Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2020 Mar;12(2):306-321. 10.4168/aair.2020.12.2.306.
Evaluation of Neo-Osteogenesis in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis Using a Nasal Polyp Murine Model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Obstructive Upper airway Research (OUaR) Laboratory, Department of Pharmacology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. charlie@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biomedical Sciences, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Ischemic/Hypoxic Disease Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2468464
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2020.12.2.306
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Osteitis refers to the development of new bone formation and remodeling of bone in chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) patients; it is typically associated with eosinophilia, nasal polyps (NPs), and recalcitrant CRS. However, the roles of ossification in CRS with or without NPs remain unclear due to the lack of appropriate animal models. Thus, it is necessary to have a suitable animal model for greater advances in the understanding of CRS pathogenesis.
METHODS
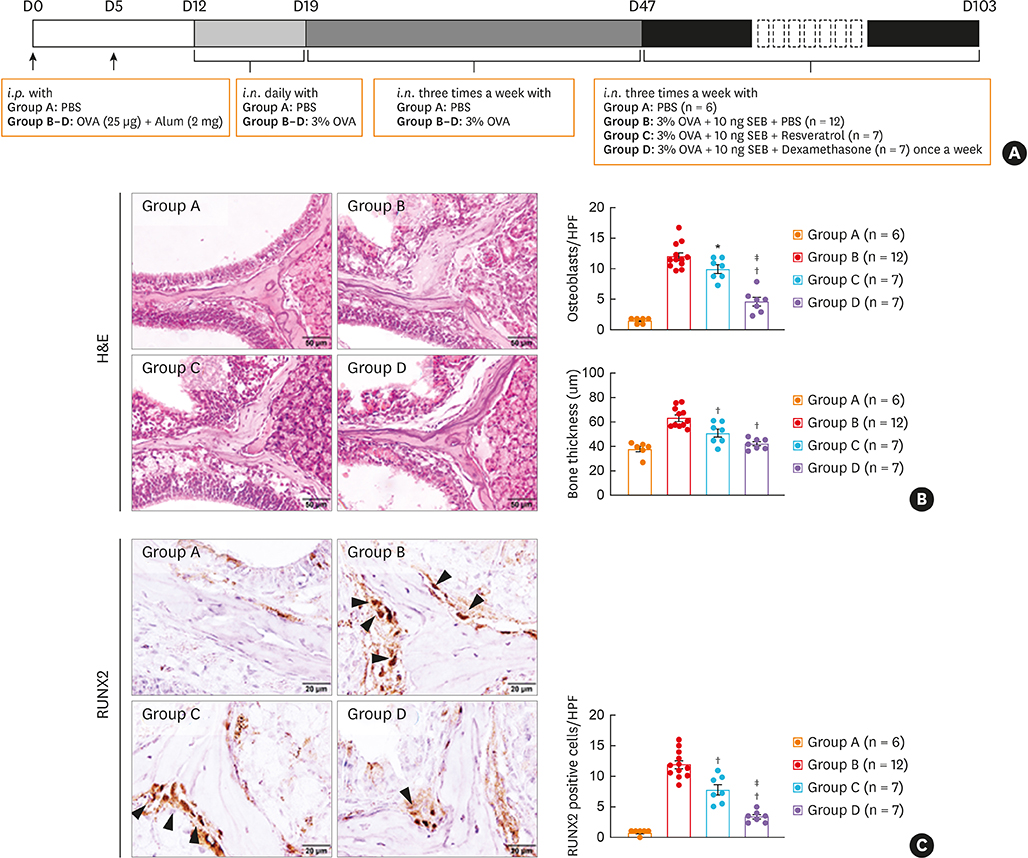
BALB/c mice were administered ovalbumin (OVA) and staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB). The numbers of osteoclasts and osteoblasts and bony changes were assessed. Micro computed tomography (micro-CT) scans were conducted to measure bone thickness. Immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry, and quantitative polymerase chain reaction were performed to evaluate runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2), osteonectin, interleukin (IL)-13, and RUNX2 downstream gene expression. Gene set enrichment analysis was performed in mucosal tissues from control and CRS patients. The effect of resveratrol was evaluated in terms of osteogenesis in a murine eosinophilic CRS NP model.
