Korean J Urol.
2013 Mar;54(3):199-203.
Effects of Long-term Administration of the Antiaging Hormone Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate on Rat Prostates and Testes as Androgen-Dependent Organs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, University of Cukurova Faculty of Medicine, Adana, Turkey. volkanizol@yahoo.com
- 2Department of Pathology, University of Cukurova Faculty of Medicine, Adana, Turkey.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study aimed to determine the effects of the long-term use of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS) on rat prostates and testes as well as on serum testosterone and DHEAS levels.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty male rats aged 4 to 5 months were studied. A DHEAS suspension of 5 mg/kg per rat was administered orally to the 15 rats in the experimental group 5 times a week, whereas saline was administered concurrently to the 15 rats in the control group. Intracardiac blood samples were drawn to determine hormone levels, and histological samples of prostate and testes were evaluated under light microscopy.
RESULTS
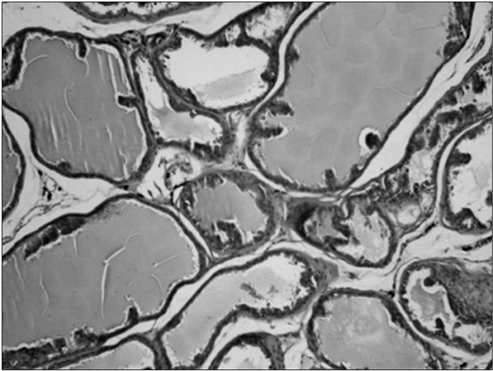
At the end of the 6-month study period, histological examinations performed on prostate preparations showed that the atrophy score of the experimental group was significantly lower than the scores of the sham and control groups (p<0.001 and p<0.001, respectively). The serum total testosterone and DHEAS levels of the rats in the study group were significantly increased (p<0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
In our study, we determined that the long-term use of DHEAS does not have any detrimental effects on the prostate or the testis; on the contrary, it protects the prostate from atrophy, which is imperative for the continuation of fertility as well as for increasing serum testosterone and DHEAS levels.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hornsby PJ. DHEA: a biologist's perspective. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1997. 45:1395–1401.2. Allolio B, Arlt W. DHEA treatment: myth or reality? Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2002. 13:288–294.3. Herbert J. The age of dehydroepiandrosterone. Lancet. 1995. 345:1193–1194.4. Morales AJ, Nolan JJ, Nelson JC, Yen SS. Effects of replacement dose of dehydroepiandrosterone in men and women of advancing age. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994. 78:1360–1367.5. Zanato VF, Martins MP, Anselmo-Franci JA, Petenusci SO, Lamano-Carvalho TL. Sexual development of male Wistar rats. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1994. 27:1273–1280.6. Rhoden EL, Gobbi D, Rhoden CR, Menti E, Roehe AN, Hartmann A, et al. Effects of chronic administration of dehydroepiandrosterone on serum testosterone levels and prostatic tissue in rats. J Urol. 2003. 170:2101–2103.7. Johnsen SG. Testicular biopsy score count: a method for registration of spermatogenesis in human testes: normal values and results in 335 hypogonadal males. Hormones. 1970. 1:2–25.8. Gobbi D, Rhoden EL, Menti E, Lulhier F, Rhoden C. Effects of the chronic use of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) on testicular weight and spermatogenesis: experimental study in rats. Int Urol Nephrol. 2003. 35:119–122.9. Hinson JP, Raven PW. DHEA deficiency syndrome: a new term for old age? J Endocrinol. 1999. 163:1–5.10. Zizzi T, Nunnery M, Cason Z, Tucci M, Benghuzzi H. The effects of dehydroepiandrosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate on the reproductive and vital organs of male rats. Biomed Sci Instrum. 1999. 35:279–284.11. Morgentaler A, Bruning CO 3rd, DeWolf WC. Occult prostate cancer in men with low serum testosterone levels. JAMA. 1996. 276:1904–1906.12. Morley JE, Perry HM 3rd, Kaiser FE, Kraenzle D, Jensen J, Houston K, et al. Effects of testosterone replacement therapy in old hypogonadal males: a preliminary study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1993. 41:149–152.13. Tenover JS. Effects of testosterone supplementation in the aging male. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992. 75:1092–1098.14. Horton RJ. Grayhack JT, Wilson JD, Scherbenske MJ, editors. Androgen hormones and prehormones in young and elderly men. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Proceedings of Workshop Sponsored by Kidney Disease and Urology Program of the NIAMDD. 1976. Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office;183–188.15. Mac Donald PC. Grayhack JT, Wilson JD, Scherbenske MJ, editors. Origin of estrogen in man. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Proceedings of Workshop Sponsored by Kidney Disease and Urology Program of the NIAMDD. 1976. Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office;191–192.16. Reiter WJ, Pycha A, Schatzl G, Klingler HC, Mark I, Auterith A, et al. Serum dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate concentrations in men with erectile dysfunction. Urology. 2000. 55:755–758.17. Flynn MA, Weaver-Osterholtz D, Sharpe-Timms KL, Allen S, Krause G. Dehydroepiandrosterone replacement in aging humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999. 84:1527–1533.18. Severi G, Morris HA, MacInnis RJ, English DR, Tilley W, Hopper JL, et al. Circulating steroid hormones and the risk of prostate cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2006. 15:86–91.19. Gould DC, Kirby RS. Testosterone replacement therapy for late onset hypogonadism: what is the risk of inducing prostate cancer? Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2006. 9:14–18.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Plasma Levels of Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate ( DHEA - S ) and Total Testosterone in the Patients with Female androgenetic Alopecia
- Dehydroepiandrosterone and cortisol concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid of dogs
- Hormone Supplement Therapy in Andropause
- Pros and Cons of Antiaging Medicine
- Declining concentrations of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate and free testosterone with advancing age