Korean J Pain.
2011 Dec;24(4):179-184. 10.3344/kjp.2011.24.4.179.
Roles of Serotonergic and Adrenergic Receptors in the Antinociception of Selective Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitor in the Rat Spinal Cord
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. kimwm@chonnam.ac.kr
- KMID: 2074011
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.4.179
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The analgesic mechanisms of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 inhibitors have been explained mainly on the basis of the inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis. However, several lines of evidence suggest that their analgesic effects are mediated through serotonergic or adrenergic transmissions. We investigated the roles of these neurotransmitters in the antinociception of a selective COX-2 inhibitor at the spinal level.
METHODS
DUP-697, a selective COX-2 inhibitor, was delivered through an intrathecal catheter to male Sprague-Dawley rats to examine its effect on the flinching responses evoked by formalin injection into the hindpaw. Subsequently, the effects of intrathecal pretreatment with dihydroergocristine, prazosin, and yohimbine, which are serotonergic, alpha1 adrenergic and alpha2 adrenergic receptor antagonists, respectively, on the analgesia induced by DUP-697 were assessed.
RESULTS
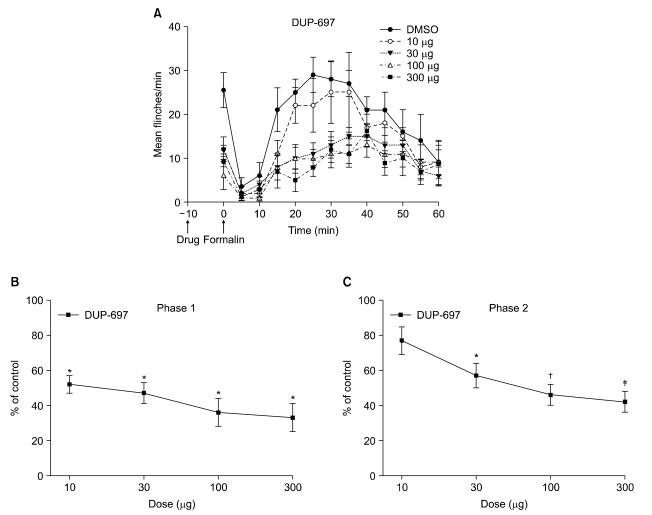
Intrathecal DUP-697 reduced the flinching response evoked by formalin injection during phase 1 and 2. But, intrathecal dihydroergocristine, prazosin, and yohimbine had little effect on the antinociception of intrathecal DUP-697 during both phases of the formalin test.
CONCLUSIONS
Intrathecal DUP-697, a selective COX-2 inhibitor, effectively relieved inflammatory pain in rats. Either the serotonergic or adrenergic transmissions might not be involved in the analgesic activity of COX-2 inhibitors at the spinal level.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adrenergic Antagonists
Analgesia
Animals
Catheters
Cyclooxygenase 2
Cyclooxygenase 2 Inhibitors
Dihydroergocristine
Formaldehyde
Humans
Male
Neurotransmitter Agents
Prazosin
Prostaglandin-Endoperoxide Synthases
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Receptors, Adrenergic
Spinal Cord
Thiophenes
Yohimbine
Adrenergic Antagonists
Cyclooxygenase 2
Cyclooxygenase 2 Inhibitors
Dihydroergocristine
Formaldehyde
Neurotransmitter Agents
Prazosin
Prostaglandin-Endoperoxide Synthases
Receptors, Adrenergic
Thiophenes
Yohimbine
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Evidence for the Participation of ATP-sensitive Potassium Channels in the Antinociceptive Effect of Curcumin
Marco Antonio De Paz-Campos, Aracely Evangelina Chávez-Piña, Mario I Ortiz, Gilberto Castañeda-Hernández
Korean J Pain. 2012;25(4):221-227. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2012.25.4.221.
Reference
-
1. Beiche F, Scheuerer S, Brune K, Geisslinger G, Goppelt-Struebe M. Up-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA in the rat spinal cord following peripheral inflammation. FEBS Lett. 1996; 390:165–169. PMID: 8706851.
Article2. Choi CH, Kim WM, Lee HG, Jeong CW, Kim CM, Lee SH, et al. Roles of opioid receptor subtype in the spinal antinociception of selective cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor. Korean J Pain. 2010; 23:236–241. PMID: 21217886.
Article3. Hamza M, Dionne RA. Mechanisms of non-opioid analgesics beyond cyclooxygenase enzyme inhibition. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2009; 2:1–14. PMID: 19779578.
Article4. Marlier L, Teilhac JR, Cerruti C, Privat A. Autoradiographic mapping of 5-HT1, 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B and 5-HT2 receptors in the rat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1991; 550:15–23. PMID: 1832328.
