Kosin Med J.
2019 Dec;34(2):106-116. 10.7180/kmj.2019.34.2.106.
Genipin Inhibits Hypoxia-Induced Accumulation of HIF-1α and VEGF Expressions in Human Cervical Carcinoma Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, College of Medicine, Kosin University, Busan, Korea. leehula@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Kosin University, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2467971
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2019.34.2.106
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
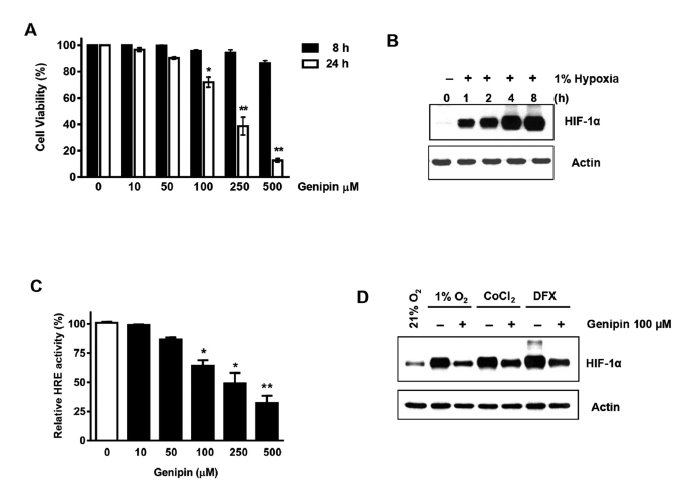
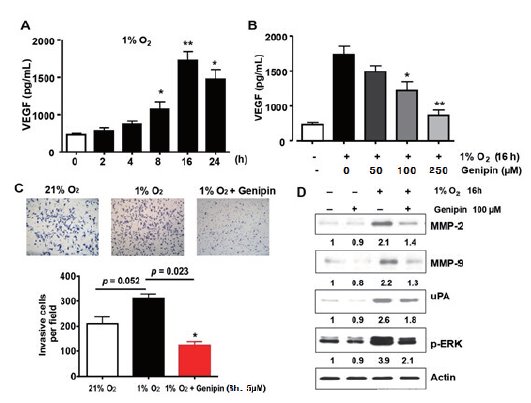
Hypoxia"”a characteristic of almost all types of solid tumors"”has been associated with poor outcomes in several human malignancies. Genipin"”an active constituent of Gardenia fruit"” has been reported to exert an anti-tumor effect in several cancers. In this study, we investigated inhibition of angiogenesis using Genipin-mediated hypoxia-induced hypoxia inducible factor (HIF-1) and VEGF expression in human cervical cancer cells.
METHODS
Under normoxic and hypoxic conditions, the expression of HIF-1α and VEGF in cervical cancer HeLa cells was detected by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and western blotting. Luciferase reporter assays were used to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying the hypoxia-induced survivin activation.
RESULTS
Surprisingly, we found that Genipin suppressed the HIF-1α accumulation during hypoxia in human liver cancer cell line (HepG2), human prostate cancer cell line (LNCaP), colon cancer cell line (HCT116), and breast cancer cell line (MDA231). Genipin treatment also significantly reduced hypoxia-induced secretion of VEGF.
CONCLUSIONS
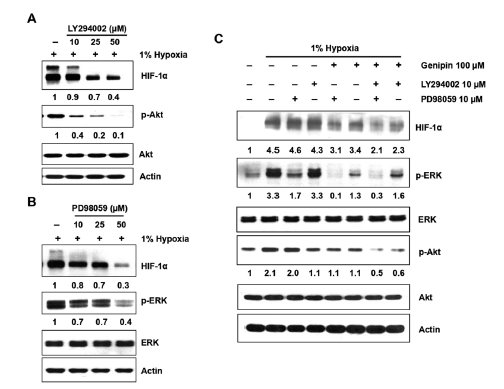
Suppression of HIF-1α accumulation following treatment with Genipin under hypoxia was associated with PI3K and MAPK pathways. Taken together, these results suggested that Genipin inhibits HIF-1α expression through inhibition of PI3K and MAPK signaling pathways. These results provide new insights into a potential mechanism of the anticancer properties of Genipin.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Folkman J. Role of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis. Semin Oncol. 2002; 29:15–18.
Article2. Ferrara N, Bunting S. Vascular endothelial growth factor, a specific regulator of angiogenesis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 1996; 5:35–44.
Article3. Krishnamachary B, Berg-Dixon S, Kelly B, Agani F, Feldser D, Ferreira G, et al. Regulation of colon carcinoma cell invasion by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cancer Res. 2003; 63:1138–1143.4. Fang J, Zhou Q, Liu LZ, Xia C, Hu X, Shi X, et al. Apigenin inhibits tumor angiogenesis through decreasing HIF-1alpha and VEGF expression. Carcinogenesis. 2007; 28:858–864.
Article5. Garcia-Maceira P, Mateo J. Silibinin inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and mTOR/p 70S6K/4E-BP1 signalling pathway in human cervical and hepatoma cancer cells: implications for anticancer therapy. Oncogene. 2009; 28:313–324.
Article6. Tang X, Zhang Q, Shi S, Yen Y, Li X, Zhang Y, et al. Bisphosphonates suppress insulin-like growth factor 1-induced angiogenesis via the HIF-1alpha/VEGF signaling pathways in human breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 2010; 126:90–103.
Article7. Kallio PJ, Wilson WJ, O'Brien S, Makino Y, Poellinger L. Regulation of the hypoxia inducible transcription factor 1alpha by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274:6519–6525.
Article8. Stiehl DP, Jelkmann W, Wenger RH, Hellwig-Burgel T. Normoxic induction of the hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha by insulin and interleukin-1beta involves the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. FEBS Lett. 2002; 512:157–162.
Article9. Fukuda R, Hirota K, Fan F, Jung YD, Ellis LM, Semenza GL. Insulin-like growth factor 1 induces hypoxia-inducible factor 1-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor expression, which is dependent on MAP kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling in colon cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:38205–38211.
Article10. Jiang BH, Liu LZ, Schafer R, Flynn DC, Barnett JB. A novel role for 3, 4-dichloropropionanilide (DCPA) in the inhibition of prostate cancer cell migration, proliferation, and hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression. BMC Cancer. 2006; 6:204.
Article11. Martin KA, Blenis J. Coordinate regulation of translation by the PI 3-kinase and mTOR-pathways. Adv Cancer Res. 2002; 86:1–39.12. Zhang Q, Tang X, Lu QY, Zhang ZF, Brown J, Le AD. Resveratrol inhibits hypoxia-induced accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and VEGF expression in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma and hepatoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005; 4:1465–1474.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor (Valproic Acid) on the Expression of Hypoxia-inducible Factor-1 Alpha in Human Retinal Müller Cells
- The Relationship between Expression of Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1alpha or Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Histopathological Characteristics in Human Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Neuregulin-1 Protects Neuronal Cells Against Damage due to CoCl2-Induced Hypoxia by Suppressing Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α and P53 in SH-SY5Y Cells
- Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α Directly Induces the Expression of Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-κB Ligand in Chondrocytes
- Overexpression of CD44 Standard Isoform Upregulates HIF-1α Signaling in Hypoxic Breast Cancer Cells