Yonsei Med J.
2019 Jun;60(6):561-569. 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.6.561.
miR-140-3p Knockdown Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Fibrogenesis in Hepatic Stellate Cells via PTEN-Mediated AKT/mTOR Signaling
- Affiliations
-
- 1Wuhan Center for Clinical Laboratory, Wuhan Forth Hospital; Puai Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China. dr54min@sina.com
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Wuhan Children's Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China.
- 3Department of Clinical Laboratory, Wuhan Children's Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China.
- KMID: 2446962
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2019.60.6.561
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Liver fibrosis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality and the outcome of various chronic liver diseases. Activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) is the key event in liver fibrosis. Studies have confirmed that miR-140-3p plays a potential regulatory effect on HSC activation. However, whether miR-140-3p mediates the liver fibrosis remains unknown.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Expression of miR-140-3p was detected by real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR). Cell proliferation was measured by MTT, while cell apoptosis rate was determined via flow cytometry. Western blot assay was used to detect the expression of cleaved PARP. The fibrogenic effect was evaluated by expression of α-smooth muscle actin and desmin. Functional experiments were performed in transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1)-induced HSC-T6 cells with transfection of anti-miR-140-3p and/or siPTEN. Target binding between miR-140-3p and PTEN was predicted by the TargetScan database and identified using luciferase reporter assay and RNA immunoprecipitation.
RESULTS
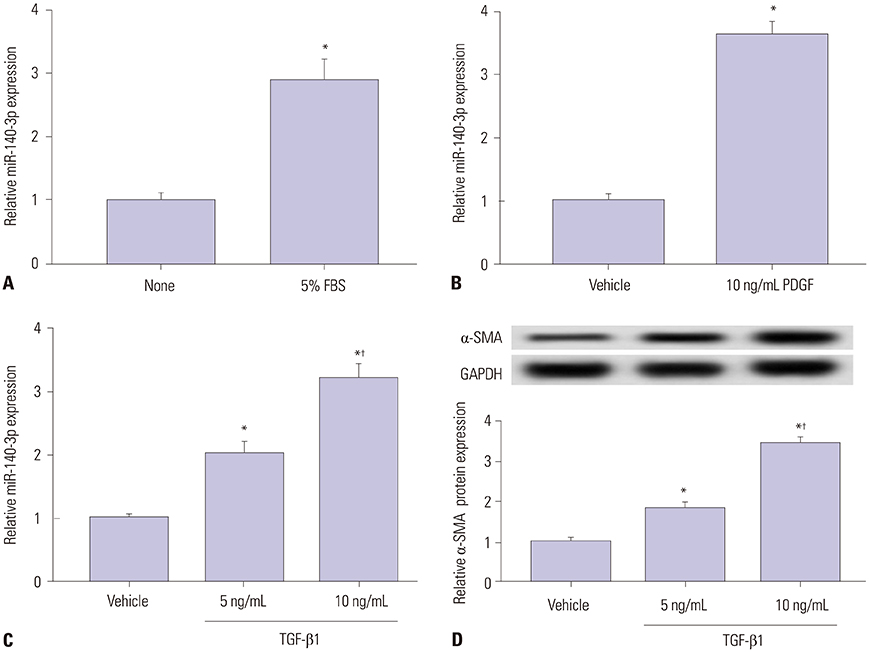
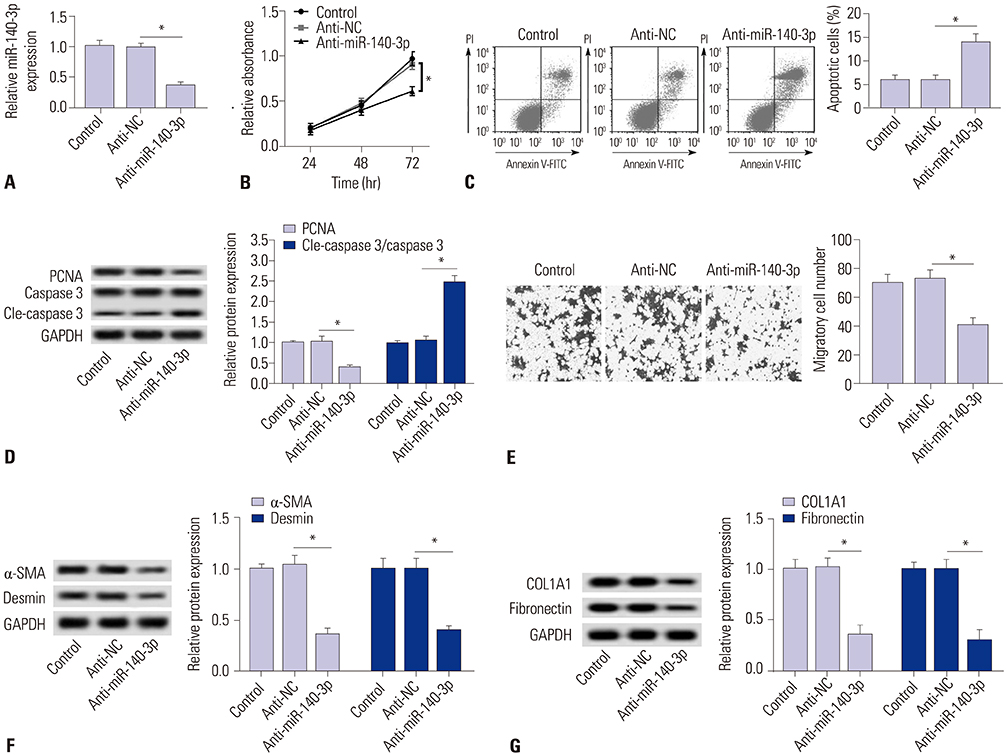
TGF-β1 induced the activation of HSC-T6 cells, and miR-140-3p expression varied according to HSC-T6 cell activation status. Knockdown of miR-140-3p reduced cell proliferation and the expressions of α-SMA and desmin, as well as increased apoptosis, in TGF-β1-induced HSC-T6 cells, which could be blocked by PTEN silencing. Additionally, inactivation of the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway stimulated by miR-140-3p knockdown was abolished when silencing PTEN expression. PTEN was negatively regulated by miR-140-3p via direct binding in HSC-T6 cells.
CONCLUSION
miR-140-3p is an important mediator in HSC-T6 cell activation, and miR-140-3p knockdown suppresses cell proliferation and fibrogenesis in TGF-β1-induced HSC-T6 cells, indicating that miR-140-3p may be a potential novel molecular target for liver fibrosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kocabayoglu P, Friedman SL. Cellular basis of hepatic fibrosis and its role in inflammation and cancer. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2013; 5:217–230.
Article2. Arriazu E, Ruiz de Galarreta M, Cubero FJ, Varela-Rey M, Pérez de Obanos MP, Leung TM, et al. Extracellular matrix and liver disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014; 21:1078–1097.
Article3. Lee UE, Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2011; 25:195–206.
Article4. Mimche PN, Lee CM, Mimche SM, Thapa M, Grakoui A, Henkemeyer M, et al. EphB2 receptor tyrosine kinase promotes hepatic fibrogenesis in mice via activation of hepatic stellate cells. Sci Rep. 2018; 8:2532.
Article5. Dooley S, ten Dijke P. TGF-β in progression of liver disease. Cell Tissue Res. 2012; 347:245–256.
Article6. Zhu J, Luo Z, Pan Y, Zheng W, Li W, Zhang Z, et al. H19/miR-148a/USP4 axis facilitates liver fibrosis by enhancing TGF-β signaling in both hepatic stellate cells and hepatocytes. J Cell Physiol. 2018; 10. 26. [Epub]. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.27656.
Article7. Preisser L, Miot C, Le Guillou-Guillemette H, Beaumont E, Foucher ED, Garo E, et al. IL-34 and macrophage colony-stimulating factor are overexpressed in hepatitis C virus fibrosis and induce profibrotic macrophages that promote collagen synthesis by hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology. 2014; 60:1879–1890.
Article8. Breitkopf-Heinlein K, Meyer C, König C, Gaitantzi H, Addante A, Thomas M, et al. BMP-9 interferes with liver regeneration and promotes liver fibrosis. Gut. 2017; 66:939–954.
Article9. Gressner AM, Weiskirchen R. Modern pathogenetic concepts of liver fibrosis suggest stellate cells and TGF-beta as major players and therapeutic targets. J Cell Mol Med. 2006; 10:76–99.
Article10. Lambrecht J, Mannaerts I, van Grunsven LA. The role of miRNAs in stress-responsive hepatic stellate cells during liver fibrosis. Front Physiol. 2015; 6:209.
Article11. Kumar V, Mahato RI. Delivery and targeting of miRNAs for treating liver fibrosis. Pharm Res. 2015; 32:341–361.
Article12. Guo CJ, Pan Q, Cheng T, Jiang B, Chen GY, Li DG. Changes in microRNAs associated with hepatic stellate cell activation status identify signaling pathways. FEBS J. 2009; 276:5163–5176.
Article13. El-Ahwany E, Nagy F, Zoheiry M, Shemis M, Nosseir M, Taleb HA, et al. Circulating miRNAs as predictor markers for activation of hepatic stellate cells and progression of HCV-induced liver fibrosis. Electron Physician. 2016; 8:1804–1810.
Article14. Wolfson B, Zhang Y, Gernapudi R, Duru N, Yao Y, Lo PK, et al. A high-fat diet promotes mammary gland myofibroblast differentiation through microRNA 140 downregulation. Mol Cell Biol. 2017; 37:e00461-16.
Article15. Wakasugi H, Takahashi H, Niinuma T, Kitajima H, Oikawa R, Matsumoto N, et al. Dysregulation of miRNA in chronic hepatitis B is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma risk after nucleos(t)ide analogue treatment. Cancer Lett. 2018; 434:91–100.
Article16. Wolfson B, Lo PK, Yao Y, Li L, Wang H, Zhou Q. Impact of miR-140 deficiency on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2018; 62:e1800189.
Article17. Blanco-Aparicio C, Renner O, Leal JF, Carnero A. PTEN, more than the AKT pathway. Carcinogenesis. 2007; 28:1379–1386.
Article18. Chen CY, Chen J, He L, Stiles BL. PTEN: tumor suppressor and metabolic regulator. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018; 9:338.
Article19. Takashima M, Parsons CJ, Ikejima K, Watanabe S, White ES, Rippe RA. The tumor suppressor protein PTEN inhibits rat hepatic stellate cell activation. J Gastroenterol. 2009; 44:847–855.
Article20. Shearn CT, Orlicky DJ, McCullough RL, Jiang H, Maclean KN, Mercer KE, et al. Liver-specific deletion of phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 significantly ameliorates chronic EtOH-induced increases in hepatocellular damage. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0154152.
Article21. Xia H, Diebold D, Nho R, Perlman D, Kleidon J, Kahm J, et al. Pathological integrin signaling enhances proliferation of primary lung fibroblasts from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Exp Med. 2008; 205:1659–1672.
Article22. Parapuram SK, Shi-wen X, Elliott C, Welch ID, Jones H, Baron M, et al. Loss of PTEN expression by dermal fibroblasts causes skin fibrosis. J Invest Dermatol. 2011; 131:1996–2003.
Article23. McClelland AD, Herman-Edelstein M, Komers R, Jha JC, Winbanks CE, Hagiwara S, et al. miR-21 promotes renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy by targeting PTEN and SMAD7. Clin Sci (Lond). 2015; 129:1237–1249.
Article24. Ciuffreda L, Falcone I, Incani UC, Del Curatolo A, Conciatori F, Matteoni S, et al. PTEN expression and function in adult cancer stem cells and prospects for therapeutic targeting. Adv Biol Regul. 2014; 56:66–80.
Article25. Xu MY, Hu JJ, Shen J, Wang ML, Zhang QQ, Qu Y, et al. Stat3 signaling activation crosslinking of TGF-β1 in hepatic stellate cell exacerbates liver injury and fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014; 1842:2237–2245.
Article26. Roderfeld M, Weiskirchen R, Wagner S, Berres ML, Henkel C, Grötzinger J, et al. Inhibition of hepatic fibrogenesis by matrix metalloproteinase-9 mutants in mice. FASEB J. 2006; 20:444–454.
Article27. de Oliveira da Silva B, Ramos LF, Moraes KCM. Molecular interplays in hepatic stellate cells: apoptosis, senescence, and phenotype reversion as cellular connections that modulate liver fibrosis. Cell Biol Int. 2017; 41:946–959.
Article28. Jiang XP, Ai WB, Wan LY, Zhang YQ, Wu JF. The roles of microRNA families in hepatic fibrosis. Cell Biosci. 2017; 7:34.
Article29. Li WQ, Chen C, Xu MD, Guo J, Li YM, Xia QM, et al. The rno-miR-34 family is upregulated and targets ACSL1 in dimethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. FEBS J. 2011; 278:1522–1532.
Article30. Zhu J, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Li W, Zheng W, Yu J, et al. MicroRNA-212 activates hepatic stellate cells and promotes liver fibrosis via targeting SMAD7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018; 496:176–183.
Article31. Diniz GP, Huang ZP, Liu J, Chen J, Ding J, Fonseca RI, et al. Loss of microRNA-22 prevents high-fat diet induced dyslipidemia and increases energy expenditure without affecting cardiac hypertrophy. Clin Sci (Lond). 2017; 131:2885–2900.
Article32. Son MK, Ryu YL, Jung KH, Lee H, Lee HS, Yan HH, et al. HS-173, a novel PI3K inhibitor, attenuates the activation of hepatic stellate cells in liver fibrosis. Sci Rep. 2013; 3:3470.
Article33. Wang J, Chu ES, Chen HY, Man K, Go MY, Huang XR, et al. microRNA-29b prevents liver fibrosis by attenuating hepatic stellate cell activation and inducing apoptosis through targeting PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget. 2015; 6:7325–7338.
Article34. Kumar P, Raeman R, Chopyk DM, Smith T, Verma K, Liu Y, et al. Adiponectin inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation by targeting the PTEN/AKT pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018; 1864:3537–3545.
Article35. Zheng J, Wu C, Xu Z, Xia P, Dong P, Chen B, et al. Hepatic stellate cell is activated by microRNA-181b via PTEN/Akt pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015; 398:1–9.
Article36. Hu TH, Wang CC, Huang CC, Chen CL, Hung CH, Chen CH, et al. Down-regulation of tumor suppressor gene PTEN, overexpression of p53, plus high proliferating cell nuclear antigen index predict poor patient outcome of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. Oncol Rep. 2007; 18:1417–1426.
Article37. Wei J, Feng L, Li Z, Xu G, Fan X. MicroRNA-21 activates hepatic stellate cells via PTEN/Akt signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 2013; 67:387–392.
Article38. Li Y, Tsang CK, Wang S, Li XX, Yang Y, Fu L, et al. MAF1 suppresses AKT-mTOR signaling and liver cancer through activation of PTEN transcription. Hepatology. 2016; 63:1928–1942.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- MSCs-Derived miR-150-5p-Expressing Exosomes Promote Skin Wound Healing by Activating PI3K/AKT Pathway through PTEN
- MiR-103a-3p Contributes to the Progression of Colorectal Cancer by Regulating GREM2 Expression
- Long non-coding RNA T-cell leukemia/lymphoma 6 serves as a sponge for miR-21 modulating the cell proliferation of retinoblastoma through PTEN
- Long Non-Coding RNA TUG1 Promotes Proliferation and Inhibits Apoptosis of Osteosarcoma Cells by Sponging miR-132-3p and Upregulating SOX4 Expression
- LncRNA STARD7-AS1 suppresses cervical cancer cell proliferation while promoting autophagy by regulating miR-31-5p/TXNIP axis to inactivate the mTOR signaling