J Korean Med Sci.
2012 Jun;27(6):644-652. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.6.644.
Bisphenol A Impairs Mitochondrial Function in the Liver at Doses below the No Observed Adverse Effect Level
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yjparkmd@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 1421617
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.6.644
Abstract
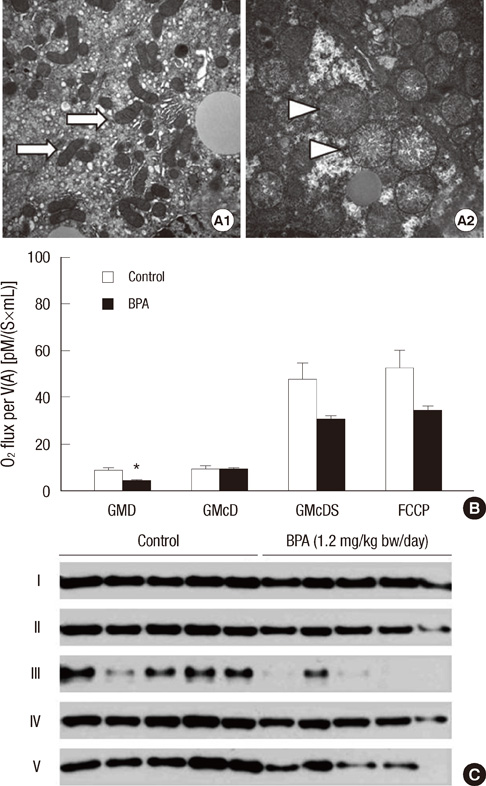
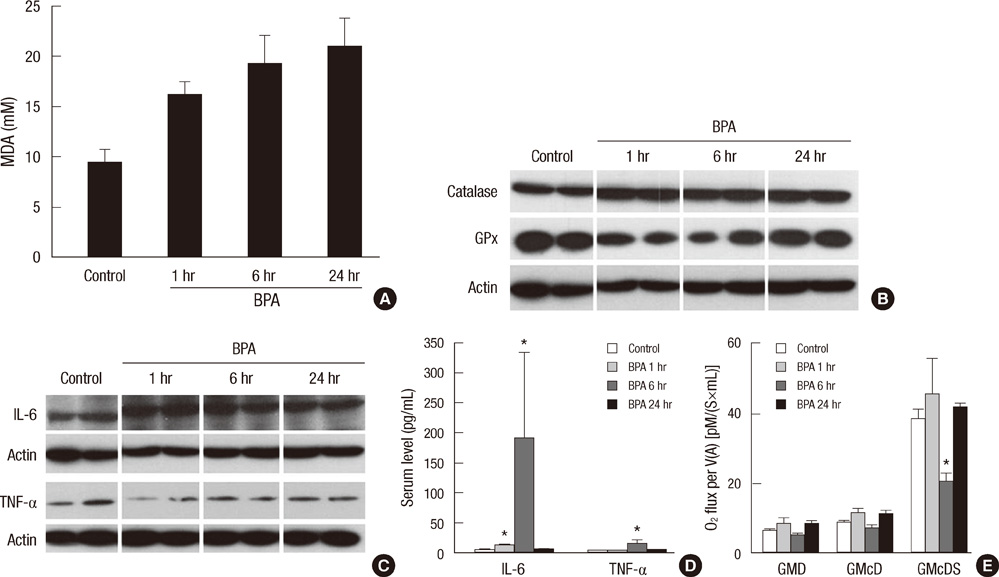
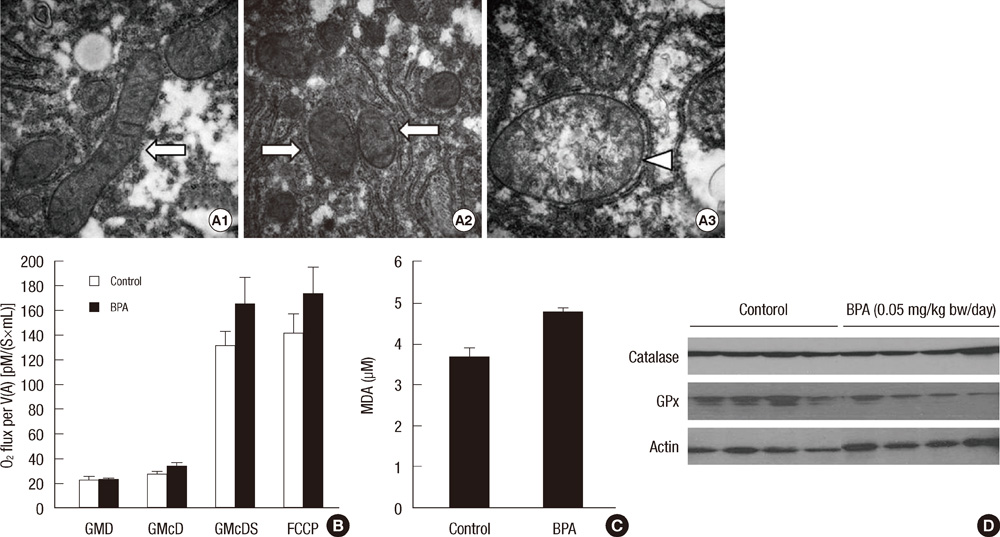
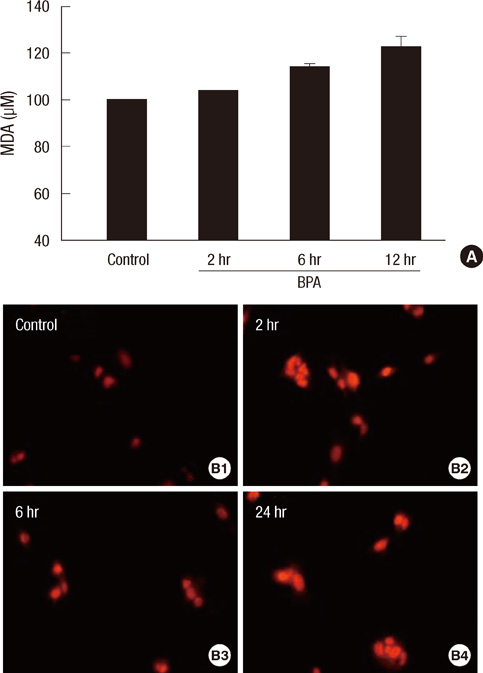
- Bisphenol A (BPA) has been reported to possess hepatic toxicity. We investigated the hypothesis that BPA, below the no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL), can induce hepatic damage and mitochondrial dysfunction by increasing oxidative stress in the liver. Two doses of BPA, 0.05 and 1.2 mg/kg body weight/day, were administered intraperitoneally for 5 days to mice. Both treatments impaired the structure of the hepatic mitochondria, although oxygen consumption rate and expression of the respiratory complex decreased only at the higher dose. The hepatic levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), a naturally occurring product of lipid peroxidation, increased, while the expression of glutathione peroxidase 3 (GPx3) decreased, after BPA treatment. The