Cancer Res Treat.
2019 Oct;51(4):1653-1665. 10.4143/crt.2018.544.
Paip1 Indicated Poor Prognosis in Cervical Cancer and Promoted Cervical Carcinogenesis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology & Cancer Research Center, Yanbian University Medical College, Yanji, China. zhlin720@ybu.edu.cn
- 2Key Laboratory of the Science and Technology, Department of Jilin Province, Yanji, China.
- 3Brain Korea 21 Project, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Oral Pathology, Oral Cancer Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2460613
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2018.544
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was aimed to investigate the role of poly(A)-binding protein-interacting protein 1 (Paip1) in cervical carcinogenesis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The expression of Paip1 in normal cervical epithelial tissues and cervical cancer (CC) tissues were detected by immunohistochemistry. In vivo and in vitro assays were performed to validate effect of Paip1 on CC progression.
RESULTS
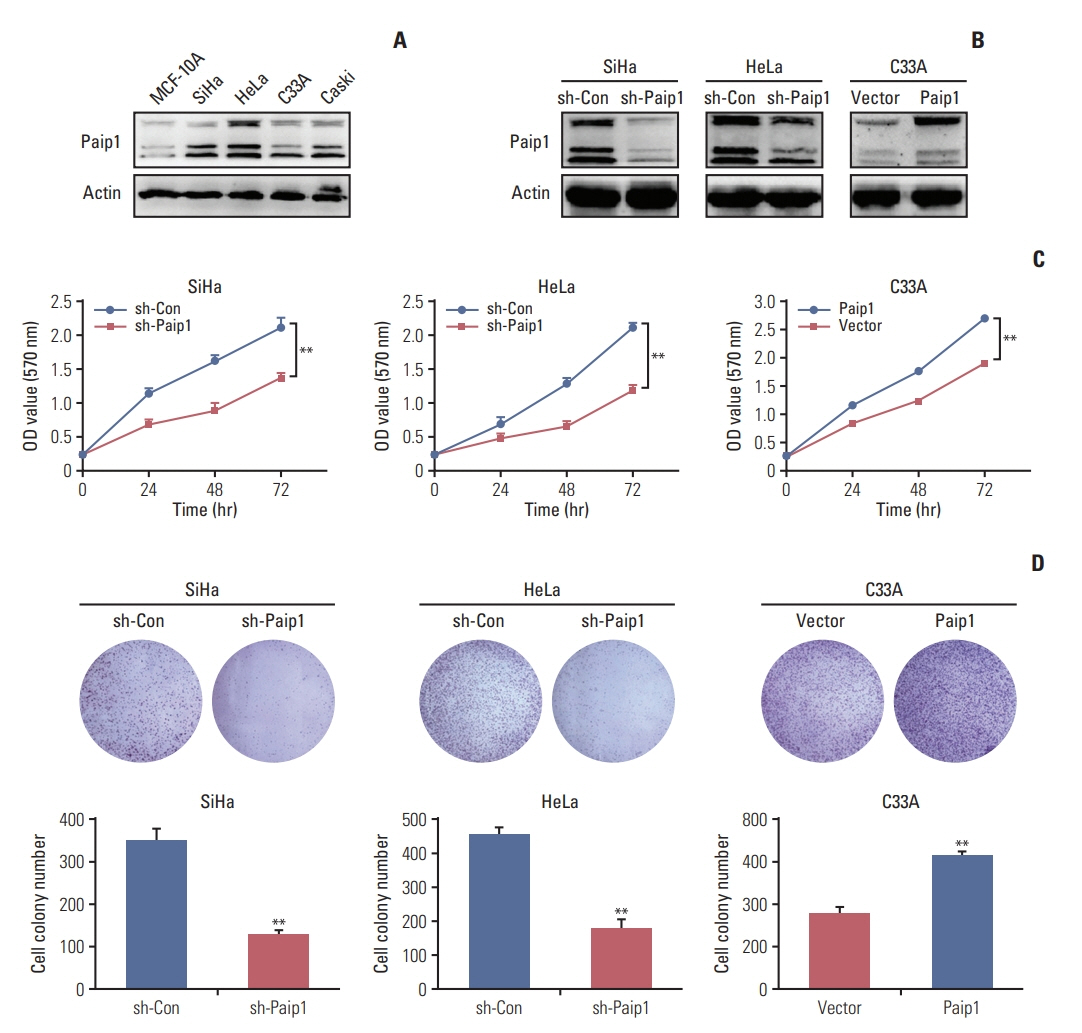
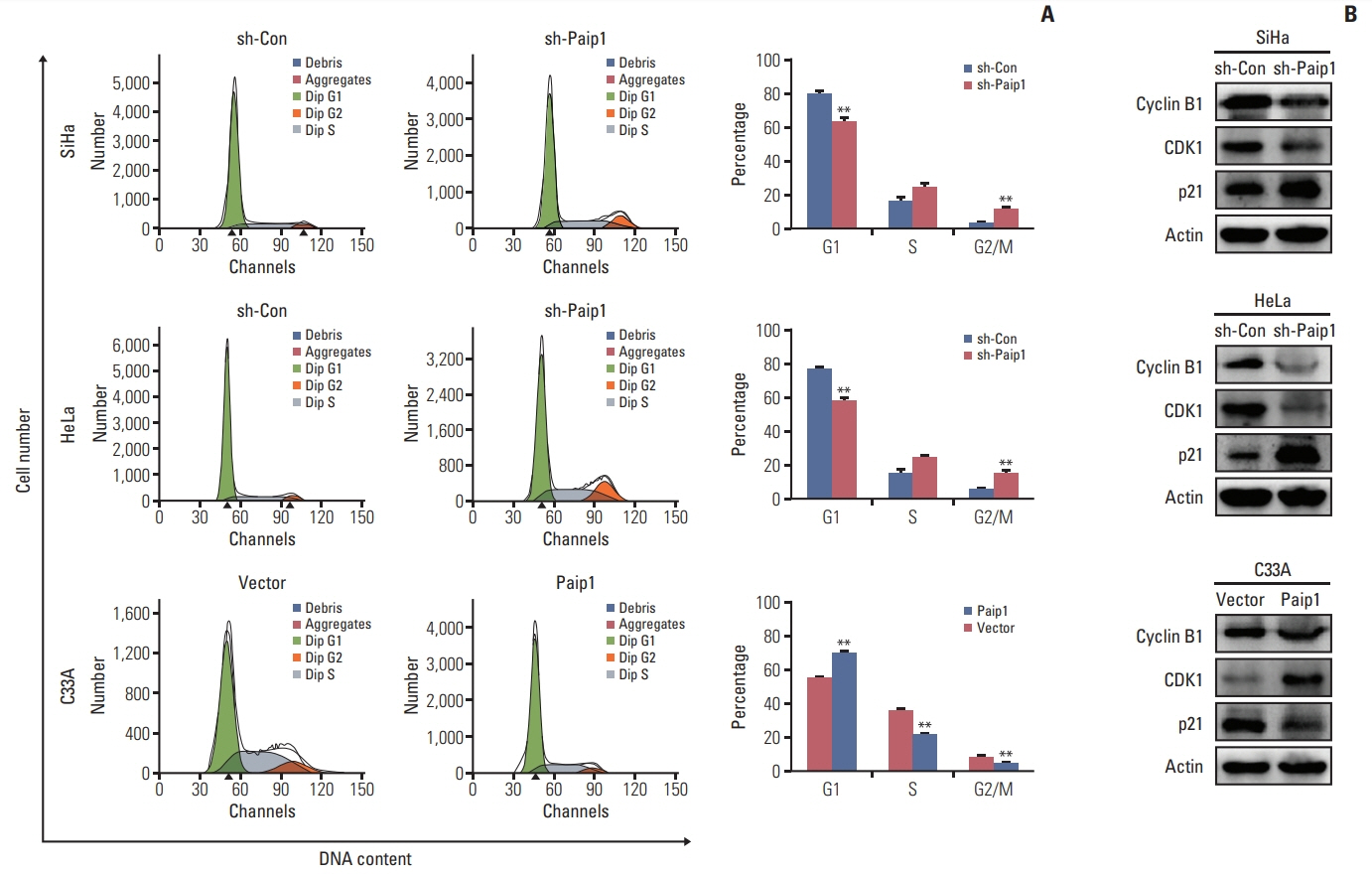
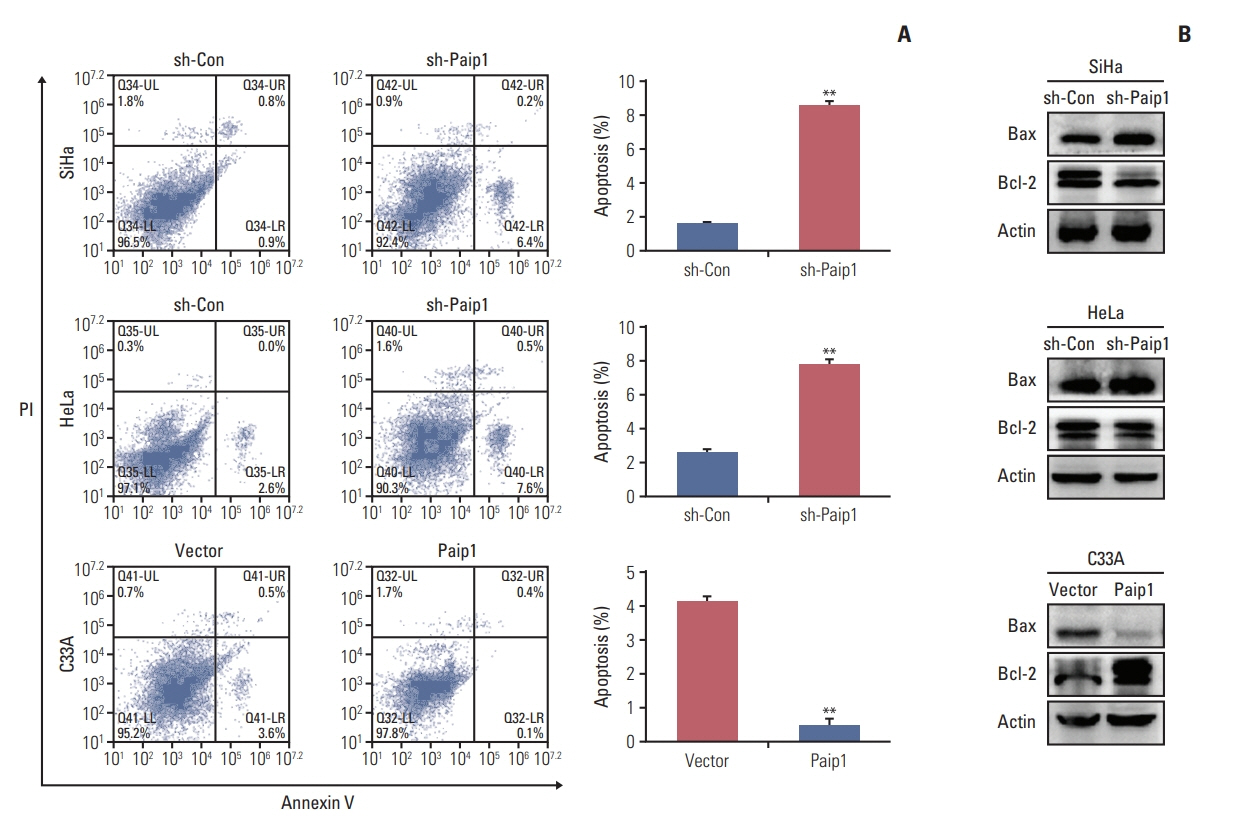
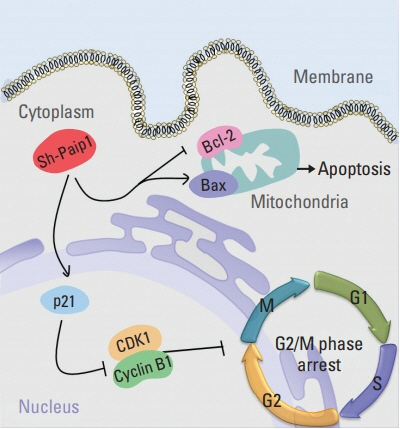
Paip1 was found to be up-regulated in CC, which was linked with shorter survival. Knockdown of Paip1 inhibited cell growth, induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in CC cells, whereas its overexpression reversed these effects. The in vivo tumor model confirmed the pro-tumor role of Paip1 in CC growth.
CONCLUSION
Altogether, the investigation demonstrated the clinical significance of Paip1 expression, which prompted that the up-regulated of Paip1 can presumably be a potential prognostic and progression marker for CC.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018; 68:7–30.
Article2. Mehlen P, Puisieux A. Metastasis: a question of life or death. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006; 6:449–58.
Article3. Kim JJ, Campos NG, Sy S, Burger EA, Cuzick J, Castle PE, et al. Inefficiencies and high-value improvements in U.S. cervical cancer screening practice: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2015; 163:589–97.4. Kodama J, Seki N, Masahiro S, Kusumoto T, Nakamura K, Hongo A, et al. Prognostic factors in stage IB-IIB cervical adenocarcinoma patients treated with radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy. J Surg Oncol. 2010; 101:413–7.
Article5. Qiao L, Zheng J, Tian Y, Zhang Q, Wang X, Chen JJ, et al. Regulator of chromatin condensation 1 abrogates the G1 cell cycle checkpoint via Cdk1 in human papillomavirus E7-expressing epithelium and cervical cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2018; 9:583.
Article6. Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015; 65:87–108.
Article7. Moore KN, Rowland MR. Treatment advances in locoregionally advanced and stage IVB/recurrent cervical cancer: can we agree that more is not always better? J Clin Oncol. 2015; 33:2125–8.
Article8. Martineau Y, Derry MC, Wang X, Yanagiya A, Berlanga JJ, Shyu AB, et al. Poly(A)-binding protein-interacting protein 1 binds to eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 to stimulate translation. Mol Cell Biol. 2008; 28:6658–67.
