Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2011 Jun;15(3):149-156. 10.4196/kjpp.2011.15.3.149.
GS28 Protects Neuronal Cell Death Induced by Hydrogen Peroxide under Glutathione-Depleted Condition
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biochemistry, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 137-701, Korea. swjeong@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pharmacology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 137-701, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 137-701, Korea.
- KMID: 1448918
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2011.15.3.149
Abstract
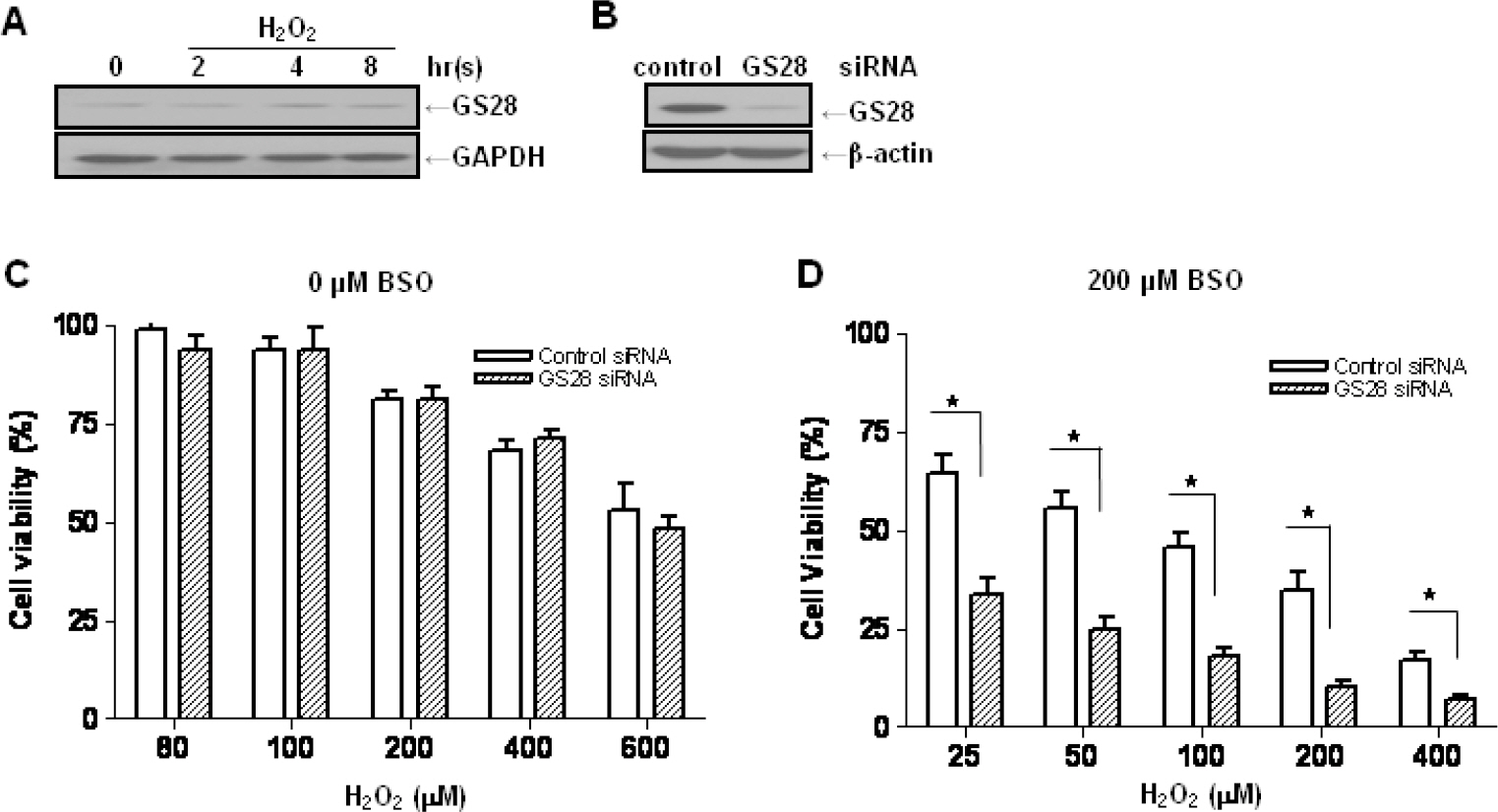
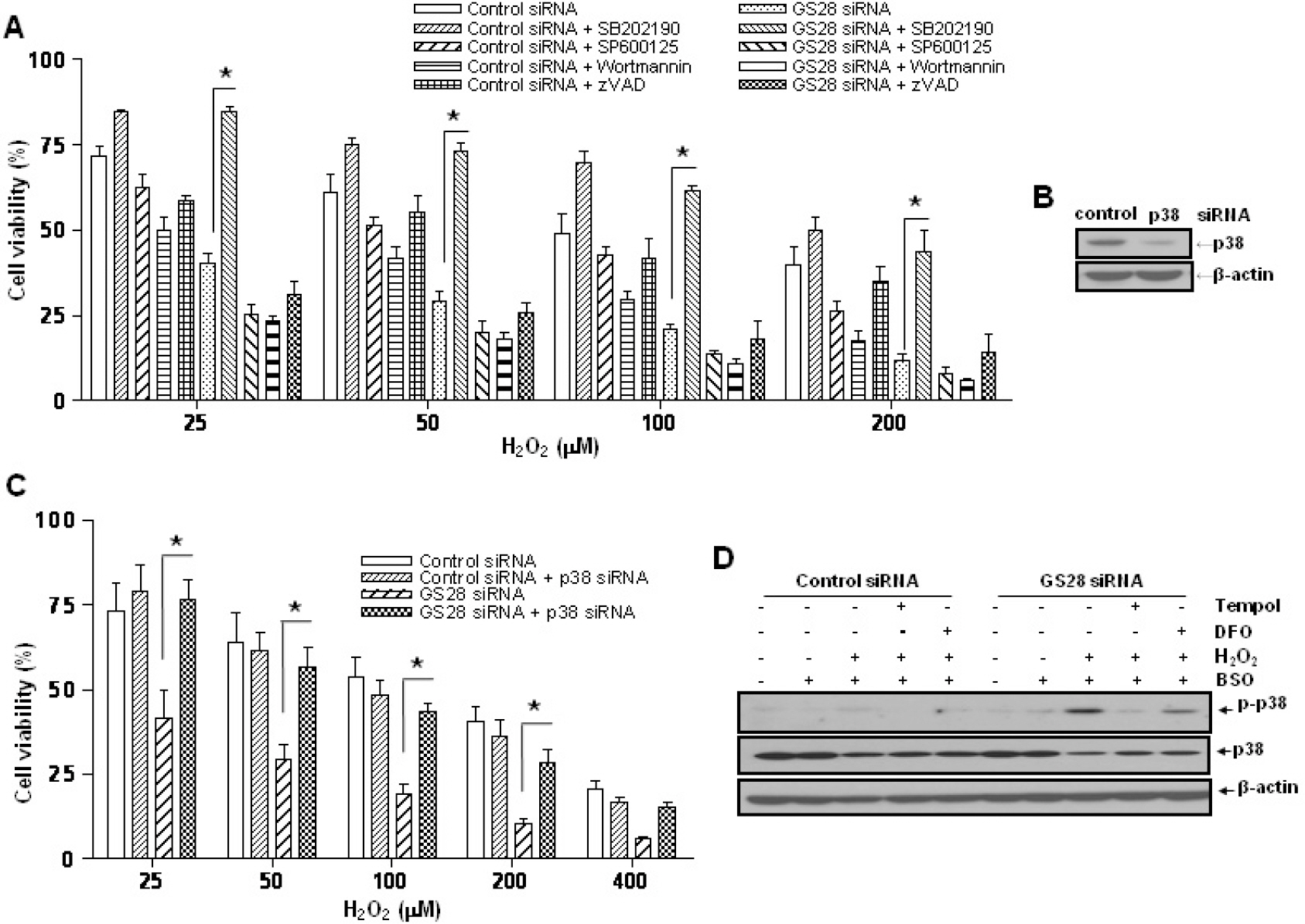
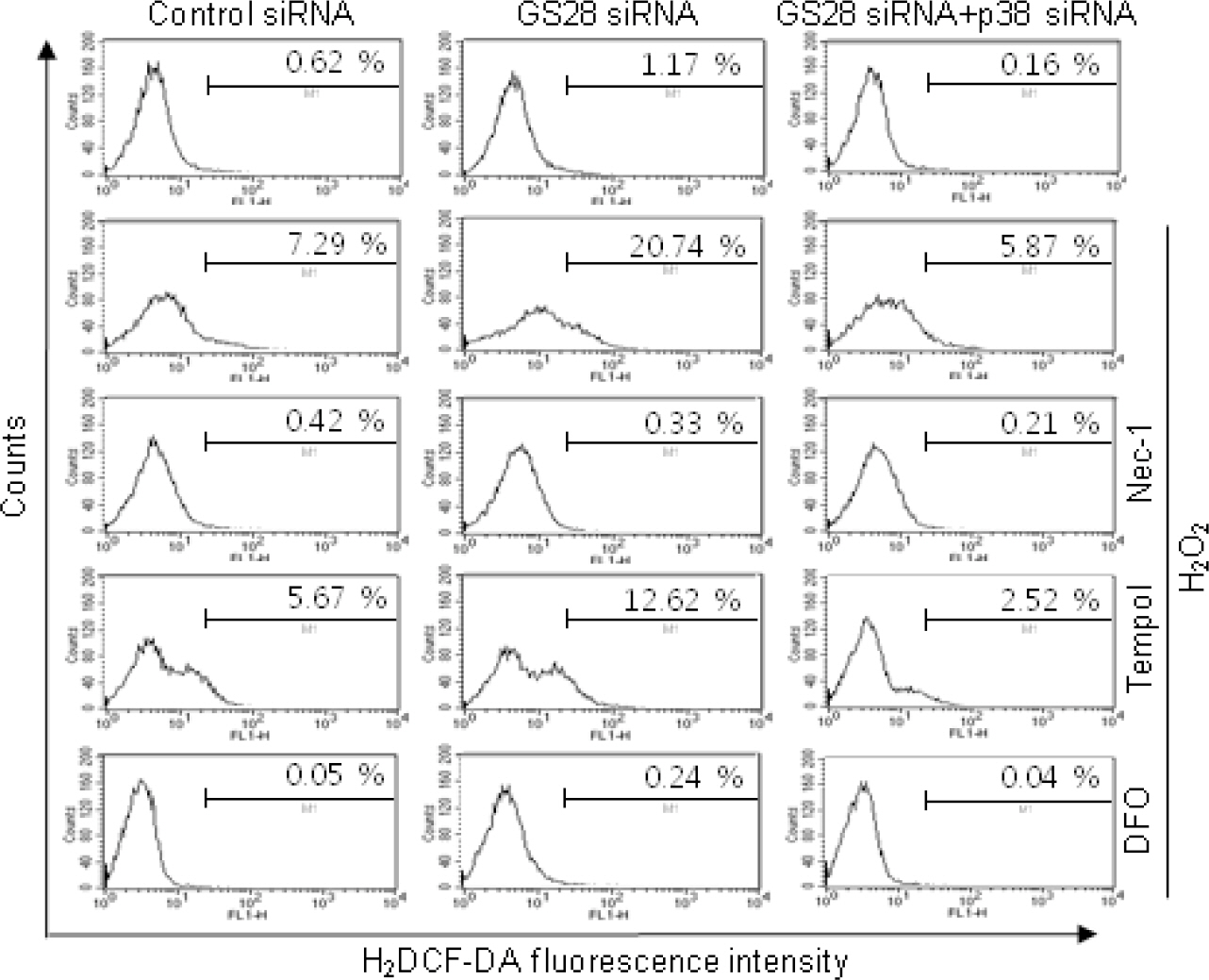
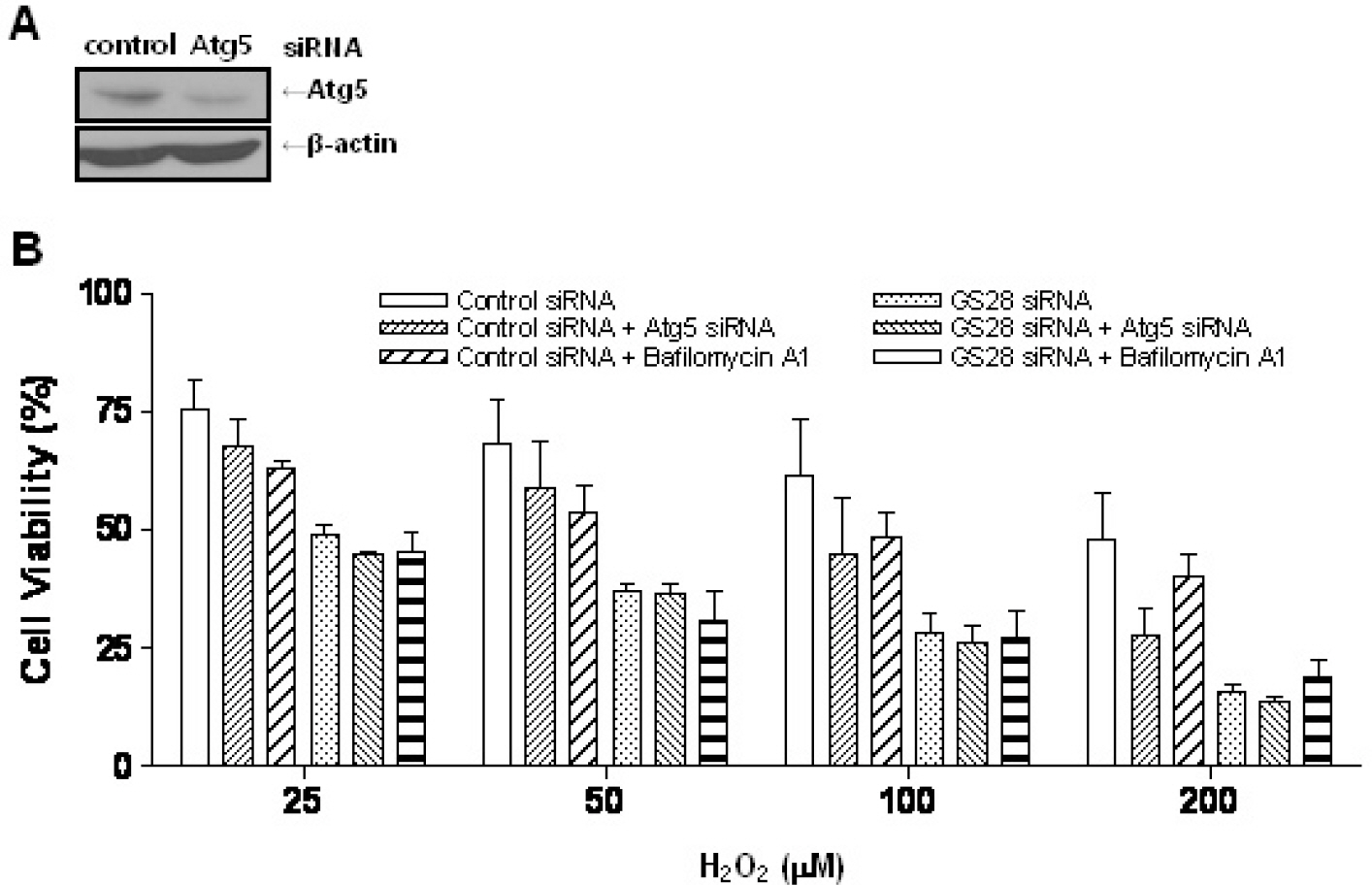
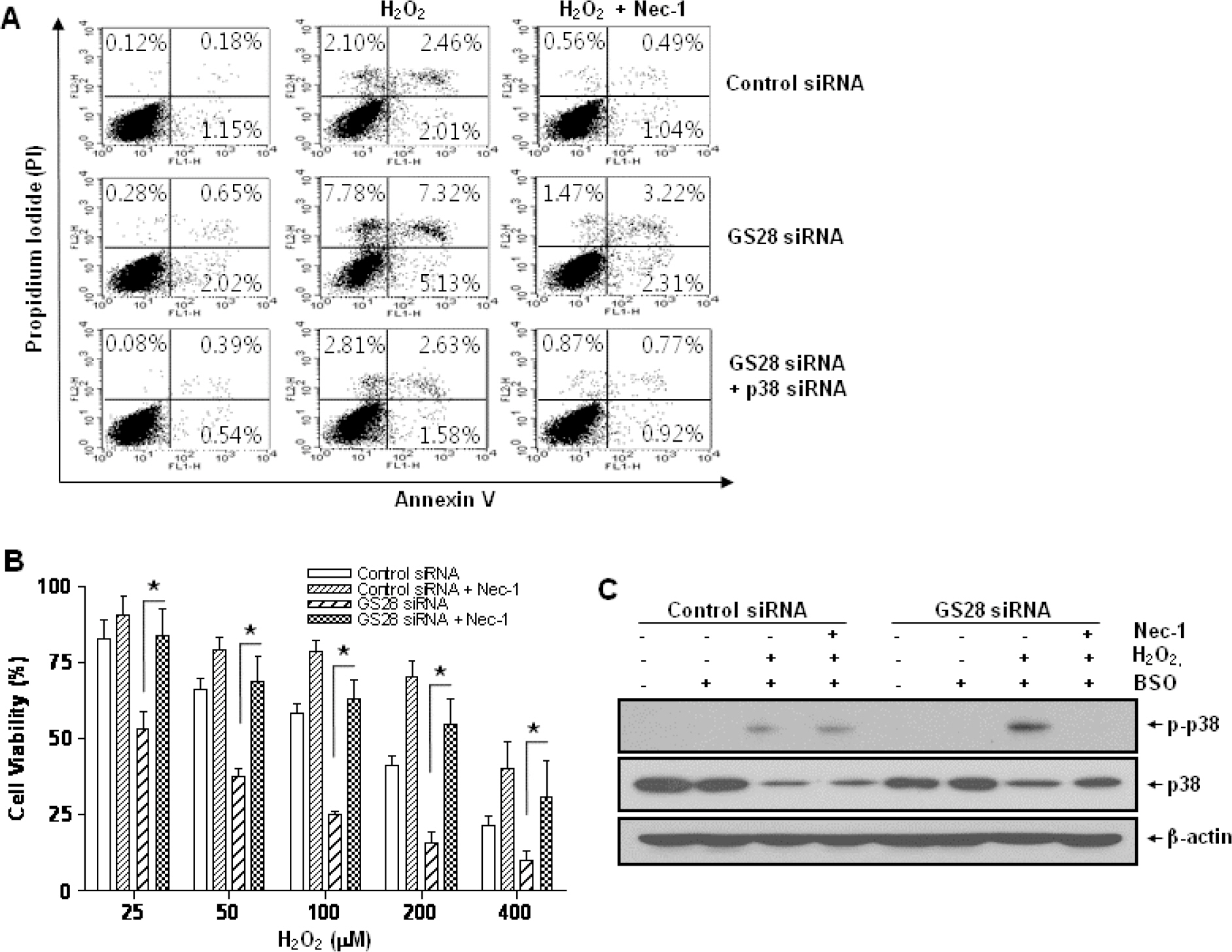
