Ann Lab Med.
2023 Jan;43(1):45-54. 10.3343/alm.2023.43.1.45.
Serotype Distribution and Antimicrobial Resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae Causing Invasive Pneumococcal Disease in Korea Between 2017 and 2019 After Introduction of the 13-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 2Paik Institute for Clinical Research, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 3Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, Semyung University, Jecheon, Korea
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Uijeongbu St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Laboratory Medicine, Jeonbuk National University Medical School and Hospital, Jeonju, Korea
- 6Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea
- 7Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, Jeju National University, Jeju, Korea
- 8Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea
- 9Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea
- 10Department of Laboratory Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea
- 11Department of Laboratory Medicine and Research Institute of Bacterial Resistance, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 12Department of Laboratory Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea
- 13Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Jinju, Korea
- 14Department of Laboratory Medicine, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 15Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea
- 16Department of Laboratory Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2551585
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.43.1.45
Abstract
- Background
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a serious pathogen causing various infections in humans. We evaluated the serotype distribution and antimicrobial resistance of S. pneumoniae causing invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD) after introduction of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV)13 in Korea and investigated the epidemiological characteristics of multidrug-resistant (MDR) isolates.
Methods
S. pneumoniae isolates causing IPD were collected from 16 hospitals in Korea between 2017 and 2019. Serotyping was performed using modified sequential multiplex PCR and the Quellung reaction. Antimicrobial susceptibility tests were performed using the broth microdilution method. Multilocus sequence typing was performed on MDR isolates for epidemiological investigations.
Results
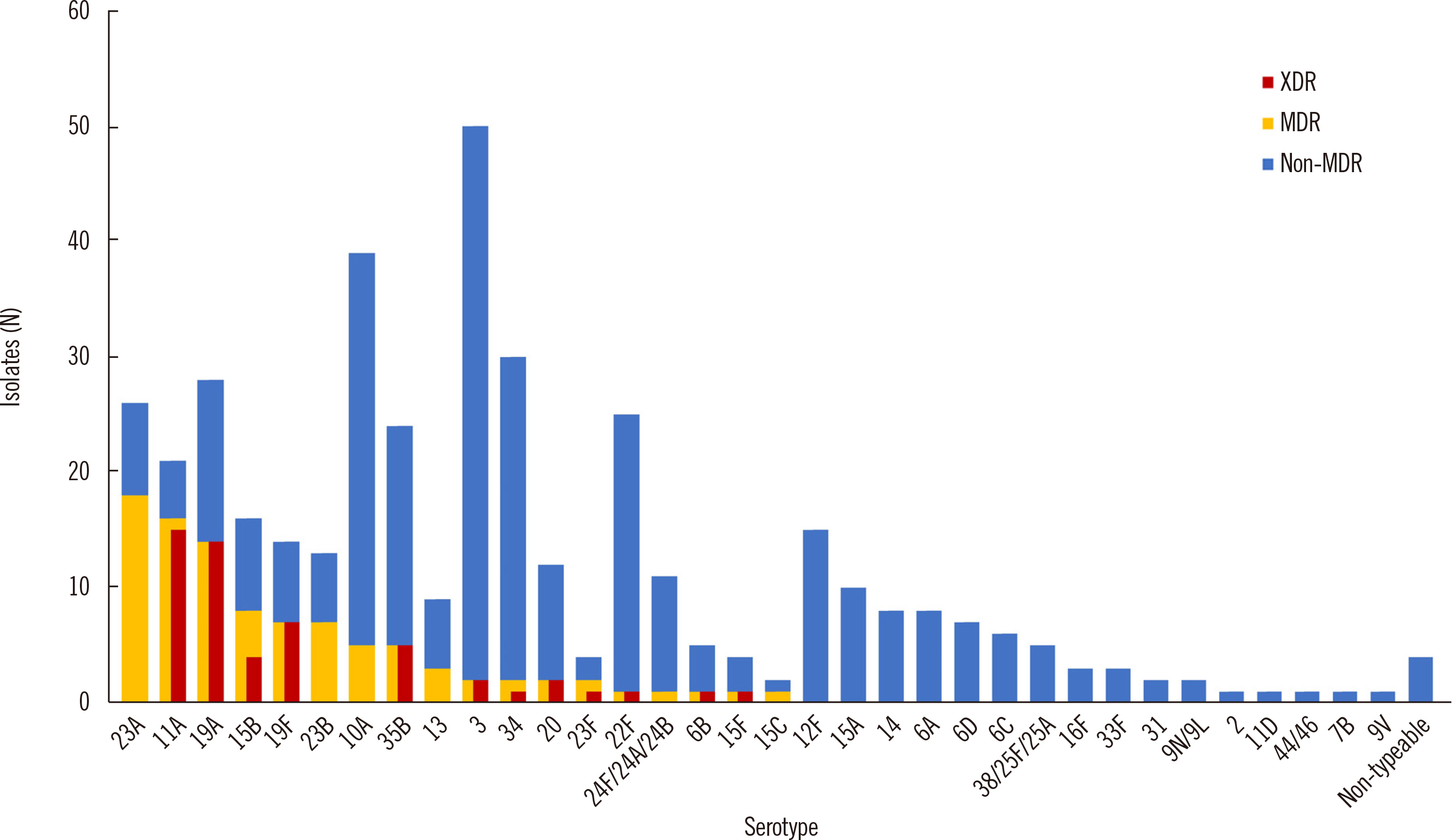
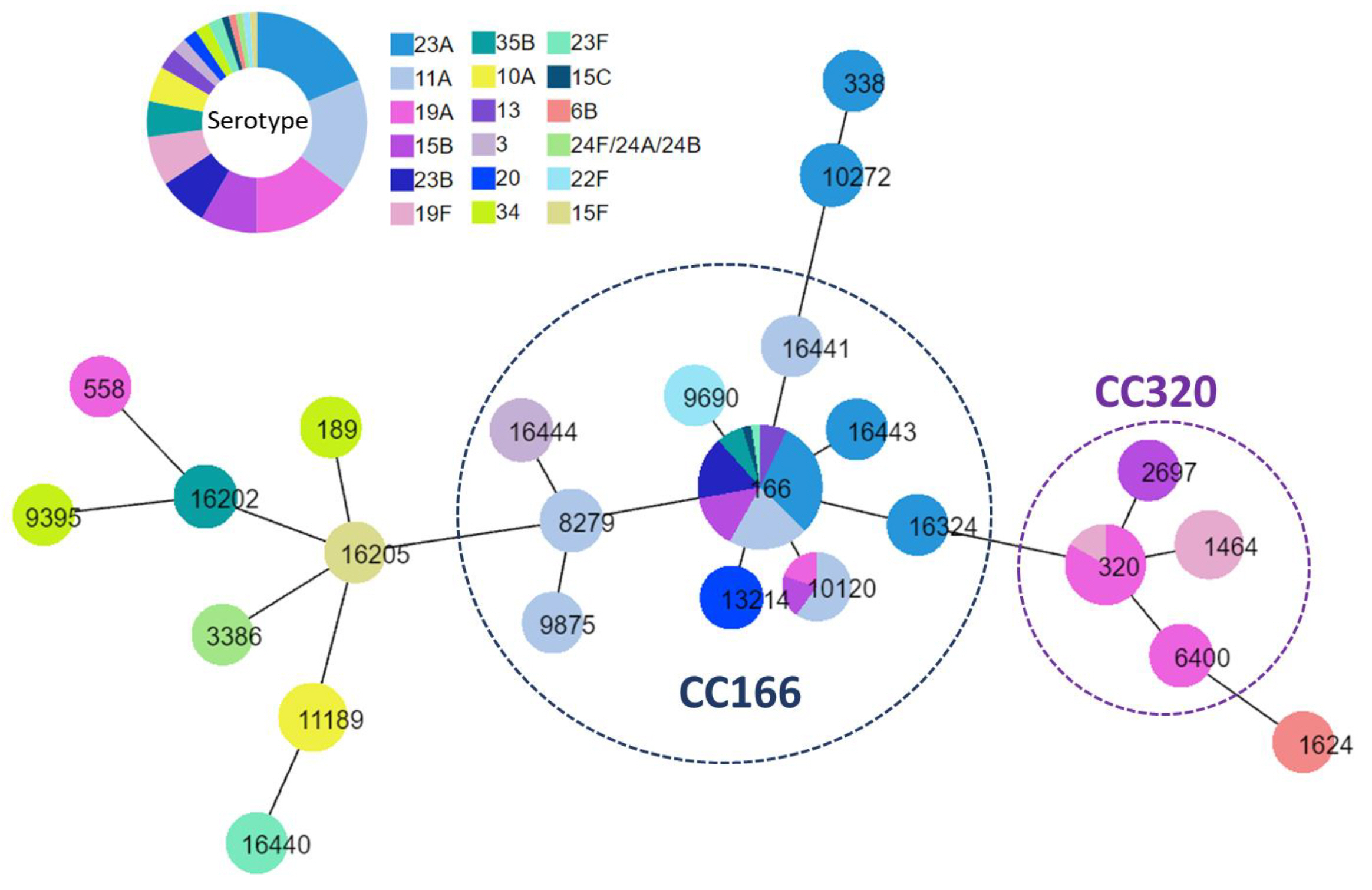
Among the 411 S. pneumoniae isolates analyzed, the most prevalent serotype was 3 (12.2%), followed by 10A (9.5%), 34 (7.3%), 19A (6.8%), 23A (6.3%), 22F (6.1%), 35B (5.8%), 11A (5.1%), and others (40.9%). The coverage rates of PCV7, PCV10, PCV13, and pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV)23 were 7.8%, 7.8%, 28.7%, and 59.4%, respectively. Resistance rates to penicillin, ceftriaxone, erythromycin, and levofloxacin were 13.1%, 9.2%, 80.3%, and 4.1%, respectively. MDR isolates accounted for 23.4% of all isolates. Serotypes 23A, 11A, 19A, and 15B accounted for the highest proportions of total isolates at 18.8%, 16.7%, 14.6%, and 8.3%, respectively. Sequence type (ST)166 (43.8%) and ST320 (12.5%) were common among MDR isolates.
Conclusions
Non-PCV13 serotypes are increasing among invasive S. pneumoniae strains causing IPD. Differences in antimicrobial resistance were found according to the specific serotype. Continuous monitoring of serotypes and antimicrobial resistance is necessary for the appropriate management of S. pneumoniae infections.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Recent Trends in Invasive Pneumococcal Disease in Korea in the Post-pneumococcal Vaccine Era
Hee Jae Huh, Heungsup Sung
Ann Lab Med. 2023;43(1):1-2. doi: 10.3343/alm.2023.43.1.1.
Reference
-
1. Manoharan A, Manchanda V, Balasubramanian S, Lalwani S, Modak M, Bai S, et al. 2017; Invasive pneumococcal disease in children aged younger than 5 years in India: a surveillance study. Lancet Infect Dis. 17:305–12. DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(16)30466-2. PMID: 27956163.
Article2. Park DC, Kim SH, Yong D, Suh IB, Kim YR, Yi J, et al. 2019; Serotype distribution and antimicrobial resistance of invasive and noninvasive Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates in Korea between 2014 and 2016. Ann Lab Med. 39:537–44. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2019.39.6.537. PMID: 31240881. PMCID: PMC6660335.
Article3. Croney CM, Nahm MH, Juhn SK, Briles DE, Crain MJ. 2013; Invasive and noninvasive Streptococcus pneumoniae capsule and surface protein diversity following the use of a conjugate vaccine. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 20:1711–8. DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00381-13. PMID: 24006139. PMCID: PMC3837785.
Article4. Diawara I, Zerouali K, Katfy K, Zaki B, Belabbes H, Najib J, et al. 2015; Invasive pneumococcal disease among children younger than 5 years of age before and after introduction of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in Casablanca, Morocco. Int J Infect Dis. 40:95–101. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2015.09.019. PMID: 26434380.
Article5. Moreno J, Duarte C, Cassiolato AP, Chacón GC, Alarcon P, Sánchez J, et al. 2020; Molecular characterization of Latin American invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 19A isolates. Vaccine. 38:3524–30. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.03.030. PMID: 32204942.
Article6. Kim CJ, Song JS, Choi SJ, Song KH, Choe PG, Park WB, et al. 2016; Serotype distribution and antimicrobial susceptibilities of invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates from adults in Korea from 1997 to 2012. J Korean Med Sci. 31:715–23. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.5.715. PMID: 27134492. PMCID: PMC4835596.
Article7. Kim SH, Chung DR, Song JH, Baek JY, Thamlikitkul V, Wang H, et al. 2020; Changes in serotype distribution and antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates from adult patients in Asia: emergence of drug-resistant non-vaccine serotypes. Vaccine. 38:6065–73. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.09.065. PMID: 31590932.
Article8. Park D, Kim SH, Bae IK, Kim NY, Kook JK, Park YH, et al. 2019; Evaluation of modified sequential multiplex PCR for Streptococcus pneumoniae serotyping. Jpn J Infect Dis. 72:224–7. DOI: 10.7883/yoken.JJID.2018.422. PMID: 30814459.
Article9. Habib M, Porter BD, Satzke C. Capsular serotyping of Streptococcus pneumoniae using the Quellung reaction. J Vis Exp. 2014; (84):e51208. DOI: 10.3791/51208. PMID: 24637727. PMCID: PMC4131683.
Article10. Steenhoff AP, Shah SS, Ratner AJ, Patil SM, McGowan KL. 2006; Emergence of vaccine-related pneumococcal serotypes as a cause of bacteremia. Clin Infect Dis. 42:907–14. DOI: 10.1086/500941. PMID: 16511752.
Article11. CLSI. 2022. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. 32nd ed. CLSI M100. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA: DOI: 10.1086/500941.12. Golden AR, Rosenthal M, Fultz B, Nichol KA, Adam HJ, Gilmour MW, et al. 2015; Characterization of MDR and XDR Streptococcus pneumoniae in Canada, 2007-13. J Antimicrob Chemother. 70:2199–202. DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkv107. PMID: 25921512.13. Enright MC, Spratt BG. 1998; A multilocus sequence typing scheme for Streptococcus pneumoniae: identification of clones associated with serious invasive disease. Microbiology (Reading). 144:3049–60. DOI: 10.1099/00221287-144-11-3049. PMID: 9846740.14. Jolley KA, Feil EJ, Chan MS, Maiden MC. 2001; Sequence type analysis and recombinational tests (START). Bioinformatics. 17:1230–1. DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/17.12.1230. PMID: 11751234.
Article15. Wu CJ, Lai JF, Huang IW, Shiau YR, Wang HY, Lauderdale TL. 2020; Serotype distribution and antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus pneumoniae in pre- and post- PCV7/13 eras, Taiwan, 2002-2018. Front Microbiol. 11:557404. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.557404. PMID: 33193140. PMCID: PMC7642986.16. Harboe ZB, Dalby T, Weinberger DM, Benfield T, Mølbak K, Slotved HC, et al. 2014; Impact of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccination in invasive pneumococcal disease incidence and mortality. Clin Infect Dis. 59:1066–73. DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciu524. PMID: 25034421.
Article17. Hink RK, Adam HJ, Golden AR, Baxter M, Martin I, Nichol KA, et al. 2021; Comparison of PCV-10 and PCV-13 vaccine coverage for invasive pneumococcal isolates obtained across Canadian geographic regions, SAVE 2011 to 2017. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 99:115282. DOI: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2020.115282. PMID: 33341491.
Article18. Suaya JA, Mendes RE, Sings HL, Arguedas A, Reinert RR, Jodar L, et al. 2020; Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype distribution and antimicrobial nonsusceptibility trends among adults with pneumonia in the United States, 2009-2017. J Infect. 81:557–66. DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.07.035. PMID: 32739491.19. Ludwig G, Garcia-Garcia S, Lanaspa M, Ciruela P, Esteva C, Fernandez de Sevilla M, et al. 2020; Serotype and clonal distribution dynamics of invasive pneumococcal strains after PCV13 introduction (2011-2016): Surveillance data from 23 sites in Catalonia, Spain. PLoS One. 15:e0228612. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228612. PMID: 32027715. PMCID: PMC7004304.
Article20. Yanagihara K, Kosai K, Mikamo H, Mukae H, Takesue Y, Abe M, et al. 2021; Serotype distribution and antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus pneumoniae associated with invasive pneumococcal disease among adults in Japan. Int J Infect Dis. 102:260–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.10.017. PMID: 33065297.21. Lee S, Bae S, Lee KJ, Yu JY, Kang Y. 2013; Changes in serotype prevalence and antimicrobial resistance among invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates in Korea, 1996-2008. J Med Microbiol. 62:1204–10. DOI: 10.1099/jmm.0.058164-0. PMID: 23657529.22. Park M, Kim HS, Shin KS, Kim HS, Park JY, Song W, et al. 2014; Changes in the incidence of Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteremia and its serotypes over 10 years in one hospital in South Korea. Vaccine. 32:6403–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.09.062. PMID: 25305566.
Article23. Gaviria-Agudelo CL, Jordan-Villegas A, Garcia C, McCracken GH Jr. 2017; The effect of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on the serotype distribution and antibiotic resistance profiles in children with invasive pneumococcal disease. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 6:253–9. DOI: 10.1093/jpids/piw005. PMID: 26907814. PMCID: PMC7107452.
Article24. Levy C, Varon E, Ouldali N, Béchet S, Bonacorsi S, Cohen R. 2020; Changes in invasive pneumococcal disease spectrum after 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine implementation. Clin Infect Dis. 70:446–54. DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciz221. PMID: 30869777.
Article25. Nakano S, Fujisawa T, Ito Y, Chang B, Matsumura Y, Yamamoto M, et al. 2020; Nationwide surveillance of paediatric invasive and non-invasive pneumococcal disease in Japan after the introduction of the 13-valent conjugated vaccine, 2015-2017. Vaccine. 38:1818–24. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.12.022. PMID: 31882246.
Article26. Desmet S, Wouters I, Heirstraeten LV, Beutels P, Van Damme P, Malhotra-Kumar S, et al. 2021; In-depth analysis of pneumococcal serotypes in Belgian children (2015-2018): diversity, invasive disease potential, and antimicrobial susceptibility in carriage and disease. Vaccine. 39:372–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.11.044. PMID: 33308889.
Article27. Yun KW, Rhie K, Kang JH, Kim KH, Ahn JG, Kim YJ, et al. 2021; Emergence of serotype 10A-ST11189 among pediatric invasive pneumococcal diseases, South Korea, 2014-2019. Vaccine. 39:5787–93. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.08.072. PMID: 34465475.
Article28. Ubukata K, Takata M, Morozumi M, Chiba N, Wajima T, Hanada S, et al. 2018; Effects of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on genotypic penicillin resistance and serotype changes, Japan, 2010-2017. Emerg Infect Dis. 24:2010–20. DOI: 10.3201/eid2411.180326. PMID: 30334707. PMCID: PMC6200004.
Article29. Imöhl M, Reinert RR, Ocklenburg C, van der Linden M. 2010; Association of serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae with age in invasive pneumococcal disease. J Clin Microbiol. 48:1291–6. DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01937-09. PMID: 20107087. PMCID: PMC2849605.30. Olarte L, Kaplan SL, Barson WJ, Romero JR, Lin PL, Tan TQ, et al. 2017; Emergence of multidrug-resistant pneumococcal serotype 35B among children in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 55:724–34. DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01778-16. PMID: 27847379. PMCID: PMC5328440.
Article31. Lo SW, Gladstone RA, van Tonder AJ, Lees JA, du Plessis M, Benisty R, et al. 2019; Pneumococcal lineages associated with serotype replacement and antibiotic resistance in childhood invasive pneumococcal disease in the post-PCV13 era: an international whole-genome sequencing study. Lancet Infect Dis. 19:759–69. DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(19)30297-X. PMID: 31196809. PMCID: PMC7641901.32. Suzuki S, Osato R, Wajima T, Hasebe T, Ishikawa H, Mitsumori H, et al. 2019; Impact of the introduction of a 13-valent pneumococcal vaccine on pneumococcal serotypes in non-invasive isolates from 2007 to 2016 at a teaching hospital in Japan. J Med Microbiol. 68:903–9. DOI: 10.1099/jmm.0.000992. PMID: 31090535.
Article33. Zhao C, Xie Y, Zhang F, Wang Z, Yang S, Wang Q, et al. 2020; Investigation of antibiotic resistance, serotype distribution, and genetic characteristics of 164 invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae from North China between April 2016 and October 2017. Infect Drug Resist. 13:2117–28. DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S256663. PMID: 32753907. PMCID: PMC7342493.34. Moore CE, Paul J, Foster D, Mahar SA, Griffiths D, Knox K, et al. 2014; Reduction of invasive pneumococcal disease 3 years after the introduction of the 13-valent conjugate vaccine in the Oxfordshire region of England. J Infect Dis. 210:1001–11. DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiu213. PMID: 24719477.
Article35. Tsai YT, Lee YL, Lu MC, Shao PL, Lu PL, Cheng SH, et al. 2022; Nationwide surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in invasive isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae in Taiwan from 2017 to 2019. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 55:215–24. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmii.2021.05.008. PMID: 34219043.36. Bao Y, Wang Q, Yao K, Xie G, Gao W, Huang L, et al. 2019; The changing phenotypes and genotypes of invasive pneumococcal isolates from children in Shenzhen during 2013-2017. Vaccine. 37:7248–55. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.09.069. PMID: 31635974.
Article37. Wang Q, Shi W, Li Y, Gao W, Yuan L, Dong F, et al. 2020; Serotype distribution of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolated from children hospitalized in Beijing Children's Hospital (2013-2019). Vaccine. 38:7858–64. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.10.005. PMID: 33164807.
Article38. Baek JY, Kim SH, Kang CI, Chung DR, Peck KR, Ko KS, et al. 2016; Prevalence of antimicrobial resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 11A isolates in Korea, during 2004-2013, due to the increase of multidrug-resistant clone, CC166. Infect Genet Evol. 38:122–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.meegid.2015.12.018. PMID: 26733441.39. Park M, Kim HS, Kim HS, Park JY, Song W, Cho HC, et al. 2016; Novel levofloxacin-resistant multidrug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 11A isolates, South Korea. Emerg Infect Dis. 22:1978–80. DOI: 10.3201/eid2211.151450. PMID: 27767906. PMCID: PMC5088008.40. Wang X, Cong Z, Huang W, Li C. 2020; Molecular characterization of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolated from pediatric patients in Shanghai, China. Pediatr Pulmonol. 55:2135–41. DOI: 10.1002/ppul.24877. PMID: 32470194.
Article41. Yun KW, Choi EH, Lee HJ, Kang JH, Kim KH, Kim DS, et al. 2018; Genetic structures of invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates from Korean children obtained between 1995 and 2013. BMC Infect Dis. 18:268. DOI: 10.1186/s12879-018-3177-7. PMID: 29884115. PMCID: PMC5994121.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Antimicrobial Resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae Clinical Serotypes between 2017 and 2022 in Crete, Greece
- Recommendation for use of the newly introduced pneumococcal protein conjugate vaccines in Korea
- Pneumococcal vaccine
- Efficacy and effectiveness of extended-valency pneumococcal conjugate vaccines
- Direct and Indirect Effects of Pneumococcal Protein Conjugate Vaccine