Korean J Orthod.
2020 Jan;50(1):42-51. 10.4041/kjod.2020.50.1.42.
The effect of cetirizine, a histamine 1 receptor antagonist, on bone remodeling after calvarial suture expansion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthodontics, Gangnam Severance Dental Hospital, College of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea. khkim@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Orthodontics and Institute of Craniofacial Deformity, College of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2468640
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2020.50.1.42
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effects of cetirizine, a histamine 1 receptor antagonist, on bone remodeling after calvarial suture expansion.
METHODS
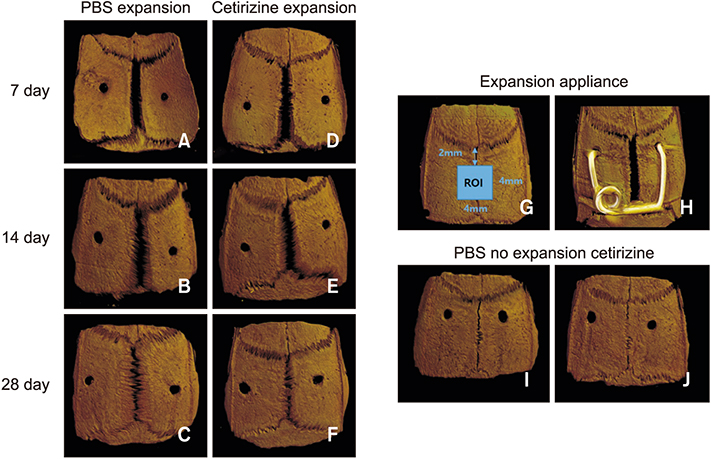
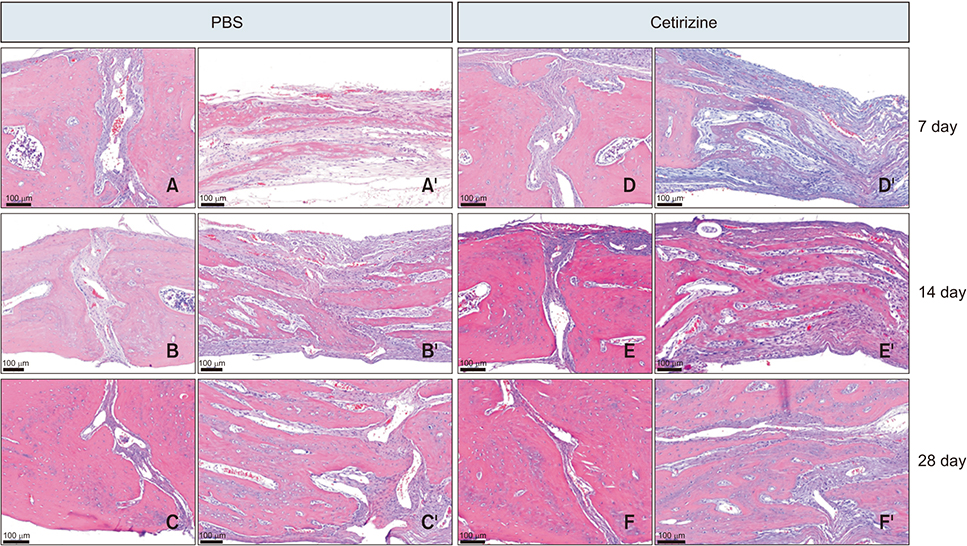
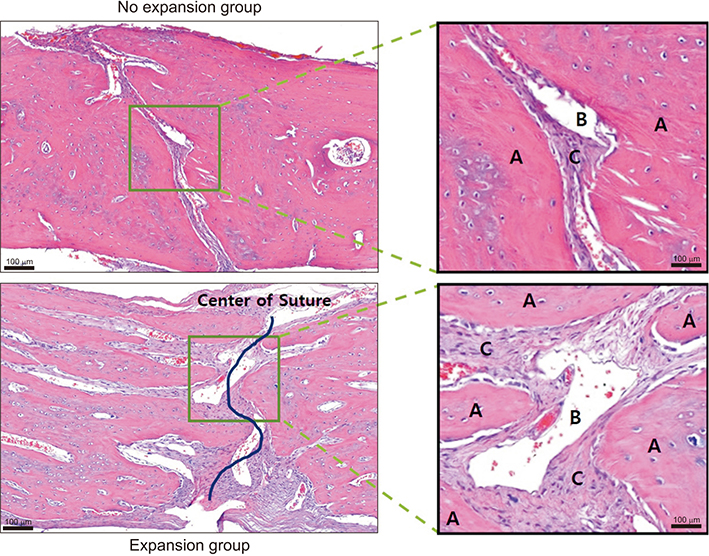
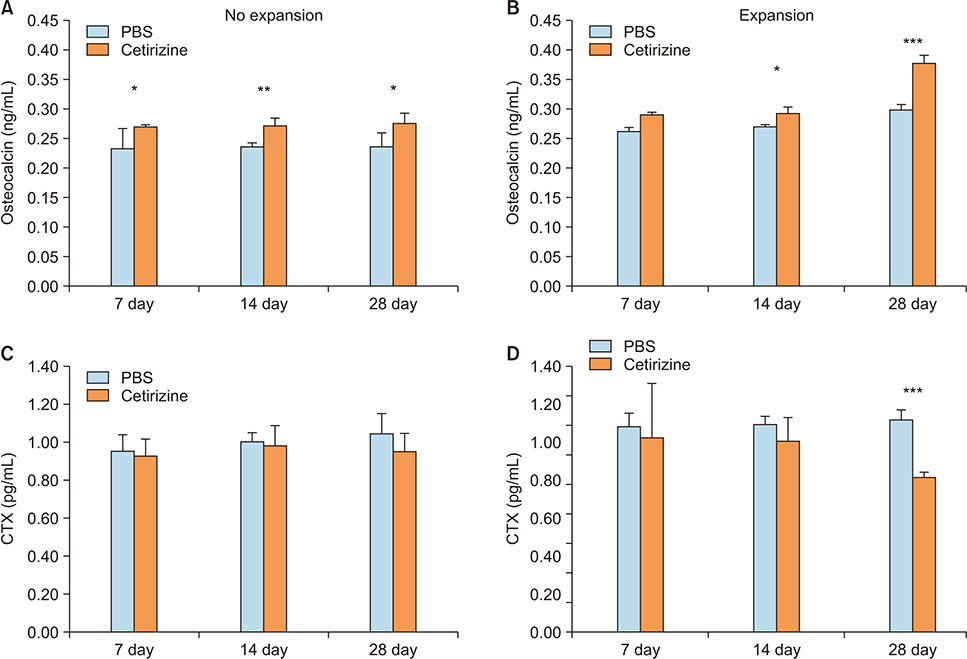
Sixty male Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into 4 groups; the phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)-injected no expansion group, cetirizine-injected no expansion group, PBS-injected expansion group, and cetirizine-injected expansion group, and were observed at 7, 14, and 28 days. Five rats per group were examined at each observation day. Daily injections of cetirizine or PBS were administered to the relevant groups starting 2 weeks prior to expander insertion. A rapid expander was inserted in the calvarial bone to deliver 100 cN of force to the parietal suture. The specimens were prepared for hematoxylin and eosin and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining. Suture opening and bone regeneration were evaluated using microcomputed tomography and bone histomorphometric analysis. Serum blood levels of osteocalcin and carboxy-terminal collagen crosslinks (CTX) were also evaluated.
RESULTS
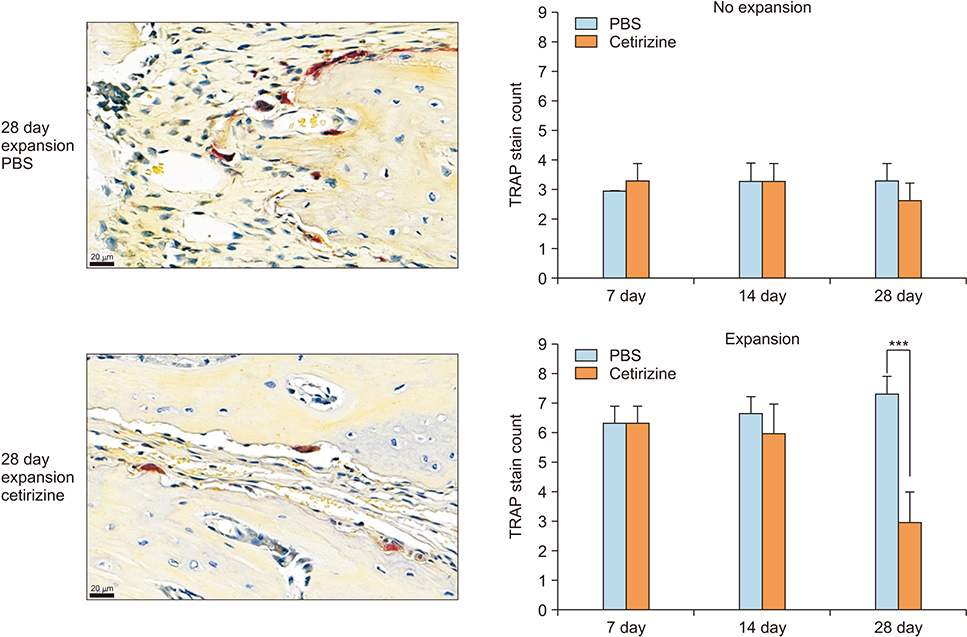
TRAP-positive cell counts and CTX levels decreased while osteocalcin levels increased in the cetirizine-injected expansion group at observation day 28. In the expansion groups, the mineralized area gradually increased throughout the observation period. At day 28, the cetirizine-injected expansion group showed greater bone volume density, greater mineralized area, and narrower average suture width than did the PBS-injected expansion group.
CONCLUSIONS
Cetirizine injection facilitated bone formation after suture expansion, mostly by suppressing osteoclastic activity. Histamine 1 receptor antagonists may aid in bone formation after calvarial suture expansion in the rat model.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acid Phosphatase
Animals
Bone Regeneration
Bone Remodeling*
Cell Count
Cetirizine*
Collagen
Eosine Yellowish-(YS)
Hematoxylin
Histamine*
Humans
Male
Miners
Models, Animal
Osteocalcin
Osteoclasts
Osteogenesis
Rabeprazole
Rats
Sutures*
X-Ray Microtomography
Acid Phosphatase
Cetirizine
Collagen
Eosine Yellowish-(YS)
Hematoxylin
Histamine
Osteocalcin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Takizawa H. Impact of air pollution on allergic diseases. Korean J Intern Med. 2011; 26:262–273.
Article2. Hajar T, Simpson EL. The rise in atopic dermatitis in young children: what is the explanation? JAMA Netw Open. 2018; 1:e184205.3. Song S, Lee K, Lee YM, Lee JH, Lee SI, Yu SD, et al. Acute health effects of urban fine and ultrafine particles on children with atopic dermatitis. Environ Res. 2011; 111:394–399.
Article4. Xu F, Yan S, Li F, Cai M, Chai W, Wu M, et al. Prevalence of childhood atopic dermatitis: an urban and rural community-based study in Shanghai, China. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e36174.
Article5. Kim YM, Kim J, Han Y, Jeon BH, Cheong HK, Ahn K. Short-term effects of weather and air pollution on atopic dermatitis symptoms in children: a panel study in Korea. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0175229.
Article6. Bachert C. Histamine--a major role in allergy? Clin Exp Allergy. 1998; 28:Suppl 6. 15–19.7. Buddenkotte J, Maurer M, Steinhoff M. Histamine and antihistamines in atopic dermatitis. In : Thurmond RL, editor. Histamine in inflammation. New York: Springer;2010. p. 73–80.8. Seeman E. Structural basis of growth-related gain and age-related loss of bone strength proceedings of a satellite symposium held on the occasion of the EULAR Congress, Paris, France, June 13, 2008. Rheumatology. 2008; 47:iv2–iv8.
Article9. Johansson C, Roupe G, Lindstedt G, Mellström D. Bone density, bone markers and bone radiological features in mastocytosis. Age Ageing. 1996; 25:1–7.
Article10. Folwarczna J, Śliwiński L, Pytlik M, Janas A. Effects of histamine H1, H2 and H3 receptor antagonists on bone mechanical properties in female rats. Bone. 2011; 48:S193.11. Dobigny C, Saffar JL. H1 and H2 histamine receptors modulate osteoclastic resorption by different pathways: evidence obtained by using receptor antagonists in a rat synchronized resorption model. J Cell Physiol. 1997; 173:10–18.
Article12. Mandhane SN, Shah JH, Thennati R. Allergic rhinitis: an update on disease, present treatments and future prospects. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011; 11:1646–1662.
Article13. Kawauchi H, Yanai K, Wang DY, Itahashi K, Okubo K. Antihistamines for allergic rhinitis treatment from the viewpoint of nonsedative properties. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20:E213.
Article14. Luzzi V, Ierardo G, Viscogliosi A, Fabbrizi M, Consoli G, Vozza I, et al. Allergic rhinitis as a possible risk factor for malocclusion: a case-control study in children. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2013; 23:274–278.
Article15. Pawankar R, Canonica GW, Holgate ST, Lockey RF, Blaiss M. World Allergy Organization (WAO) white book on allergy. Milwaukee, WI: World Allergy Organization;2011.16. Meh A, Sprogar S, Vaupotic T, Cör A, Drevenšek G, Marc J, et al. Effect of cetirizine, a histamine (H(1)) receptor antagonist, on bone modeling during orthodontic tooth movement in rats. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2011; 139:e323–e329.
Article17. Parfitt AM, Drezner MK, Glorieux FH, Kanis JA, Malluche H, Meunier PJ, et al. Bone histomorphometry: standardization of nomenclature, symbols, and units. Report of the ASBMR Histomorphometry Nomenclature Committee. J Bone Miner Res. 1987; 2:595–610.
Article18. Mao JJ, Wang X, Kopher RA. Biomechanics of craniofacial sutures: orthopedic implications. Angle Orthod. 2003; 73:128–135.19. Kobayashi ET, Hashimoto F, Kobayashi Y, Sakai E, Miyazaki Y, Kamiya T, et al. Force-induced rapid changes in cell fate at midpalatal suture cartilage of growing rats. J Dent Res. 1999; 78:1495–1504.
Article20. Opperman LA. Cranial sutures as intramembranous bone growth sites. Dev Dyn. 2000; 219:472–485.
Article21. Wu BH, Kou XX, Zhang C, Zhang YM, Cui Z, Wang XD, et al. Stretch force guides finger-like pattern of bone formation in suture. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0177159.
Article22. Hou B, Fukai N, Olsen BR. Mechanical force-induced midpalatal suture remodeling in mice. Bone. 2007; 40:1483–1493.
Article23. Lai RF, Zhou ZY, Chen T. Accelerating bone generation and bone mineralization in the interparietal sutures of rats using an rhBMP-2/ACS composite after rapid expansion. Exp Anim. 2013; 62:189–196.
Article24. Matuszewska A, Nowak B, Jędrzejuk D, Landwójtowicz M, Sadanowicz E, Sozański T, et al. Effect of long-term administration of ranitidine, a histamine H2 receptor antagonist, on bone metabolism in young growing rats. Pharmacol Rep. 2018; 70:951–954.
Article25. Biosse-Duplan M, Baroukh B, Dy M, de Vernejoul MC, Saffar JL. Histamine promotes osteoclastogenesis through the differential expression of histamine receptors on osteoclasts and osteoblasts. Am J Pathol. 2009; 174:1426–1434.
Article26. Lesclous P, Guez D, Saffar JL. Short-term prevention of osteoclastic resorption and osteopenia in ovariectomized rats treated with the H(2) receptor antagonist cimetidine. Bone. 2002; 30:131–136.
Article27. Yamaura K, Yonekawa T, Nakamura T, Yano S, Ueno K. The histamine H2-receptor antagonist, cimetidine, inhibits the articular osteopenia in rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis by suppressing the osteoclast differentiation induced by histamine. J Pharmacol Sci. 2003; 92:43–49.
Article28. Civitelli R, Armamento-Villareal R, Napoli N. Bone turnover markers: understanding their value in clinical trials and clinical practice. Osteoporos Int. 2009; 20:843–851.
Article29. Garnero P, Ferreras M, Karsdal MA, Nicamhlaoibh R, Risteli J, Borel O, et al. The type I collagen fragments ICTP and CTX reveal distinct enzymatic pathways of bone collagen degradation. J Bone Miner Res. 2003; 18:859–867.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Modulatory Role of Spinally Located Histamine Receptors in the Regulation of the Blood Glucose Level in D-Glucose-Fed Mice
- Effects of cetirizine in dogs with chronic atopic dermatitis: a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial
- Two Cases of Urticaria Induced by Ebastine
- Efficacy of a Combination with Pranlukast and Cetirizine in the Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis
- Effects of Histamine 2 Antagonist in the Treatment of Perennial Allergic Rhinitis