Yonsei Med J.
2017 Mar;58(2):272-281. 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.2.272.
Comparative Effects of Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma on Migration and Invasion in Oral Squamous Cell Cancer, by Gas Type
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. ostium@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea.
- 5Department of Life Science, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea.
- 6Ajou University, Suwon, Korea.
- 7ICD Co., Ltd., Anseong, Korea.
- KMID: 2427114
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2017.58.2.272
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The fourth state of matter, plasma is known as an ionized gas with electrons, radicals and ions. The use of non-thermal plasma (NTP) in cancer research became possible because of the progresses in plasma medicine. Previous studies on the potential NTP-mediated cancer therapy have mainly concentrated on cancer cell apoptosis. In the present study, we compared the inhibitory effect of NTP on cell migration and invasion in the oral squamous cancer cell lines.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
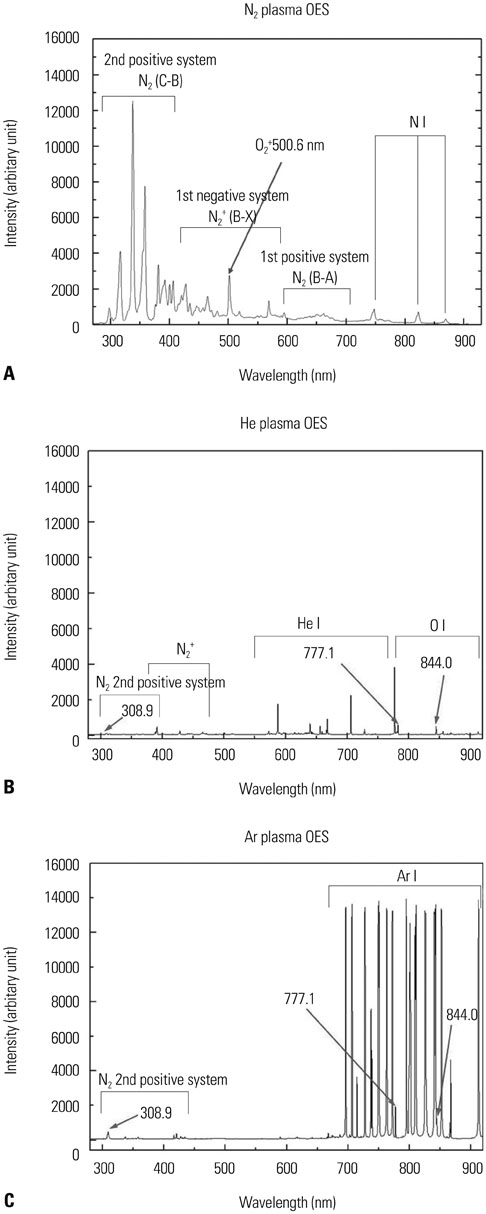
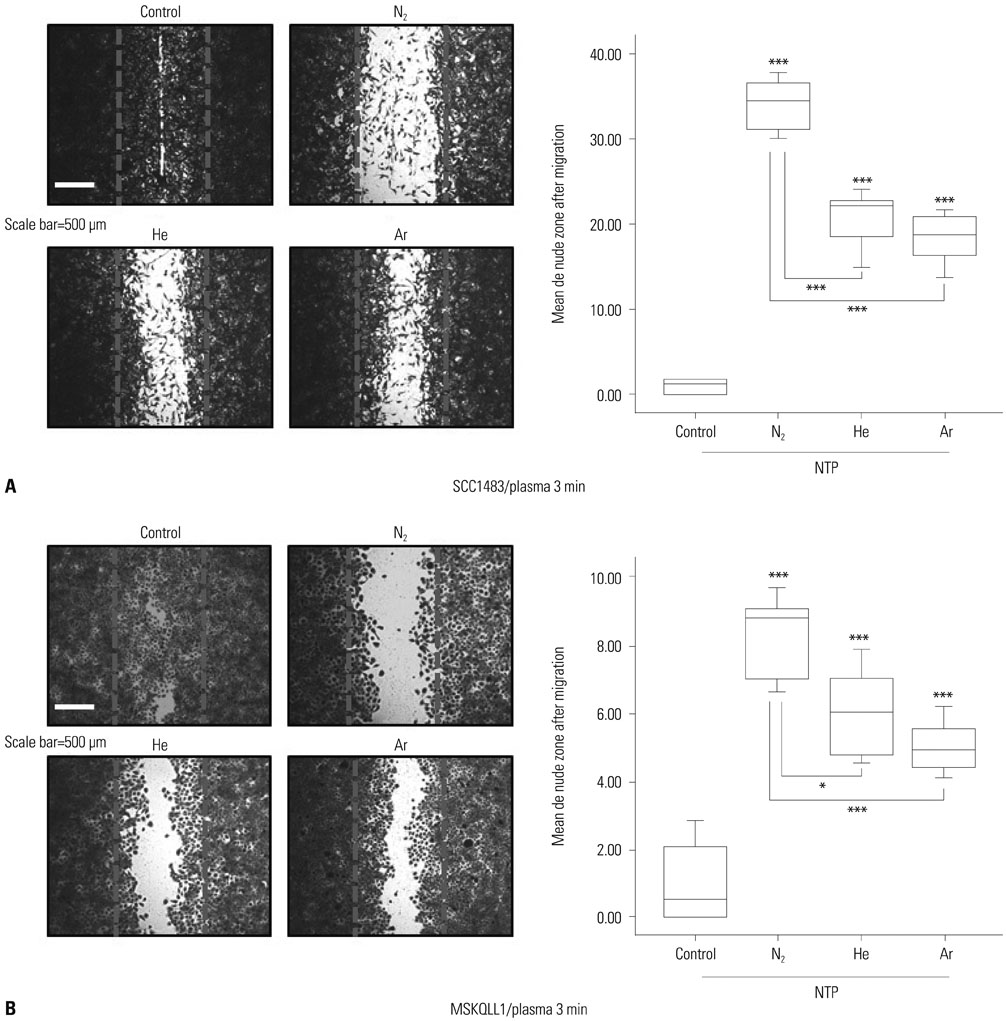
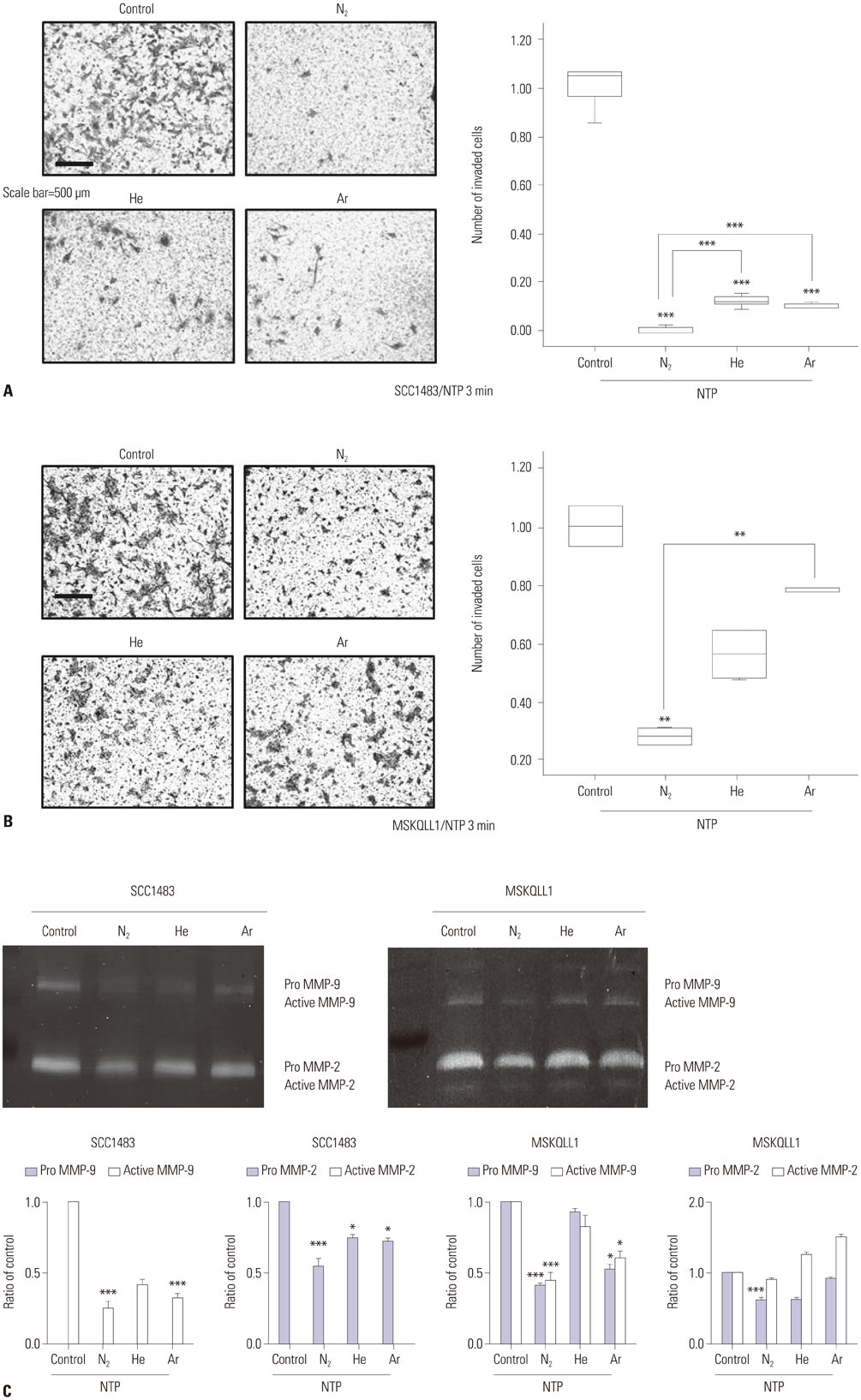
We used oral squamous cancer cell lines (SCC1483, MSKQLL1) and different gases (Nâ‚‚, He, and Ar). To investigate the mechanism of plasma treatment, using different gases (Nâ‚‚, He, and Ar) which induces anti-migration and anti-invasion properties, we performed wound healing assay, invasion assay and gelatin zymography.
RESULTS
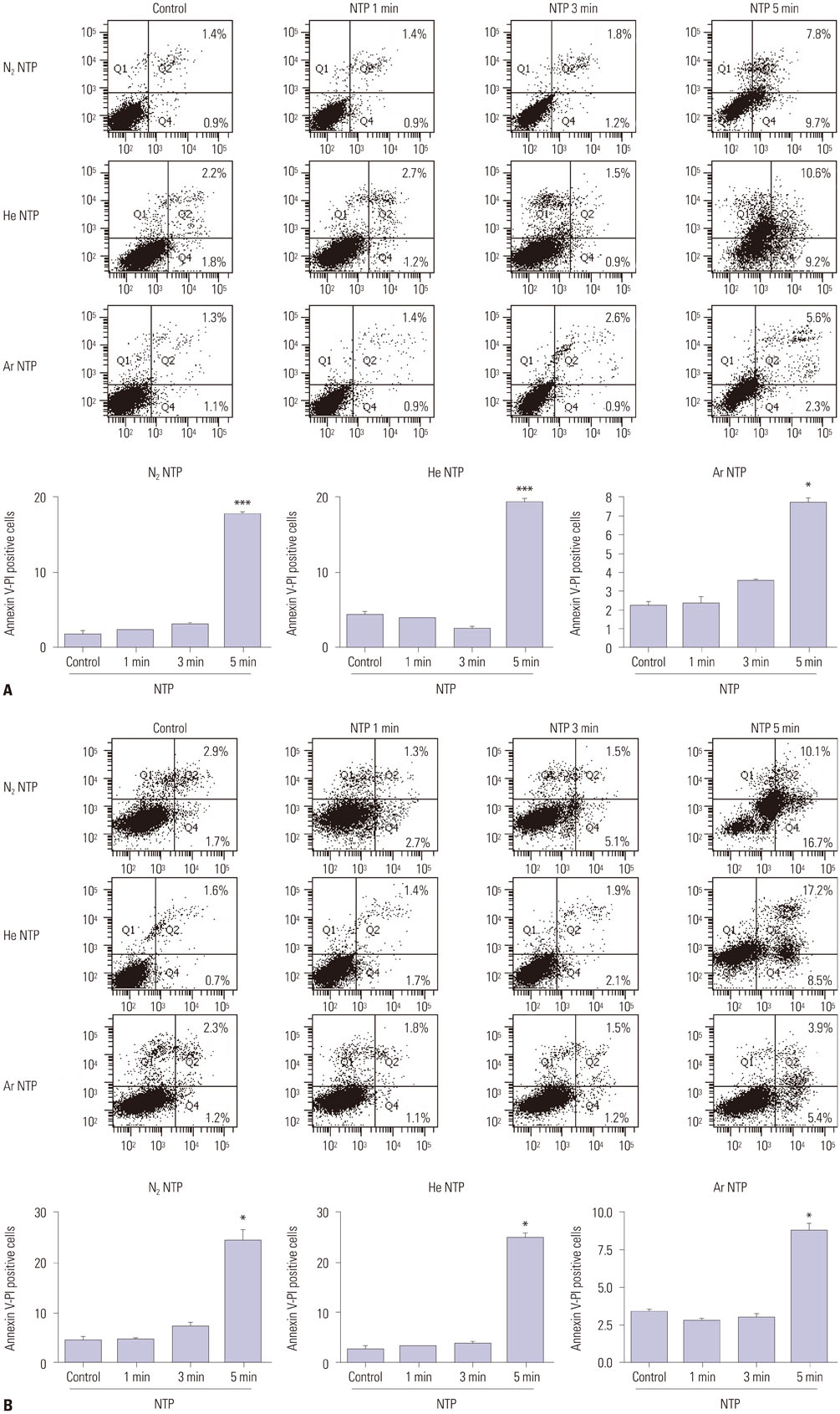
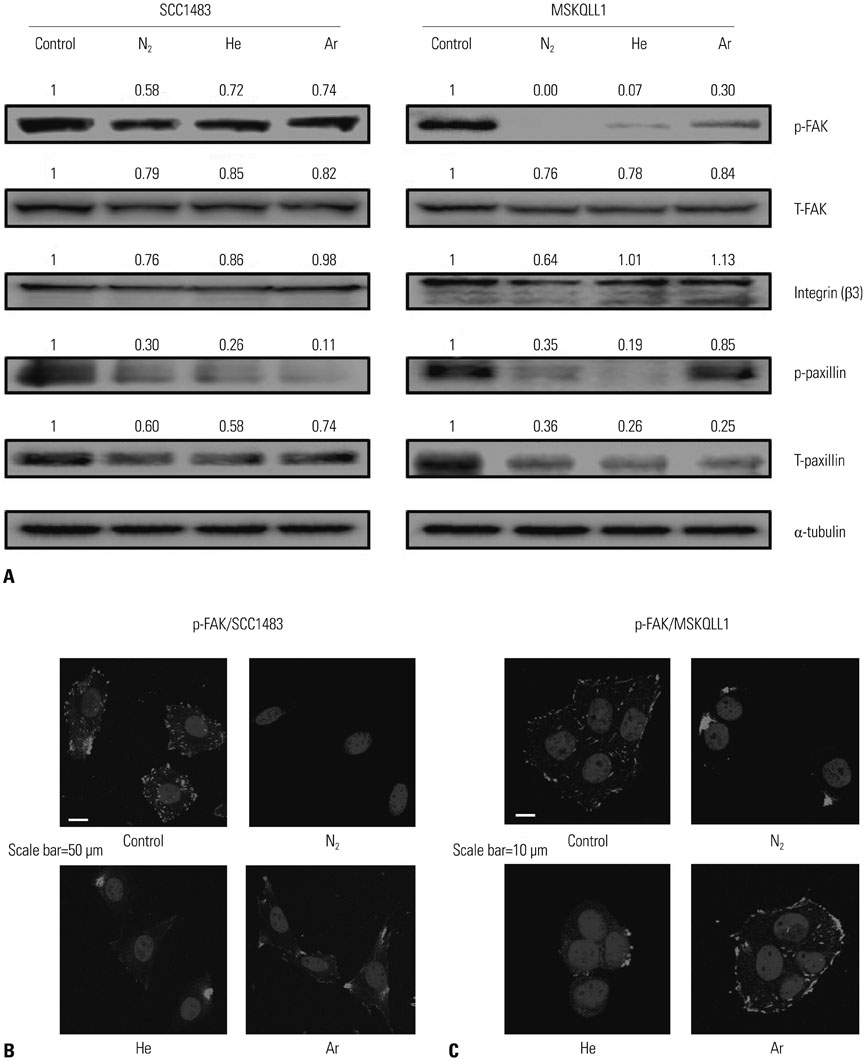
The results showed that NTP inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion of oral squamous cancer cell. In addition, focal adhesion kinase expression and matrix metalloproteinase-2/9 activity were also inhibited.
CONCLUSION
The suppression of cancer cell invasion by NTP varied depending on the type of gas. Comparison of the three gases revealed that Nâ‚‚ NTP inhibited cell migration and invasion most potently via decreased expression of focal adhesion kinase and matrix metalloproteinase activity.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Apoptosis/drug effects
Carcinoma, Squamous Cell/*metabolism
Cell Line, Tumor
Cell Movement/*drug effects
Focal Adhesion Protein-Tyrosine Kinases
Humans
Matrix Metalloproteinase 2/genetics/*metabolism
Matrix Metalloproteinase 9/genetics/*metabolism
Mouth Neoplasms/metabolism/*therapy
Neoplasm Invasiveness
Plasma Gases/*pharmacology
Wound Healing
Plasma Gases
Focal Adhesion Protein-Tyrosine Kinases
Matrix Metalloproteinase 2
Matrix Metalloproteinase 9
Figure
Reference
-
1. Argiris A, Karamouzis MV, Raben D, Ferris RL. Head and neck cancer. Lancet. 2008; 371:1695–1709.
Article2. Chang JW, Kang SU, Shin YS, Seo SJ, Kim YS, Yang SS, et al. Combination of NTP with cetuximab inhibited invasion/migration of cetuximab-resistant OSCC cells: Involvement of NF-κB signaling. Sci Rep. 2015; 5:18208.
Article3. Chan KT, Cortesio CL, Huttenlocher A. FAK alters invadopodia and focal adhesion composition and dynamics to regulate breast cancer invasion. J Cell Biol. 2009; 185:357–370.
Article4. Chang JW, Kang SU, Shin YS, Kim KI, Seo SJ, Yang SS, et al. Non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma inhibits thyroid papillary cancer cell invasion via cytoskeletal modulation, altered MMP-2/-9/uPA activity. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e92198.
Article5. Heerboth S, Housman G, Leary M, Longacre M, Byler S, Lapinska K, et al. EMT and tumor metastasis. Clin Transl Med. 2015; 4:6.
Article6. Moreau M, Orange N, Feuilloley MG. Non-thermal plasma technologies: new tools for bio-decontamination. Biotechnol Adv. 2008; 26:610–617.
Article7. Kim CH, Kwon S, Bahn JH, Lee K, Jun SI, Rack PD, et al. Effects of atmospheric nonthermal plasma on invasion of colorectal cancer cells. Appl Phys Lett. 2010; 96:243701.
Article8. Kim CH, Bahn JH, Lee SH, Kim GY, Jun SI, Lee K, et al. Induction of cell growth arrest by atmospheric non-thermal plasma in colorectal cancer cells. J Biotechnol. 2010; 150:530–538.
Article9. Panngom K, Baik KY, Nam MK, Han JH, Rhim H, Choi EH. Preferential killing of human lung cancer cell lines with mitochondrial dysfunction by nonthermal dielectric barrier discharge plasma. Cell Death Dis. 2013; 4:e642.
Article10. Sensenig R, Kalghatgi S, Cerchar E, Fridman G, Shereshevsky A, Torabi B, et al. Non-thermal plasma induces apoptosis in melanoma cells via production of intracellular reactive oxygen species. Ann Biomed Eng. 2011; 39:674–687.
Article11. Chang JW, Kang SU, Shin YS, Kim KI, Seo SJ, Yang SS, et al. Non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma induces apoptosis in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: involvement of DNA-damage-triggering sub-G(1) arrest via the ATM/p53 pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014; 545:133–140.
Article12. Kang SU, Cho JH, Chang JW, Shin YS, Kim KI, Park JK, et al. Nonthermal plasma induces head and neck cancer cell death: the potential involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Cell Death Dis. 2014; 5:e1056.
Article13. Wang M, Holmes B, Cheng X, Zhu W, Keidar M, Zhang LG. Cold atmospheric plasma for selectively ablating metastatic breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e73741.
Article14. Volotskova O, Shashurin A, Stepp MA, Pal-Ghosh S, Keidar M. Plasma-controlled cell migration: localization of cold plasma-cell interaction region. Plasma Med. 2011; 1:85–92.
Article15. Seo YS, Mohamed A-AH, Woo KC, Lee HW, Lee JK, Kim KT. Comparative studies of atmospheric pressure plasma characteristics between He and Ar working gases for sterilization. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci. 2010; 38:2954–2962.
Article16. Sagawa T, Takayama T, Oku T, Hayashi T, Ota H, Okamoto T, et al. Argon plasma coagulation for successful treatment of early gastric cancer with intramucosal invasion. Gut. 2003; 52:334–339.
Article17. Esposito AR, Kamikawa CM, Lucchesi C, Ferreira BMP, Duek EAdR. Benefits of oxygen and nitrogen plasma treatment in Vero cell affinity to poly(lactide-co-glycolide acid). Mater Res. 2013; 16:695–702.
Article18. Watts AE, Fubini SL, Vernier-Singer M, Golkowski C, Shin S, Todhunter RJ. In vitro analysis of nonthermal plasma as a disinfecting agent. Am J Vet Res. 2006; 67:2030–2035.
Article19. Ermolaeva SA, Sysolyatina EV, Kolkova NI, Bortsov P, Tuhvatulin AI, Vasiliev MM, et al. Non-thermal argon plasma is bactericidal for the intracellular bacterial pathogen Chlamydia trachomatis. J Med Microbiol. 2012; 61(Pt 6):793–799.
Article20. Kramer A, Lindequist U, Weltmann KD, Wilke C, von Woedtke T. Plasma Medicine - its perspective for wound therapy. GMS Krankenhhyg Interdiszip. 2008; 3:Doc16.21. Ahn HJ, Kim KI, Hoan NN, Kim CH, Moon E, Choi KS, et al. Targeting cancer cells with reactive oxygen and nitrogen species generated by atmospheric-pressure air plasma. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e86173.
Article22. Ahn HJ, Kim KI, Kim G, Moon E, Yang SS, Lee JS. Atmospheric-pressure plasma jet induces apoptosis involving mitochondria via generation of free radicals. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e28154.
Article23. Hieken TJ, Ronan SG, Farolan M, Shilkaitis AL, Das Gupta TK. Molecular prognostic markers in intermediate-thickness cutaneous malignant melanoma. Cancer. 1999; 85:375–382.
Article24. Tuhvatulin AI, Sysolyatina EV, Scheblyakov DV, Logunov DY, Vasiliev MM, Yurova MA, et al. Non-thermal plasma causes p53-dependent apoptosis in human colon carcinoma cells. Acta Naturae. 2012; 4:82–87.
Article25. Kohn EC, Liotta LA. Molecular insights into cancer invasion: strategies for prevention and intervention. Cancer Res. 1995; 55:1856–1862.26. Scorilas A, Karameris A, Arnogiannaki N, Ardavanis A, Bassilopoulos P, Trangas T, et al. Overexpression of matrix-metalloproteinase-9 in human breast cancer: a potential favourable indicator in node-negative patients. Br J Cancer. 2001; 84:1488–1496.
Article27. Yang YN, Wang F, Zhou W, Wu ZQ, Xing YQ. TNF-α stimulates MMP-2 and MMP-9 activities in human corneal epithelial cells via the activation of FAK/ERK signaling. Ophthalmic Res. 2012; 48:165–170.
Article28. Rosado P, Lequerica-Fernández P, Peña I, Alonso-Durán L, de Vicente JC. In oral squamous cell carcinoma, high FAK expression is correlated with low P53 expression. Virchows Arch. 2012; 461:163–168.
Article29. Lu Z, Lu N, Li C, Li F, Zhao K, Lin B, et al. Oroxylin A inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-2/9 expression and activation by up-regulating tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 and suppressing the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Toxicol Lett. 2012; 209:211–220.
Article30. Kwiatkowska A, Kijewska M, Lipko M, Hibner U, Kaminska B. Downregulation of Akt and FAK phosphorylation reduces invasion of glioblastoma cells by impairment of MT1-MMP shuttling to lamellipodia and downregulates MMPs expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011; 1813:655–667.
Article31. Webb DJ, Donais K, Whitmore LA, Thomas SM, Turner CE, Parsons JT, et al. FAK-Src signalling through paxillin, ERK and MLCK regulates adhesion disassembly. Nat Cell Biol. 2004; 6:154–161.
Article32. Shibata K, Kikkawa F, Nawa A, Thant AA, Naruse K, Mizutani S, et al. Both focal adhesion kinase and c-Ras are required for the enhanced matrix metalloproteinase 9 secretion by fibronectin in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1998; 58:900–903.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Non-Thermal Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma Possible Application in Wound Healing
- New Conversing Technology; Plasma Medicine
- Evaluation of the safety of non-thermal atmospheric-pressure plasma in hairless mouse tissues
- Anti-inflammatory effect of non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma for periodontitis treatment: in vitro pilot study
- Sterilization effect of atmospheric pressure non-thermal air plasma on dental instruments