Korean J Pain.
2010 Dec;23(4):236-241. 10.3344/kjp.2010.23.4.236.
Roles of Opioid Receptor Subtype in the Spinal Antinociception of Selective Cyclooxygenase 2 Inhibitor
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. kimwm@chonnam.ac.kr
- KMID: 1454706
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2010.23.4.236
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Selective inhibitors of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 are commonly used analgesics in various pain conditions. Although their actions are largely thought to be mediated by the blockade of prostaglandin (PG) biosynthesis, evidences suggesting endogenous opioid peptide link in spinal antinociception of COX inhibitor have been reported. We investigated the roles of opioid receptor subtypes in the spinal antinociception of selective COX-2 inhibitor.
METHODS
To examine the antinociception of a selective COX-2 inhibitor, DUP-697 was delivered through an intrathecal catheter, 10 minutes before the formalin test in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Then, the effect of intrathecal pretreatment with CTOP, naltrindole and GNTI, which are micro, delta and kappa opioid receptor antagonist, respectively, on the analgesia induced by DUP-697 was assessed.
RESULTS
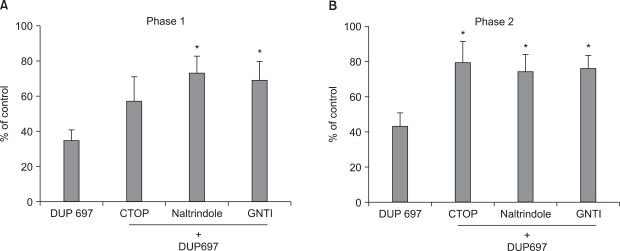
Intrathecal DUP-697 reduced the flinching response evoked by formalin injection during phase 1 and 2. Naltrindole and GNTI attenuated the antinociceptive effect of intrathecal DUP-697 during both phases of the formalin test. CTOP reversed the antinociception of DUP-697 during phase 2, but not during phase 1.
CONCLUSIONS
Intrathecal DUP-697, a selective COX-2 inhibitor, effectively relieved inflammatory pain in rats. The delta and kappa opioid receptors are involved in the activity of COX-2 inhibitor on the facilitated state as well as acute pain at the spinal level, whereas the micro opioid receptor is related only to facilitated pain.
MeSH Terms
-
Acute Pain
Aluminum Hydroxide
Analgesia
Analgesics
Animals
Carbonates
Catheters
Cyclooxygenase 2
Formaldehyde
Humans
Male
Naltrexone
Opioid Peptides
Pain Measurement
Prostaglandin-Endoperoxide Synthases
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Receptors, Opioid
Receptors, Opioid, kappa
Somatostatin
Thiophenes
Aluminum Hydroxide
Analgesics
Carbonates
Cyclooxygenase 2
Formaldehyde
Naltrexone
Opioid Peptides
Prostaglandin-Endoperoxide Synthases
Receptors, Opioid
Receptors, Opioid, kappa
Somatostatin
Thiophenes
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Roles of Serotonergic and Adrenergic Receptors in the Antinociception of Selective Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitor in the Rat Spinal Cord
Hye Jin Jeong, Seong Heon Lee, Soo Young Cho, Cha Sup Lee, Cheol Won Jeong, Myung Ha Yoon, Woong Mo Kim
Korean J Pain. 2011;24(4):179-184. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2011.24.4.179.Evaluation of the antinociceptive effects of a selection of triazine derivatives in mice
Valiollah Hajhashemi, Ghadamali Khodarahmi, Parvin Asadi, Hamed Rajabi
Korean J Pain. 2022;35(4):440-446. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2022.35.4.440.
Reference
-
1. Herrero JF, Headley PM. Reversal by naloxone of the spinal antinociceptive actions of a systemically-administered NSAID. Br J Pharmacol. 1996; 118:968–972. PMID: 8799570.
Article2. Troullos E, Hargreaves KM, Dionne RA. Ibuprofen elevates immunoreactive beta-endorphin levels in humans during surgical stress. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1997; 62:74–81. PMID: 9246021.
Article3. Michel RE, Holt JC, Domer FR. Ketorolac causes the release of methionine-enkephalin in rats. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol. 1996; 91:249–252. PMID: 8832917.4. França DS, Ferreira-Alves DL, Duarte ID, Ribeiro MC, Rezende RM, Bakhle YS, et al. Endogenous opioids mediate the hypoalgesia induced by selective inhibitors of cyclooxygenase 2 in rat paws treated with carrageenan. Neuropharmacology. 2006; 51:37–43. PMID: 16620880.