- Golgi SNAP receptor complex 1 (GS28) has been implicated in vesicular transport between intra-Golgi networks and between endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi. Additional role(s) of GS28 within cells have not been well characterized. We observed decreased expression of GS28 in rat ischemic hippocampus. In this study, we examined the role of GS28 and its molecular mechanisms in neuronal (SK-N-SH) cell death induced by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). GS28 siRNA-transfected cells treated with H2O2 showed a significant increase in cytotoxicity under glutathione (GSH)-depleted conditions after pretreatment with buthionine sulfoximine, which corresponded to an increase of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the cells. Pretreatment of GS28 siRNA-transfected cells with p38 chemical inhibitor significantly inhibited cytotoxicity; we also observed that p38 was activated in the cells by immunoblot analysis. We confirmed the role of p38 MAPK in cotransfected cells with GS28 siRNA and p38 siRNA in the cell viability assay, flow cytometry, and immunoblot. Involvement of apoptotic or autophagic processes in the cells was not shown in the cell viability, flow cytometry, and immunoblot analyses. However, pretreatment of the cells with necrostatin-1 completely inhibited H2O2-induced cytotoxicity, ROS generation, and p38 activation, indicating that the cell death is necroptotic. Collectively these data imply that H2O2 induces necroptotic cell death in the GS28 siRNA-transfected cells and that the necroptotic signals are mediated by sequential activations in RIP1/p38/ROS. Taken together, these results indicate that GS28 has a protective role in H2O2-induced necroptosis via inhibition of p38 MAPK in GSH-depleted neuronal cells.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Buthionine Sulfoximine
Cell Death
Cell Survival
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Flow Cytometry
Glutathione
Hippocampus
Hydrogen
Hydrogen Peroxide
Imidazoles
Indoles
Methionine
Neurons
p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Rats
Reactive Oxygen Species
RNA, Small Interfering
SNARE Proteins
Buthionine Sulfoximine
Glutathione
Hydrogen
Hydrogen Peroxide
Imidazoles
Indoles
Methionine
RNA, Small Interfering
Reactive Oxygen Species
SNARE Proteins
p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Protective Effect of Quercetin-3-O-β-D-Glucuronopyranoside on Ethanol-induced Damage in Cultured Feline Esophageal Epithelial Cells
Jung Hyun Cho, Sun Young Park, Ho Sung Lee, Wan Kyunn Whang, Uy Dong Sohn
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011;15(6):319-326. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2011.15.6.319.
Reference
-
References
1. Ryter SW, Kim HP, Hoetzel A, Park JW, Nakahira K, Wang X, Choi AM. Mechanisms of cell death in oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2007; 9:49–89.
Article2. Inoue M, Sato EF, Nishikawa M, Park AM, Kira Y, Imada I, Utsumi K. Mitochondrial generation of reactive oxygen species and its role in aerobic life. Curr Med Chem. 2003; 10:2495–2505.
Article3. Reiter RJ. Oxidative processes and antioxidative defense mechanisms in the aging brain. FASEB J. 1995; 9:526–533.4. Schafer FQ, Buettner GR. Redox environment of the cell as viewed through the redox state of the glutathione disulfide/glutathione couple. Free Radic Biol Med. 2001; 30:1191–1212.
Article5. Martindale JL, Holbrook NJ. Cellular response to oxidative stress: signaling for suicide and survival. J Cell Physiol. 2002; 192:1–15.
Article6. Kim KC, Lee C. Curcumin induces downregulation of E2F4 expression and apoptotic cell death in HCT116 human colon cancer cells; involvement of reactive oxygen species. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010; 14:391–397.
Article7. Kitanaka C, Kuchino Y. Caspase-independent programmed cell death with necrotic morphology. Cell Death Differ. 1999; 6:508–515.
Article8. Degterev A, Huang Z, Boyce M, Li Y, Jagtap P, Mizushima N, Cuny GD, Mitchison TJ, Moskowitz MA, Yuan J. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol. 2005; 1:112–119.
Article9. Azad MB, Chen Y, Gibson SB. Regulation of autophagy by reactive oxygen species (ROS): implications for cancer progression and treatment. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009; 11:777–790.
Article10. Son MJ, Lee SB, Byun YJ, Lee HO, Kim HS, Kwon OJ, Jeong SW. Sodium nitroprusside induces autophagic cell death in glutathione-depleted osteoblasts. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2010; 24:313–322.
