J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2019 Apr;54(2):141-149. 10.4055/jkoa.2019.54.2.141.
Correction of Single Thoracic Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Using Pedicle Screw Instrumentation: Comparison of Stainless Steel to Titanium Alloy Instruments
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea. scd25@paik.ac.kr
- 3Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2444779
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2019.54.2.141
Abstract
- PURPOSE
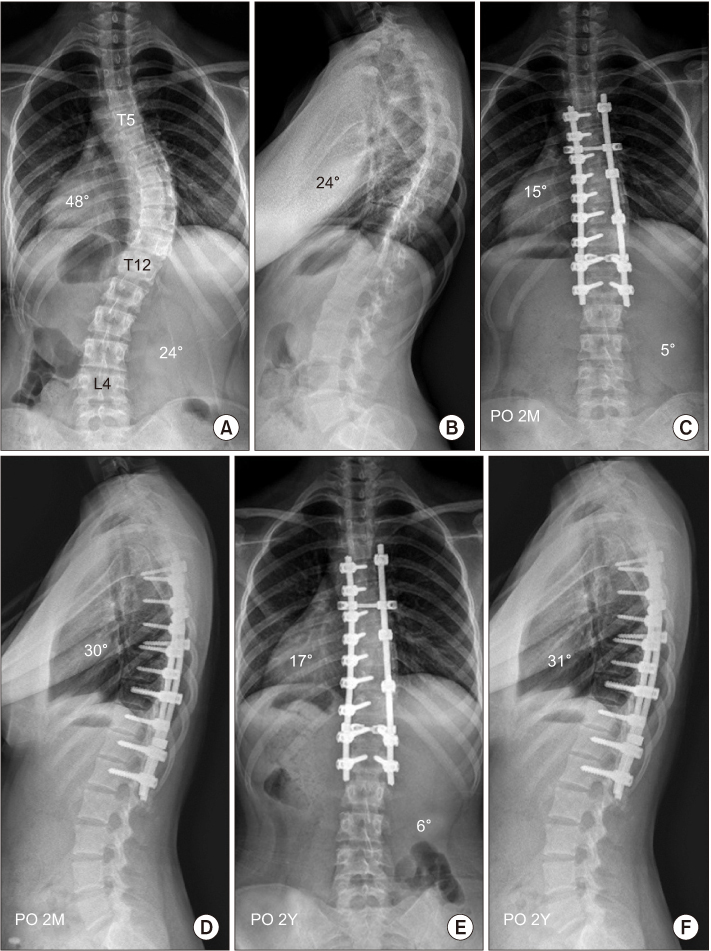
To compare the results of two different instruments made of stainless steel and titanium alloy for correction of single thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) using pedicle screw instrumentation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 141 patients with single thoracic AIS treated with pedicle screw instrumentation and selective thoracic fusion were retrospectively reviewed after a follow-up of 2 years. The patients had a main thoracic curve of 40° to 75° and were divided into two groups based on instrument materials; S group (stainless steel, n=90) and T group (titanium alloy, n=51). The diameter of the stainless steel rod used was 7.0 mm while that of the titanium alloy rod was 6.35 mm or 6.0 mm. Standing long-cassette radiographic measurements including various coronal and sagittal parameters for the preoperative, early postoperative and 2-year postoperative follow-up were analyzed. There were no significant differences in the preoperative curve characteristics between the two groups.
RESULTS
In the S group, the preoperative main thoracic curve of 51.3°±8.4° was improved to 19.0°±7.6° (63.1% correction) and the lumbar curve of 32.3°±8.4° spontaneously decreased to 12.7°±8.2° (62.9% correction) at 2 years postoperatively. In the T group, the preoperative main thoracic curve of 49.5°±8.4° and the lumbar curve of 30.3°±8.9° was improved to 18.8°±7.4° (62.2% correction) and 11.3°±5.4° (63.3% correction), respectively. The corrections of coronal curves were not statistically different between the two groups (p>0.05). The thoracic kyphosis was changed from 16.8°±8.5° to 24.3°±6.1° in the S group and from 19.6°±11.2° to 26.6°±8.5° in the T group. There were no significant differences in the changes of sagittal curves, coronal and sagittal balances at the 2-year follow-up and the number of fused segments and used screws between the two groups (p>0.05).
CONCLUSION
When conducting surgery for single thoracic AIS using pedicles screw instrumentation, two different instruments made of stainless steel and titanium alloy showed similar corrections for coronal and sagittal curves.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Suk SI, Lee CK, Kim WJ, Chung YJ, Park YB. Segmental pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995; 20:1399–1405.
Article2. Cotrel Y, Dubousset J, Guillaumat M. New universal instrumentation in spinal surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; 227:10–23.
Article3. Suk SI, Kim JH, Cho KJ, Kim SS, Lee JJ, Han YT. Is anterior release necessary in severe scoliosis treated by posterior segmental pedicle screw fixation? Eur Spine J. 2007; 16:1359–1365.
Article4. Muschik M, Schlenzka D, Robinson PN, Kupferschmidt C. Dorsal instrumentation for idiopathic adolescent thoracic scoliosis: rod rotation versus translation. Eur Spine J. 1999; 8:93–99.
Article5. Webb JK, Burwell RG, Cole AA, Lieberman I. Posterior instrumentation in scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 1995; 4:2–5.
Article6. Suk SI, Kim JH, Kim SS, Lim DJ. Pedicle screw instrumentation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS). Eur Spine J. 2012; 21:13–22.
Article7. Kim SS, Kim JH, Suk SI. Effect of direct vertebral rotation on the uninstrumented lumbar curve in thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Asian Spine J. 2017; 11:127–137.
Article8. Boucher HH. A method of spinal fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1959; 41:248–259.
Article9. Roy-Camille R, Saillant G, Mazel C. Internal fixation of the lumbar spine with pedicle screw plating. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986; 203:7–17.
Article10. Roy-Camille R, Saillant G, Mazel C. Plating of thoracic, thoracolumbar, and lumbar injuries with pedicle screw plates. Orthop Clin North Am. 1986; 17:147–159.
Article11. Binyamin G, Shafi BM, Mery CM. Biomaterials: a primer for surgeons. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2006; 15:276–283.
Article12. Di Silvestre M, Bakaloudis G, Lolli F, Giacomini S. Late-developing infection following posterior fusion for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2011; 20:S121–S127.
Article13. Dick JC, Bourgeault CA. Notch sensitivity of titanium alloy, commercially pure titanium, and stainless steel spinal implants. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:1668–1672.
Article14. Gotman I. Characteristics of metals used in implants. J Endourol. 1997; 11:383–389.
Article15. Lindsey C, Deviren V, Xu Z, Yeh RF, Puttlitz CM. The effects of rod contouring on spinal construct fatigue strength. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31:1680–1687.
Article16. Pienkowski D, Stephens GC, Doers TM, Hamilton DM. Multicycle mechanical performance of titanium and stainless steel transpedicular spine implants. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998; 23:782–788.
Article17. Di Silvestre M, Lolli F, Bakaloudis G, Maredi E, Vommaro F, Pastorelli F. Apical vertebral derotation in the posterior treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: myth or reality? Eur Spine J. 2013; 22:313–323.
Article18. Fu G, Kawakami N, Goto M, Tsuji T, Ohara T, Imagama S. Comparison of vertebral rotation corrected by different techniques and anchors in surgical treatment of adolescent thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2009; 22:182–189.
Article19. Kim YJ, Kassab F, Berven SH, et al. Serum levels of nickel and chromium after instrumented posterior spinal arthrodesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:923–926.
Article20. Knott PT, Mardjetko SM, Kim RH, et al. A comparison of magnetic and radiographic imaging artifact after using three types of metal rods: stainless steel, titanium, and vitallium. Spine J. 2010; 10:789–794.
Article21. Okada E, Watanabe K, Hosogane N, et al. Comparison of stainless steel and titanium alloy instruments in posterior correction and fusion surgery for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis-prospective cohort study with minimum 2-year follow-up. J Med Biol Eng. 2013; 33:325–329.22. Di Silvestre M, Bakaloudis G, Ruosi C, et al. Segmental vs non-segmental thoracic pedicle screws constructs in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Is there any implant alloy effect? Eur Spine J. 2017; 26:533–538.
Article23. Clements DH, Betz RR, Newton PO, Rohmiller M, Marks MC, Bastrom T. Correlation of scoliosis curve correction with the number and type of fixation anchors. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34:2147–2150.
Article24. Gebhart S, Alton TB, Bompadre V, Krengel WF. Do anchor density or pedicle screw density correlate with short-term outcome measures in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis surgery? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014; 39:E104–E110.
Article25. Quan GM, Gibson MJ. Correction of main thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis using pedicle screw instrumentation: does higher implant density improve correction? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010; 35:562–567.26. Lamerain M, Bachy M, Delpont M, Kabbaj R, Mary P, Vialle R. CoCr rods provide better frontal correction of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis treated by all-pedicle screw fixation. Eur Spine J. 2014; 23:1190–1196.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Comparison of Rigid and Semi-rigid Rod for the Correctability of the Thoracic Hypokyphosis of the Idiopathic Scoliosis
- Bending Stiffness of Rod in Pedicle Screw Systems
- Experimental Observation of Pedicle Screws in Postoperative CT scan - Stainless steel vs. Titanium
- Segmental pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of Thoracic idiopathic scoliosis
- Pedicle Screw Instrumentation for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: The Insertion Technique, the Fusion Levels and Direct Vertebral Rotation