Ann Lab Med.
2019 Nov;39(6):537-544. 10.3343/alm.2019.39.6.537.
Serotype Distribution and Antimicrobial Resistance of Invasive and Noninvasive Streptococcus pneumoniae Isolates in Korea between 2014 and 2016
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. jhsmile@inje.ac.kr
- 2Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, Semyung University, Jecheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine and Research Institute of Bacterial Resistance, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Kangwon National University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 5Department of Laboratory Medicine, School of Medicine, Jeju National University, Jeju, Korea.
- 6Department of Laboratory Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 7Department of Laboratory Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 8Department of Laboratory Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 9Department of Laboratory Medicine, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 10Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 11Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- 12Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chonbuk National University Medical School and Hospital, Jeonju, Korea.
- 13Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea.
- 14Department of Laboratory Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- 15Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 16Department of Laboratory Medicine, Wonkwang University College of Medicine, Iksan, Korea.
- 17Department of Laboratory Medicine, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- 18Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea.
- 19Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 20Department of Laboratory Medicine, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Ilsan, Korea.
- 21Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 22Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu, Korea.
- 23Department of Laboratory Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 24Department of Laboratory Medicine, International St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, Catholic Kwandong University, Incheon, Korea.
- 25Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 26Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 27Department of Laboratory Medicine, Bundang Jesaeng General Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 28Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea.
- 29Department of Laboratory Medicine, Cheju Halla General Hospital, Jeju, Korea.
- 30Department of Laboratory Medicine, Daegu Catholic University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 31Department of Laboratory Medicine, Eulji University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 32Department of Laboratory Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- 33Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 34Department of Laboratory Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 35Department of Laboratory Medicine, Dongnam Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Busan, Korea.
- 36Paik Institute for Clinical Research, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2450948
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2019.39.6.537
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Several factors contribute to differences in Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype distribution. We investigated the serotype distribution and antimicrobial resistance of S. pneumoniae isolated between 2014 and 2016 in Korea.
METHODS
We collected a total of 1,855 S. pneumoniae isolates from 44 hospitals between May 2014 and May 2016, and analyzed the serotypes by sequential multiplex PCR. We investigated the distribution of each serotype by patient age, source of the clinical specimen, and antimicrobial resistance pattern.
RESULTS
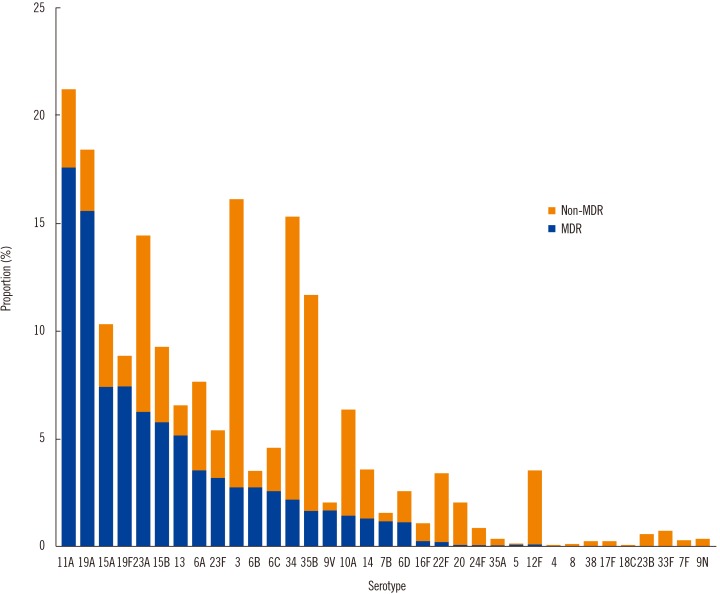
The most common serotypes were 11A (10.1%), followed by 19A (8.8%), 3 (8.5%), 34 (8.1%), 23A (7.3%), and 35B (6.2%). The major invasive serotypes were 3 (12.6%), 19A (7.8%), 34 (7.8%), 10A (6.8%), and 11A (6.8%). Serotypes 10A, 15B, 19A, and 12F were more common in patients ≤5 years old, while serotype 3 was more common in patients ≥65 years old compared with the other age groups. The coverage rates of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV)7, PCV10, PCV13, and pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine 23 were 11.8%, 12.12%, 33.3%, and 53.6%, respectively. Of the 1,855 isolates, 857 (46.2%) were multi-drug resistant (MDR), with serotypes 11A and 19A predominant among the MDR strains. The resistance rates against penicillin, cefotaxime, and levofloxacin were 22.8%, 12.5%, and 9.4%, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
There were significant changes in the major S. pneumoniae serotypes in the community. Non-PCV13 serotypes increased in patients ≤5 years old following the introduction of national immunization programs with the 10- and 13-polyvalent vaccines.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Recent Trends in Invasive Pneumococcal Disease in Korea in the Post-pneumococcal Vaccine Era
Hee Jae Huh, Heungsup Sung
Ann Lab Med. 2023;43(1):1-2. doi: 10.3343/alm.2023.43.1.1.Serotype Distribution and Antimicrobial Resistance of
Streptococcus pneumoniae Causing Invasive Pneumococcal Disease in Korea Between 2017 and 2019 After Introduction of the 13-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine
Gyu Ri Kim, Eun-Young Kim, Si Hyun Kim, Hae Kyung Lee, Jaehyeon Lee, Jong Hee Shin, Young Ree Kim, Sae Am Song, Joseph Jeong, Young Uh, Yu Kyung Kim, Dongeun Yong, Hyun Soo Kim, Sunjoo Kim, Young Ah Kim, Kyeong Seob Shin, Seok Hoon Jeong, Namhee Ryoo, Jeong Hwan Shin
Ann Lab Med. 2023;43(1):45-54. doi: 10.3343/alm.2023.43.1.45.
Reference
-
1. Kalin M, Ortqvist A, Almela M, Aufwerber E, Dwyer R, Henriques B, et al. Prospective study of prognostic factors in community-acquired bacteremic pneumococcal disease in 5 countries. J Infect Dis. 2000; 182:840–847. PMID: 10950779.2. O'Brien KL, Wolfson LJ, Watt JP, Henkle E, Deloria-Knoll M, McCall N, et al. Burden of disease caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae in children younger than 5 years: global estimates. Lancet. 2009; 374:893–902. PMID: 19748398.3. Walker CLF, Rudan I, Liu L, Nair H, Theodoratou E, Bhutta ZA, et al. Global burden of childhood pneumonia and diarrhoea. Lancet. 2013; 381:1405–1416. PMID: 23582727.4. Kim SH, Song JH, Chung DR, Thamlikitkul V, Yang Y, Wang H, et al. Changing trends in antimicrobial resistance and serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates in Asian countries: an Asian Network for Surveillance of Resistant Pathogens (ANSORP) study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012; 56:1418–1426. PMID: 22232285.5. Konradsen HB, Kaltoft MS. Invasive pneumococcal infections in Denmark from 1995 to 1999: epidemiology, serotypes, and resistance. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002; 9:358–365. PMID: 11874878.6. Whitney CG, Farley MM, Hadler J, Harrison LH, Bennett NM, Lynfield R, et al. Decline in invasive pneumococcal disease after the introduction of protein-polysaccharide conjugate vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348:1737–1746. PMID: 12724479.7. Kaplan SL, Barson WJ, Lin PL, Romero JR, Bradley JS, Tan TQ, et al. Early trends for invasive pneumococcal infections in children after the introduction of the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2013; 32:203–207. PMID: 23558320.8. Moore MR, Gertz RE Jr, Woodbury RL, Barkocy-Gallagher GA, Schaffner W, Lexau C, et al. Population snapshot of emergent Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 19A in the United States, 2005. J Infect Dis. 2008; 197:1016–1027. PMID: 18419539.9. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Direct and indirect effects of routine vaccination of children with 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on incidence of invasive pneumococcal disease-United States, 1998–2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2005; 54:893–897. PMID: 16163262.10. Hsu HE, Shutt KA, Moore MR, Beall BW, Bennett NM, Craig AS, et al. Effect of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on pneumococcal meningitis. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:244–256. PMID: 19144940.11. Choi EH, Kim SH, Eun BW, Kim SJ, Kim NH, Lee J, et al. Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 19A in children, South Korea. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008; 14:275–281. PMID: 18258121.12. Miller E, Andrews NJ, Waight PA, Slack MP, George RC. Herd immunity and serotype replacement 4 years after seven-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccination in England and Wales: an observational cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2011; 11:760–768. PMID: 21621466.13. Lepoutre A, Varon E, Georges S, Dorléans F, Janoir C, Gutmann L, et al. Impact of the pneumococcal conjugate vaccines on invasive pneumococcal disease in France, 2001-2012. Vaccine. 2015; 33:359–366. PMID: 25448105.14. Klugman KP. Pneumococcal resistance to antibiotics. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990; 3:171–196. PMID: 2187594.15. Jacobs MR, Koornhof HJ, Robins-Browne RM, Stevenson CM, Vermaak ZA, Freiman I, et al. Emergence of multiply resistant pneumococci. N Engl J Med. 1978; 299:735–740. PMID: 29219.16. Kim SH, Bae IK, Park D, Lee K, Kim NY, Song SA, et al. Serotype distribution and antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates causing invasive and noninvasive pneumococcal diseases in Korea from 2008 to 2014. Biomed Res Int. 2016; 2016:6950482. PMID: 27314035.17. Kim SH, Song SA, Yi J, Song D, Chang CL, Park DC, et al. Distribution and antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae at four university hospitals in Busan and Gyeongnam. Ann Clin Microbiol. 2016; 19:48–53.18. CLSI. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. 18th ed. Informational supplement M100-S18. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2008.19. Brito DA, Ramirez M, de Lencastre H. Serotyping Streptococcus pneumoniae by multiplex PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 2003; 41:2378–2384. PMID: 12791852.20. CLSI. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing M100. 27th ed. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2017.21. Choi WS, Choi JH, Kwon KT, Seo K, Kim MA, Lee SO, et al. Revised adult immunization guideline recommended by the Korean society of infectious diseases, 2014. Infect Chemother. 2015; 47:68–79. PMID: 25844267.22. Richter SS, Diekema DJ, Heilmann KP, Dohrn CL, Riahi F, Doern GV. Changes in pneumococcal serotypes and antimicrobial resistance after introduction of the 13-valent conjugate vaccine in the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014; 58:6484–6489. PMID: 25136018.23. Richter SS, Heilmann KP, Dohrn CL, Riahi F, Diekema DJ, Doern GV. Evaluation of pneumococcal serotyping by multiplex PCR and quellung reactions. J Clin Microbiol. 2013; 51:4193–4195. PMID: 24025905.24. Galanis I, Lindstrand A, Darenberg J, Browall S, Nannapaneni P, Sjöström K, et al. Effects of PCV7 and PCV13 on invasive pneumococcal disease and carriage in Stockholm, Sweden. Eur Respir J. 2016; 47:1208–1218. PMID: 26797033.25. van der Linden M, Perniciaro S, Imöhl P. Increase of serotypes 15A and 23B in IPD in Germany in the PCV13 vaccination era. BMC Infect Dis. 2015; 15:207. PMID: 25940580.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Antimicrobial Resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae Clinical Serotypes between 2017 and 2022 in Crete, Greece
- Changes in the Serotype Distribution among Antibiotic Resistant Carriage Streptococcus pneumoniae Isolates in Children after the Introduction of the Extended-Valency Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine
- Serotype Distribution and Antimicrobial Resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae Causing Invasive Pneumococcal Disease in Korea Between 2017 and 2019 After Introduction of the 13-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine
- The Evolving Epidemiology of Serotype Distribution and Antimicrobial Resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae Strains Isolated from Adults in Crete, Greece, 2009–2016
- Changes in Serotype Distribution and Antibiotic Resistance of Nasopharyngeal Isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae from Children in Korea, after Optional Use of the 7-Valent Conjugate Vaccine