Korean J Radiol.
2009 Dec;10(6):613-622. 10.3348/kjr.2009.10.6.613.
Dual-Modal Nanoprobes for Imaging of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplant by MRI and Fluorescence Imaging
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul Metropolitan Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 156-707, Korea. sckmd@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-747, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiological Science, College of Health Science, Yonsei University, Kangwon-do 220-710, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology, Konkuk University Medical Center, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul 143-729, Korea.
- 5Department of Radiology and the Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-744, Korea.
- 6Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul Metropolitan Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 156-707, Korea.
- KMID: 1102565
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2009.10.6.613
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
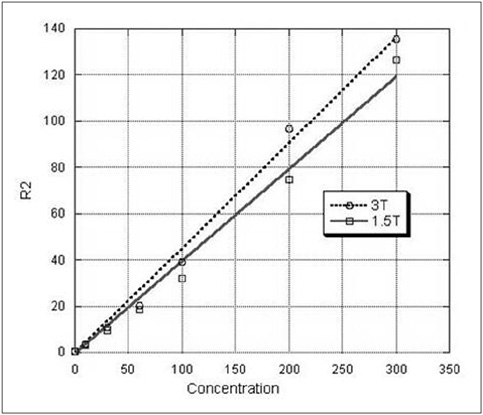
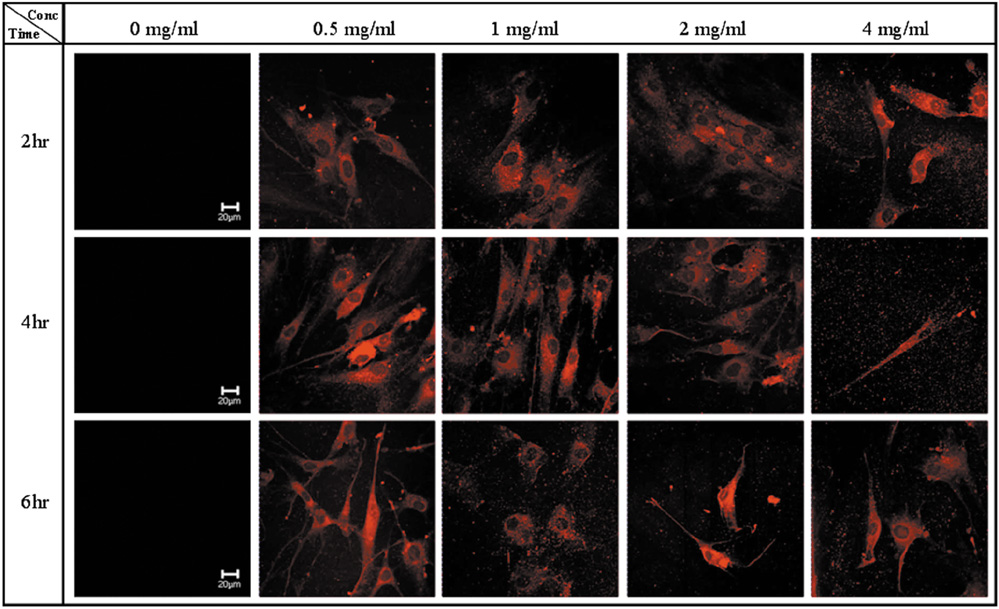
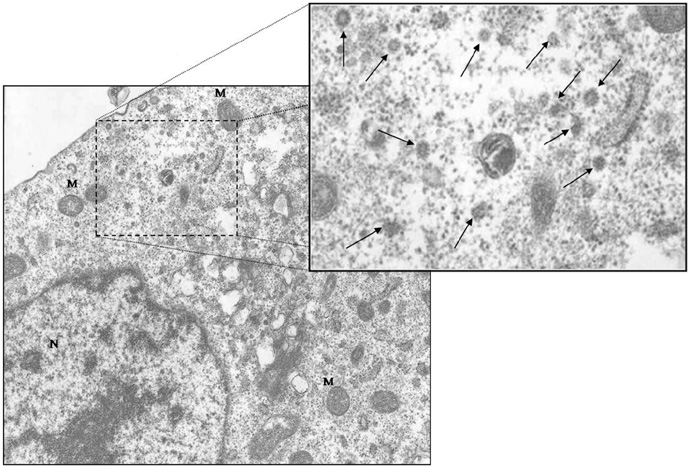
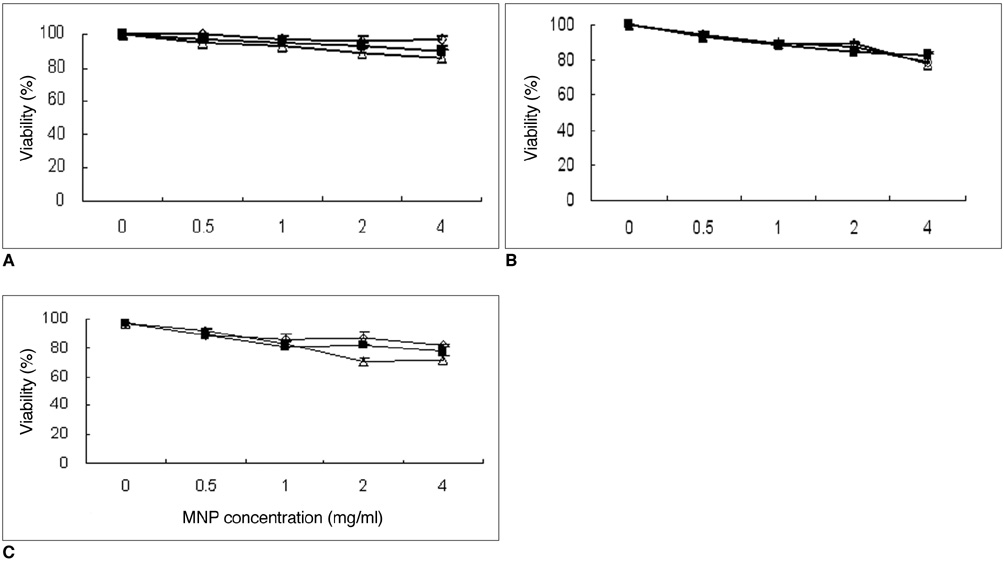
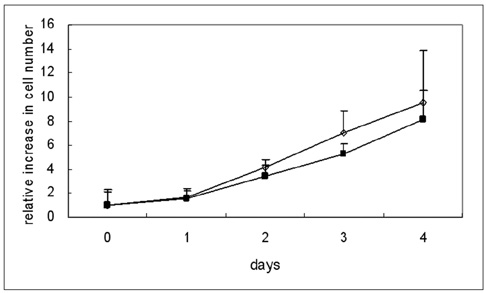
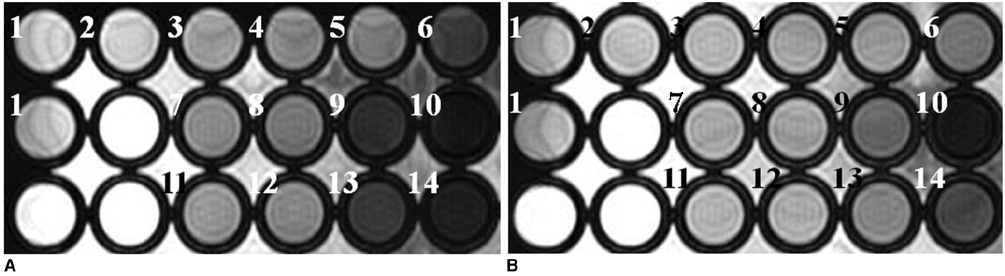
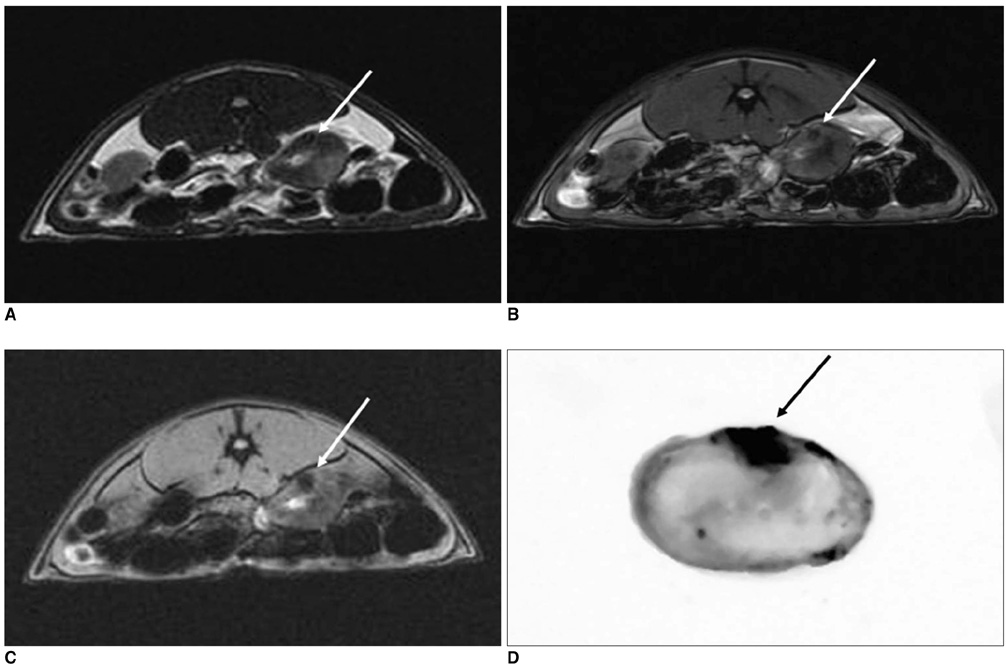
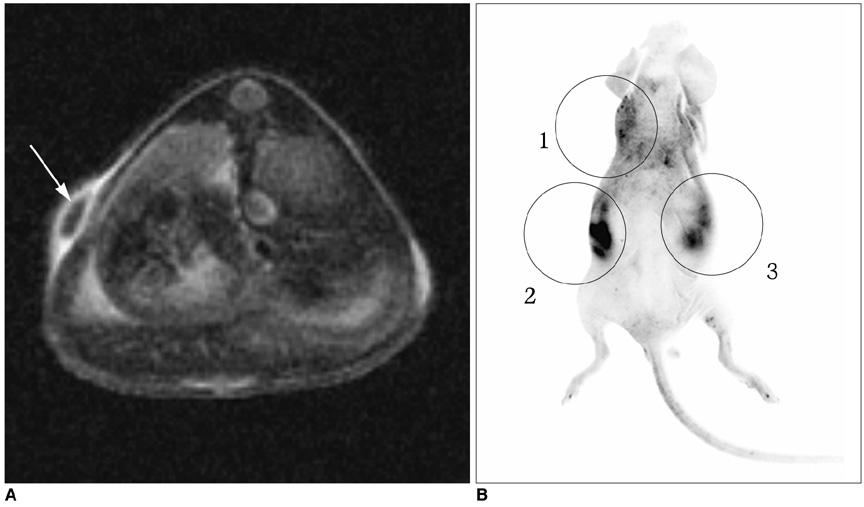
To determine the feasibility of labeling human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) with bifunctional nanoparticles and assessing their potential as imaging probes in the monitoring of hMSC transplantation. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The T1 and T2 relaxivities of the nanoparticles (MNP@SiO2[RITC]-PEG) were measured at 1.5T and 3T magnetic resonance scanner. Using hMSCs and the nanoparticles, labeling efficiency, toxicity, and proliferation were assessed. Confocal laser scanning microscopy and transmission electron microscopy were used to specify the intracellular localization of the endocytosed iron nanoparticles. We also observed in vitro and in vivo visualization of the labeled hMSCs with a 3T MR scanner and optical imaging. RESULTS: MNP@SiO2(RITC)-PEG showed both superparamagnetic and fluorescent properties. The r1 and r2 relaxivity values of the MNP@SiO2(RITC)-PEG were 0.33 and 398 mM-1 s-1 at 1.5T, respectively, and 0.29 and 453 mM-1 s-1 at 3T, respectively. The effective internalization of MNP@SiO2(RITC)-PEG into hMSCs was observed by confocal laser scanning fluorescence microscopy. The transmission