J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2003 Jun;10(2):180-190. 10.4184/jkss.2003.10.2.180.
Direct Vertebral Rotation (DVR): A New Technique of 3-D Deformity Correction with Segmental Pedicle Screw Fixation in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (AIS)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Seoul Spine Institute, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital. snoopy5@unitel.co.kr
- KMID: 2003216
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2003.10.2.180
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: A prospective study.
OBJECTIVES
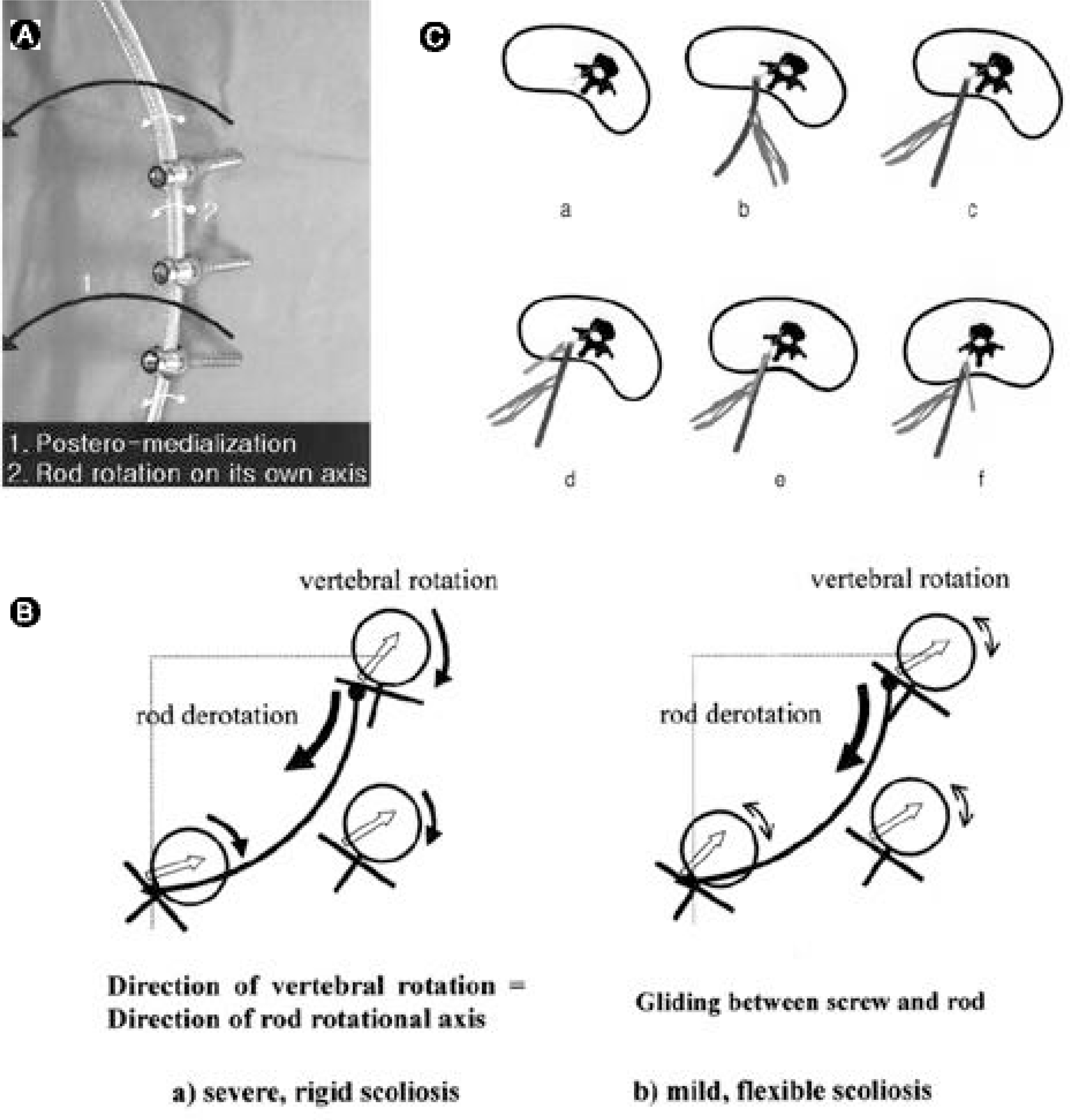
To introduce a new technique, direct vertebral rotation (DVR), and to compare the surgical results with those of a simple rod derotation (SRD). SUMMARY OF BACKGROUND DATA: Pedicle screw fixation, with a simple rod derotation maneuver, enables powerful coronal and sagittal plane corrections in scoliosis surgery. However, the ability for rotational correction is still unclear.