Article5. Yaksh TL, Rudy TA. Chronic catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space. Physiol Behav. 1976; 17:1031–1036. PMID: 14677603.
Article6. Choi JI, Yoo KY, Yoon MH. Effect of serotonergic receptors on the antinociception of intrathecal gabapentin in the formalin test of rats. J Korean Pain Soc. 2002; 15:19–25.7. Jones RM, Portoghese PS. 5'-Guanidinonaltrindole, a highly selective and potent kappa-opioid receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000; 396:49–52. PMID: 10822054.
Article8. Seibert K, Masferrer JL, Needleman P, Salvemini D. Pharmacological manipulation of cyclo-oxygenase-2 in the inflamed hydronephrotic kidney. Br J Pharmacol. 1996; 117:1016–1020. PMID: 8882591.
Article9. Raynor K, Kong H, Chen Y, Yasuda K, Yu L, Bell GI, et al. Pharmacological characterization of the cloned kappa-, delta-, and mu-opioid receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1994; 45:330–334. PMID: 8114680.10. Yoon MH, Kim WM, Lee HG, Kim YO, Huang LJ, An TH. Roles of opioid receptor subtypes on the antinociceptive effect of intrathecal sildenafil in the formalin test of rats. Neurosci Lett. 2008; 441:125–128. PMID: 18585861.
Article11. Puig S, Sorkin LS. Formalin-evoked activity in identified primary afferent fibers: systemic lidocaine suppresses phase-2 activity. Pain. 1996; 64:345–355. PMID: 8740613.
Article12. Nishiyama T. Analgesic effects of intrathecally administered celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, in the tail flick test and the formalin test in rats. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2006; 50:228–233. PMID: 16430547.
Article13. Domer F. Characterization of the analgesic activity of ketorolac in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990; 177:127–135. PMID: 2311674.
Article14. Pini LA, Vitale G, Ottani A, Sandrini M. Naloxone-reversible antinociception by paracetamol in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997; 280:934–940. PMID: 9023309.15. Rezende RM, Dos Reis WG, Duarte ID, Lima PP, Bakhle YS, de Francischi JN. The analgesic actions of centrally administered celecoxib are mediated by endogenous opioids. Pain. 2009; 142:94–100. PMID: 19186002.
Article16. Herrero JF, Headley PM. The effects of sham and full spinalization on the systemic potency of mu- and kappa-opioids on spinal nociceptive reflexes in rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1991; 104:166–170. PMID: 1664760.
Article17. Taiwo YO, Levine JD. Prostaglandins inhibit endogenous pain control mechanisms by blocking transmission at spinal noradrenergic synapses. J Neurosci. 1988; 8:1346–1349. PMID: 2833584.
Article18. Koetzner L, Hua XY, Lai J, Porreca F, Yaksh T. Nonopioid actions of intrathecal dynorphin evoke spinal excitatory amino acid and prostaglandin E2 release mediated by cyclooxygenase-1 and -2. J Neurosci. 2004; 24:1451–1458. PMID: 14960618.
Article19. Riley RC, Zhao ZQ, Duggan AW. Spinal release of immunoreactive dynorphin A(1-8) with the development of peripheral inflammation in the rat. Brain Res. 1996; 710:131–142. PMID: 8963652.
Article20. Iadarola MJ, Douglass J, Civelli O, Naranjo JR. Differential activation of spinal cord dynorphin and enkephalin neurons during hyperalgesia: evidence using cDNA hybridization. Brain Res. 1988; 455:205–212. PMID: 2900057.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Roles of Serotonergic and Adrenergic Receptors in the Antinociception of Selective Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitor in the Rat Spinal Cord
- Additive Antinociception between Intrathecal Sildenafil and Morphine in the Rat Formalin Test
- Differential expression of spinal γ-aminobutyric acid and opioid receptors modulates the analgesic effects of intrathecal curcumin on postoperative/inflammatory pain in rats
- Melittin-induced Nociceptive Responses are Alleviated by Cyclooxygenase-1 Inhibitor
- Effect of Intrathecal COX Inhibitors on Inflammatory Pain and c-Fos Expression in Central Nervous System Induced by Formalin Injection in Rat