RESULTS
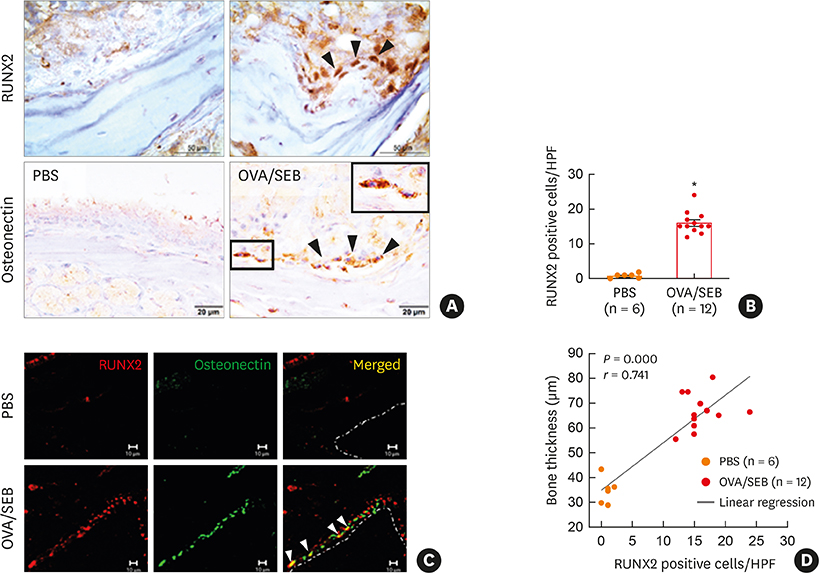
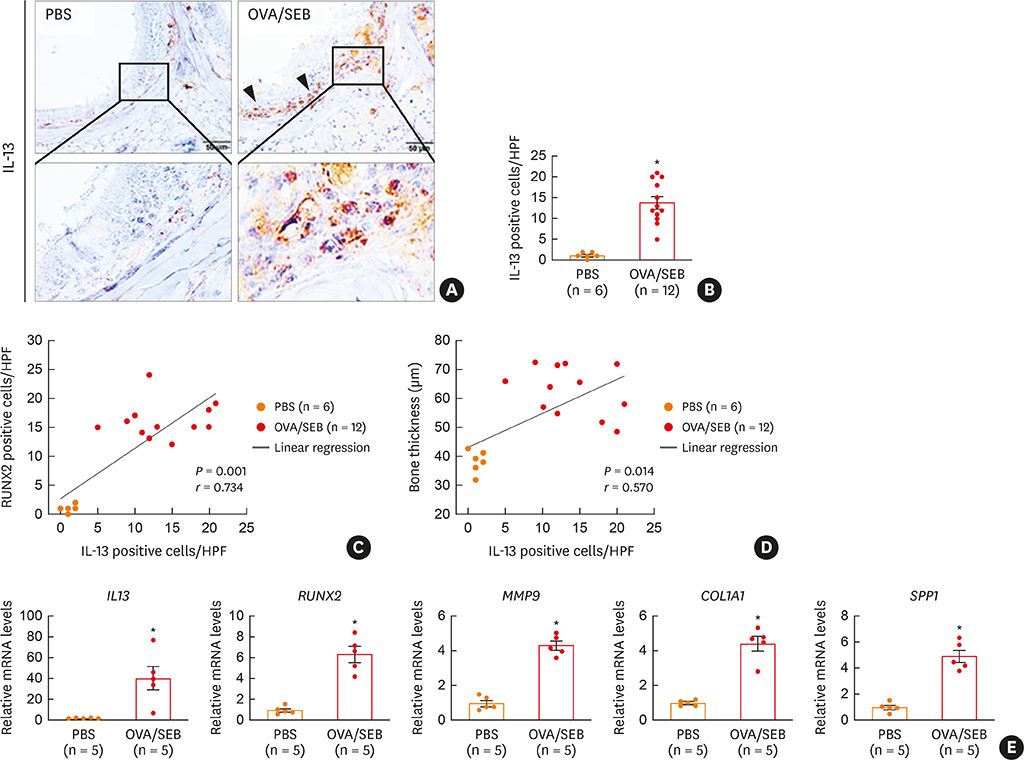
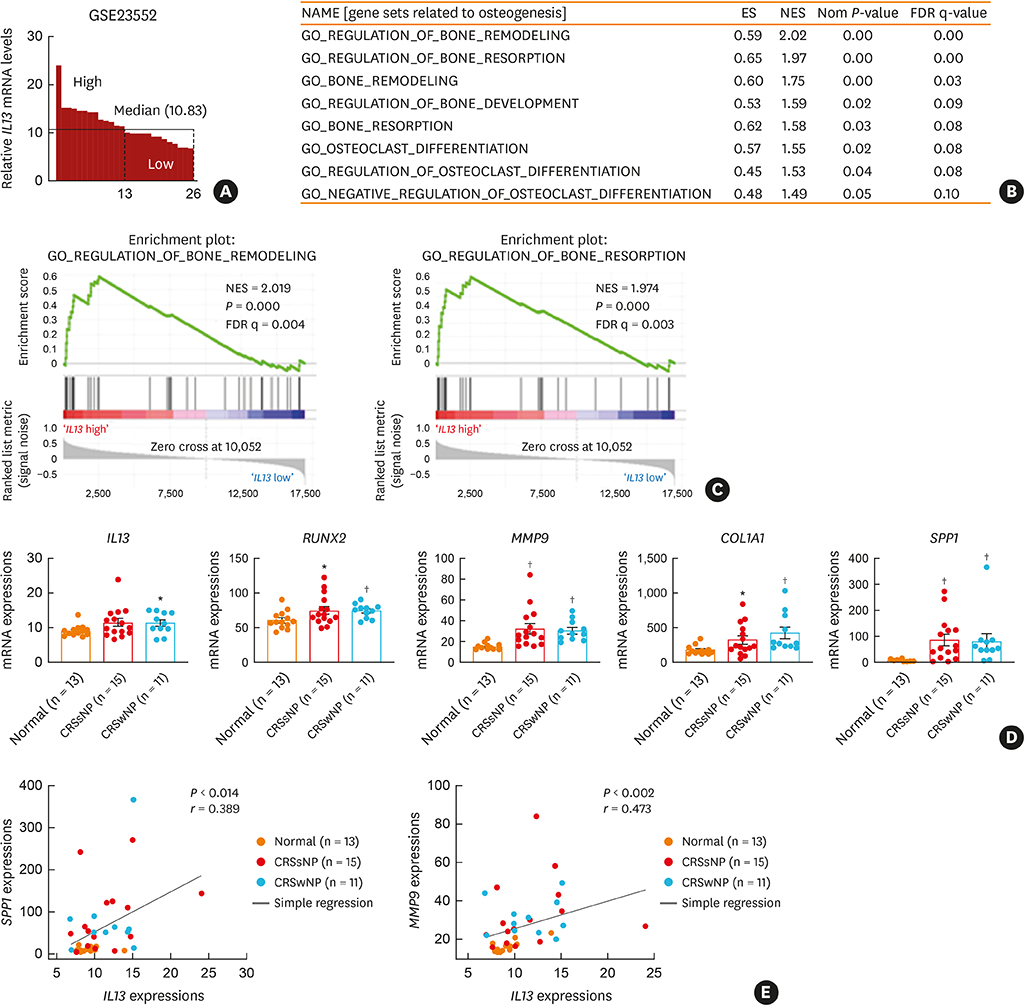
The histopathologic changes showed markedly thickened bones with significant increase in osteoblast numbers in OVA/SEB-treated mice compared to the phosphate-buffered saline-treated mice. The structural changes in bone on micro-CT were consistent with the histopathological features. The expression of RUNX2 and IL-13 was increased by the administration of OVA/SEB and showed a positive correlation. RUNX2 expression mainly co-localized with osteoblasts. Bioinformatic analysis using human CRS transcriptome revealed that IL-13-induced bony changes via RUNX2. Treatment with resveratrol, a candidate drug against osteitis, diminished the expression of IL-13 and RUNX2, and the number of osteoblasts in OVA/SEB-treated mice.
CONCLUSIONS
In the present study, we found the histopathological and radiographic evidence of osteogenesis using a previously established murine eosinophilic CRS NP model. This animal model could provide new insights into the pathophysiology of neo-osteogenesis and provide a basis for developing new therapeutics.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Computational Biology
Core Binding Factor Alpha 1 Subunit
Enterotoxins
Eosinophilia
Eosinophils*
Fluorescent Antibody Technique
Gene Expression
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
Interleukin-13
Interleukins
Mice
Models, Animal
Mucous Membrane
Nasal Polyps*
Nose
Osteitis
Osteoblasts
Osteoclasts
Osteogenesis
Osteonectin
Ovalbumin
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Sinusitis
Transcription Factors
Transcriptome
Core Binding Factor Alpha 1 Subunit
Enterotoxins
Interleukin-13
Interleukins
Osteonectin
Ovalbumin
Transcription Factors
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Crosstalk Between Mucosal Inflammation and Bone Metabolism in Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Roza Khalmuratova, Hyun-Woo Shin
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2021;14(1):43-49. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2020.00416.
Reference
-
1. Hamilos DL. Chronic rhinosinusitis: epidemiology and medical management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 128:693–707.
Article2. Stevens WW, Lee RJ, Schleimer RP, Cohen NA. Chronic rhinosinusitis pathogenesis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015; 136:1442–1453.
Article3. Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, Bachert C, Alobid I, Baroody F, et al. EPOS 2012: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists. Rhinology. 2012; 50:1–12.
Article4. Kim YS, Han D, Kim J, Kim DW, Kim YM, Mo JH, et al. In-depth, proteomic analysis of nasal secretions from patients with chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019; 11:691–708.
Article5. Bhandarkar ND, Sautter NB, Kennedy DW, Smith TL. Osteitis in chronic rhinosinusitis: a review of the literature. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013; 3:355–363.
Article6. Kennedy DW, Senior BA, Gannon FH, Montone KT, Hwang P, Lanza DC. Histology and histomorphometry of ethmoid bone in chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope. 1998; 108:502–507.
Article7. Perloff JR, Gannon FH, Bolger WE, Montone KT, Orlandi R, Kennedy DW. Bone involvement in sinusitis: an apparent pathway for the spread of disease. Laryngoscope. 2000; 110:2095–2099.
Article8. Giacchi RJ, Lebowitz RA, Yee HT, Light JP, Jacobs JB. Histopathologic evaluation of the ethmoid bone in chronic sinusitis. Am J Rhinol. 2001; 15:193–197.
Article9. Snidvongs K, McLachlan R, Chin D, Pratt E, Sacks R, Earls P, et al. Osteitic bone: a surrogate marker of eosinophilia in chronic rhinosinusitis. Rhinology. 2012; 50:299–305.
Article10. Lee JT, Kennedy DW, Palmer JN, Feldman M, Chiu AG. The incidence of concurrent osteitis in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis: a clinicopathological study. Am J Rhinol. 2006; 20:278–282.
Article11. Videler WJ, Georgalas C, Menger DJ, Freling NJ, van Drunen CM, Fokkens WJ. Osteitic bone in recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis. Rhinology. 2011; 49:139–147.12. Kim HY, Dhong HJ, Lee HJ, Chung YJ, Yim YJ, Oh JW, et al. Hyperostosis may affect prognosis after primary endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006; 135:94–99.
Article13. Richtsmeier WJ. Top 10 reasons for endoscopic maxillary sinus surgery failure. Laryngoscope. 2001; 111:1952–1956.
Article14. Bhandarkar ND, Mace JC, Smith TL. The impact of osteitis on disease severity measures and quality of life outcomes in chronic rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2011; 1:372–378.
Article15. Georgalas C, Videler W, Freling N, Fokkens W. Global Osteitis Scoring Scale and chronic rhinosinusitis: a marker of revision surgery. Clin Otolaryngol. 2010; 35:455–461.
Article16. Mehta V, Campeau NG, Kita H, Hagan JB. Blood and sputum eosinophil levels in asthma and their relationship to sinus computed tomographic findings. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008; 83:671–678.
Article17. Khalid AN, Hunt J, Perloff JR, Kennedy DW. The role of bone in chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope. 2002; 112:1951–1957.
Article18. Bolger WE, Leonard D, Dick EJ Jr, Stierna P. Gram negative sinusitis: a bacteriologic and histologic study in rabbits. Am J Rhinol. 1997; 11:15–25.
Article19. Norlander T, Forsgren K, Kumlien J, Stierna P, Carlsöö B. Cellular regeneration and recovery of the maxillary sinus mucosa. An experimental study in rabbits. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1992; 492:33–37.20. Westrin KM, Norlander T, Stierna P, Carlsöö B, Nord CE. Experimental maxillary sinusitis induced by Bacteroides fragilis. A bacteriological and histological study in rabbits. Acta Otolaryngol. 1992; 112:107–114.21. Antunes MB, Feldman MD, Cohen NA, Chiu AG. Dose-dependent effects of topical tobramycin in an animal model of Pseudomonas sinusitis. Am J Rhinol. 2007; 21:423–427.
Article22. Kim DW, Khalmuratova R, Hur DG, Jeon SY, Kim SW, Shin HW, et al. Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B contributes to induction of nasal polypoid lesions in an allergic rhinosinusitis murine model. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2011; 25:e255–61.
Article23. Shin HW. Animal models in CRS and pathophysiologic insights gained: a systematic review. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2016; 1:116–123.
Article24. Lee M, Kim DW, Khalmuratova R, Shin SH, Kim YM, Han DH, et al. The IFN-γ-p38, ERK kinase axis exacerbates neutrophilic chronic rhinosinusitis by inducing the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Mucosal Immunol. 2019; 12:601–611.
Article25. Lee M, Kim DW, Yoon H, So D, Khalmuratova R, Rhee CS, et al. Sirtuin 1 attenuates nasal polypogenesis by suppressing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016; 137:87–98.e7.
Article26. Jacob A, Chole RA. Survey anatomy of the paranasal sinuses in the normal mouse. Laryngoscope. 2006; 116:558–563.
Article27. Khalmuratova R, Lee M, Kim DW, Park JW, Shin HW. Induction of nasal polyps using house dust mite and Staphylococcal enterotoxin B in C57BL/6 mice. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2016; 44:66–75.
Article28. Lee M, Park CG, Huh BK, Kim SN, Lee SH, Khalmuratova R, et al. Sinonasal delivery of resveratrol via mucoadhesive nanostructured microparticles in a nasal polyp mouse model. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:40249.
Article29. Telmesani LM, Al-Shawarby M. Osteitis in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: a comparative study between primary and recurrent cases. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2010; 267:721–724.
Article30. Khalmuratova R, Lee M, Mo JH, Jung Y, Park JW, Shin HW. Wogonin attenuates nasal polyp formation by inducing eosinophil apoptosis through HIF-1α and survivin suppression. Sci Rep. 2018; 8:6201.
Article31. Raggatt LJ, Partridge NC. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of bone remodeling. J Biol Chem. 2010; 285:25103–25108.
Article32. Khalmuratova R, Shin HW, Kim DW, Park JW. Interleukin (IL)-13 and IL-17A contribute to neo-osteogenesis in chronic rhinosinusitis by inducing RUNX2. EBioMedicine. 2019; 46:330–341.
Article33. Tanaka Y, Nakayamada S, Okada Y. Osteoblasts and osteoclasts in bone remodeling and inflammation. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2005; 4:325–328.
Article34. Komori T. Roles of Runx2 in skeletal development. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017; 962:83–93.
Article35. Loi F, Córdova LA, Pajarinen J, Lin TH, Yao Z, Goodman SB. Inflammation, fracture and bone repair. Bone. 2016; 86:119–130.
Article36. Glowacki AJ, Yoshizawa S, Jhunjhunwala S, Vieira AE, Garlet GP, Sfeir C, et al. Prevention of inflammation-mediated bone loss in murine and canine periodontal disease via recruitment of regulatory lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013; 110:18525–18530.
Article37. Khalmuratova R, Park JW, Shin HW. Immune cell responses and mucosal barrier disruptions in chronic rhinosinusitis. Immune Netw. 2017; 17:60–67.
Article38. Wang M, Ye T, Liang N, Huang Z, Cui S, Li Y, et al. Differing roles for TGF-β/Smad signaling in osteitis in chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyps. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2015; 29:e152–9.
Article39. Silfverswärd CJ, Larsson S, Ohlsson C, Frost A, Nilsson O. Reduced cortical bone mass in mice with inactivation of interleukin-4 and interleukin-13. J Orthop Res. 2007; 25:725–731.
Article40. Wang Y, Wu NN, Mou YQ, Chen L, Deng ZL. Inhibitory effects of recombinant IL-4 and recombinant IL-13 on UHMWPE-induced bone destruction in the murine air pouch model. J Surg Res. 2013; 180:e73–81.
Article41. Onoe Y, Miyaura C, Kaminakayashiki T, Nagai Y, Noguchi K, Chen QR, et al. IL-13 and IL-4 inhibit bone resorption by suppressing cyclooxygenase-2-dependent prostaglandin synthesis in osteoblasts. J Immunol. 1996; 156:758–764.42. Shi N, Zhang J, Chen SY. Runx2, a novel regulator for goblet cell differentiation and asthma development. FASEB J. 2017; 31:412–420.
Article43. Baur JA, Sinclair DA. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: the in vivo evidence. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006; 5:493–506.44. Tao K, Bai X, Jia W, Liu Y, Zhu X, Han J, et al. Effects of resveratrol on the treatment of inflammatory response induced by severe burn. Inflammation. 2015; 38:1273–1280.
Article45. Rafe T, Shawon PA, Salem L, Chowdhury NI, Kabir F, Bin Zahur SM, et al. Preventive role of Resveratrol against inflammatory cytokines and related diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 2019; 25:1345–1371.
Article46. Kim SW, Kim DW, Khalmuratova R, Kim JH, Jung MH, Chang DY, et al. Resveratrol prevents development of eosinophilic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in a mouse model. Allergy. 2013; 68:862–869.
Article47. Hur DG, Khalmuratova R, Ahn SK, Ha YS, Min YG. Roles of periostin in symptom manifestation and airway remodeling in a murine model of allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:222–230.
Article48. Shin HW, Cho K, Kim DW, Han DH, Khalmuratova R, Kim SW, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 mediates nasal polypogenesis by inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012; 185:944–954.
Article49. Boonrungsiman S, Gentleman E, Carzaniga R, Evans ND, McComb DW, Porter AE, et al. The role of intracellular calcium phosphate in osteoblast-mediated bone apatite formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012; 109:14170–14175.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Medical treatment according to phenotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis
- The Role of Allergy in the Severity of Chronic Rhinosinusitis
- Clinical Characteristics and Expression Pattern of IL-33 and IL-25 According to Histologic Classification in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyposis
- Distribution of Histologic Type of Nasal Polyp and Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor According to Nasal Polyp Type
- Update on Biologics in Treatment of Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyposis