Clin Orthop Surg.
2011 Jun;3(2):89-100. 10.4055/cios.2011.3.2.89.
Pedicle Screw Instrumentation for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: The Insertion Technique, the Fusion Levels and Direct Vertebral Rotation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Seoul Spine Institute, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea. seilsuk@unitel.co.kr
- KMID: 1719304
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2011.3.2.89
Abstract
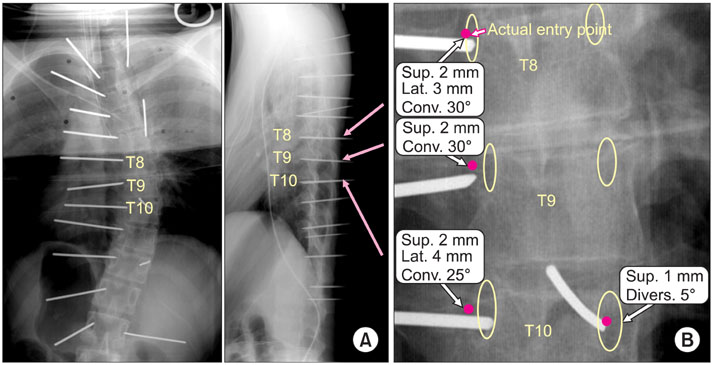
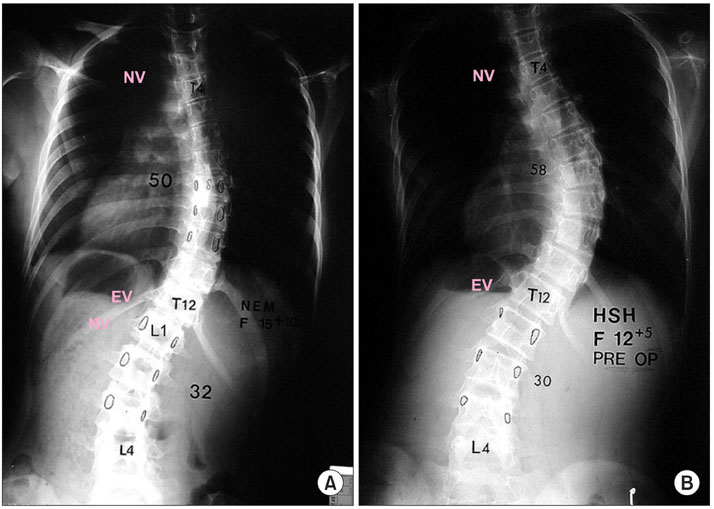
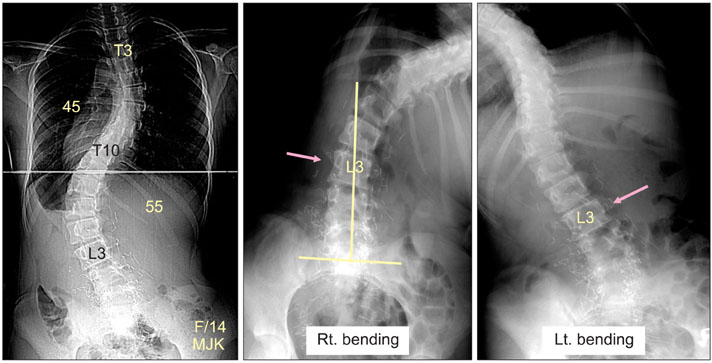
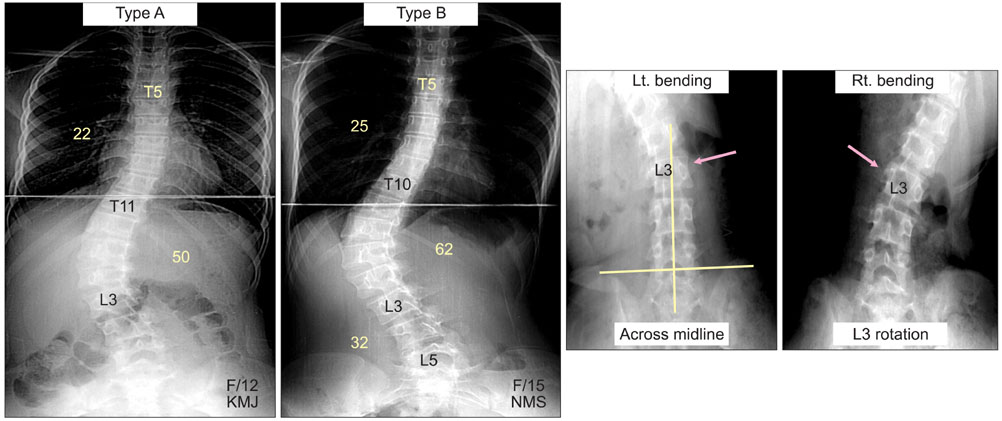
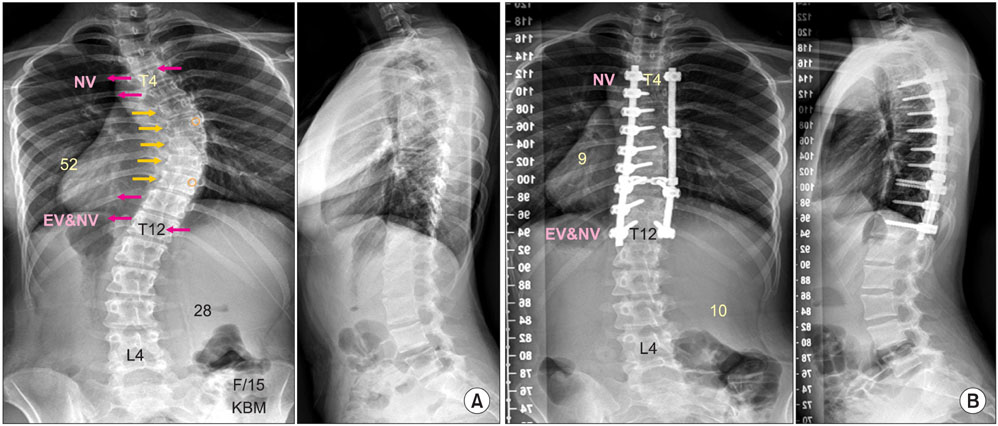
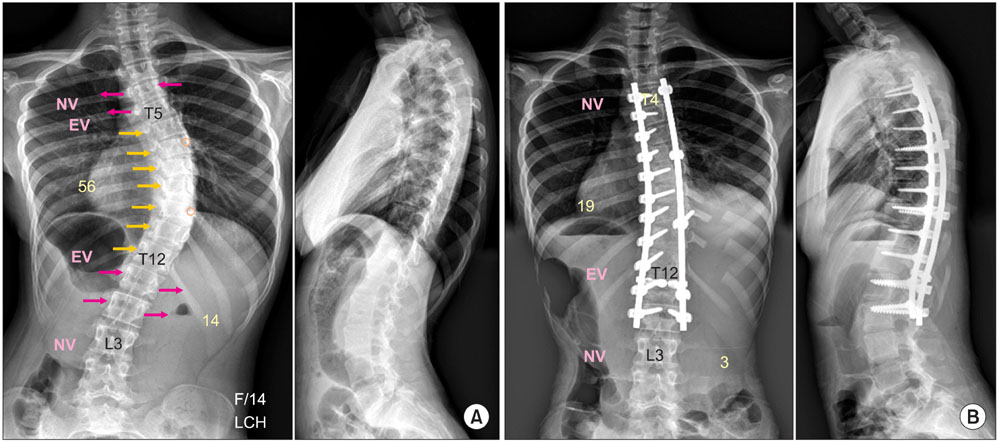
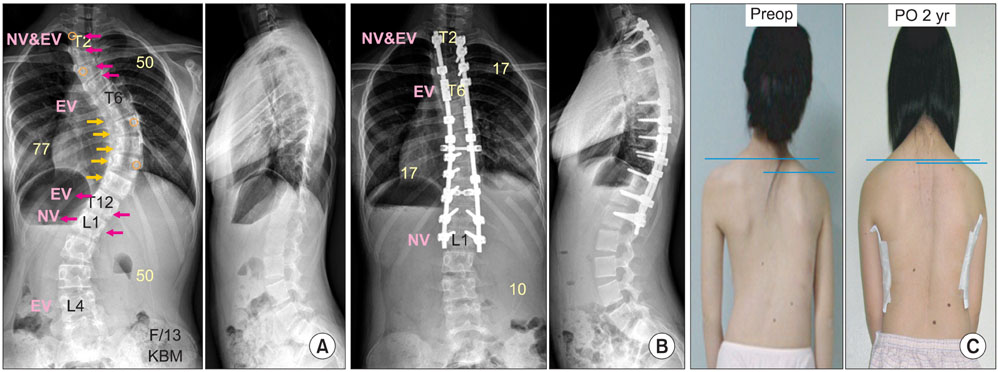
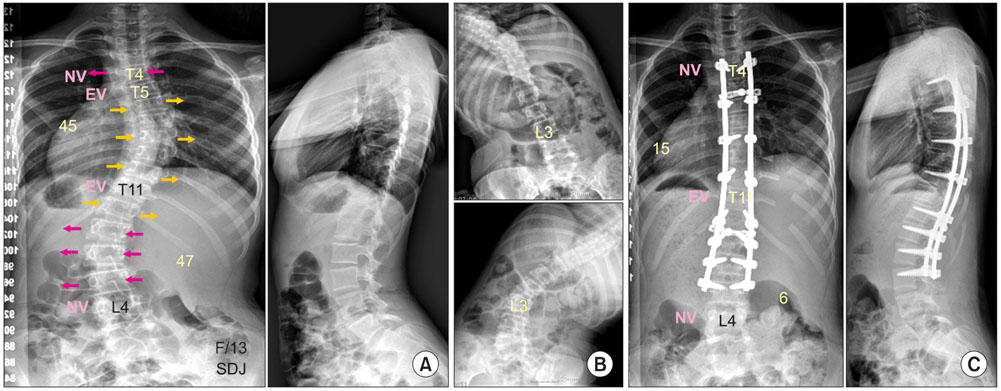
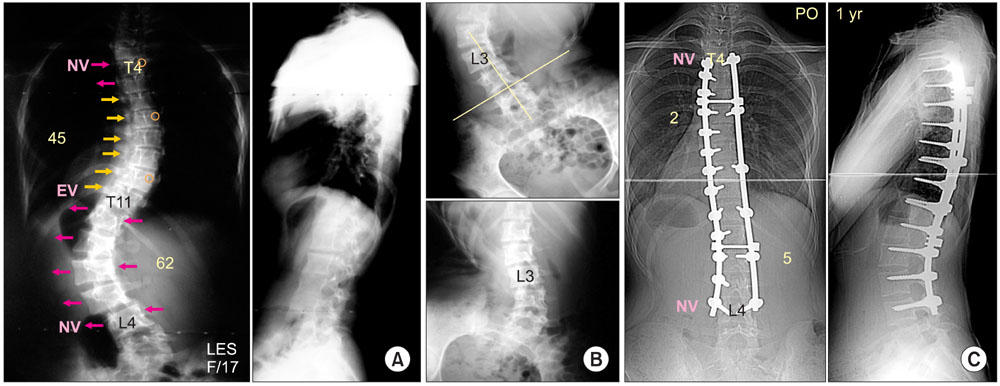
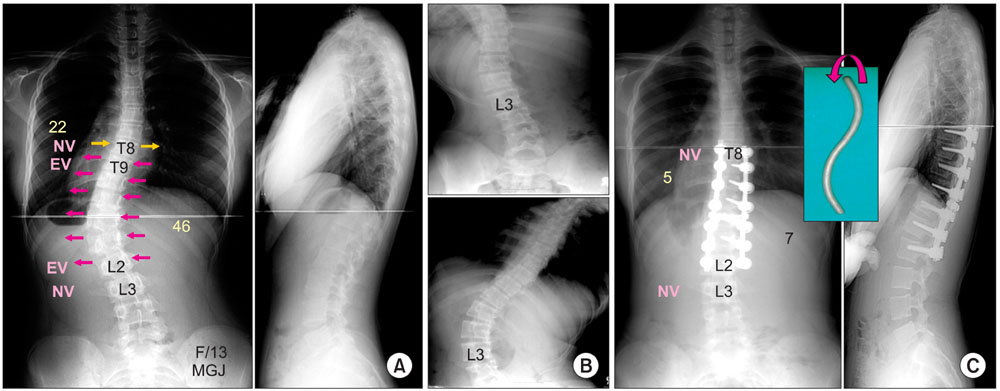
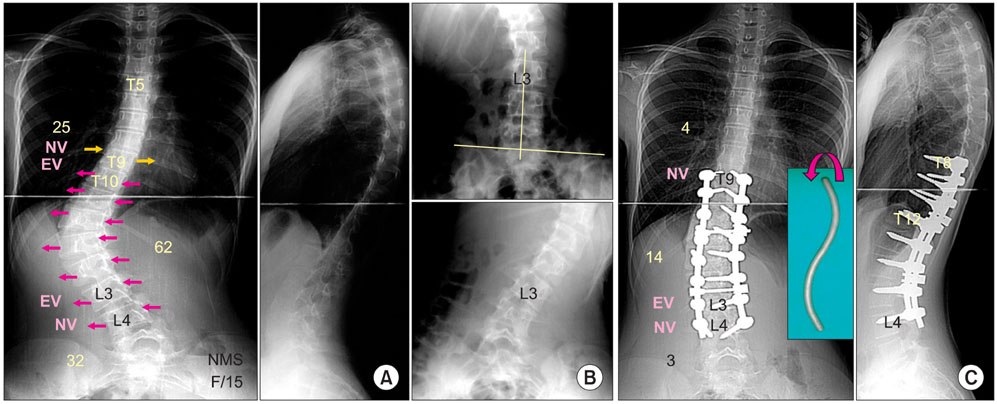
- The pedicle is a power nucleus of the vertebra and offers a secure grip of all 3 columns. Pedicle screw instrumentation has advantages of rigid fixation with improved three-dimensional (3D) correction and it is accepted as a reliable method with a high margin of safety. Accurate placement of the pedicle screws is important to reduce possible irreversible complications. Many methods of