METHODS
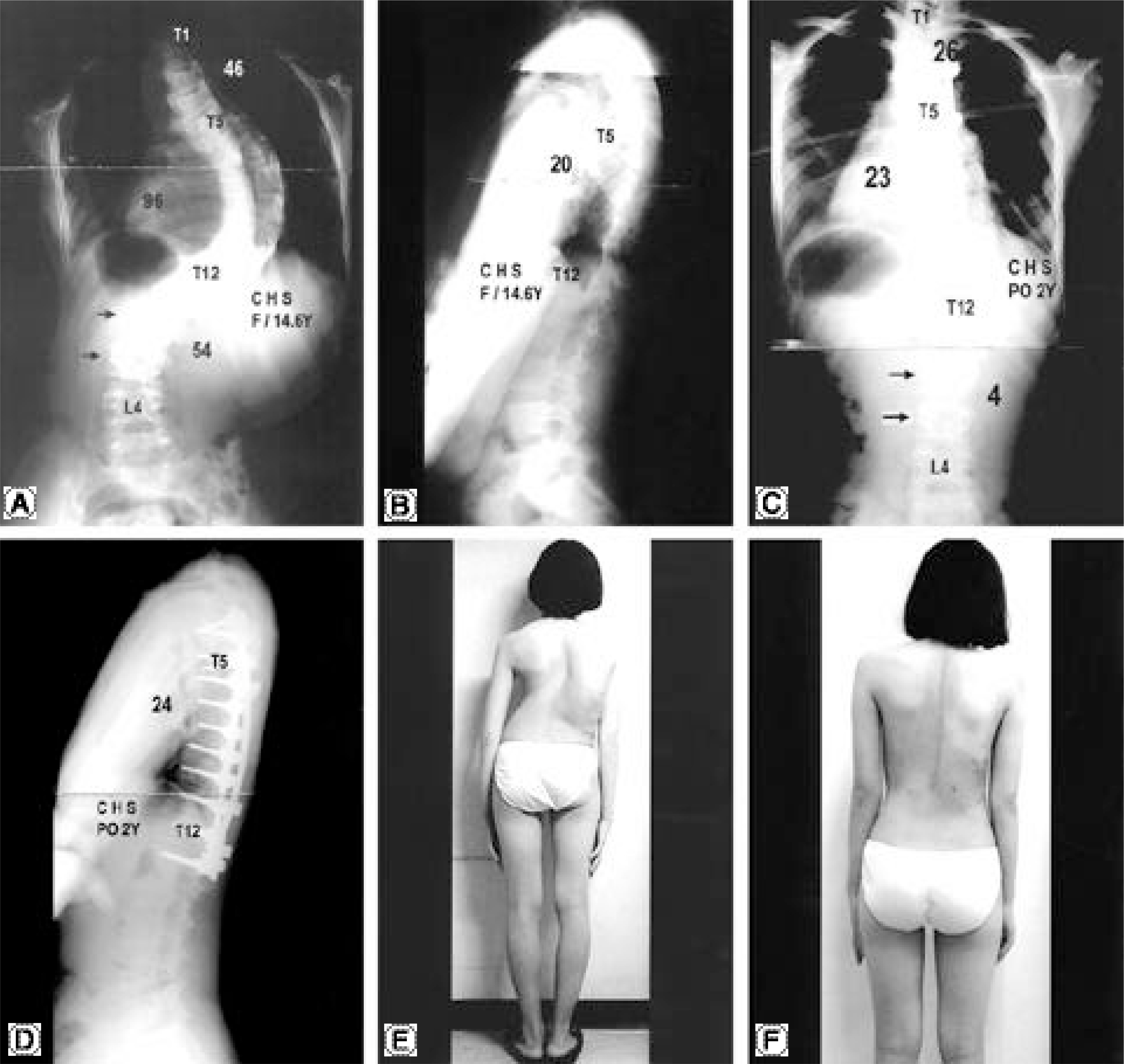
Thirty-eight AIS patients, treated with segmental pedicle screw fixation, were analyzed. The first group (n=17) was treated by DVR, and the second (n=21) by SRD. Having similar preoperative curve patterns, both groups were evaluated for the deformity correction and spinal balance.
