Yonsei Med J.
2019 Nov;60(11):1036-1044. 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.11.1036.
Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Transplantation Inhibits Vascular Inflammatory Responses and Endothelial Dysfunction in Rats with Atherosclerosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dardiovascular, Pingliang People's Hospital, Pingliang, China.
- 2Department of Pathology, Second Provincial People's Hospital, Lanzhou, China. niedengmei@163.com
- KMID: 2460220
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2019.60.11.1036
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study aimed to investigate the effect of adipose-derived stem cell (ADSC) transplantation on atherosclerosis (AS) and its underlying mechanisms.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
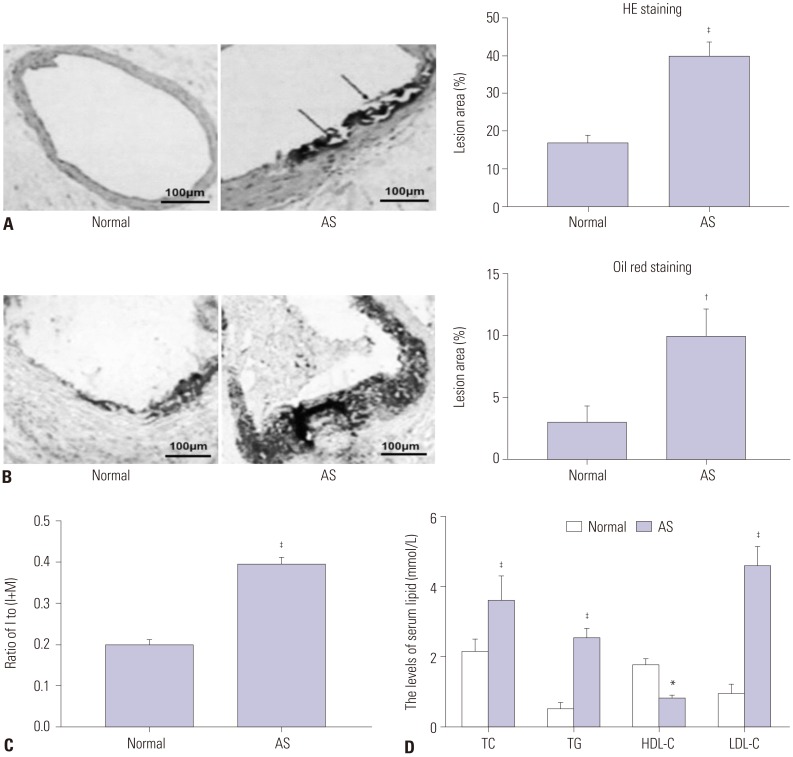
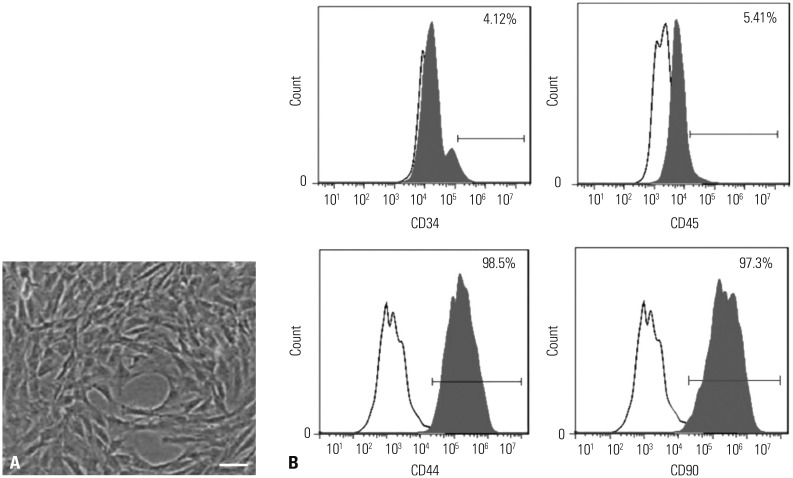
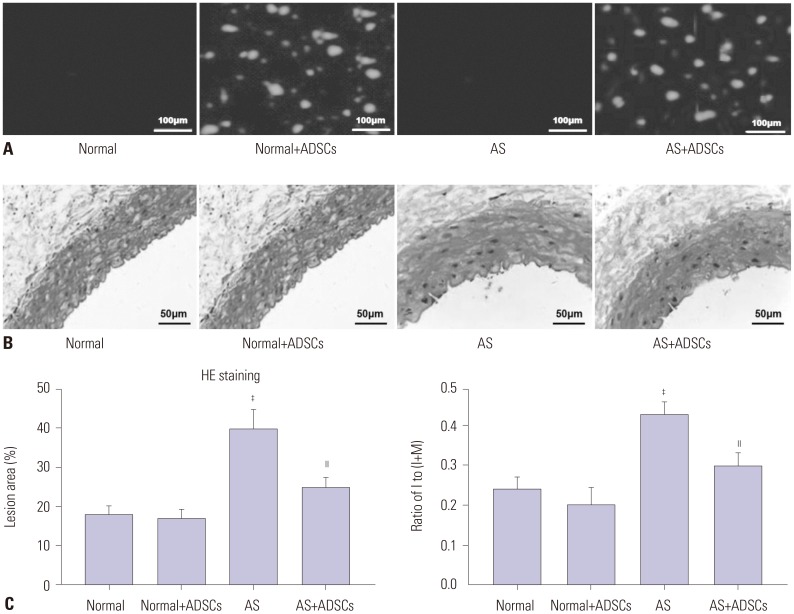
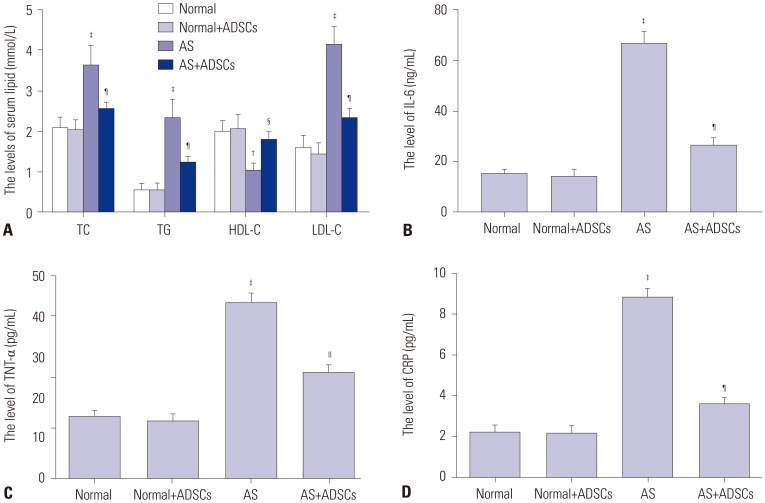
In our study, rat AS model was established, and ADSCs were isolated and cultured. Atherosclerotic plaque and pathological symptoms of thoracic aorta were measured by Oil Red O staining and Hematoxylin-Eosin staining, respectively. Total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels were measured by an automatic biochemical analyzer. Expressions of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), aortic endothelin-1 (ET-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6), c-reactive protein (CRP), and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) were measured by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay, VEGF, VCAM-1, ICAM-1, ET-1, respectively, and NF-κB p65 mRNA expressions were detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Protein expressions of VEGF, VCAM-1, ICAM-1, ET-1, NF-κB p65, p-NF-κB p65, and IκBα were measured by western blot. Moreover, NF-κB p65 expression was measured by immunofluorescence staining.
RESULTS
ADSC transplantation alleviated the pathological symptoms of aortic AS. ADSC transplantation decreased the levels of TC, TG, and LDL-C and increased serum HDL-C level. Meanwhile, ADSC transplantation decreased the levels of IL-6, CRP, and TNF-α in AS rats. Moreover, the expressions of VEGF, ET-1, VCAM-1, and ICAM-1 were decreased by ADSC transplantation. ADSC transplantation inhibited phosphorylation of NF-κB p65 and promoted IκBα expression in AS rats.
CONCLUSION
Our study demonstrated that ADSC transplantation could inhibit vascular inflammatory responses and endothelial dysfunction by suppressing NF-κB pathway in AS rats.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Aorta, Thoracic
Atherosclerosis*
Blotting, Western
C-Reactive Protein
Cholesterol
Endothelin-1
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Fluorescent Antibody Technique
Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1
Interleukin-6
Lipoproteins
Phosphorylation
Plaque, Atherosclerotic
Rats*
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
RNA, Messenger
Stem Cell Transplantation*
Stem Cells*
Triglycerides
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
C-Reactive Protein
Cholesterol
Endothelin-1
Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1
Interleukin-6
Lipoproteins
RNA, Messenger
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Figure
Reference
-
1. Emini Veseli B, Perrotta P, De Meyer GRA, Roth L, Van der Donckt C, Martinet W, et al. Animal models of atherosclerosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017; 816:3–13. PMID: 28483459.
Article2. Ross R. Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory disease. Am Heart J. 1999; 138(5 Pt 2):S419–S420. PMID: 10539839.
Article3. Libby P, Ridker PM, Hansson GK. Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature. 2011; 473:317–325. PMID: 21593864.
Article4. Weber C, Noels H. Atherosclerosis: current pathogenesis and therapeutic options. Nat Med. 2011; 17:1410–1422. PMID: 22064431.
Article5. Hansson GK. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:1685–1695. PMID: 15843671.
Article6. Schlosser S, Dennler C, Schweizer R, Eberli D, Stein JV, Enzmann V, et al. Paracrine effects of mesenchymal stem cells enhance vascular regeneration in ischemic murine skin. Microvasc Res. 2012; 83:267–275. PMID: 22391452.
Article7. Mimeault M, Hauke R, Batra SK. Stem cells: a revolution in therapeutics-recent advances in stem cell biology and their therapeutic applications in regenerative medicine and cancer therapies. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007; 82:252–264. PMID: 17671448.
Article8. Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, De Ugarte DA, Huang JI, Mizuno H, et al. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2002; 13:4279–4295. PMID: 12475952.
Article9. Choi JS, Ryu HA, Cheon SH, Kim SW. Human adipose derived stem cells exhibit enhanced liver regeneration in acute liver injury by controlled releasing hepatocyte growth factor. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019; 52:935–950. PMID: 30964610.
Article10. Zhang Y, Deng H, Hu Y, Pan C, Wu G, Li Q, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells stereotactic transplantation alleviate brain edema from intracerebral hemorrhage. J Cell Biochem. 2019; 120:14372–14382. PMID: 30963640.
Article11. Onat D, Brillon D, Colombo PC, Schmidt AM. Human vascular endothelial cells: a model system for studying vascular inflammation in diabetes and atherosclerosis. Curr Diab Rep. 2011; 11:193–202. PMID: 21337131.
Article12. Libby P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012; 32:2045–2051. PMID: 22895665.
Article13. Negi G, Sharma SS. Inhibition of IκB kinase (IKK) protects against peripheral nerve dysfunction of experimental diabetes. Mol Neurobiol. 2015; 51:591–598. PMID: 24946751.
Article14. Charo IF, Taub R. Anti-inflammatory therapeutics for the treatment of atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011; 10:365–376. PMID: 21532566.
Article15. Taleb S. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2016; 109:708–715. PMID: 27595467.
Article16. Baranowska A, Skowron B, Nowak B, Ciesielczyk K, Guzdek P, Gil K, et al. Changes in viability of rat adipose-derived stem cells isolated from abdominal/perinuclear adipose tissue stimulated with pulsed electromagnetic field. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017; 68:253–264. PMID: 28614775.17. Maziarz A, Kocan B, Bester M, Budzik S, Cholewa M, Ochiya T, et al. How electromagnetic fields can influence adult stem cells: positive and negative impacts. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016; 7:54. PMID: 27086866.
Article18. Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999; 284:143–147. PMID: 10102814.
Article19. Liu MH, Li Y, Han L, Zhang YY, Wang D, Wang ZH, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells were impaired in restricting CD4(+)T cell proliferation and polarization in type 2 diabetic ApoE(−/−) mouse. Mol Immunol. 2017; 87:152–160. PMID: 28445787.20. Lee JS, Hong JM, Moon GJ, Lee PH, Ahn YH, Bang OY, et al. A long-term follow-up study of intravenous autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with ischemic stroke. Stem Cells. 2010; 28:1099–1106. PMID: 20506226.
Article21. Skrzep-Poloczek B, Tomasik A, Tarnawski R, Hyla-Klekot L, Dyduch A, Wojciechowska C, et al. Nephrotic origin hyperlipidemia, relative reduction of vitamin E level and subsequent oxidative stress may promote atherosclerosis. Nephron. 2001; 89:68–72. PMID: 11528235.
Article22. Giannotti G, Landmesser U. Endothelial dysfunction as an early sign of atherosclerosis. Herz. 2007; 32:568–572. PMID: 17972030.
Article23. Fang Y, Sang H, Yuan N, Sun H, Yao S, Wang J, et al. Ethanolic extract of propolis inhibits atherosclerosis in ApoE-knockout mice. Lipids Health Dis. 2013; 12:123. PMID: 23941539.
Article24. Hou HF, Yuan N, Guo Q, Sun T, Li C, Liu JB, et al. Citreoviridin enhances atherogenesis in hypercholesterolemic ApoE-deficient mice via upregulating inflammation and endothelial dysfunction. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0125956. PMID: 25933220.
Article25. Krieglstein CF, Granger DN. Adhesion molecules and their role in vascular disease. Am J Hypertens. 2001; 14(6 Pt 2):44S–54S. PMID: 11411765.
Article26. Kim I, Moon SO, Kim SH, Kim HJ, Koh YS, Koh GY. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1), and E-selectin through nuclear factor-kappa B activation in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:7614–7620. PMID: 11108718.27. Wang HW, Lo HH, Chiu YL, Chang SJ, Huang PH, Liao KH, et al. Dysregulated miR-361-5p/VEGF axis in the plasma and endothelial progenitor cells of patients with coronary artery disease. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e98070. PMID: 24865854.
Article28. Alexander MR, Moehle CW, Johnson JL, Yang Z, Lee JK, Jackson CL, et al. Genetic inactivation of IL-1 signaling enhances atherosclerotic plaque instability and reduces outward vessel remodeling in advanced atherosclerosis in mice. J Clin Invest. 2012; 122:70–79. PMID: 22201681.
Article29. Gao Y, Jiang W, Dong C, Li C, Fu X, Min L, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of sophocarpine in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells via NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways. Toxicol In Vitro. 2012; 26:1–6. PMID: 21978812.
Article30. Israf DA, Khaizurin TA, Syahida A, Lajis NH, Khozirah S. Cardamonin inhibits COX and iNOS expression via inhibition of p65NF-kappaB nuclear translocation and Ikappa-B phosphorylation in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Mol Immunol. 2007; 44:673–679. PMID: 16777230.31. Pateras I, Giaginis C, Tsigris C, Patsouris E, Theocharis S. NF-κB signaling at the crossroads of inflammation and atherogenesis: searching for new therapeutic links. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014; 18:1089–1101. PMID: 25005042.
Article32. Brånén L, Hovgaard L, Nitulescu M, Bengtsson E, Nilsson J, Jovinge S. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-alpha reduces atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004; 24:2137–2142. PMID: 15345516.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Therapeutic Angiogenesis with Somatic Stem Cell Transplantation
- Clinical assessment after human adipose stem cell transplantation into dogs
- Adipose-derived stem cells: characterization and clinical application
- Stem Cell Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction
- Adipose Stem Cells as Alternatives for Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Oral Ulcer Healing