Infect Chemother.
2018 Dec;50(4):328-339. 10.3947/ic.2018.50.4.328.
The Evolving Epidemiology of Serotype Distribution and Antimicrobial Resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae Strains Isolated from Adults in Crete, Greece, 2009–2016
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Microbiology and Microbial Pathogenesis, University Hospital of Heraklion, Crete, Greece. sofiamaraki@yahoo.gr
- 2University of Crete Medical School, Heraklion, Crete, Greece.
- 3Infectious Diseases Unit, University Hospital of Heraklion and University of Crete Medical School, Heraklion, Crete, Greece.
- KMID: 2429936
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2018.50.4.328
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Pneumococcal disease is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, especially in patients with comorbidities and advanced age. This study evaluated trends in epidemiology of adult pneumococcal disease in Crete, Greece, by identifying serotype distribution and antimicrobial resistance of consecutive Streptococcus pneumoniae strains isolated from adults during an 8-year time period (2009-2016) and the indirect effect of the infant pneumococcal higher-valent conjugate vaccines 10-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV10) and 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Antimicrobial susceptibility was performed by E-test and serotyping by Quellung reaction. Multidrug resistance (MDR) was defined as non-susceptibility to penicillin (PNSP) combined with resistance to ≥2 non-β-lactam antimicrobials.
RESULTS
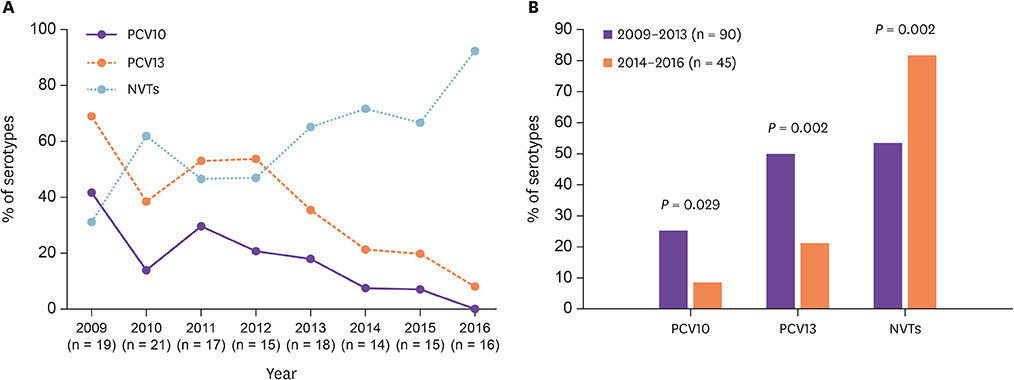
A total of 135 S. pneumoniae strains were isolated from adults during the study period. Twenty-one serotypes were identified with 17F, 15A, 3, 19A, and 11A, being the most common. The coverage rates of PCV10, and PCV13 were 17.8% and 37.8%, respectively. PCV13 serotypes decreased significantly from 68.4% in 2009 to 8.3% in 2016 (P = 0.002). The most important emerging non-PCV13 serotypes were 17F, 15A, and 11A, with 15A being strongly associated with antimicrobial resistance and MDR. Among all study isolates, penicillin-resistant and MDR strains represented 7.4% and 14.1%, respectively. Predominant PNSP serotypes were 19A (21.7%), 11A (17.4%), and 15A (17.4%). Erythromycin, clindamycin, tetracycline, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and levofloxacin resistant rates were 30.4%, 15.6%, 16.3%, 16.3%, and 1.5%, respectively.
CONCLUSION
Although pneumococcal disease continues to be a health burden in adults in Crete, our study reveals a herd protection effect of the infant pneumococcal higher-valent conjugate vaccination. Surveillance of changes in serotype distribution and antimicrobial resistance among pneumococcal isolates are necessary to guide optimal prevention and treatment strategies.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult*
Clindamycin
Comorbidity
Drug Resistance, Multiple
Epidemiology*
Erythromycin
Greece*
Humans
Infant
Levofloxacin
Mortality
Penicillins
Pneumonia
Serogroup*
Serotyping
Streptococcus pneumoniae*
Streptococcus*
Tetracycline
Trimethoprim, Sulfamethoxazole Drug Combination
Vaccination
Vaccines, Conjugate
Clindamycin
Erythromycin
Penicillins
Tetracycline
Trimethoprim, Sulfamethoxazole Drug Combination
Vaccines, Conjugate
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bogaert D, De Groot R, Hermans PW. Streptococcus pneumoniae colonisation: the key to pneumococcal disease. Lancet Infect Dis. 2004; 4:144–154.2. Musher DM. Streptococcus pneumoniae. In : Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R, editors. Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 6th ed. New York: Elsevier, Churchill Livingstone;2010. p. 2623–2642.3. Marrie TJ, Tyrrell GJ, Majumdar SR, Eurich DT. Effect of age on the manifestations and outcomes of invasive pneumococcal diseases in adults. Am J Med. 2018; 131:100.e1–100.e7.4. Shea KM, Edelsberg J, Weycker D, Farkouh RA, Strutton DR, Pelton SI. Rates of pneumococcal disease in adults with chronic medical conditions. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2014; 1:ofu024.
Article5. Said MA, Johnson HL, Nonyane BA, Deloria-Knoll M, O'Brien KL. AGEDD Adult Pneumococcal Burden Study Team. Andreo F, Beovic B, Blanco S, Boersma WG, Boulware DR, Butler JC, Carratalà J, Chang FY, Charles PG, Diaz AA, Domínguez J, Ehara N, Endeman H, Falcó V, Falguera M, Fukushima K, Garcia-Vidal C, Genne D, Guchev IA, Gutierrez F, Hernes SS, Hoepelman AI, Hohenthal U, Johansson N, Kolek V, Kozlov RS, Lauderdale TL, Mareković I, Masiá M, Matta MA, Miró Ò, Murdoch DR, Nuermberger E, Paolini R, Perelló R, Snijders D, Plečko V, Sordé R, Strålin K, van der Eerden MM, Vila-Corcoles A, Watt JP. Estimating the burden of pneumococcal pneumonia among adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic techniques. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e60273.
Article6. GBD 2015 LRI Collaborators. Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of lower respiratory tract infections in 195 countries: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017; 17:1133–1161.7. Welte T, Torres A, Nathwani D. Clinical and economic burden of community-acquired pneumonia among adults in Europe. Thorax. 2012; 67:71–79.
Article8. Castiglia P. Recommendations for pneumococcal immunization outside routine childhood immunization programs in Western Europe. Adv Ther. 2014; 31:1011–1044.
Article9. Klugman KP. Herd protection induced by pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. Lancet Glob Health. 2014; 2:e365–e366.
Article10. Huang SS, Johnson KM, Ray GT, Wroe P, Lieu TA, Moore MR, Zell ER, Linder JA, Grijalva CG, Metlay JP, Finkelstein JA. Healthcare utilization and cost of pneumococcal disease in the United States. Vaccine. 2011; 29:3398–3412.
Article11. Maraki S, Mantadakis E, Samonis G. Serotype distribution and antimicrobial resistance of adult Streptococcus pneumoniae clinical isolates over the period 2001-2008 in Crete, Greece. Chemotherapy. 2010; 56:325–332.
Article12. Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; twenty-sixth informational supplement. Wayne, Pa: CLSI;2016.13. Tsaban G, Ben-Shimol S. Indirect (herd) protection, following pneumococcal conjugated vaccines introduction: A systematic review of the literature. Vaccine. 2017; 35:2882–2891.
Article14. Tzanakaki G. National Meningitis Reference Laboratory Data 1993–2015. 2015. Accessed 23 June 2018. Available from: http://www.nsph.gr/files/001_Dimosias_Dioikitikis_Ygieinis/ EKAM/ApologismoiEKAM/Apol-2015-1.pdf.15. Regev-Yochay G, Katzir M, Strahilevitz J, Rahav G, Finn T, Miron D, Maor Y, Chazan B, Schindler Y, Dagan R. IAIPD group. The herd effects of infant PCV7/PCV13 sequential implementation on adult invasive pneumococcal disease, six years post implementation; a nationwide study in Israel. Vaccine. 2017; 35:2449–2456.
Article16. Waight PA, Andrews NJ, Ladhani SN, Sheppard CL, Slack MP, Miller E. Effect of the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on invasive pneumococcal disease in England and Wales 4 years after its introduction: an observational cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015; 15:535–543.
Article17. Rodrigo C, Bewick T, Sheppard C, Greenwood S, Mckeever TM, Trotter CL, Slack M, George R, Lim WS. Impact of infant 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on serotypes in adult pneumonia. Eur Respir J. 2015; 4:1632–1641.
Article18. Menéndez R, España PP, Pérez-Trallero E, Uranga A, Méndez R, Cilloniz C, Marimón JM, Cifuentes I, Méndez C, Torres A. The burden of PCV13 serotypes in hospitalized pneumococcal pneumonia in Spain using a novel urinary antigen detection test. CAPA study. Vaccine. 2017; 35:5264–5270.
Article19. España PP, Menendez R, Torres A, Fernández-Villar JA, Marimon JM, Martínez De La Fuente AP, Brusola AG, Reverte FM, Vasallo-Vidal F, Ercibengoa M, Cifuentes I, Méndez C. Differences in the burden of all-cause CAP due to PCV13 serotypes based in the different use of vaccine by regions in Spain (the CAPA study). In : 28th European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases; 2018 Apr 21-24; Madrid, Spain.20. WHO. Immunization, Vaccines and Biologicals - Data, statistics and graphics. Accessed 2 May 2018. Available from: http://www.who.int/immunization/monitoring_surveillance/data/en/.21. Kazmierczak K, Hackel M, Henry LI, Kalamatas J, Hilton B, Sings H, Isturiz R. Distribution of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes among global population. In : 27th European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases; 2017 Apr 22-25; Vienna, Austria.22. Kazmierczak K, Hackel M, Kalamatas J, Hall-Murray C, Sings H, Isturiz R. Distribution of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes among non-sterile isolates from adults 18 years and older in Europe and the United States, 2014-2015. In : 27th European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases; 2017 Apr 22-25; Vienna, Austria.23. Horácio AN, Silva-Costa C, Lopes JP, Ramirez M, Melo-Cristino J. Portuguese Group for the Study of Streptococcal Infections. Serotype 3 remains the leading cause of invasive pneumococcal disease in adults in Portugal (2012-2014) despite continued reductions in other 13-valent conjugate vaccine serotypes. Front Microbiol. 2016; 7:1616.
Article24. Corcoran M, Vickers I, Mereckiene J, Murchan S, Cotter S, Fitzgerald M, McElligott M, Cafferkey M, O'Flanagan D, Cunney R, Humphreys H. The epidemiology of invasive pneumococcal disease in older adults in the post-PCV era. Has there been a herd effect? Epidemiol Infect. 2017; 145:2390–2399.
Article25. van der Linden M, Falkenhorst G, Perniciaro S, Imöhl M. Effects of infant pneumococcal conjugate vaccination on serotype distribution in invasive pneumococcal disease among children and adults in Germany. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0131494.
Article26. Izurieta P, Bahety P, Adegbola R, Clarke C, Hoet B, Andrews NJ, Waight PA, Burbidge P, Pearce E, Roalfe L, Zancolli M, Slack M, Ladhani SN, Miller E, Goldblatt D. Public health impact of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine infant immunization programs: assessment of invasive pneumococcal disease burden and serotype distribution. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2018; 17:479–493.
Article27. Feikin DR, Kagucia EW, Loo JD, Link-Gelles R, Puhan MA, Cherian T, Levine OS, Whitney CG, O'Brien KL, Moore MR. Serotype Replacement Study Group. Serotype-specific changes in invasive pneumococcal disease after pneumococcal conjugate vaccine introduction: a pooled analysis of multiple surveillance sites. PLoS Med. 2013; 10:e1001517.
Article28. Hausdorff WP, Hanage WP. Interim results of an ecological experiment - Conjugate vaccination against the pneumococcus and serotype replacement. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016; 12:358–374.
Article29. Moore MR, Link-Gelles R, Schaffner W, Lynfield R, Lexau C, Bennett NM, Petit S, Zansky SM, Harrison LH, Reingold A, Miller L, Scherzinger K, Thomas A, Farley MM, Zell ER, Taylor TH Jr, Pondo T, Rodgers L, McGee L, Beall B, Jorgensen JH, Whitney CG. Effect of use of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in children on invasive pneumococcal disease in children and adults in the USA: analysis of multisite, population-based surveillance. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015; 15:301–309.
Article30. Hays C, Vermee Q, Agathine A, Dupuis A, Varon E, Poyart C, Ploy MC, Raymond J. and the ORP IIe de France Quest. Demonstration of the herd effect in adults after the implementation of pneumococcal vaccination with PCV13 in children. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2017; 36:831–838.
Article31. Falcó V, Burgos J, Pahissa A. The spectrum of invasive pneumococcal disease in adults in the XXI century. Clin Pulm Med. 2013; 20:214–220.
Article32. Dagan R, Juergens C, Trammel J, Patterson S, Greenberg D, Givon-Lavi N, Porat N, Gurtman A, Gruber WC, Scott DA. Efficacy of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) versus that of 7-valent PCV (PCV7) against nasopharyngeal colonization of antibiotic-nonsusceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae . J Infect Dis. 2015; 211:1144–1153.
Article33. Woodhead M, Blasi F, Ewig S, Garau J, Huchon G, Ieven M, Ortqvist A, Schaberg T, Torres A, van der Heijden G, Read R, Verheij TJ. Joint Taskforce of the European Respiratory Society and European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Guidelines for the management of adult lower respiratory tract infections--full version. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011; 17:Suppl 6. E1–59.34. Goossens H, Ferech M, Vander Stichele R, Elseviers M. ESAC Project Group. Outpatient antibiotic use in Europe and association with resistance: a cross-national database study. Lancet. 2005; 365:579–587.
Article35. Imöhl M, Reinert RR, van der Linden M. Antibiotic susceptibility rates of invasive pneumococci before and after the introduction of pneumococcal conjugate vaccination in Germany. Int J Med Microbiol. 2015; 305:776–783.
Article36. Mendes RE, Costello AJ, Jacobs MR, Biek D, Critchley IA, Jones RN. Serotype distribution and antimicrobial susceptibility of USA Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates collected prior to and post introduction of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014; 80:19–25.
Article37. Hauser C, Kronenberg A, Allemann A, Mühlemann K, Hilty M. Serotype/serogroup-specific antibiotic non-susceptibility of invasive and non-invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae, Switzerland, 2004 to 2014. Euro Surveill. 2016; 21(21):
Article38. Soeters HM, von Gottberg A, Cohen C, Quan V, Klugman KP. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole prophylaxis and antibiotic nonsusceptibility in invasive pneumococcal disease. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012; 56:1602–1605.
Article39. Cornick JE, Harris SR, Parry CM, Moore MJ, Jassi C, Kamng'ona A, Kulohoma B, Heyderman RS, Bentley SD, Everett DB. Genomic identification of a novel co-trimoxazole resistance genotype and its prevalence amongst Streptococcus pneumoniae in Malawi. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014; 69:368–374.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Antimicrobial Resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae Clinical Serotypes between 2017 and 2022 in Crete, Greece
- Distribution and Antimicrobial Resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae at Four University Hospitals in Busan and Gyeongnam
- Epidemiology, Microbiological and Clinical Features, Treatment, and Outcomes of Infective Endocarditis in Crete, Greece
- Changes in the Serotype Distribution among Antibiotic Resistant Carriage Streptococcus pneumoniae Isolates in Children after the Introduction of the Extended-Valency Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine
- Pulsed field gel electrophoresis profile of erythromycin-clindamycin resistant Streptococcus pyogenes isolated in Korea