RESULTS
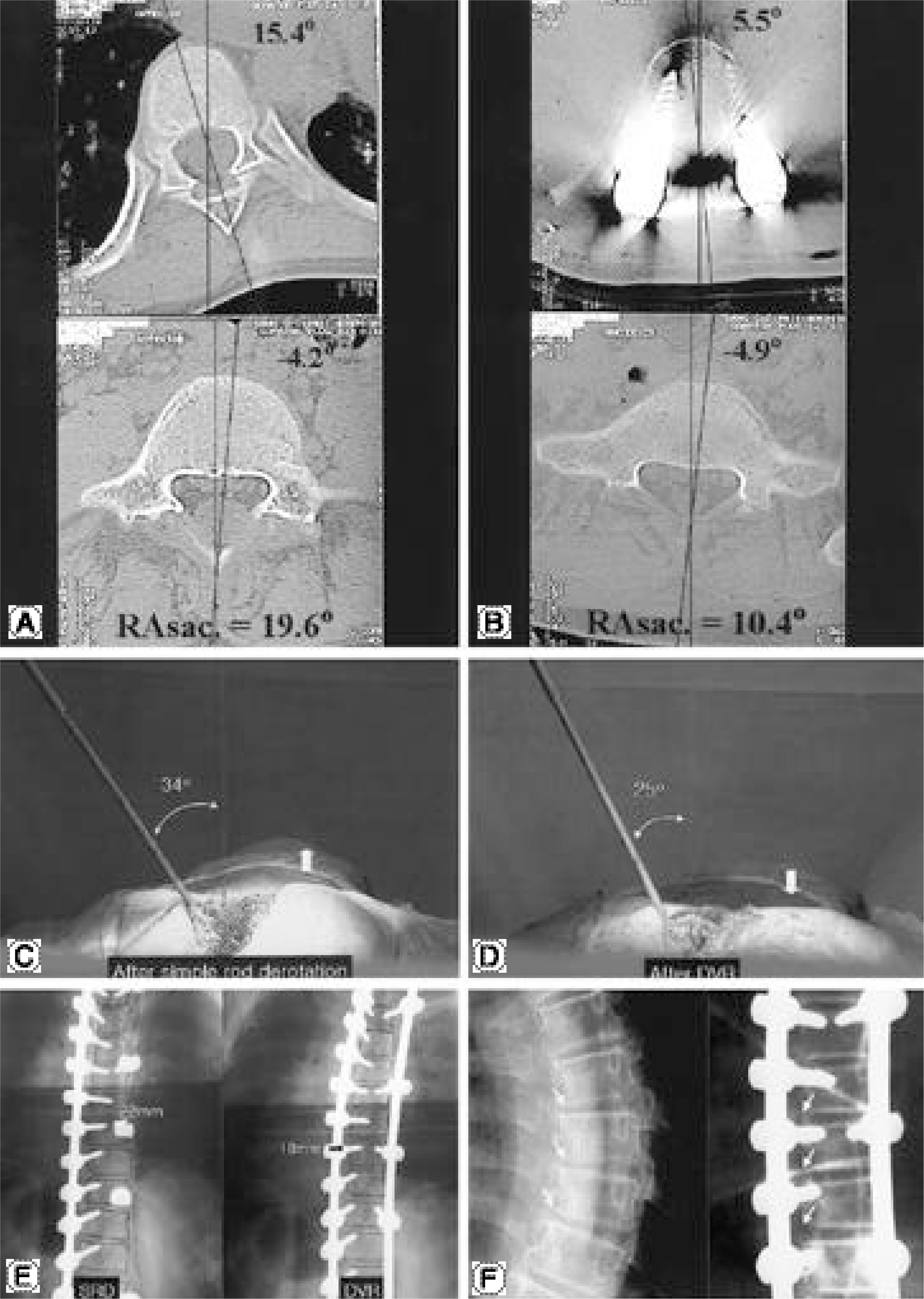
In the DVR group, the average preoperative AVR of 16.7 degrees was corrected to 9.6 degrees, showing a 42.5% correction, while in the SRD group, the correction was negligible, from 16.1 degrees to 15.7 degrees(2.4%). In the DVR group, the preoperative thoracic curve of 55 degreeswas corrected to 12 degrees(79.6%), and the lumbar curve from 39 degreesto 7 degrees(80.5%). In the SRD group, the preoperative thoracic curve of 53 degreeswas corrected to 17 degrees(68.9%), and the lumbar curve from 39 degreesto 16 degrees(62.2%). The average LIVT correction was 80.6 and 66.3% in the DVR and SRD group, respectively. There were statistically significant differences in the coronal curve, LIVT and rotational correction (p<0.05, Mann-Whitney u test).