expression levels of proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) also increased. In HepG2 cells, 10 or 100 nM of BPA also decreased the oxygen consumption rate, ATP production, and the mitochondrial membrane potential. In conclusion, doses of BPA below the NOAEL induce mitochondrial dysfunction in the liver, and this is associated with an increase in oxidative stress and inflammation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adenosine Triphosphate/metabolism
Animals
Glutathione Peroxidase/metabolism
Hep G2 Cells
Humans
Inflammation/chemically induced/metabolism/pathology
Injections, Intraperitoneal
Interleukin-6/metabolism
Lipid Peroxidation/drug effects
Liver/*drug effects/metabolism/pathology
Male
Malondialdehyde/metabolism
Membrane Potential, Mitochondrial/drug effects
Mice
Mice, Inbred C57BL
Mitochondria/drug effects/*metabolism
Oxidative Stress/drug effects
Oxygen Consumption/drug effects
Phenols/*toxicity
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha/metabolism
Interleukin-6
Phenols
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Malondialdehyde
Adenosine Triphosphate
Glutathione Peroxidase
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Environmental Pollutant and Cardiovascular Disease
Min Kyong Moon, Kyong Soo Park
J Lipid Atheroscler. 2014;3(1):1-10. doi: 10.12997/jla.2014.3.1.1.
Reference
-
1. Brotons JA, Olea-Serrano MF, Villalobos M, Pedraza V, Olea N. Xenoestrogens released from lacquer coatings in food cans. Environ Health Perspect. 1995. 103:608–612.2. Olea N, Pulgar R, Pérez P, Olea-Serrano F, Rivas A, Novillo-Fertrell A, Pedraza V, Soto AM, Sonnenschein C. Estrogenicity of resin-based composites and sealants used in dentistry. Environ Health Perspect. 1996. 104:298–305.3. Ikezuki Y, Tsutsumi O, Takai Y, Kamei Y, Taketani Y. Determination of bisphenol A concentrations in human biological fluids reveals significant early prenatal exposure. Hum Reprod. 2002. 17:2839–2841.4. Calafat AM, Kuklenyik Z, Reidy JA, Caudill SP, Ekong J, Needham LL. Urinary concentrations of bisphenol A and 4-nonylphenol in a human reference population. Environ Health Perspect. 2005. 113:391–395.5. Bisphenol A action plan summary. USEPA. accessed on 1 March 2012. Available at http://www.epa.gov/oppt/existingchemicals/pubs/actionplans/bpa.html.6. Draft assessment of bisphenol A for use in food contact appliations. USFDA. accessed on 1 March 2012. Available at http://www.fda.gov/ForConsumers/ConsumerUpdates/UCM169136.7. European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Statement of EFSA on a study associating bisphenol A with medical disorders. EFSA J. 2008. 838:1–3.8. Tyl RW, Myers CB, Marr MC, Thomas BF, Keimowitz AR, Brine DR, Veselica MM, Fail PA, Chang TY, Seely JC, et al. Three-generation reproductive toxicity study of dietary bisphenol A in CD Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicol Sci. 2002. 68:121–146.9. Tyl RW, Myers CB, Marr MC, Sloan CS, Castillo NP, Veselica MM, Seely JC, Dimond SS, Van Miller JP, Shiotsuka RN, et al. Two-generation reproductive toxicity study of dietary bisphenol A in CD-1 (Swiss) mice. Toxicol Sci. 2008. 104:362–384.10. vom Saal FS, Hughes C. An extensive new literature concerning low-dose effects of bisphenol A shows the need for a new risk assessment. Environ Health Perspect. 2005. 113:926–933.11. Welshons WV, Nagel SC, vom Saal FS. Large effects from small exposures. III Endocrine mechanisms mediating effects of bisphenol A at levels of human exposure. Endocrinology. 2006. 147:S56–S69.12. Dairkee SH, Seok J, Champion S, Sayeed A, Mindrinos M, Xiao W, Davis RW, Goodson WH. Bisphenol A induces a profile of tumor aggressiveness in high-risk cells from breast cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2008. 68:2076–2080.13. Wetherill YB, Hess-Wilson JK, Comstock CE, Shah SA, Buncher CR, Sallans L, Limbach PA, Schwemberger S, Babcock GF, Knudsen KE. Bisphenol A facilitates bypass of androgen ablation therapy in prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006. 5:3181–3190.14. Hiroi H, Tsutsumi O, Momoeda M, Takai Y, Osuga Y, Taketani Y. Differential interactions of bisphenol A and 17beta-estradiol with estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) and ERbeta. Endocr J. 1999. 46:773–778.15. Kurosawa T, Hiroi H, Tsutsumi O, Ishikawa T, Osuga Y, Fujiwara T, Inoue S, Muramatsu M, Momoeda M, Taketani Y. The activity of bisphenol A depends on both the estrogen receptor subtype and the cell type. Endocr J. 2002. 49:465–471.16. Takeuchi T, Tsutsumi O, Ikezuki Y, Takai Y, Taketani Y. Positive relationship between androgen and the endocrine disruptor, bisphenol A, in normal women and women with ovarian dysfunction. Endocr J. 2004. 51:165–169.17. Zhang X, Chang H, Wiseman S, He Y, Higley E, Jones P, Wong CK, Al-Khedhairy A, Giesy JP, Hecker M. Bisphenol A disrupts steroidogenesis in human H295R cells. Toxicol Sci. 2011. 121:320–327.18. Ben-Jonathan N, Hugo ER, Brandebourg TD. Effects of bisphenol A on adipokine release from human adipose tissue: implications for the metabolic syndrome. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009. 304:49–54.19. Wetherill YB, Akingbemi BT, Kanno J, McLachlan JA, Nadal A, Sonnenschein C, Watson CS, Zoeller RT, Belcher SM. In vitro molecular mechanisms of bisphenol A action. Reprod Toxicol. 2007. 24:178–198.20. Nakagawa Y, Tayama S. Metabolism and cytotoxicity of bisphenol A and other bisphenols in isolated rat hepatocytes. Arch Toxicol. 2000. 74:99–105.21. Bindhumol V, Chitra KC, Mathur PP. Bisphenol A induces reactive oxygen species generation in the liver of male rats. Toxicology. 2003. 188:117–124.22. Asahi J, Kamo H, Baba R, Doi Y, Yamashita A, Murakami D, Hanada A, Hirano T. Bisphenol A induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated apoptosis in mouse non-parenchymal hepatocytes. Life Sci. 2010. 87:431–438.23. Knaak JB, Sullivan LJ. Metabolism of bisphenol A in the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1966. 8:175–184.24. Lang IA, Galloway TS, Scarlett A, Henley WE, Depledge M, Wallace RB, Melzer D. Association of urinary bisphenol A concentration with medical disorders and laboratory abnormalities in adults. JAMA. 2008. 300:1303–1310.25. Yoon YS, Byun HO, Cho H, Kim BK, Yoon G. Complex II defect via down-regulation of iron-sulfur subunit induces mitochondrial dysfunction and cell cycle delay in iron chelation-induced senescence-associated growth arrest. J Biol Chem. 2003. 278:51577–51586.26. Ott M, Gogvadze V, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B. Mitochondria, oxidative stress and cell death. Apoptosis. 2007. 12:913–922.27. Turrens JF. Superoxide production by the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Biosci Rep. 1997. 17:3–8.28. Dong W, Simeonova PP, Gallucci R, Matheson J, Flood L, Wang S, Hubbs A, Luster MI. Toxic metals stimulate inflammatory cytokines in hepatocytes through oxidative stress mechanisms. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1998. 151:359–366.29. Babbar N, Casero RA Jr. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha increases reactive oxygen species by inducing spermine oxidase in human lung epithelial cells: a potential mechanism for inflammation-induced carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2006. 66:11125–11130.30. Kabuto H, Hasuike S, Minagawa N, Shishibori T. Effects of bisphenol A on the metabolisms of active oxygen species in mouse tissues. Environ Res. 2003. 93:31–35.31. Chitra KC, Latchoumycandane C, Mathur PP. Induction of oxidative stress by bisphenol A in the epididymal sperm of rats. Toxicology. 2003. 185:119–127.32. Pottenger LH, Domoradzki JY, Markham DA, Hansen SC, Cagen SZ, Waechter JM Jr. The relative bioavailability and metabolism of bisphenol A in rats is dependent upon the route of administration. Toxicol Sci. 2000. 54:3–18.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mitochondrial oxidative damage by co-exposure to bisphenol A and acetaminophen in rat testes and its amelioration by melatonin
- Targeting Mitochondrial Dysfunction for the Prevention and Treatment of Metabolic Disease by Bioactive Food Components
- Evaluation of bioenergetic and mitochondrial function in liver transplantation
- A Survey of Disinfection Methods for Formula Bottle
- The effect of bisphenol A on cell apoptosis pattern in the spinal cord of chick embryos