Blood Res.
2023 Sep;58(3):133-137. 10.5045/br.2023.2023097.
MicroRNA-765 is upregulated in myelodysplastic syndromes and induces apoptosis via PLP2 inhibition in leukemia cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chosun University College of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea
- 2International St. Mary’s Hospital, Catholic Kwandong University, Incheon, Korea
- KMID: 2546314
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2023.2023097
Abstract
- Background
Epigenetic studies, particularly research on microRNA (miRNA), have flourished. The abnormal expression of miRNA contributes to the development of hematologic malignancies. miR-765 has been reported to inhibit cell proliferation by downregulating proteolipid protein 2 (PLP2), which causes apoptosis. We investigated miR-765 dysregulation in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS).
Methods
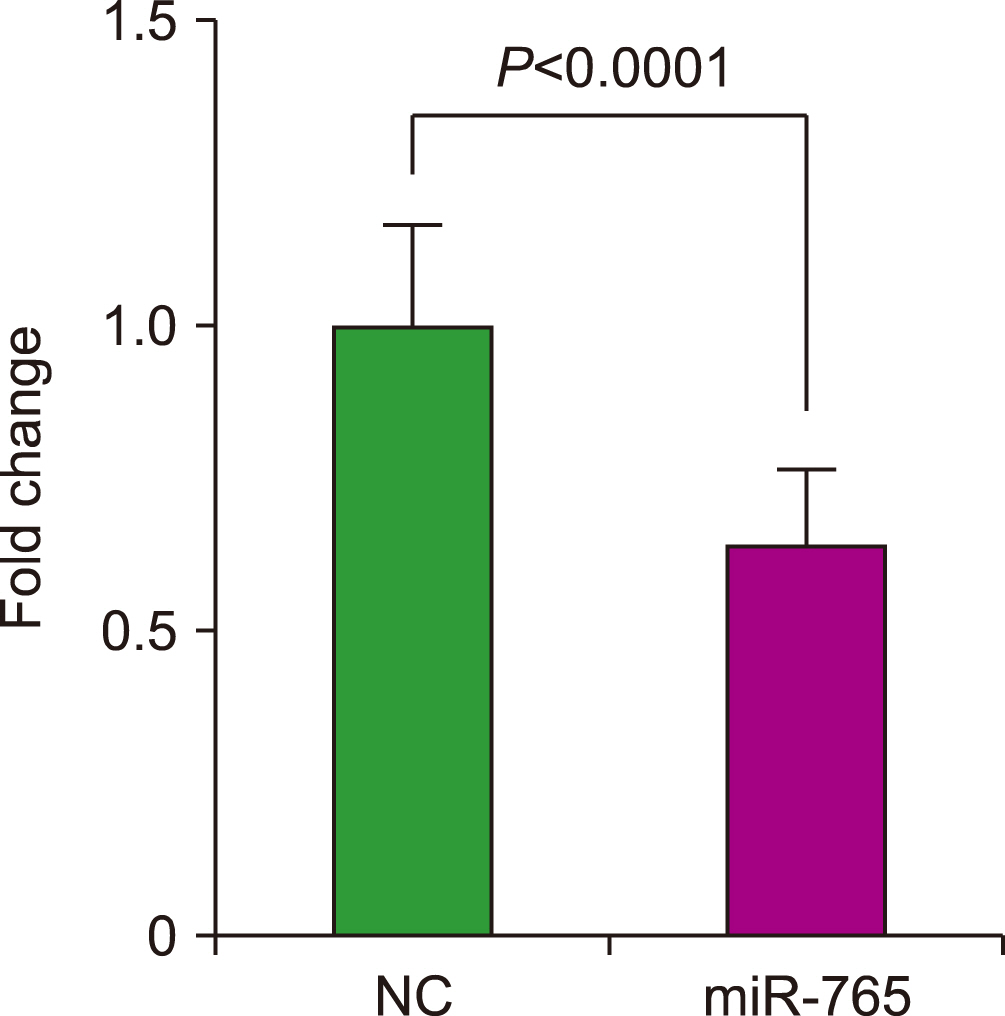
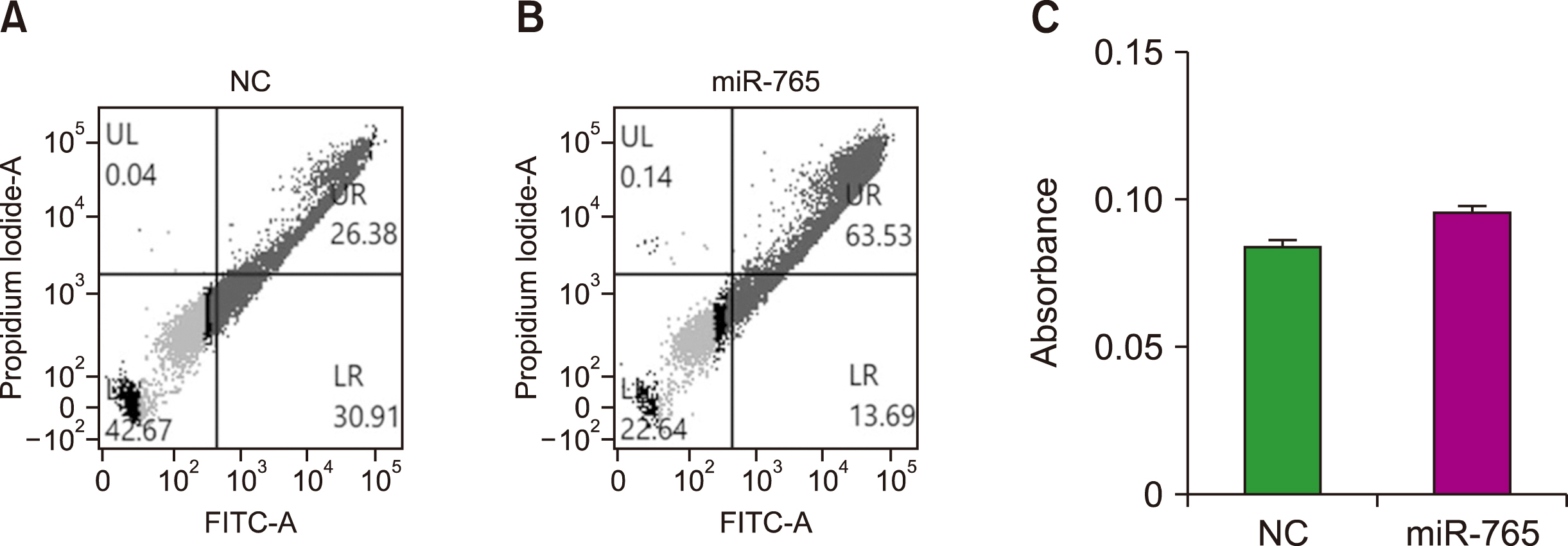
We compared the expression profiles of miR-765 in 65 patients with MDS and 11 controls. Cell proliferation and apoptosis assays were performed to determine the in vitro effects of miR-765 on leukemia cells transfected with the miR-765 mimic. Reverse transcription quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) and western blotting were performed to examine the targets of miR-765.
Results
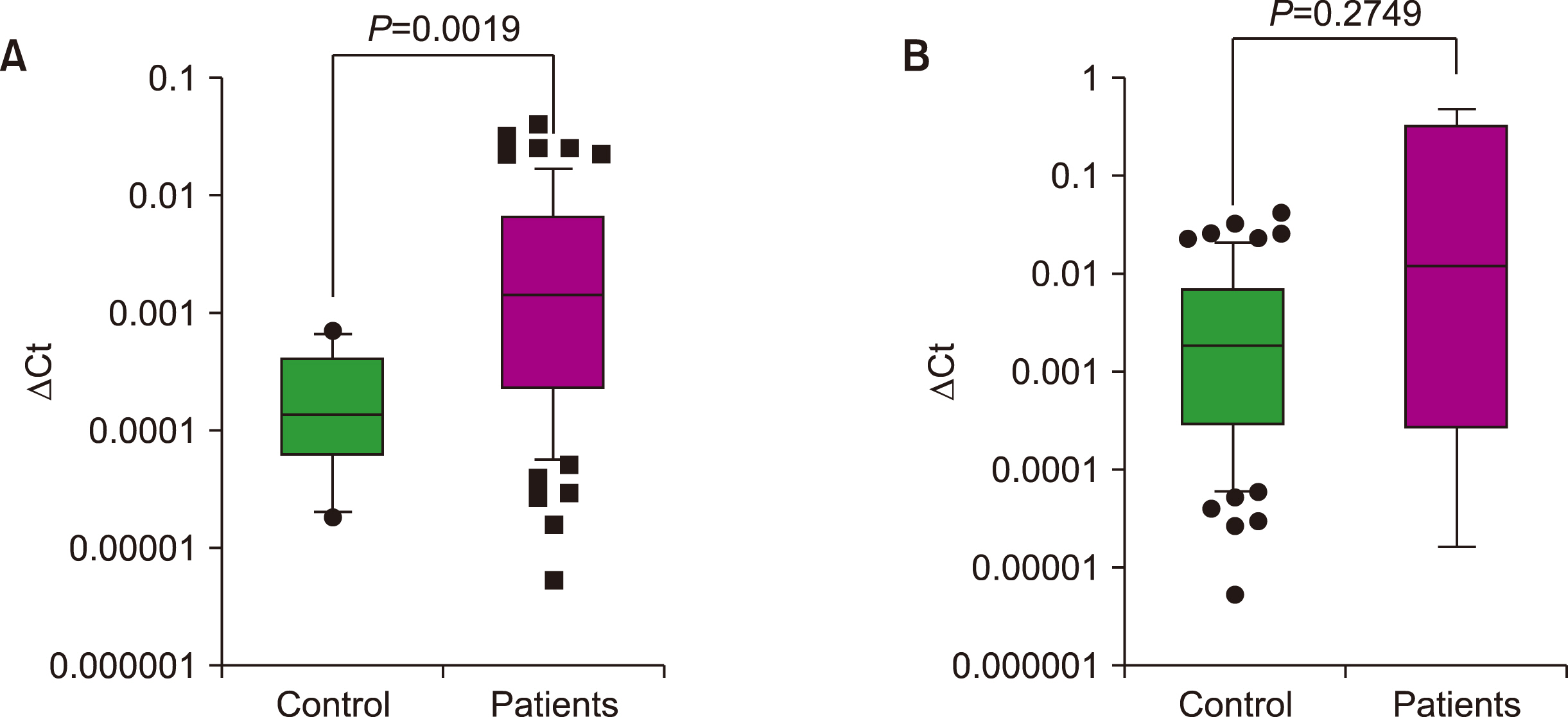
We found that miR-765 levels were upregulated 10.2-fold in patients with MDS compared to controls. In refractory cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia, the percentage of patients with elevated miR-765 levels was significantly higher than in other forms of MDS. Experiments with leukemia cells revealed that transfection with a miR-765 mimic inhibited cell proliferation and induced apoptosis. RT-qPCR and western blotting demonstrated that the target of miR-765 was PLP2.
Conclusion
These findings imply that upregulation of miR-765 induces apoptosis via downregulation of PLP2 and may have a role in MDS pathogenesis.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Raza A, Galili N. 2012; The genetic basis of phenotypic heterogeneity in myelodysplastic syndromes. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:849–59. DOI: 10.1038/nrc3321. PMID: 23175121.
Article2. Cazzola M. 2020; Myelodysplastic syndromes. N Engl J Med. 383:1358–74. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1904794. PMID: 32997910.
Article3. Fang J, Varney M, Starczynowski DT. 2012; Implication of microRNAs in the pathogenesis of MDS. Curr Pharm Des. 18:3170–9. DOI: 10.2174/1381612811209023170. PMID: 22571695. PMCID: PMC4863958.
Article4. Starczynowski DT, Morin R, McPherson A, et al. 2011; Genome-wide identification of human microRNAs located in leukemia-associated genomic alterations. Blood. 117:595–607. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-03-277012. PMID: 20962326.
Article5. Rhyasen GW, Starczynowski DT. 2012; Deregulation of microRNAs in myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia. 26:13–22. DOI: 10.1038/leu.2011.221. PMID: 21852786.
Article6. Xiao W, Wang C, Chen K, et al. 2020; miR-765 functions as a tumour suppressor and eliminates lipids in clear cell renal cell carcinoma by downregulating PLP2. EBioMedicine. 51:102622. DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.102622. PMID: 31901870. PMCID: PMC6948168.
Article7. Lee DS, Kim SH, Seo EJ, et al. 2002; Predominance of trisomy 1q in myelodysplastic syndromes in Korea: is there an ethnic difference? A 3-year multi-center study. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 132:97–101. DOI: 10.1016/S0165-4608(01)00533-7. PMID: 11850068.8. Jung SW, Lee SY, Jekarl DW, et al. 2011; Cytogenetic characteristics and prognosis analysis in 231 myelodysplastic syndrome patients from a single institution. Leuk Res. 35:735–40. DOI: 10.1016/j.leukres.2010.11.009. PMID: 21146871.
Article9. Choi JS, Nam MH, Yoon SY, Kang SH. 2015; MicroRNA-194-5p could serve as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk Res. 39:763–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.leukres.2015.04.013. PMID: 25975751.
Article10. Kang SH, Kim HB, Choi JS. 2022; Upregulation of microRNA-597 in myelodysplastic syndromes induces apoptosis through FOSL2 inhibition. Eur J Haematol. 109:680–5. DOI: 10.1111/ejh.13852. PMID: 36018564.11. Meng K, Li Z, Cui X. 2021; Three LHPP gene-targeting co-expressed microRNAs (microRNA-765, microRNA-21, and microRNA-144) promote proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion, and are independent prognostic biomarkers in renal cell carcinomas patients. J Clin Lab Anal. 35:e24077. DOI: 10.1002/jcla.24077. PMID: 34699621. PMCID: PMC8649365.
Article12. Lin W, Miao Y, Meng X, Huang Y, Zhao W, Ruan J. 2020; miRNA-765 mediates multidrug resistance via targeting BATF2 in gastric cancer cells. FEBS Open Bio. 10:1021–30. DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.12838. PMID: 32166887. PMCID: PMC7262883. PMID: 2f225db1118043f3845c488ad3b680f7.
Article13. Jiao Y, Yuan C, Wu H, Li X, Yu J. 2020; Oncogenic microRNA-765 promotes the growth and metastasis of breast carcinoma by directly targeting ING4. J Cell Biochem. 121:3887–900. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.29545. PMID: 31724215.
Article14. Zhang L, Wang T, Valle D. 2015; Reduced PLP2 expression increases ER-stress-induced neuronal apoptosis and risk for adverse neurological outcomes after hypoxia ischemia injury. Hum Mol Genet. 24:7221–6. DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddv422. PMID: 26512060. PMCID: PMC4664164.
Article15. Feng Z, Zhou W, Wang J, et al. 2020; Reduced expression of proteolipid protein 2 increases ER stress-induced apoptosis and autophagy in glioblastoma. J Cell Mol Med. 24:2847–56. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14840. PMID: 31778016. PMCID: PMC7077595.
Article16. Bai H, Zhu Y, Xu P, Chen B. 2020; PLP2 expression as a prognostic and therapeutic indicator in high-risk multiple myeloma. Biomed Res Int. 2020:4286101. DOI: 10.1155/2020/4286101. PMID: 32596309. PMCID: PMC7303762.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correction: MicroRNA‑765 is upregulated in myelodysplastic syndromes and induces apoptosis via PLP2 inhibition in leukemia cells
- Sweet's Syndrome with Myelodysplastic Syndrome Progressing to Acute Myelogenous Leukemia
- A Case of Leukemia Cutis in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Evolving into An Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
- Evolution of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia from refractory anemia: the unusual course of a myelodysplastic syndrome
- Mesenchymal stromal cells in myeloid malignancies