Article11. Jang H, Choi SY, Cho EJ, Youn HD. Cabin1 restrains p53 activity on chromatin. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009; 16:910–915.
Article12. Kim SY, Lee MY, Cho KC, Choi YS, Choi JS, Sung KW, Kwon OJ, Kim HS, Kim IK, Jeong SW. Alterations in mRNA expression of ribosomal protein S9 in hydrogen peroxide-treated neurotumor cells and in rat hippocampus after transient ischemia. Neurochem Res. 2003; 28:925–931.13. Bains JS, Shaw CA. Neurodegenerative disorders in humans: the role of glutathione in oxidative stress-mediated neuronal death. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1997; 25:335–358.
Article14. Peuchen S, Bolaños JP, Heales SJ, Almeida A, Duchen MR, Clark JB. Interrelationships between astrocyte function, oxidative stress and antioxidant status within the central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1997; 52:261–281.
Article15. Lang CA, Naryshkin S, Schneider DL, Mills BJ, Lindeman RD. Low blood glutathione levels in healthy aging adults. J Lab Clin Med. 1992; 120:720–725.16. Byun YJ, Kim SK, Kim YM, Chae GT, Jeong SW, Lee SB. Hydrogen peroxide induces autophagic cell death in C6 glioma cells via BNIP3-mediated suppression of the mTOR pathway. Neurosci Lett. 2009; 461:131–135.
Article17. Zhang T, Hong W. Ykt6 forms a SNARE complex with syntaxin 5, GS28, and Bet1 and participates in a late stage in endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi transport. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:27480–27487.
Article18. Maekawa M, Inoue T, Kobuna H, Nishimura T, Gengyo-Ando K, Mitani S, Arai H. Functional analysis of GS28, an intra-Golgi SNARE, in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genes Cells. 2009; 14:1003–1013.19. Lewén A, Matz P, Chan PH. Free radical pathways in CNS injury. J Neurotrauma. 2000; 17:871–890.20. Vandenabeele P, Galluzzi L, Vanden Berghe T, Kroemer G. Molecular mechanisms of necroptosis: an ordered cellular explosion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010; 11:700–714.
Article21. Rosenbaum DM, Degterev A, David J, Rosenbaum PS, Roth S, Grotta JC, Cuny GD, Yuan J, Savitz SI. Necroptosis, a novel form of caspase-independent cell death, contributes to neuronal damage in a retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury model. J Neurosci Res. 2010; 88:1569–1576.
Article22. Berghe TV, Vanlangenakker N, Parthoens E, Deckers W, Devos M, Festjens N, Guerin CJ, Brunk UT, Declercq W, Vandenabeele P. Necroptosis, necrosis and secondary necrosis converge on similar cellular disintegration features. Cell Death Differ. 2010; 17:922–930.
Article23. Ji D, Kamalden TA, del Olmo-Aguado S, Osborne NN. Light- and sodium azide-induced death of RGC-5 cells in culture occurs via different mechanisms. Apoptosis. 2011; 16:425–437.
Article24. Asare N, Låg M, Lagadic-Gossmann D, Rissel M, Schwarze P, Holme JA. 3-Nitrofluoranthene (3-NF) but not 3-aminofluoranthene (3-AF) elicits apoptosis as well as programmed necrosis in Hepa1c1c7 cells. Toxicology. 2009; 255:140–150.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Neuroprotective Effects of Methanol Extracts of Jeju Native Plants on Hydrogen Peroxide-induced Cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Human Neuroblastoma Cells
- Effects of Glutathione on Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Cytotoxicity in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cell Line
- Glutathione Protects Brain Endothelial Cells from Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Stress by Increasing Nrf2 Expression
- Cyclosporin A aggravates hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death in kidney proximal tubule epithelial cells
- Glutamine Deprivation Causes Hydrogen Peroxide-induced Interleukin-8 Expression via Jak1/Stat3 Activation in Gastric Epithelial AGS Cells