Cancer Res Treat.
2019 Oct;51(4):1620-1631. 10.4143/crt.2018.340.
Low Doses of Nonylphenol Promote Growth of Colon Cancer Cells through Activation of ERK1/2 via G Protein‒Coupled Receptor 30
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical College, Zunyi, China. yangxuefeng923@163.com
- KMID: 2460610
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2018.340
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Nonylphenol (NP) is an endocrine disruptor found in products such as cleaners, plastics, and detergents. It exerts actions similar to endogenous 17β-estradiol (E2) and is reported to influence various cancers. However, its role in colon cancer remains elusive.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Colon cancer cell lines COLO 205 and SW480 were employed in our study. The cells were treated with NP or E2 followed by measurement of apoptosis and proliferation using flow cytometry and MTT assays, respectively. G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 30 (GPR30) expression was visualized using immunofluorescence and Western blot. To investigate the underlying mechanism, the expression levels of GPR30, p-protein kinase A (PKA), c-myc, cyclin D1, and ERK1/2 were analyzed using Western blot. Meanwhile, the GPR30 antagonist G15 was utilized to validate the role of GPR30 in colon cancer progression. Finally, the effect of a GPR30 inhibitor on tumor growth was determined in vivo using tumor xenograft mouse models.
RESULTS
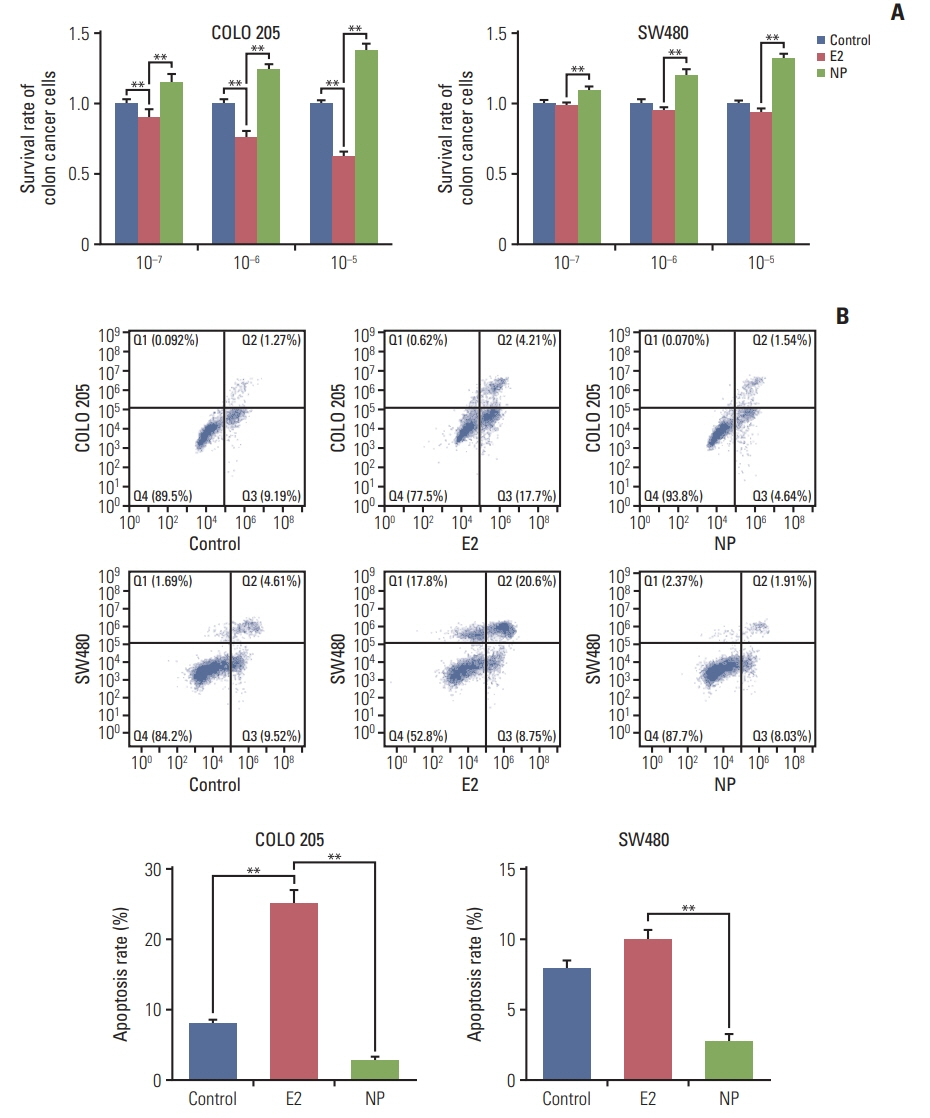
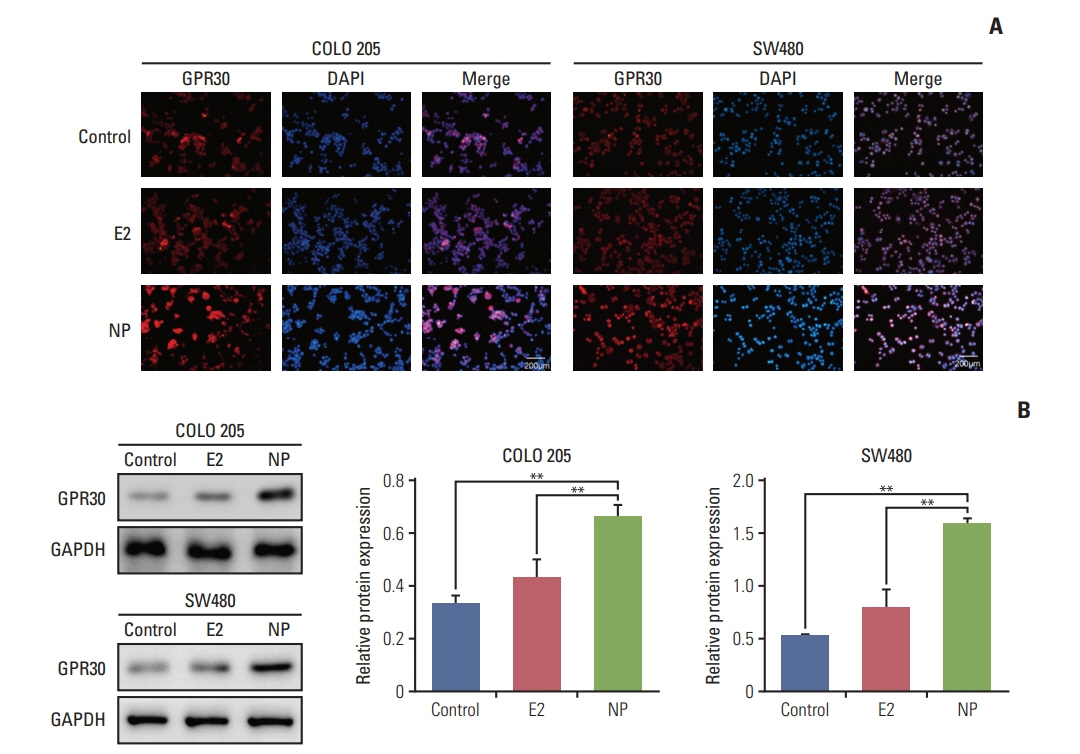
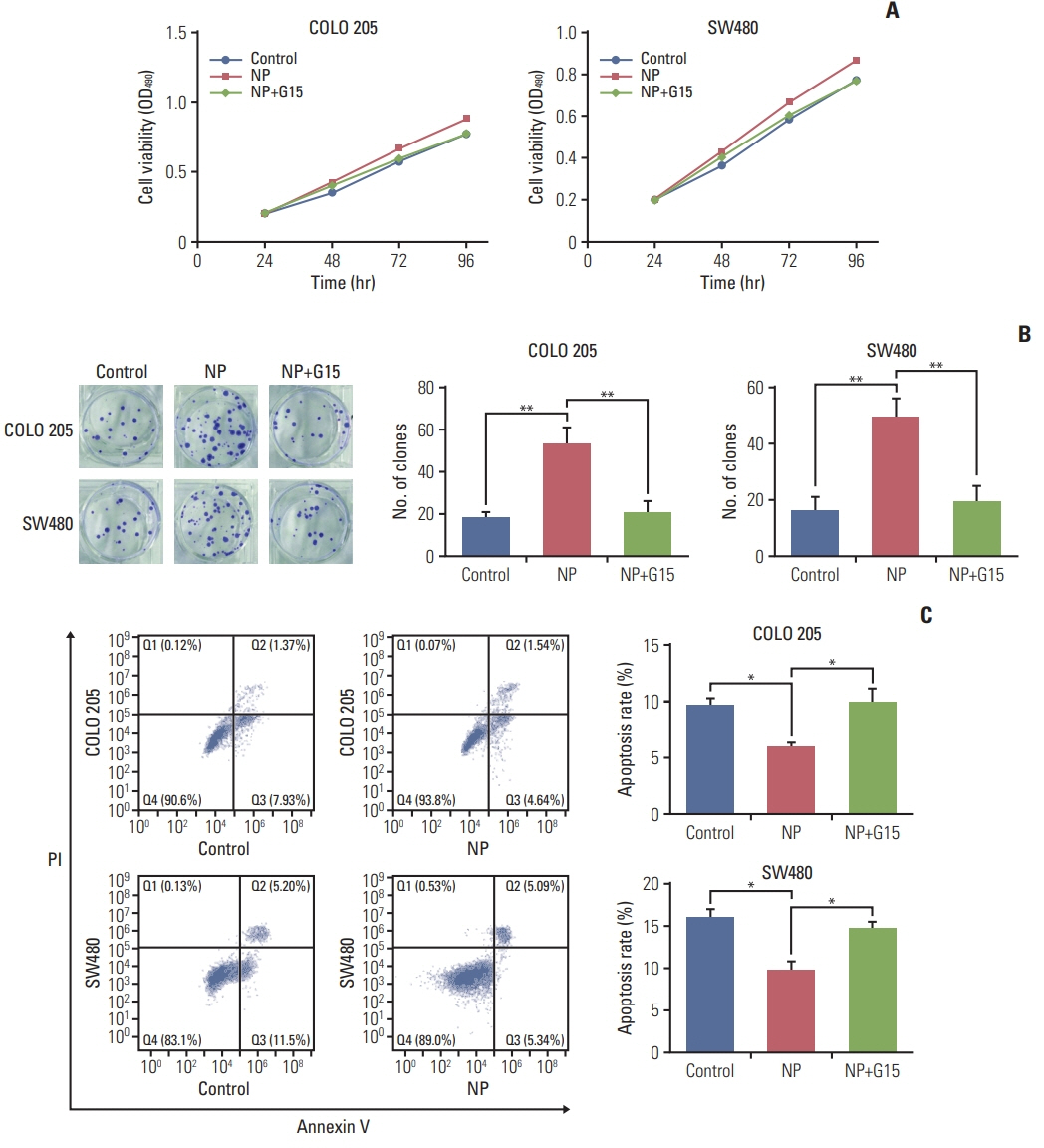
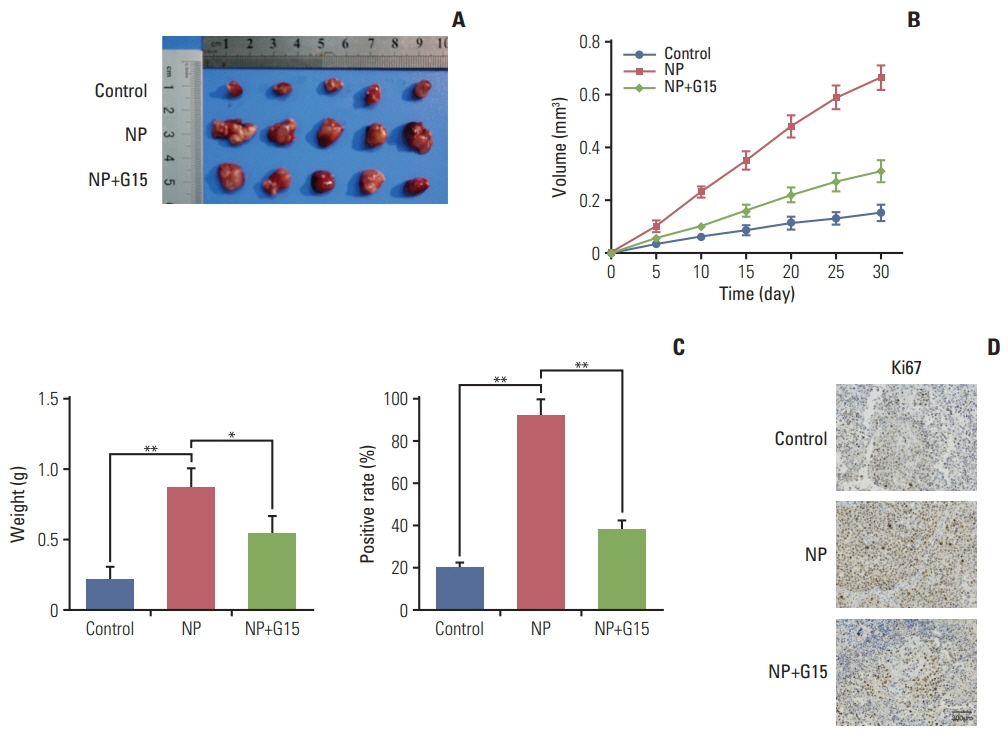
NP facilitated the proliferation of colon cancer cells and induced apoptosis failure in vitro. Western blot revealed increased GPR30 expression levels in response to NP treatment. Cyclin D1, p-PKA, c-myc, and proliferating cell nuclear antigen, proteins that regulate the cell cycle, were all upregulated by NP, and NP-mediated ERK1/2 activation and subsequent cell proliferation were abrogated by the GPR30 inhibitor G15. Moreover, colon cancer mice that received G15 administration demonstrated impaired tumor growth in vivo.
CONCLUSION
Low dose NP promotes the growth of colon tumors through GPR30-mediated activation of ERK1/2 signaling.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Apoptosis
Blotting, Western
Cell Cycle
Cell Line
Cell Proliferation
Colon*
Colonic Neoplasms*
Cyclin D1
Detergents
Estrogens
Flow Cytometry
Fluorescent Antibody Technique
Heterografts
In Vitro Techniques
Mice
Phosphotransferases
Plastics
Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen
Cyclin D1
Detergents
Estrogens
Phosphotransferases
Plastics
Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Liu MM, Albanese C, Anderson CM, Hilty K, Webb P, Uht RM, et al. Opposing action of estrogen receptors alpha and beta on cyclin D1 gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:24353–60.2. Prossnitz ER, Arterburn JB, Sklar LA. GPR30: a G protein-coupled receptor for estrogen. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007; 265-266:138–42.
Article3. Filardo EJ, Quinn JA, Frackelton AR Jr, Bland KI. Estrogen action via the G protein-coupled receptor, GPR30: stimulation of adenylyl cyclase and cAMP-mediated attenuation of the epidermal growth factor receptor-to-MAPK signaling axis. Mol Endocrinol. 2002; 16:70–84.
Article4. Kanda N, Watanabe S. 17beta-estradiol inhibits oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in keratinocytes by promoting Bcl-2 expression. J Invest Dermatol. 2003; 121:1500–9.5. Maggiolini M, Vivacqua A, Fasanella G, Recchia AG, Sisci D, Pezzi V, et al. The G protein-coupled receptor GPR30 mediates c-fos up-regulation by 17beta-estradiol and phytoestrogens in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279:27008–16.6. Caiazza F, Galluzzo P, Lorenzetti S, Marino M. 17Beta-estradiol induces ERbeta up-regulation via p38/MAPK activation in colon cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007; 359:102–7.7. Barzi A, Lenz AM, Labonte MJ, Lenz HJ. Molecular pathways: estrogen pathway in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2013; 19:5842–8.
Article8. Wetherill YB, Akingbemi BT, Kanno J, McLachlan JA, Nadal A, Sonnenschein C, et al. In vitro molecular mechanisms of bisphenol A action. Reprod Toxicol. 2007; 24:178–98.
Article9. Fernandez SV, Russo J. Estrogen and xenoestrogens in breast cancer. Toxicol Pathol. 2010; 38:110–22.
Article10. Lee JW, Han HK, Park S, Moon EY. Nonylphenol increases tumor formation and growth by suppressing gender-independent lymphocyte proliferation and macrophage activation. Environ Toxicol. 2017; 32:1679–87.
Article11. Kim SH, Nam KH, Hwang KA, Choi KC. Influence of hexabromocyclododecane and 4-nonylphenol on the regulation of cell growth, apoptosis and migration in prostatic cancer cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 2016; 32:240–7.
Article12. Konstantinopoulos PA, Kominea A, Vandoros G, Sykiotis GP, Andricopoulos P, Varakis I, et al. Oestrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) is abundantly expressed in normal colonic mucosa, but declines in colon adenocarcinoma paralleling the tumour's dedifferentiation. Eur J Cancer. 2003; 39:1251–8.13. Campbell-Thompson M, Lynch IJ, Bhardwaj B. Expression of estrogen receptor (ER) subtypes and ERbeta isoforms in colon cancer. Cancer Res. 2001; 61:632–40.14. Prossnitz ER, Sklar LA, Oprea TI, Arterburn JB. GPR30: a novel therapeutic target in estrogen-related disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2008; 29:116–23.
Article15. He YY, Cai B, Yang YX, Liu XL, Wan XP. Estrogenic G protein-coupled receptor 30 signaling is involved in regulation of endometrial carcinoma by promoting proliferation, invasion potential, and interleukin-6 secretion via the MEK/ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Cancer Sci. 2009; 100:1051–61.
Article16. Kleuser B, Malek D, Gust R, Pertz HH, Potteck H. 17-Betaestradiol inhibits transforming growth factor-beta signaling and function in breast cancer cells via activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase through the G protein-coupled receptor 30. Mol Pharmacol. 2008; 74:1533–43.17. Chakrabarti S, Davidge ST. G-protein coupled receptor 30 (GPR30): a novel regulator of endothelial inflammation. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e52357.
Article18. Ge LC, Chen ZJ, Liu HY, Zhang KS, Liu H, Huang HB, et al. Involvement of activating ERK1/2 through G protein coupled receptor 30 and estrogen receptor α/β in low doses of bisphenol A promoting growth of Sertoli TM4 cells. Toxicol Lett. 2014; 226:81–9.
Article19. Mo Z, Liu M, Yang F, Luo H, Li Z, Tu G, et al. GPR30 as an initiator of tamoxifen resistance in hormone-dependent breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2013; 15:R114.
Article20. Arias-Pulido H, Royce M, Gong Y, Joste N, Lomo L, Lee SJ, et al. GPR30 and estrogen receptor expression: new insights into hormone dependence of inflammatory breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010; 123:51–8.
Article21. Jala VR, Radde BN, Haribabu B, Klinge CM. Enhanced expression of G-protein coupled estrogen receptor (GPER/GPR30) in lung cancer. BMC Cancer. 2012; 12:624.
Article22. He YY, Du GQ, Cai B, Yan Q, Zhou L, Chen XY, et al. Estrogenic transmembrane receptor of GPR30 mediates invasion and carcinogenesis by endometrial cancer cell line RL95-2. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012; 138:775–83.
Article23. Qiu Y, Waters CE, Lewis AE, Langman MJ, Eggo MC. Oestrogen-induced apoptosis in colonocytes expressing oestrogen receptor beta. J Endocrinol. 2002; 174:369–77.
Article24. Marino M, Galluzzo P, Ascenzi P. Estrogen signaling multiple pathways to impact gene transcription. Curr Genomics. 2006; 7:497–508.
Article25. Filardo E, Quinn J, Pang Y, Graeber C, Shaw S, Dong J, et al. Activation of the novel estrogen receptor G protein-coupled receptor 30 (GPR30) at the plasma membrane. Endocrinology. 2007; 148:3236–45.
Article26. Bustos V, Nolan AM, Nijhuis A, Harvey H, Parker A, Poulsom R, et al. GPER mediates differential effects of estrogen on colon cancer cell proliferation and migration under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:84258–75.
Article27. Recchia AG, Vivacqua A, Gabriele S, Carpino A, Fasanella G, Rago V, et al. Xenoestrogens and the induction of proliferative effects in breast cancer cells via direct activation of oestrogen receptor alpha. Food Addit Contam. 2004; 21:134–44.28. Nguyen-Vu T, Wang J, Mesmar F, Mukhopadhyay S, Saxena A, McCollum CW, et al. Estrogen receptor beta reduces colon cancer metastasis through a novel miR-205: PROX1 mechanism. Oncotarget. 2016; 7:42159–71.29. Hartman J, Edvardsson K, Lindberg K, Zhao C, Williams C, Strom A, et al. Tumor repressive functions of estrogen receptor beta in SW480 colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2009; 69:6100–6.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- G Protein–Coupled Receptor 30 Mediates the Anticancer Effects Induced by Eicosapentaenoic Acid in Ovarian Cancer Cells
- Forkhead Box C1 (FOXC1) Expression in Stromal Cells within the Microenvironment of T and NK Cell Lymphomas: Association with Tumor Dormancy and Activation
- Novel Effect of Hyaluronan and Proteoglycan Link Protein 1 (HAPLN1) on Hair Follicle Cells Proliferation and Hair Growth
- Phytoestrogen-Induced Phosphorylation of MAP Kinase in Osteoblasts is Mediated by Membrane Estrogen Receptor
- Recent Progress in Understanding the Conformational Mechanism of Heterotrimeric G Protein Activation