electron microscopy images showed that MNP@SiO2(RITC)-PEG was internalized into the cells and mainly resided in the cytoplasm. The viability and proliferation of MNP@SiO2(RITC)-PEG-labeled hMSCs were not significantly different from the control cells. MNP@SiO2(RITC)-PEG-labeled hMSCs were observed in vitro and in vivo with optical and MR imaging. CONCLUSION: MNP@SiO2(RITC)-PEG can be a useful contrast agent for stem cell imaging, which is suitable for a bimodal detection by MRI and optical imaging.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Biocompatible Materials
Cells, Cultured
Cobalt
Feasibility Studies
Ferric Compounds
Humans
Magnetic Resonance Imaging/*methods
*Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Mice
Mice, Nude
Microscopy, Confocal
Microscopy, Electron
Nanoparticles/*chemistry
Phantoms, Imaging
Polyethylene Glycols
Rats
Rhodamines
Silicon Dioxide
Staining and Labeling/methods
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Trastuzumab-Conjugated Liposome-Coated Fluorescent Magnetic Nanoparticles to Target Breast Cancer
Mijung Jang, Young Il Yoon, Yong Soo Kwon, Tae-Jong Yoon, Hak Jong Lee, Sung Il Hwang, Bo La Yun, Sun Mi Kim
Korean J Radiol. 2014;15(4):411-422. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2014.15.4.411.
Reference
-
1. Bussolati B, Camussi G. Adult stem cells and renal repair. J Nephrol. 2006. 19:706–709.2. Strauer BE, Kornowski R. Stem cell therapy in perspective. Circulation. 2003. 107:929–934.3. Daldrup-Link HE, Rudelius M, Piontek G, Metz S, Brauer R, Debus G, et al. Migration of iron oxide-labeled human hematopoietic progenitor cells in a mouse model: in vivo monitoring with 1.5-T MR imaging equipment. Radiology. 2005. 234:197–205.4. Frangioni JV, Hajjar RJ. In vivo tracking of stem cells for clinical trials in cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 2004. 110:3378–3383.5. Hoshino K, Ly HQ, Frangioni JV, Hajjar RJ. In vivo tracking in cardiac stem cell-based therapy. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2007. 49:414–420.6. Suzuki Y, Yeung AC, Yang PC. Cardiovascular MRI for stem cell therapy. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2007. 9:45–50.7. Chang NK, Jeong YY, Park JS, Jeong HS, Jang S, Jang MJ, et al. Tracking of neural stem cells in rats with intracerebral hemorrhage by the use of 3T MRI. Korean J Radiol. 2008. 9:196–204.8. Weissleder R, Cheng HC, Bogdanova A, Bogdanov A Jr. Magnetically labeled cells can be detected by MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1997. 7:258–263.9. Yeh TC, Zhang W, Ildstad ST, Ho C. Intracellular labeling of T-cells with superparamagnetic contrast agents. Magn Reson Med. 1993. 30:617–625.10. Moore A, Basilion JP, Chiocca EA, Weissleder R. Measuring transferrin receptor gene expression by NMR imaging. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998. 1402:239–249.11. Handgretinger R, Lang P, Schumm M, Taylor G, Neu S, Koscielank E, et al. Isolation and transplantation of autologous peripheral CD34+ progenitor cells highly purified by magnetic-activated cell sorting. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1998. 21:987–999.12. Bulte JW, Douglas T, Witwer B, Zhang SC, Strable E, Lewis BK, et al. Magnetodendrimers allow endosomal magnetic labeling and in vivo tracking of stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2001. 19:1141–1147.13. Jendelová P, Herynek V, DeCroos J, Glogarova K, Andersson B, Hájek M, et al. Imaging the fate of implanted bone marrow stromal cells labeled with superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Magn Reson Med. 2003. 50:767–776.14. Song M, Moon WK, Kim Y, Lim D, Song IC, Yoon BW. Labeling efficacy of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles to human neural stem cells: comparison of ferumoxides, monocrystalline iron oxide, cross-linked iron oxide (CLIO)-NH2 and tat-CLIO. Korean J Radiol. 2007. 8:365–371.15. Hill JM, Dick AJ, Raman VK, Thompson RB, Yu ZX, Hinds KA, et al. Serial cardiac magnetic resonance imaging of injected mesenchymal stem cells. Circulation. 2003. 108:1009–1014.16. Huh YM, Jun YW, Song HT, Kim S, Choi JS, Lee JH, et al. In vivo magnetic resonance detection of cancer by using multifunctional magnetic nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc. 2005. 127:12387–12391.17. Mulder WJ, Koole R, Brandwijk RJ, Storm G, Chin PT, Strijkers GJ, et al. Quantum dots with a paramagnetic coating as a bimodal molecular imaging probe. Nano Lett. 2006. 6:1–6.18. Lu CW, Hung Y, Hsiao JK, Yao M, Chung TH, Lin YS, et al. Bifunctional magnetic silica nanoparticles for highly efficient human stem cell labeling. Nano Lett. 2007. 7:149–154.19. Yoon TJ, Kim JS, Kim BG, Yu KN, Cho MH, Lee JK. Multifunctional nanoparticles possessing a "magnetic motor effect" for drug or gene delivery. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2005. 44:1068–1071.20. Yoon TJ, Yu KN, Kim E, Kim JS, Kim BG, Yun SH, et al. Specific targeting, cell sorting, and bioimaging with smart magnetic silica core-shell nanomaterials. Small. 2006. 2:209–215.21. Jendelová P, Herynek V, Urdziková L, Glogarová K, Kroupová J, Andersson B, et al. Magnetic resonance tracking of transplanted bone marrow and embryonic stem cells labeled by iron oxide nanoparticles in rat brain and spinal cord. J Neurosci Res. 2004. 76:232–243.22. Frank JA, Miller BR, Arbab AS, Zywicke HA, Jordan EK, Lewis BK, et al. Clinically applicable labeling of mammalian and stem cells by combining superparamagnetic iron oxides and transfection agents. Radiology. 2003. 228:480–487.23. Veiseh O, Sun C, Gunn J, Kohler N, Gabikian P, Lee D, et al. Optical and MRI multifunctional nanoprobe for targeting gliomas. Nano Lett. 2005. 5:1003–1008.24. Chang JS, Chang KL, Hwang DF, Kong ZL. In vitro cytotoxicitiy of silica nanoparticles at high concentrations strongly depends on the metabolic activity type of the cell line. Environ Sci Technol. 2007. 41:2064–2068.25. Huang DM, Hung Y, Ko B, Hsu SC, Chen WH, Chien CL, et al. Highly efficient cellular labeling of mesoporous nanoparticles in human mesenchymal stem cells: implication for stem cell tracking. FASEB J. 2005. 19:2014–2016.26. Kim JS, Yoon TJ, Yu KN, Noh MS, Woo M, Kim BG, et al. Cellular uptake of magnetic nanoparticle is mediated through energy-dependent endocytosis in A549 cells. J Vet Sci. 2006. 7:321–326.27. Kirchner C, Liedl T, Kudera S, Pellegrino T, Muñoz Javier A, Gaub HE, et al. Cytotoxicity of colloidal CdSe and CdSe/ZnS nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2005. 5:331–338.28. Kircher MF, Mahmood U, King RS, Weissleder R, Josephson L. A multimodal nanoparticle for preoperative magnetic resonance imaging and intraoperative optical brain tumor delineation. Cancer Res. 2003. 63:8122–8125.29. Kim JS, Yoon TJ, Kim HK, Kim SS, Chae HS, Choi MG, et al. Sentinel lymph node mapping of the stomach using fluorescent magnetic nanoparticles in rabbits. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008. 51:19–24.30. Weissleder R. A clearer vision for in vivo imaging. Nat Biotechnol. 2001. 19:316–317.31. Summer R, Fine A. Mesenchymal progenitor cell research: limitations and recommendations. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2008. 5:707–710.32. Bussolati B, Tetta C, Camussi G. Contribution of stem cells to kidney repair. Am J Nephrol. 2008. 28:813–822.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Tracking of Stem Cells for Treatment in Cardiovascular Disease
- In Vivo Stem Cell Imaging Principles and Applications
- In vitro MRI and Characterization of Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cells Transduced with Ferritin as MR Reporter Gene
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of a Hypertrophy of Cartilage and Simultaneous Regeneration of a Damaged Meniscus after Autologous Bone Marrow Aspirates Concentrate (BMAC) Transplantation: a Case Report and Literature Review
- Current Concept of Stem Cell Therapy for Spinal Cord Injury: A Review