Ann Clin Microbiol.
2016 Jun;19(2):48-53. 10.5145/ACM.2016.19.2.48.
Distribution and Antimicrobial Resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae at Four University Hospitals in Busan and Gyeongnam
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. jhsmile@inje.ac.kr
- 2Paik Institute for Clinical Research, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea.
- 4Department of Preventive Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2307783
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5145/ACM.2016.19.2.48
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common human pathogen causing community-acquired pneumonia. There is little information on the recent antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of S. pneumoniae in Busan and Gyeongnam of Korea. The aim of this study was to investigate the distribution and antimicrobial resistance of S. pneumoniae at 4 university hospitals in Busan and Gyeongnam.
METHODS
We collected and analyzed the antimicrobial susceptibility results of 850 S. pneumoniae strains isolated from regional 4 university hospitals during the last 2 years from July 2013 through June 2015.
RESULTS
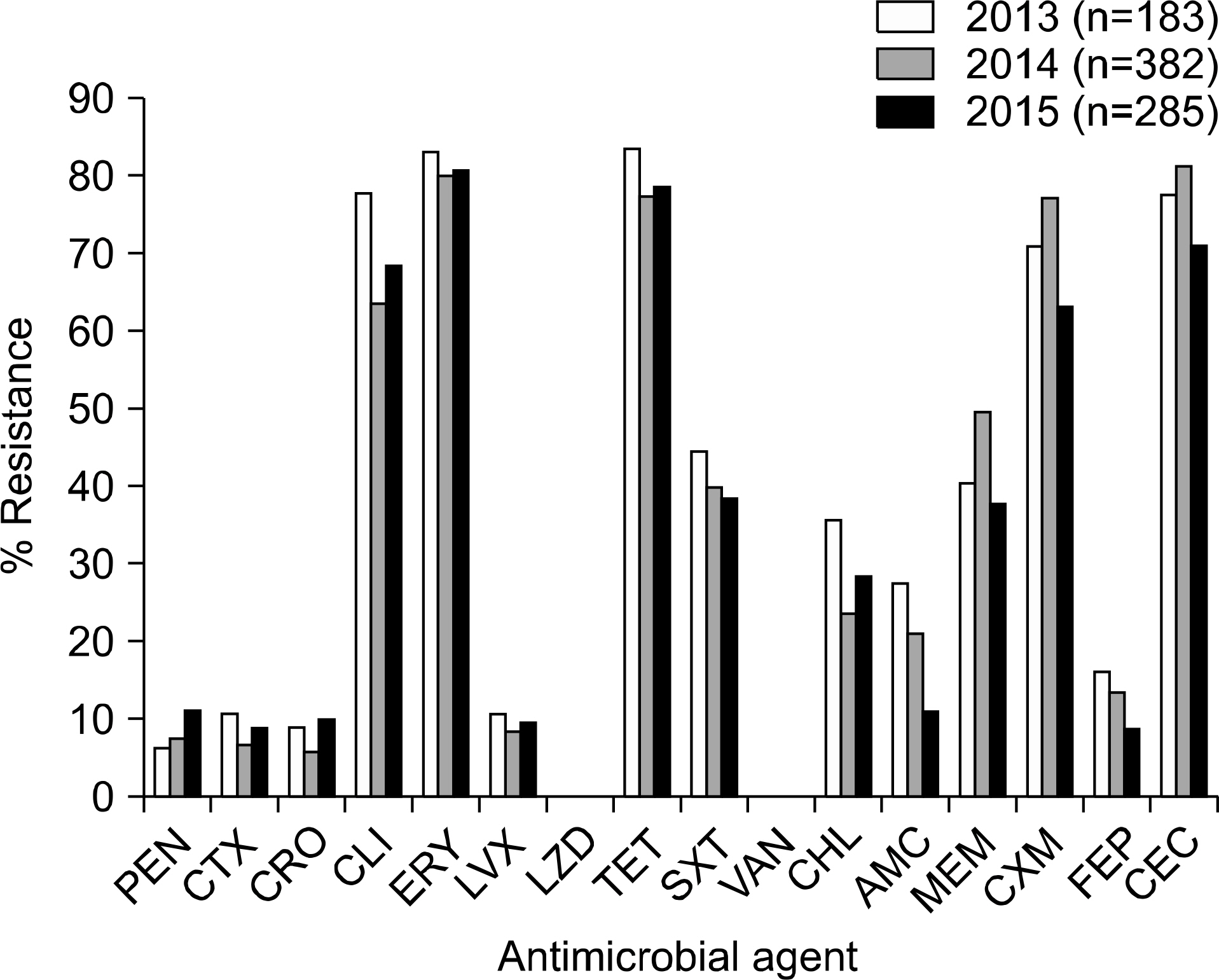
Among 850 S. pneumoniae strains, 635 strains were isolated from respiratory specimens, followed by blood (N=121), CSF (N=13), and others (N=81). Antimicrobial susceptibility rates to penicillin, cefotaxime and ceftriaxone were 79.4%, 76.6% and 83.6%, respectively. The resistant rates to erythromycin and clindamycin were 80.9% and 68.2%, respectively. The resistant rates to levofloxacin were 9.2%. There were some differences in resistant rates by age groups, years, and specimen types.
CONCLUSION
We found the changes of antimicrobial resistance of S. pneumoniae during the last 2 years. It is necessary to monitor the antimicrobial susceptibility of S. pneumoniae regularly for empirical therapy and for early detection of the changes of resistance.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. File TM Jr. Streptococcus pneumoniae and community-acquired pneumonia: a cause for concern. Am J Med. 2004; 117(Suppl 3A):39S–50S.
Article2. Sanz Herrero F and Blanquer Olivas J. Microbiology and risk factors for community-acquired pneumonia. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2012; 33:220–31.
Article3. Kaplan M, Rudensky B, Beck A. Perinatal infections with Streptococcus pneumoniae. Am J Perinatol. 1993; 10:1–4.4. Hoffman JA, Mason EO, Schutze GE, Tan TQ, Barson WJ, Givner LB, et al. Streptococcus pneumoniae infections in the neonate. Pediatrics. 2003; 112:1095–102.
Article5. Robinson KA, Baughman W, Rothrock G, Barrett NL, Pass M, Lexau C, et al. Epidemiology of invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae infections in the United States, 1995–1998: Opportunities for prevention in the conjugate vaccine era. JAMA. 2001; 285:1729–35.6. Kalin M, Ortqvist A, Almela M, Aufwerber E, Dwyer R, Henriques B, et al. Prospective study of prognostic factors in community-acquired bacteremic pneumococcal disease in 5 countries. J Infect Dis. 2000; 182:840–7.
Article7. Klugman KP. Pneumococcal resistance to antibiotics. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990; 3:171–96.
Article8. Jacobs MR, Koornhof HJ, Robins-Browne RM, Stevenson CM, Vermaak ZA, Freiman I, et al. Emergence of multiply resistant pneumococci. N Engl J Med. 1978; 299:735–40.
Article9. Kim KH, Kim JE, Park SH, Song YH, Ahn JY, Park PW, et al. Impact of revised penicillin breakpoints for Streptococcus pneumoniae (CLSI M100-S18) on the penicillin susceptibililty rate. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2010; 13:68–72.10. CLSI. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; 25th informational supplement. CLSI Document M100-S25. Wayne, PA: Clinical Laboratory Standard Institute;2015.11. Brown SD, Farrell DJ, Morrissey I. Prevalence and molecular analysis of macrolide and fluoroquinolone resistance among isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae collected during the 2000–2001 PROTEKT US Study. J Clin Microbiol. 2004; 42:4980–7.12. Niederman MS and Luna CM. Community-acquired pneumonia guidelines: a global perspective. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2012; 33:298–310.
Article13. Postma DF, van Werkhoven CH, van Elden LJ, Thijsen SF, Hoepelman AI, Kluytmans JA, et al. Antibiotic treatment strategies for community-acquired pneumonia in adults. N Engl J Med. 2015; 372:1312–23.
Article14. Feldman C and Anderson R. Recent advances in our understanding of Streptococcus pneumoniae infection. F1000Prime Rep. 2014; 6:82.
Article15. Korean Centers for Disease Control & Prevention and Korea National Institute of Health. Korean antimicrobial resistance monitoring system 2011 annual report. Chungbuk: KNIH;2013.16. Kim SH, Song JH, Chung DR, Thamlikitkul V, Yang Y, Wang H, et al. Changing trends in antimicrobial resistance and serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates in Asian countries: an Asian Network for Surveillance of Resistant Pathogens (ANSORP) study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012; 56:1418–26.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Antibiotic-Resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Penicillin resistance in streptococcus pneumoniae
- Antimicrobial Resistance in Gram-positive Cocci: Past 50 Years, Present and Future
- Emergence and spread of antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae in Korea
- Current status and future strategies of antimicrobial resistance in Korea