Article5. Hösli E, Hösli L. Evidence for the existence of alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors on neurones and glial cells of cultured rat central nervous system--an autoradiographic study. Neuroscience. 1982; 7:2873–2881. PMID: 6296724.
Article6. Fürst S. Transmitters involved in antinociception in the spinal cord. Brain Res Bull. 1999; 48:129–141. PMID: 10230704.7. Sandrini M, Vitale G, Pini LA. Effect of rofecoxib on nociception and the serotonin system in the rat brain. Inflamm Res. 2002; 51:154–159. PMID: 12005206.
Article8. Taiwo YO, Levine JD. Prostaglandins inhibit endogenous pain control mechanisms by blocking transmission at spinal noradrenergic synapses. J Neurosci. 1988; 8:1346–1349. PMID: 2833584.
Article9. Yaksh TL, Rudy TA. Chronic catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space. Physiol Behav. 1976; 17:1031–1036. PMID: 14677603.
Article10. Choi JI, Yoo KY, Yoon MH. Effect of serotonergic receptors on the antinociception of intrathecal gabapentin in the formalin test of rats. J Korean Pain Soc. 2002; 15:19–25.11. Coppi G. Dihydroergocristine. A review of pharmacology and toxicology. Arzneimittelforschung. 1992; 42:1381–1390. PMID: 1492857.12. Grognet JM, Rivière R, Istin M, Zanotti A, Coppi G. The pharmacokinetics of dihydroergocristine after intravenous and oral administration in rats. Arzneimittelforschung. 1992; 42:1394–1396. PMID: 1492859.13. Doxey JC, Roach AG, Smith CF. Studies on RX 781094: a selective, potent and specific antagonist of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1983; 78:489–505. PMID: 6132640.
Article14. Hamilton CA, Reid JL, Vincent J. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies with two alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists, doxazosin and prazosin in the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol. 1985; 86:79–87. PMID: 2864970.
Article15. Hubbard JW, Pfister SL, Biediger AM, Herzig TC, Keeton TK. The pharmacokinetic properties of yohimbine in the conscious rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988; 337:583–587. PMID: 3412496.
Article16. Yoon MH, Choi JI, Jeong SW. Spinal gabapentin and antinociception: mechanisms of action. J Korean Med Sci. 2003; 18:255–261. PMID: 12692425.
Article17. Puig S, Sorkin LS. Formalin-evoked activity in identified primary afferent fibers: systemic lidocaine suppresses phase-2 activity. Pain. 1996; 64:345–355. PMID: 8740613.
Article18. Nishiyama T. Analgesic effects of intrathecally administered celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, in the tail flick test and the formalin test in rats. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2006; 50:228–233. PMID: 16430547.
Article19. Pini LA, Vitale G, Sandrini M. Serotonin and opiate involvement in the antinociceptive effect of acetylsalicylic acid. Pharmacology. 1997; 54:84–91. PMID: 9088041.
Article20. Vitale G, Pini LA, Ottani A, Sandrini M. Effect of acetylsalicylic acid on formalin test and on serotonin system in the rat brain. Gen Pharmacol. 1998; 31:753–758. PMID: 9809474.
Article21. Courade JP, Caussade F, Martin K, Besse D, Delchambre C, Hanoun N, et al. Effects of acetaminophen on monoaminergic systems in the rat central nervous system. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2001; 364:534–537. PMID: 11770008.
Article22. Bonnefont J, Alloui A, Chapuy E, Clottes E, Eschalier A. Orally administered paracetamol does not act locally in the rat formalin test: evidence for a supraspinal, serotonin-dependent antinociceptive mechanism. Anesthesiology. 2003; 99:976–981. PMID: 14508334.
Article23. Fairbanks CA. Spinal delivery of analgesics in experimental models of pain and analgesia. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2003; 55:1007–1041. PMID: 12935942.
Article24. Xu JJ, Walla BC, Diaz MF, Fuller GN, Gutstein HB. Intermittent lumbar puncture in rats: a novel method for the experimental study of opioid tolerance. Anesth Analg. 2006; 103:714–720. PMID: 16931686.
Article25. Pinardi G, Sierralta F, Miranda HF. Interaction between the antinociceptive effect of ketoprofen and adrenergic modulatory systems. Inflammation. 2001; 25:233–239. PMID: 11580099.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Roles of Opioid Receptor Subtype in the Spinal Antinociception of Selective Cyclooxygenase 2 Inhibitor
- The Role of Adrenergic and Cholinergic Receptors on the Antinociception of Intrathecal Zaprinast in the Formalin Test of Rats
- Effect of Serotonergic Receptors on the Antinociception of Intrathecal Gabapentin in the Formalin Test of Rats
- The role of spinal adrenergic receptors on the antinociception of ginsenosides in a rat postoperative pain model
- The Role of Adrenergic and Cholinergic Receptors on the Antinociception of Korean Red Ginseng in the Spinal Cord of Rats