screw insertion have been reported. The author has been using the K-wire method coupled with the intraoperative single posteroanterior and lateral radiographs, which is the most safe, accurate and fast method. Identification of the curve patterns and determining the fusion levels are very important. The ideal classification of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis should address the all patterns, predict the extent of accurate fusion and have good inter/intraobserver reliability. My classification system matches with the ideal classification system, and it is simple and easy to learn; and my classification system has only 4 structural curve patterns and each curve has 2 types. Scoliosis is a 3D deformity; the coronal and sagittal curves can be corrected with rod rotation, and rotational deformity has to be corrected with direct vertebral rotation (DVR). Rod derotation and DVR are true methods of 3D deformity correction with shorter fusion and improved correction of both the fused and unfused curves, and this is accomplished using pedicle screw fixation. The direction of DVR is very important and it should be opposite to the direction of the rotational deformity of the vertebra. A rigid rod has to be used to prevent rod bend-out during the derotation and DVR.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Transpedicular Curettage and Drainage of Infective Lumbar Spondylodiscitis: Technique and Clinical Results
Byung Ho Lee, Hwan-Mo Lee, Tae-Hwan Kim, Hak-Sun Kim, Eun-Soo Moon, Jin-Oh Park, Hyun-Soo Chong, Seong-Hwan Moon
Clin Orthop Surg. 2012;4(3):200-208. doi: 10.4055/cios.2012.4.3.200.Transpedicular Curettage and Drainage of Infective Lumbar Spondylodiscitis: Technique and Clinical Results
Byung Ho Lee, Hwan-Mo Lee, Tae-Hwan Kim, Hak-Sun Kim, Eun-Soo Moon, Jin-Oh Park, Hyun-Soo Chong, Seong-Hwan Moon
Clin Orthop Surg. 2012;4(3):200-208. doi: 10.4055/cios.2012.4.3.200.
Reference
-
1. Harrington PR. Treatment of scoliosis: correction and internal fixation by spine instrumentation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1962. 44(4):591–610.2. Goldstein LA. Treatment of idiopathic scoliosis by Harrington instrumentation and fusion with fresh autogenous iliac bone grafts. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969. 51(2):209–222.
Article3. Cotrel Y, Dubousset J, Guillaumat M. New universal instrumentation in spinal surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988. 227:10–23.
Article4. Bridwell KH, McAllister JW, Betz RR, Huss G, Clancy M, Schoenecker PL. Coronal decompensation produced by Cotrel-Dubousset "derotation" maneuver for idiopathic right thoracic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1991. 16(7):769–777.
Article5. Shufflebarger HL, Clark CE. Fusion levels and hook patterns in thoracic scoliosis with Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1990. 15(9):916–920.
Article6. Suk SI, Lee CK, Chung SS. Comparison of Zielke ventral derotation system and Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation in the treatment of idiopathic lumbar and thoracolumbar scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994. 19(4):419–429.
Article7. Labelle H, Dansereau J, Bellefleur C, de Guise J, Rivard CH, Poitras B. Peroperative three-dimensional correction of idiopathic scoliosis with the Cotrel-Dubousset procedure. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995. 20(12):1406–1409.
Article8. Suk SI, Lee CK, Min HJ, Cho KH, Oh JH. Comparison of Cotrel-Dubousset pedicle screws and hooks in the treatment of idiopathic scoliosis. Int Orthop. 1994. 18(6):341–346.
Article9. Suk SI, Lee CK, Kim WJ, Chung YJ, Park YB. Segmental pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995. 20(12):1399–1405.
Article10. Liljenqvist UR, Halm HF, Link TM. Pedicle screw instrumentation of the thoracic spine in idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997. 22(19):2239–2245.
Article11. Roy-Camille R, Saillant G, Mazel C. Internal fixation of the lumbar spine with pedicle screw plating. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986. (203):7–17.
Article12. Brown CA, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Geideman WM, Hasan SA, Blanke K. Complications of pediatric thoracolumbar and lumbar pedicle screws. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998. 23(14):1566–1571.
Article13. Suk SI, Kim WJ, Kim JH, Lee SM. Restoration of thoracic kyphosis in the hypokyphotic spine: a comparison between multiple-hook and segmental pedicle screw fixation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Spinal Disord. 1999. 12(6):489–495.14. Esses SI, Sachs BL, Dreyzin V. Complications associated with the technique of pedicle screw fixation: a selected survey of ABS members. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993. 18(15):2231–2238.
Article15. Lonstein JE, Denis F, Perra JH, Pinto MR, Smith MD, Winter RB. Complications associated with pedicle screws. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999. 81(11):1519–1528.
Article16. Suk SI, Kim WJ, Lee SM, Kim JH, Chung ER. Thoracic pedicle screw fixation in spinal deformities: are they really safe? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001. 26(18):2049–2057.17. Brown CW, editor. Spinal instrumentation techniques. 1998. Rosemont, IL: Scoliosis Research Society.18. Suk SI, Cha SI, Lee CK, et al. A study on the pullout strength of pedicle screws in relation to the size of the drill holes and inserted screws. Paper presented at: The 30th Annual Meeting of the Scoliosis Research Society. 1995 Sep 13-16; Asheville, NC, USA.19. Zindrick MR, Wiltse LL, Doornik A, et al. Analysis of the morphometric characteristics of the thoracic and lumbar pedicles. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1987. 12(2):160–166.
Article20. Misenhimer GR, Peek RD, Wiltse LL, Rothman SL, Widell EH Jr. Anatomic analysis of pedicle cortical and cancellous diameter as related to screw size. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1989. 14(4):367–372.
Article21. Suk SI, Lee JH. A study of the diameter and change of the vertebral pedicle after screw insertion. Paper presented at: Third International Meeting SIROT. 1994 Oct; Boston, MA, USA.22. Suk SI, Kim WJ, Lee CS, et al. Indications of proximal thoracic curve fusion in thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: recognition and treatment of double thoracic curve pattern in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis treated with segmental instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000. 25(18):2342–2349.
Article23. Suk SI, Lee SM, Chung ER, Kim JH, Kim WJ, Sohn HM. Determination of distal fusion level with segmental pedicle screw fixation in single thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003. 28(5):484–491.
Article24. Margulies JY, Floman Y, Robin GC, et al. An algorithm for selection of instrumentation levels in scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 1998. 7(2):88–94.
Article25. King HA, Moe JH, Bradford DS, Winter RB. The selection of fusion levels in thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983. 65(9):1302–1313.
Article26. Lenke LG, Betz RR, Bridwell KH, Harms J, Clements DH, Lowe TG. Spontaneous lumbar curve coronal correction after selective anterior or posterior thoracic fusion in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999. 24(16):1663–1671.
Article27. Lee CK, Denis F, Winter RB, Lonstein JE. Analysis of the upper thoracic curve in surgically treated idiopathic scoliosis: a new concept of the double thoracic curve pattern. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993. 18(12):1599–1608.
Article28. Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, O'Brien MF, Baldus C, Blanke K. Recognition and treatment of the proximal thoracic curve in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis treated with Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994. 19(14):1589–1597.
Article29. Winter RB, Denis F. The King V curve pattern: its analysis and surgical treatment. Orthop Clin North Am. 1994. 25(2):353–362.30. Arlet V, Marchesi D, Papin P, Aebi M. Decompensation following scoliosis surgery: treatment by decreasing the correction of the main thoracic curve or "letting the spine go". Eur Spine J. 2000. 9(2):156–160.
Article31. Lee SM, Suk SI, Chung ER. Direct vertebral rotation: a new technique of three-dimensional deformity correction with segmental pedicle screw fixation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004. 29(3):343–349.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Direct Vertebral Rotation on the Uninstrumented Lumbar Curve in Thoracic Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
- Direct Vertebral Rotation (DVR): A New Technique of 3-D Deformity Correction with Segmental Pedicle Screw Fixation in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (AIS)
- Changes in Vertebral Rotation Following Segmental Pedicle Screw Instrumentation and Rod Derotation in Idiopathic Thoracic Scoliosis : Part I - CT Evaluation
- Clinical Results of Selective Thoracic Fusion by Segmental Pedicle Screws in King type II Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis ( AIS )
- Safety of Pedicle Screws in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Surgery