH, Kim DJ, Kim H, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 facilitates expression of chondrogenic, not osteogenic, phenotype of human intervertebral disc cells. Spine. 2003; 28:2679–2684.
Article17). Qi WN, Scully SP. Extracellular collagen modulates the regulation of chondrocytes by transforming growth factor-β1. J Orthod Res. 1997; 15:483–490.
Article18). Itoh H, Aso Y, Furuse M, et al. A honeycomb collagen carrier for cell culture as a tissue engineering scaffold. Artificial Organs. 2001; 25:213–217.
Article19). Sato M, Asazuma T Ishihara M, et al. An atelocollagen honeycomb-shaped scaffold with a membrane seal (ACHMS-scaffold) for the culture of annulus fibrosus cells from an intervertebral disc. J biomed Mater Res. 2003; 64A:248–256.
Article20). Sato M, Kikuchi T, Asazuma T, Yamada H, Maeda H, Fujikawa K. Glycosaminoglycan accumulation in primary culture of rabbit intervertebral disc cells. Spine. 2001; 26:2653–2660.
Article21). Sato M, Asazuma T, Ishihara M, et al. An experimental study of the regeneration of the intervertebral disc with an allograft of cultured annulus fibrosus cells using a tissue-engineering method. Spine. 2003; 28:548–553.
Article22). Park SN, Lee HJ, Lee KH, Suh H. Biological character -ization of EDC-crosslinked collagen hyaluronic acid matrix in dermal tissue restoration. Biomaterials. 2003; 24:1631–1641.23). Park SN, Kim JK, Suh H. Evaluation of antibiotic-loaded collagen-hyaluronic acid matrix as a skin substi -tute. Biomaterials. 2004; 25:3689–3698.24). Wang EA, Rosen V, D'alessandro JS, et al. Recombi -nant human bone morphogenetic protein induces bone for -mation. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1990; 87:2220–2224.25). Sakai D, Mochida J, Yamamoto Y, et al. Tran splantation of mesenchymal stem cells embedded in atelocollagen gel to the intervertebral disc: a potential therapeutic model for disc degeneration. Biomaterials. 2003; 24:3531–3541.26). Vizarova K, Bakos D, Rehakova M, et al. Modification of layered atelocollagen: enzymatic degradation and cytotoxicity evaluation. Biomaterials. 1995; 16:1217–1221.
Article27). Ochiya T, Nagahara S, Sano A, Itoh H, Terada M. Biomaterials for gene delivery: atelocollagen-mediated controlled release of molecular medicines. Curr Gene Ther. 2001; 1(1):31–52.
Article28). Sobajima S, Kim JS, Gilbertson LG, Kang JD. Gene therapy for degenerative disc disease. Gene Ther. 2004; 11:390–401.
Article29). Moon SH, Gibertson LG, Nishida K, et al. Human inter - vertebral disc cells are genetically modifiable by aden -ovirus-mediated gene transfer. Spine. 2000; 25:2573–2579.30). Nishida K, Kang JD, Gilbertson LG, et al. Modulation of the biologic activity of the rabbit intervertebral disc by gene therapy: an in vivo study of adenovirus-mediated transfer of the human transforming growth factor β1 encoding gene. Spine. 1999; 24:2419–2425.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Tissue Engineering of the Intervertebral Disc with Cultured Nucleus Pulposus Cells Using Atelocollagen Scaffold and Gene Therapy
- Biochemical Factors of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Implications for Disc Regeneration
- Biological Effect of TGF - B 1 on Human Intervertebral Disc by Cell Culture System
- Effects of Growth Hormone on the Degenerative Changes in the Intervertebral Disc of Rabbits
- Mechanical Stimulation and Diameter of Fiber Scaffolds Affect the Differentiation of Rabbit Annulus Fibrous Stem Cells