CONCLUSIONS
The segmental pedicle screw fixation with 'direct vertebral rotation'showed better rotational and coronal corrections than the 'simple rod derotation'.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1). Aaro S., Dahlborn M. Estimation of vertebral rotation and the spinal and rib cage deformity in scoliosis by computer tomography. Spine,. 6:460–7. 1981.
Article2). Bridwell KH. Surgical treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: the basics and the controversies. Spine,. 19:1095–100. 1994.3). Cotrel Y., Dubousset J., Guillaumat M. New universal instrumentation in spinal surgery. Clin Orthop,. 227:10–23. 1988.
Article4). Delorme S., Labelle H., Aubin CE, et al. Intraoperative comparison of two instrumentation techniques for the cor -rection of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Rod rotation and translation. Spine,. 24:2011–7. 1999.5). Gardner-Morse M., Stokes IA. Three-dimensional simulations of the scoliosis derotation maneuver with Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation. J Biomech,. 27:177–81. 1994.
Article6). Ghanem IB., Hagnere F., Dubousset JF, et al. Intraoper -ative optoelectronic analysis of three-dimensional verte -bral displacement after Cotrel-Dubousset rod rotation. A preliminary report. Spine,. 22:1913–21. 1997.7). Gray JM., Smith BW., Ashley RK, et al. Derotat ional analysis of Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation in idiopathic scoliosis. Spine,. 16:S391–3. 1991.8). Kaneda K., Shono Y., Satoh S, et al. Anterior correction of thoracic scoliosis with Kaneda anterior spinal system. A preliminary report. Spine,. 22:1358–68. 1997.9). Kim WJ., Suk SI., Kwon CS, et al. Changes in vertebral rotation following segmental pedicle screw instrumentation and rod derotation in idiopathic thoracic scoliosis: Part I - CT evaluation. J of Korean Orthop Assoc,. 33:1164–9. 1998.10). Krismer M., Bauer R., Sterzinger W. Scoliosis correction by Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation. The effect of derotation and three-dimensional correction. Spine,. 17:S263–9. 1992.11). Labelle H., Dansereau J., Bellefleur C, et al. Preoperative three-dimensional correction of idiopathic scoliosis with the Cotrel-Dubousset procedure. Spine,. 20:1406–9. 1995.12). Lenke LG., Bridwell KH., Baldus C, et al. C o t r e l -Dubousset instrumentation for adolescent idiopathic scol -iosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am,. 74:1056–67. 1992.13). Muschik M., Schlenzka D., Robinson PN, et al. Dorsal instrumentation for idiopathic adolescent thoracic scolio -sis: rod rotation versus translation. Eur Spine J,. 8:93–9. 1999.14). Papin P., Labelle H., Delorme S, et al. Long-term three-dimensional changes of the spine after posterior spinal instrumentation and fusion in adolescent idiopathic scolio -sis. Eur Spine J,. 8:16–21. 1999.15). Perdriolle R., Vidal J. Morphology of scoliosis: three-dimensional evolution. Orthopedics,. 10:909–15. 1987.
Article16). Pollock FE., Pollock FE Jr. Idiopathic scoliosis: cor -rection of lateral and rotational deformities using the Cotrel-Dubousset spinal instrumentation system. South Med J,. 83:161–5. 1990.17). Suk SI., Lee CK., Chung SS. Comparison of Zielke ven -tral derotation system and Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation in the treatment of idiopathic lumbar and thoracolum -bar scoliosis. Spine,. 19:419–29. 1994.18). Suk SI., Lee CK., Kim WJ, et al. Segmental pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. Spine,. 20:1399–405. 1995.
Article19). Turi M., Johnston CE 2nd., Richards BS. Anterior cor -rection of idiopathic scoliosis using TSRH instrumentation. Spine,. 18:417–22. 1993.20). Wood KB., Olsewski JM., Schendel MJ, et al. Rotational changes of the vertebral pelvic axis after sublaminar instrumentation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine,. 22:51–7. 1997.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pedicle Screw Instrumentation for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: The Insertion Technique, the Fusion Levels and Direct Vertebral Rotation
- Clinical Results of Selective Thoracic Fusion by Segmental Pedicle Screws in King type II Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis ( AIS )
- Effect of Direct Vertebral Rotation on the Uninstrumented Lumbar Curve in Thoracic Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
- The Influence of Segmental Pedicle Screw Fixation on Distal Fusion Level in KingType I Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis(AIS)
- Decompensation in Selective Thoracic Fusion by Segmental Pedicle Screw Fixation in King type II Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (AIS): Causative Factors and its Prevention