Article9. Craig AW, Haghighat A, Yu AT, Sonenberg N. Interaction of polyadenylate-binding protein with the eIF4G homologue PAIP enhances translation. Nature. 1998; 392:520–3.
Article10. Kanaan AS, Frank F, Maedler-Kron C, Verma K, Sonenberg N, Nagar B. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of the middle domain of Paip1. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2009; 65(Pt 10):1060–4.
Article11. Fukada Y, Yasui K, Kitayama M, Doi K, Nakano T, Watanabe Y, et al. Gene expression analysis of the murine model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: studies of the Leu126delTT mutation in SOD1. Brain Res. 2007; 1160:1–10.
Article12. Scotto L, Narayan G, Nandula SV, Subramaniyam S, Kaufmann AM, Wright JD, et al. Integrative genomics analysis of chromosome 5p gain in cervical cancer reveals target overexpressed genes, including Drosha. Mol Cancer. 2008; 7:58.
Article13. Piao J, Chen L, Jin T, Xu M, Quan C, Lin Z. Paip1 affects breast cancer cell growth and represents a novel prognostic biomarker. Hum Pathol. 2018; 73:33–40.
Article14. Yang Y, Wu Q, Li N, Che S, Jin T, Nan Y, et al. Upregulation of Tiam1 contributes to cervical cancer disease progression and indicates poor survival outcome. Hum Pathol. 2018; 75:179–88.
Article15. Chen L, Jin T, Zhu K, Piao Y, Quan T, Quan C, et al. PI3K/ mTOR dual inhibitor BEZ235 and histone deacetylase inhibitor Trichostatin A synergistically exert anti-tumor activity in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:11937–49.16. Li N, Wang Y, Che S, Yang Y, Piao J, Liu S, et al. HBXIP over expression as an independent biomarker for cervical cancer. Exp Mol Pathol. 2017; 102:133–7.
Article17. Gao J, Yu H, Guo W, Kong Y, Gu L, Li Q, et al. The anticancer effects of ferulic acid is associated with induction of cell cycle arrest and autophagy in cervical cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2018; 18:102.
Article18. Gorelick-Ashkenazi A, Weiss R, Sapozhnikov L, Florentin A, Tarayrah-Ibraheim L, Dweik D, et al. Caspases maintain tissue integrity by an apoptosis-independent inhibition of cell migration and invasion. Nat Commun. 2018; 9:2806.
Article19. Watkins SJ, Norbury CJ. Translation initiation and its deregulation during tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer. 2002; 86:1023–7.
Article20. Bitterman PB, Polunovsky VA. Translational control of cell fate: from integration of environmental signals to breaching anticancer defense. Cell Cycle. 2012; 11:1097–107.
Article21. Pestova TV, Kolupaeva VG. The roles of individual eukaryotic translation initiation factors in ribosomal scanning and initiation codon selection. Genes Dev. 2002; 16:2906–22.
Article22. Spilka R, Ernst C, Mehta AK, Haybaeck J. Eukaryotic translation initiation factors in cancer development and progression. Cancer Lett. 2013; 340:9–21.
Article23. Grosset C, Chen CY, Xu N, Sonenberg N, Jacquemin-Sablon H, Shyu AB. A mechanism for translationally coupled mRNA turnover: interaction between the poly(A) tail and a c-fos RNA coding determinant via a protein complex. Cell. 2000; 103:29–40.24. Santo L, Siu KT, Raje N. Targeting cyclin-dependent kinases and cell cycle progression in human cancers. Semin Oncol. 2015; 42:788–800.
Article25. Taylor WR, Stark GR. Regulation of the G2/M transition by p53. Oncogene. 2001; 20:1803–15.
Article26. Lucantoni F, Lindner AU, O'Donovan N, Dussmann H, Prehn JH. Systems modeling accurately predicts responses to genotoxic agents and their synergism with BCL-2 inhibitors in triple negative breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2018; 9:42.
Article27. Merino D, Lok SW, Visvader JE, Lindeman GJ. Targeting BCL2 to enhance vulnerability to therapy in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Oncogene. 2016; 35:1877–87.
Article28. Zhu L, Hao J, Cheng M, Zhang C, Huo C, Liu Y, et al. Hyperglycemia-induced Bcl-2/Bax-mediated apoptosis of Schwann cells via mTORC1/S6K1 inhibition in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Exp Cell Res. 2018; 367:186–95.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The clinical significance of Interleukin-6 mRNA expression in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer
- The Role of HPV E6 and E7 Oncoproteins in HPV-associated Cervical Carcinogenesis
- The annexin II expression in invasive cervical cancer
- The Expression of MT1-MMP and E-cadherin mRNA in Invasive Cervical Cancer
- Metastatic Breast Cancer from Cervical Cancer