Yonsei Med J.
2019 Jun;60(6):585-591. 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.6.585.
Upregulation of miR-27b Facilitates Apoptosis of TNF-α-Stimulated Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rheumatism and Immunology, Gansu Provincial Hospital, Lanzhou, Gansu, China.
- 2Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang, Guangdong, China.
- 3Department of Orthopedics, Jiangxi Provincial People's Hospital Affiliated to Nanchang University, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China. 14242356@qq.com
- KMID: 2446965
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2019.60.6.585
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to explore the function of microRNA-27b (miR-27b) in fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) stimulated by tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
mRNA expression of miR-27b in FLS cells (MH7A) treated with or without TNF-α was determined by q-PCR. MiR-27b mimics was transfected into MH7A cells to upregulate miR-27b expression. MTT assay and flow cytometry analysis were performed to investigate the effect of miR-27b on MH7A cell viability and apoptosis. The targets of miR-27b were predicted by TargetScan. The direct regulation of miR-27b on IL-1β expression was verified by luciferase assay. The protein expression levels of apoptosis-related proteins, IL-1β, and NF-κB signaling-related proteins were detected by Western blot.
RESULTS
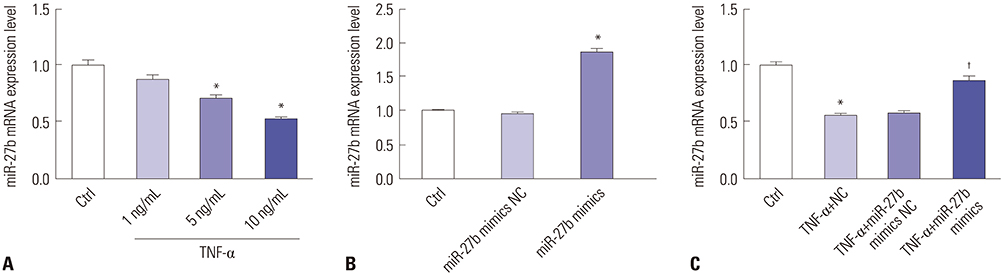
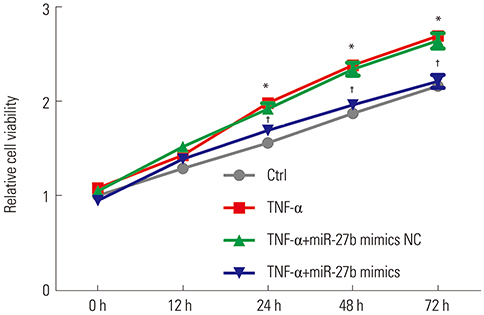
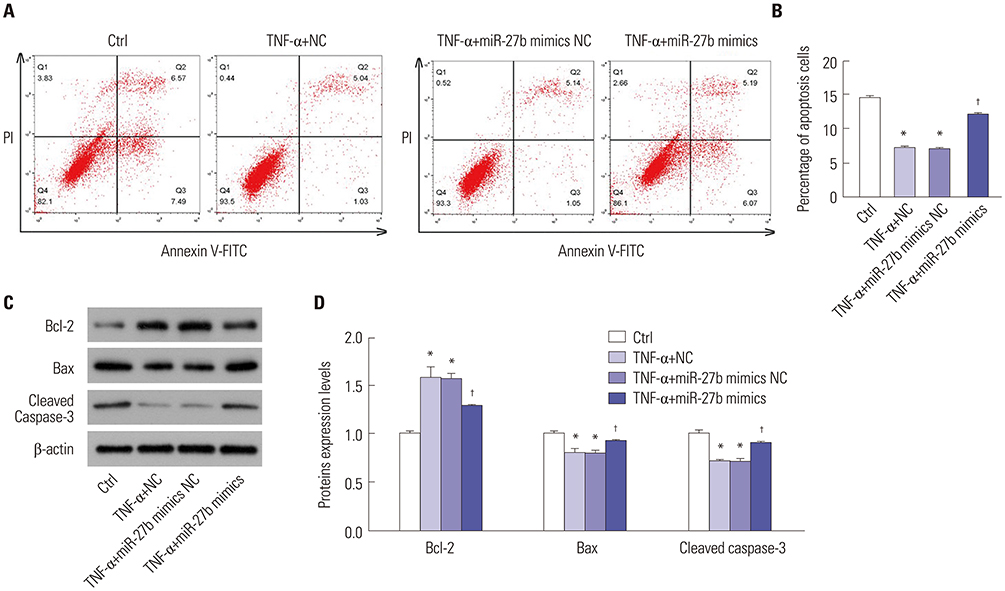
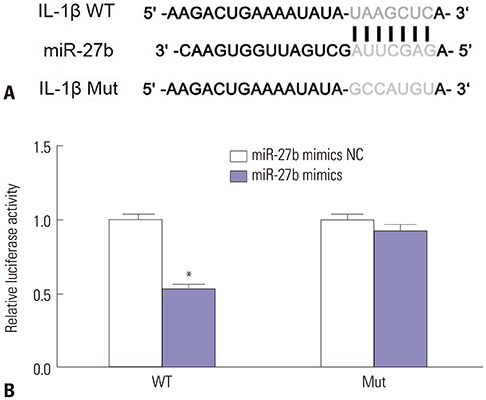
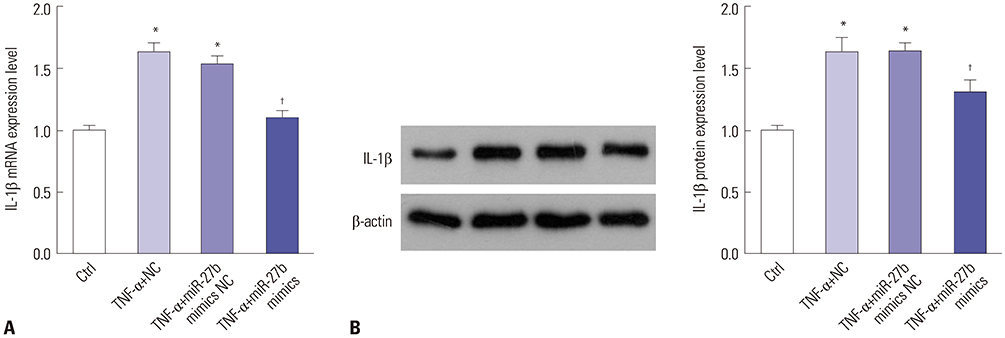
We discovered that miR-27b expression was decreased in MH7A cells stimulated by TNF-α. Upregulation of miR-27b by miR-27b mimics significantly inhibited the proliferation and promoted the apoptosis of TNF-α-stimulated MH7A cells. Consistently, upregulation of miR-27 decreased the level of Bcl-2 and increased Bax and caspase-3 expression in MH7A cells stimulated by TNF-α. Luciferase assay revealed that IL-1β was indeed a target of miR-27b. By quantitative real-time PCR and Western blot, we found that the expression of IL-1β is negatively regulated by miR-27b. Moreover, the NF-κB signaling pathway was significantly inhibited by miR-27b.
CONCLUSION
Taken together, our results illustrated that enhanced miR-27b expression results in the suppression of proliferation and the promotion of apoptosis in FLSs stimulated by TNF-α, partially by regulating IL-1β expression and NF-κB signaling.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Scott DL, Wolfe F, Huizinga TW. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2010; 376:1094–1108.
Article2. Niederer F, Trenkmann M, Ospelt C, Karouzakis E, Neidhart M, Stanczyk J, et al. Down-regulation of microRNA-34a* in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts promotes apoptosis resistance. Arthritis Rheum. 2012; 64:1771–1779.
Article3. Qu Y, Wu J, Deng JX, Zhang YP, Liang WY, Jiang ZL, et al. MicroRNA-126 affects rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblast proliferation and apoptosis by targeting PIK3R2 and regulating PI3K-AKT signal pathway. Oncotarget. 2016; 7:74217–74226.
Article4. Yang KY, Chen DL. Shikonin inhibits inflammatory response in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts via lncRNA-NR024118. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015; 2015:631737.
Article5. van der Linden MP, le Cessie S, Raza K, van der Woude D, Knevel R, Huizinga TW, et al. Long-term impact of delay in assessment of patients with early arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 62:3537–3546.
Article6. Yeo L, Adlard N, Biehl M, Juarez M, Smallie T, Snow M, et al. Expression of chemokines CXCL4 and CXCL7 by synovial macrophages defines an early stage of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016; 75:763–771.
Article7. Kim VN. MicroRNA biogenesis: coordinated cropping and dicing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005; 6:376–385.
Article8. Alsaleh G, François A, Philippe L, Gong YZ, Bahram S, Cetin S, et al. MiR-30a-3p negatively regulates BAFF synthesis in systemic sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis fibroblasts. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e111266.
Article9. Stanczyk J, Pedrioli DM, Brentano F, Sanchez-Pernaute O, Kolling C, Gay RE, et al. Altered expression of microRNA in synovial fibroblasts and synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 58:1001–1009.
Article10. Churov AV, Oleinik EK, Knip M. MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: altered expression and diagnostic potential. Autoimmun Rev. 2015; 14:1029–1037.
Article11. Wang H, Peng W, Ouyang X, Li W, Dai Y. Circulating microRNAs as candidate biomarkers in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Transl Res. 2012; 160:198–206.
Article12. Pauley KM, Satoh M, Chan AL, Bubb MR, Reeves WH, Chan EK. Upregulated miR-146a expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008; 10:R101.
Article13. Stanczyk J, Ospelt C, Karouzakis E, Filer A, Raza K, Kolling C, et al. Altered expression of microRNA-203 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts and its role in fibroblast activation. Arthritis Rheum. 2011; 63:373–381.
Article14. Nakamachi Y, Kawano S, Takenokuchi M, Nishimura K, Sakai Y, Chin T, et al. MicroRNA-124a is a key regulator of proliferation and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 secretion in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009; 60:1294–1304.
Article15. Frleta M, Rainey AA, Gilchrist DS, Crawford L, Baxter D, Kurowskastolarska M, et al. Mir-27b as biomarker and regulator of IL-6R pathway in resistant rheumatoid arthritis monocyte. In : 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting; October 25–30, 2013; San Diego, CA.16. Li HX, Kong FJ, Bai SZ, He W, Xing WJ, Xi YH, et al. Involvement of calcium-sensing receptor in oxLDL-induced MMP-2 production in vascular smooth muscle cells via PI3K/Akt pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012; 362:115–122.
Article17. Chen Y, Xiao Y, Ge W, Zhou K, Wen J, Yan W, et al. miR-200b inhibits TGF-α1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes growth of intestinal epithelial cells. Cell Death Dis. 2013; 4:e541.
Article18. Akhtar N, Rasheed Z, Ramamurthy S, Anbazhagan AN, Voss FR, Haqqi TM. MicroRNA-27b regulates the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 13 in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 62:1361–1371.
Article19. Zhou B, Li H, Shi J. miR27 inhibits the NF-κB signaling pathway by targeting leptin in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Int J Mol Med. 2017; 40:523–530.
Article20. Tang W, Zhu J, Su S, Wu W, Liu Q, Su F, et al. MiR-27 as a prognostic marker for breast cancer progression and patient survival. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e51702.
Article21. Urbich C, Kaluza D, Frömel T, Knau A, Bennewitz K, Boon RA, et al. MicroRNA-27a/b controls endothelial cell repulsion and angiogenesis by targeting semaphorin 6A. Blood. 2012; 119:1607–1616.
Article22. Xu W, Liu M, Peng X, Zhou P, Zhou J, Xu K, et al. miR-24-3p and miR-27a-3p promote cell proliferation in glioma cells via cooperative regulation of MXI1. Int J Oncol. 2013; 42:757–766.
Article23. Scholz CC, Cavadas MA, Tambuwala MM, Hams E, Rodríguez J, von Kriegsheim A, et al. Regulation of IL-1β-induced NF-κB by hydroxylases links key hypoxic and inflammatory signaling pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013; 110:18490–18495.
Article24. Napetschnig J, Wu H. Molecular basis of NF-κB signaling. Annu Rev Biophys. 2013; 42:443–468.
Article25. Zhang D, Cao X, Li J, Zhao G. MiR-210 inhibits NF-κB signaling pathway by targeting DR6 in osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2015; 5:12775.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Upregulation of miR-20b Protects Against Cerebral Ischemic Stroke by Targeting Thioredoxin Interacting Protein (TXNIP)
- MicroRNA-765 is upregulated in myelodysplastic syndromes and induces apoptosis via PLP2 inhibition in leukemia cells
- Phytoceramide Alleviates the Carrageenan/Kaolin-Induced Arthritic Symptoms by Modulation of Inflammation
- MiR-484 Protects Rat Myocardial Cells from Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 during Apoptosis
- Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA 665 Regulates Viability, Apoptosis, and Autophagy via the MiR-186-5p/MAP4K3 Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma