Yonsei Med J.
2018 Dec;59(10):1205-1213. 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.10.1205.
miR-34a Inhibitor May Effectively Protect against Sevoflurane-Induced Hippocampal Apoptosis through the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway by Targeting Wnt1
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan, China.
- 2Department of Anesthesiology, Yantai Yuhuangding Hospital, Yantai, China. Lfdoctor86@sina.com
- 3Department of Anesthesiology, Shandong Provincial Hospital, Jinan, China.
- KMID: 2426335
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2018.59.10.1205
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Research has shown that sevoflurane-induced toxicity causes neurodegeneration in the developing brain. miR-34a has been found to negatively regulate ketamine-induced hippocampal apoptosis and memory impairment. However, the role of miR-34a in sevoflurane-induced hippocampal neurodegeneration remains largely unclear.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
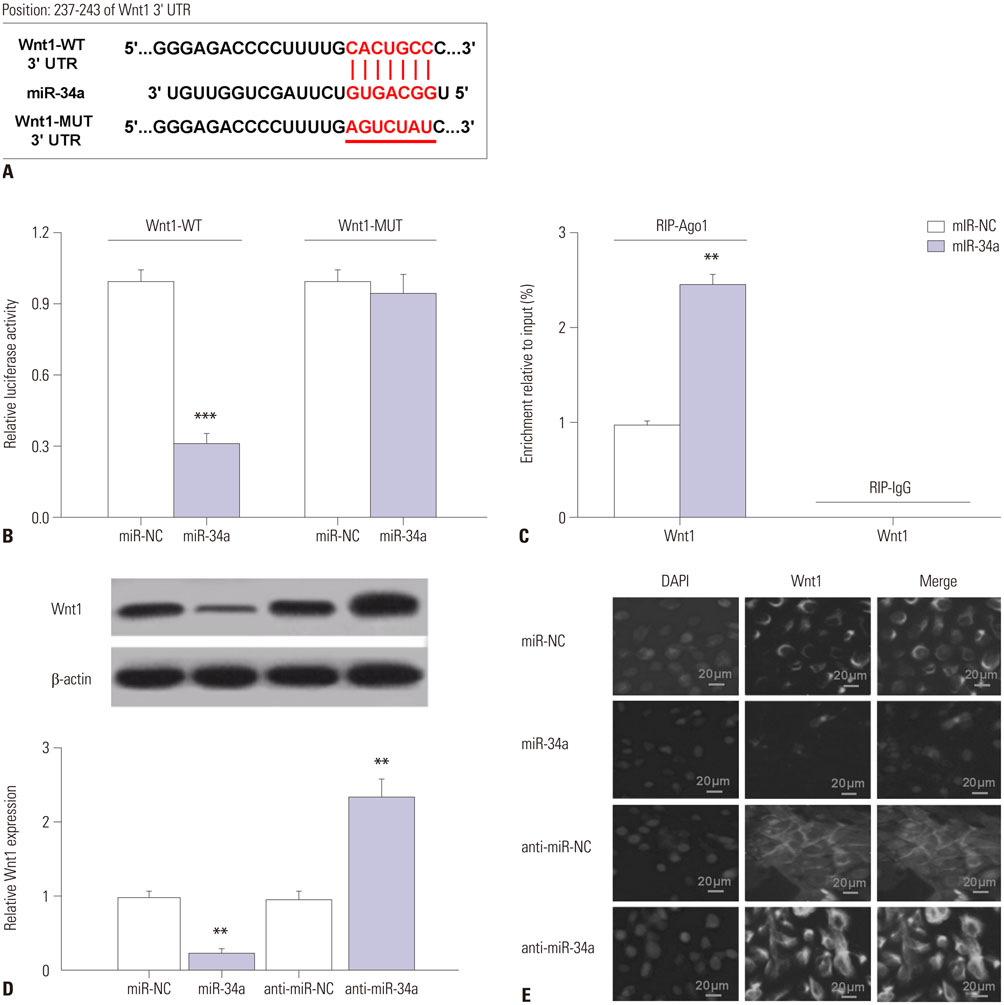
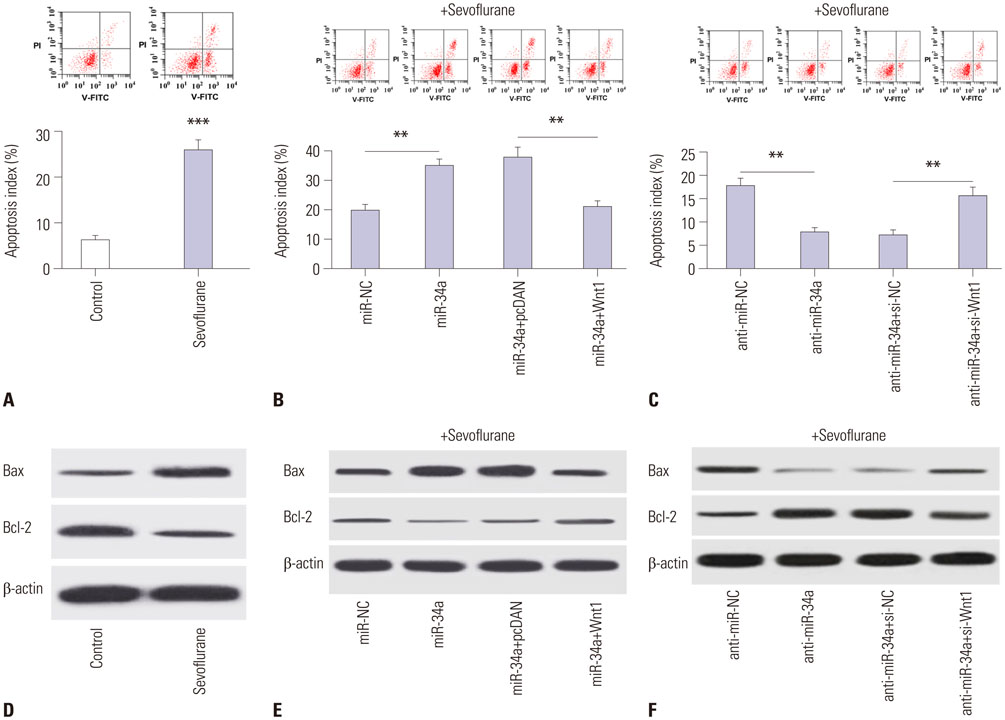
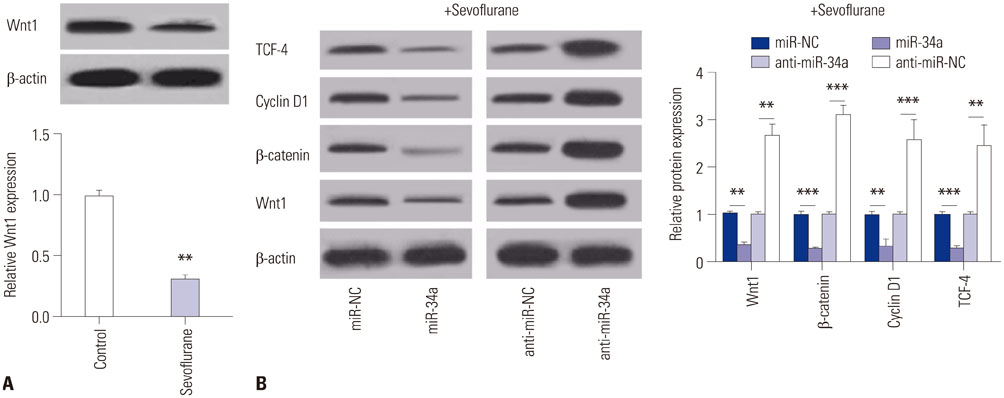
C57/BL6 mice (7-day-old) inhaled 2.3% sevoflurane for 2 h/day over 3 consecutive days. miR-34a expression was reduced through intracerebroventricular injection with miR-34a interference lentivirus vector (LV-anti-miR-34a) into mouse hippocampus after anesthesia on the first day of exposure. Hippocampal apoptosis was detected by TUNEL assay and flow cytometry analysis. Spatial memory ability was evaluated by the Morris water maze test. The interaction between miR-34a and Wnt1 was confirmed by luciferase reporter assay, RNA immunoprecipitation, Western blot, and immunofluorescence staining. The effects of miR-34a on protein levels of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), bcl-2-like protein 4 (Bax), and Wnt/β-catenin pathway-related proteins were evaluated using Western blot analysis.
RESULTS
Sevoflurane upregulated hippocampal miR-34a, and miR-34a inhibitor attenuated sevoflurane-induced hippocampal apoptosis and memory impairment. miR-34a negatively regulated Wnt1 expression by targeting miR-34a in hippocampal neurons. Moreover, forced expression of Wnt1 markedly undermined miR-34a-mediated enhancement of sevoflurane-induced apoptosis of hippocampal neurons, while Wnt1 silencing greatly restored anti-miR-34a-mediated repression of sevoflurane-induced apoptosis of hippocampal neurons. Increased expression of miR-34a inhibited the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in hippocampal neurons exposed to sevoflurane, while anti-miR-34a exerted the opposite effects.
CONCLUSION
miR-34a inhibitor may effectively protect against sevoflurane-induced hippocampal apoptosis via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by targeting Wnt1.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bittner EA, Yue Y, Xie Z. Brief review: anesthetic neurotoxicity in the elderly, cognitive dysfunction and Alzheimer's disease. Can J Anaesth. 2011; 58:216–223.
Article2. Flick RP, Nemergut ME, Christensen K, Hansen TG. Anesthetic-related neurotoxicity in the young and outcome measures: the devil is in the details. Anesthesiology. 2014; 120:1303–1305.3. Hu N, Guo D, Wang H, Xie K, Wang C, Li Y, et al. Involvement of the blood-brain barrier opening in cognitive decline in aged rats following orthopedic surgery and high concentration of sevoflurane inhalation. Brain Res. 2014; 1551:13–24.
Article4. Zhang X, Xue Z, Sun A. Subclinical concentration of sevoflurane potentiates neuronal apoptosis in the developing C57BL/6 mouse brain. Neurosci Lett. 2008; 447:109–114.
Article5. Pan Z, Lu XF, Shao C, Zhang C, Yang J, Ma T, et al. The effects of sevoflurane anesthesia on rat hippocampus: a genomic expression analysis. Brain Res. 2011; 1381:124–133.
Article6. Goto G, Hori Y, Ishikawa M, Tanaka S, Sakamoto A. Changes in the gene expression levels of microRNAs in the rat hippocampus by sevoflurane and propofol anesthesia. Mol Med Rep. 2014; 9:1715–1722.
Article7. Chen K, Rajewsky N. The evolution of gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2007; 8:93–103.
Article8. Juhila J, Sipilä T, Icay K, Nicorici D, Ellonen P, Kallio A, et al. MicroRNA expression profiling reveals miRNA families regulating specific biological pathways in mouse frontal cortex and hippocampus. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e21495.
Article9. Miranda RC. MicroRNAs and fetal brain development: implications for ethanol teratology during the second trimester period of neurogenesis. Front Genet. 2012; 3:77.
Article10. Goedeke L, Fernández-Hernando C. MicroRNAs: a connection between cholesterol metabolism and neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis. 2014; 72 Pt A:48–53.
Article11. Rokavec M, Li H, Jiang L, Hermeking H. The p53/miR-34 axis in development and disease. J Mol Cell Biol. 2014; 6:214–230.
Article12. Jiang XL, Du BX, Chen J, Liu L, Shao WB, Song J. MicroRNA-34a negatively regulates anesthesia-induced hippocampal apoptosis and memory impairment through FGFR1. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014; 7:6760–6767.13. Tan LP, Seinen E, Duns G, de Jong D, Sibon OC, Poppema S, et al. A high throughput experimental approach to identify miRNA targets in human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009; 37:e137.
Article14. Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2ΔΔCT Method. Methods. 2001; 25:402–408.
Article15. Si W, Li Y, Shao H, Hu R, Wang W, Zhang K, et al. MiR-34a inhibits breast cancer proliferation and progression by targeting Wnt1 in Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Am J Med Sci. 2016; 352:191–199.
Article16. Huang A, Yang Y, Chen S, Xia F, Sun D, Fang D, et al. MiR-34a promotes DCs development and inhibits their function on T cell activation by targeting WNT1. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:17191–17201.
Article17. Loepke AW, Hansen TG. Is this your (paediatric patient's) brain on (anaesthetic) drugs?: The search for a potential neurological phenotype of anaesthesia-related neurotoxicity in humans. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2015; 32:298–300.18. Young C, Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Qin YQ, Tenkova T, Wang H, Labruyere J, et al. Potential of ketamine and midazolam, individually or in combination, to induce apoptotic neurodegeneration in the infant mouse brain. Br J Pharmacol. 2005; 146:189–197.
Article19. Guo S, Liu L, Wang C, Jiang Q, Dong Y, Tian Y. Repeated exposure to sevoflurane impairs the learning and memory of older male rats. Life Sci. 2018; 192:75–83.
Article20. Zhou X, Xian D, Xia J, Tang Y, Li W, Chen X, et al. MicroRNA-34c is regulated by p53 and is involved in sevoflurane-induced apoptosis in the developing rat brain potentially via the mitochondrial pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2017; 15:2204–2212.
Article21. Pai SG, Carneiro BA, Mota JM, Costa R, Leite CA, Barroso-Sousa R, et al. Wnt/beta-catenin pathway: modulating anticancer immune response. J Hematol Oncol. 2017; 10:101.
Article22. Libro R, Bramanti P, Mazzon E. The role of the Wnt canonical signaling in neurodegenerative diseases. Life Sci. 2016; 158:78–88.
Article23. Huang K, Zhang JX, Han L, You YP, Jiang T, Pu PY, et al. MicroRNA roles in beta-catenin pathway. Mol Cancer. 2010; 9:252.
Article24. Wang Y, Li Y, Xing Q, Han XG, Dong X, Lu Y, et al. Sevoflurane anesthesia in pregnant rats negatively affects nerve function in offspring potentially via inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2017; 15:2753–2759.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- MiR-148a-3p Regulates the Invasion and Odontoblastic Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells via the Wnt1/β-Catenin Pathway
- The Long Noncoding RNA NEAT1 Targets miR-34a-5p and Drives Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Progression via Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling
- Effects of microRNA-135a on the epithelial–mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells by targeting GSK3β through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Effects of Wnt-1 on the Growth and Apoptosis of FRTL-5 Cells
- Natural Products Targeting Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathway