Yonsei Med J.
2019 Apr;60(4):336-345. 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.4.336.
The Long Noncoding RNA NEAT1 Targets miR-34a-5p and Drives Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Progression via Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling
- Affiliations
-
- 1Ear-Nose-Throat Department, Xingtai People's Hospital, Xingtai, China.
- 2CT/MRI Department, Xingtai People's Hospital, Xingtai, China. yuanlisoly@163.com
- KMID: 2450188
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2019.60.4.336
Abstract
- PURPOSE
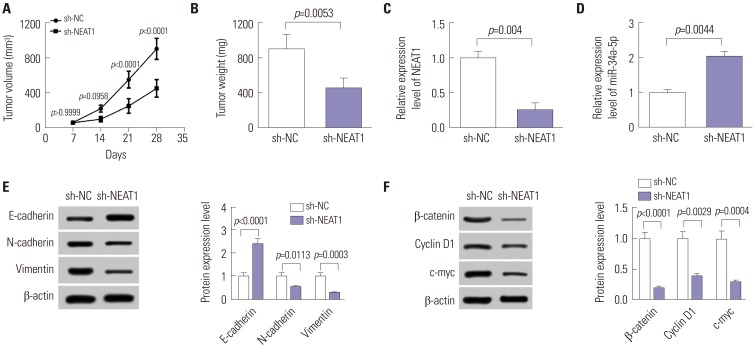
Long noncoding RNA nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1) has been deemed an oncogene in many human cancers. However, the underlying mechanism of NEAT1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) progression remains largely unclear.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Quantitative real-time PCR assay was performed to assess the expression of NEAT1 and miR-34a-5p in NPC tissues and cells. Western blot analysis was used to observe cell epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) and the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in 5-8F cells. MiRNA directly interacting with NEAT1 were verified by dual-luciferase reporter assay and RNA immunoprecipitation. Cell proliferation ability was determined by CCK-8 assay, and cell migration and invasion capacities were assessed by transwell assays. An animal model was used to investigate the regulatory effect of NEAT1 on tumor growth in vivo.
RESULTS
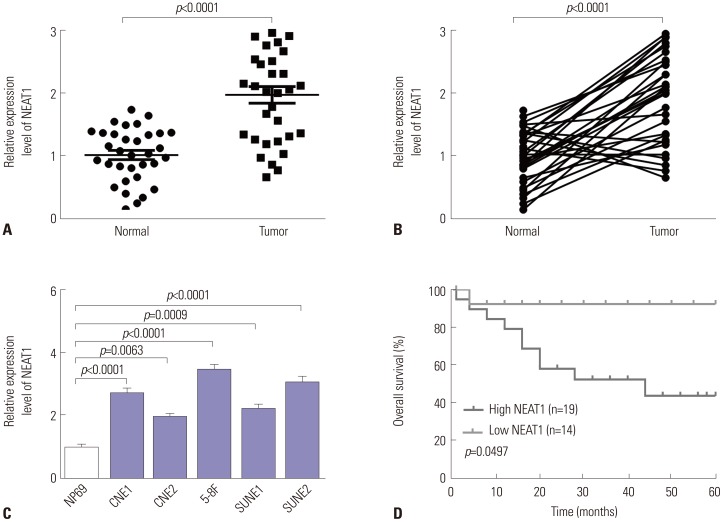
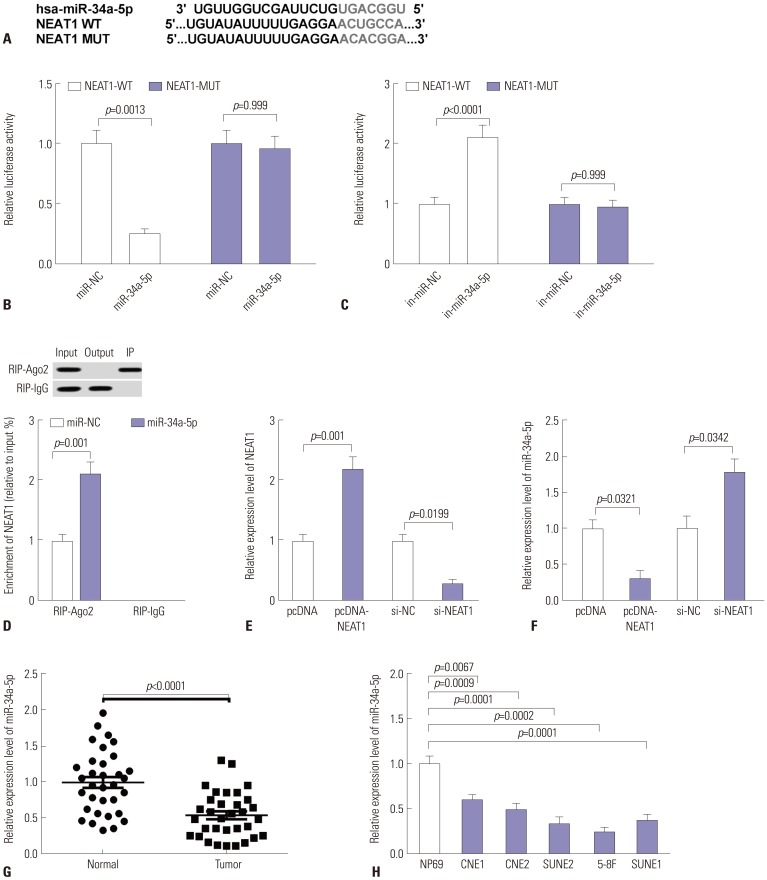
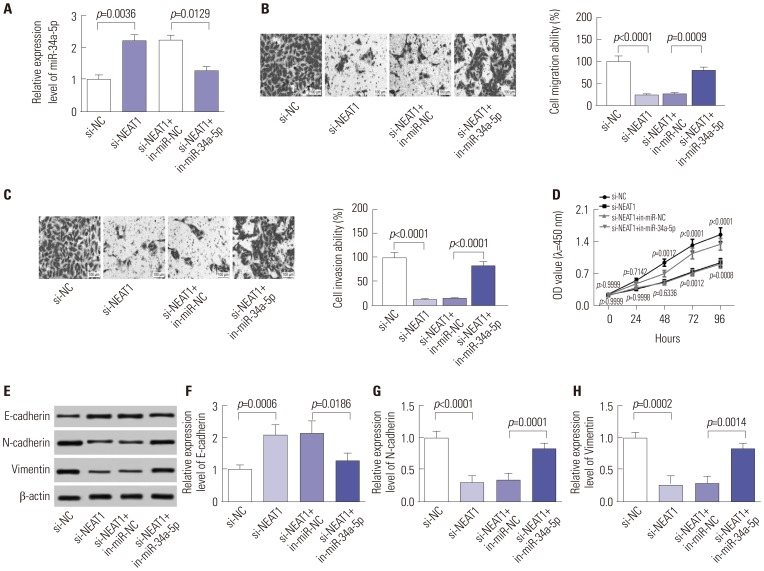
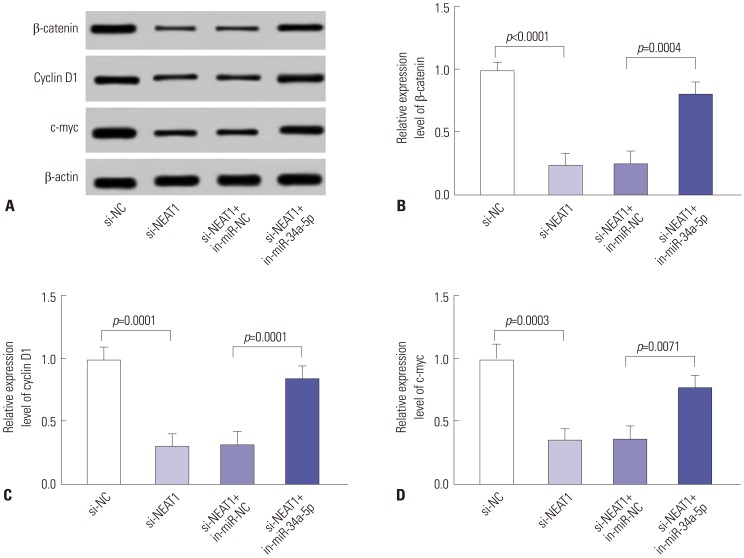
Our data revealed that NEAT1 is upregulated, while miR-34a-5p is downregulated in NPC tissues and cell lines. NEAT1 knockdown repressed tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Additionally, we discovered that NEAT1 directly binds to miR-34a-5p and suppresses miR-34a-5p expression. Moreover, NEAT1 knockdown exerted suppression effects on cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT by miR-34a-5p. NEAT1 knockdown blocked Wnt/β-catenin signaling via miR-34a-5p.
CONCLUSION
Our study demonstrated that NEAT1 targets miR-34a-5p at least partly to drive NPC progression by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling, suggesting a potential therapeutic target for NPC.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Circular RNAs Regulate Cancer Onset and Progression via Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
Yun-Feng Li, Jian Zhang, Lei Yu
Yonsei Med J. 2019;60(12):1117-1128. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.12.1117.
Reference
-
1. Lee VH, Lam KO, Chang AT, Lam TC, Chiang CL, So TH, et al. Management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: is adjuvant therapy needed? J Oncol Pract. 2018; 14:594–602. PMID: 30312564.
Article2. Yip TT, Ngan RK, Fong AH, Law SC. Application of circulating plasma/serum EBV DNA in the clinical management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2014; 50:527–538. PMID: 24440146.
Article3. Wu F, Wang R, Lu H, Wei B, Feng G, Li G, et al. Concurrent chemoradiotherapy in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: treatment outcomes of a prospective, multicentric clinical study. Radiother Oncol. 2014; 112:106–111. PMID: 24933452.
Article4. Lai SZ, Li WF, Chen L, Luo W, Chen YY, Liu LZ, et al. How does intensity-modulated radiotherapy versus conventional two-dimensional radiotherapy influence the treatment results in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011; 80:661–668. PMID: 20643517.5. Spizzo R, Almeida MI, Colombatti A, Calin GA. Long non-coding RNAs and cancer: a new frontier of translational research? Oncogene. 2012; 31:4577–4587. PMID: 22266873.
Article6. Schmitt AM, Chang HY. Long noncoding RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell. 2016; 29:452–463. PMID: 27070700.
Article7. Bhan A, Mandal SS. LncRNA HOTAIR: a master regulator of chromatin dynamics and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015; 1856:151–164. PMID: 26208723.
Article8. Schmitt AM, Chang HY. Gene regulation: long RNAs wire up cancer growth. Nature. 2013; 500:536–537. PMID: 23945584.9. Choudhry H, Albukhari A, Morotti M, Haider S, Moralli D, Smythies J, et al. Tumor hypoxia induces nuclear paraspeckle formation through HIF-2α dependent transcriptional activation of NEAT1 leading to cancer cell survival. Oncogene. 2015; 34:4482–4490. PMID: 25417700.
Article10. Wang P, Wu T, Zhou H, Jin Q, He G, Yu H, et al. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 promotes laryngeal squamous cell cancer through regulating miR-107/CDK6 pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016; 35:22. PMID: 26822763.
Article11. Fu JW, Kong Y, Sun X. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 is an unfavorable prognostic factor and regulates migration and invasion in gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016; 142:1571–1579. PMID: 27095450.
Article12. Chai Y, Liu J, Zhang Z, Liu L. HuR-regulated lncRNA NEAT1 stability in tumorigenesis and progression of ovarian cancer. Cancer Med. 2016; 5:1588–1598. PMID: 27075229.13. Cheng N, Guo Y. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression through regulation of miR-124/NF-κB pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 2017; 10:5843–5853. PMID: 29270022.14. Lu Y, Li T, Wei G, Liu L, Chen Q, Xu L, et al. The long non-coding RNA NEAT1 regulates epithelial to mesenchymal transition and radioresistance in through miR-204/ZEB1 axis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2016; 37:11733–11741. PMID: 27020592.
Article15. Chen Y, Gao DY, Huang L. In vivo delivery of miRNAs for cancer therapy: challenges and strategies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015; 81:128–141. PMID: 24859533.
Article16. Cheng JZ, Chen JJ, Wang ZG, Yu D. MicroRNA-185 inhibits cell proliferation while promoting apoptosis and autophagy through negative regulation of TGF-β1/mTOR axis and HOXC6 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2018; 23:107–123. PMID: 29991129.
Article17. Zhu X, Li W, Zhang R, Liu Y. MicroRNA-342 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by directly targeting ZEB1. Oncol Lett. 2018; 16:1298–1304. PMID: 30061949.
Article18. Zhang P, Hong H, Sun X, Jiang H, Ma S, Zhao S, et al. MicroRNA-10b regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition by modulating KLF4/Notch1/E-cadherin in cisplatin-resistant nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Am J Cancer Res. 2016; 6:141–156. PMID: 27186392.19. Fodde R, Brabletz T. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in cancer stemness and malignant behavior. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007; 19:150–158. PMID: 17306971.20. Fu M, Zou C, Pan L, Liang W, Qian H, Xu W, et al. Long noncoding RNAs in digestive system cancers: functional roles, molecular mechanisms, and clinical implications (review). Oncol Rep. 2016; 36:1207–1218. PMID: 27431376.
Article21. Jin C, Yan B, Lu Q, Lin Y, Ma L. The role of MALAT1/miR-1/slug axis on radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2016; 37:4025–4033. PMID: 26482776.
Article22. Ma DD, Yuan LL, Lin LQ. LncRNA HOTAIR contributes to the tumorigenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via up-regulating FASN. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017; 21:5143–5152. PMID: 29228426.23. Yang L, Tang Y, He Y, Wang Y, Lian Y, Xiong F, et al. High expression of LINC01420 indicates an unfavorable prognosis and modulates cell migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Cancer. 2017; 8:97–103. PMID: 28123602.
Article24. Sun Q, Liu H, Li L, Zhang S, Liu K, Liu Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA-LET, which is repressed by EZH2, inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell. Med Oncol. 2015; 32:226. PMID: 26243049.
Article25. Chak WP, Lung RW, Tong JH, Chan SY, Lun SW, Tsao SW, et al. Downregulation of long non-coding RNA MEG3 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 2017; 56:1041–1054. PMID: 27597634.
Article26. Liz J, Esteller M. lncRNAs and microRNAs with a role in cancer development. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016; 1859:169–176. PMID: 26149773.
Article27. Gao J, Li N, Dong Y, Li S, Xu L, Li X, et al. miR-34a-5p suppresses colorectal cancer metastasis and predicts recurrence in patients with stage II/III colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2015; 34:4142–4152. PMID: 25362853.
Article28. Jia D, Niu Y, Li D, Liu Z. lncRNA C2dat1 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting miR-34a-5p in osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Res. 2018; 26:753–764. PMID: 28810936.
Article29. Huang G, Du MY, Zhu H, Zhang N, Lu ZW, Qian LX, et al. MiRNA-34a reversed TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via suppression of SMAD4 in NPC cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018; 106:217–224. PMID: 29960168.
Article30. Song P, Ye LF, Zhang C, Peng T, Zhou XH. Long non-coding RNA XIST exerts oncogenic functions in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting miR-34a-5p. Gene. 2016; 592:8–14. PMID: 27461945.
Article31. Maroni P, Puglisi R, Mattia G, Carè A, Matteucci E, Bendinelli P, et al. In bone metastasis miR-34a-5p absence inversely correlates with Met expression, while Met oncogene is unaffected by miR-34a-5p in non-metastatic and metastatic breast carcinomas. Carcinogenesis. 2017; 38:492–503. PMID: 28334277.
Article32. Wickström M, Dyberg C, Milosevic J, Einvik C, Calero R, Sveinbjörnsson B, et al. Wnt/β-catenin pathway regulates MGMT gene expression in cancer and inhibition of Wnt signalling prevents chemoresistance. Nat Commun. 2015; 6:8904. PMID: 26603103.
Article33. Mao J, Fan S, Ma W, Fan P, Wang B, Zhang J, et al. Roles of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the gastric cancer stem cells proliferation and salinomycin treatment. Cell Death Dis. 2014; 5:e1039. PMID: 24481453.
Article34. Jang GB, Kim JY, Cho SD, Park KS, Jung JY, Lee HY, et al. Blockade of Wnt/β-catenin signaling suppresses breast cancer metastasis by inhibiting CSC-like phenotype. Sci Rep. 2015; 5:12465. PMID: 26202299.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Long Non-Coding RNA CASC2 Suppresses Cell Viability, Migration, and Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Directly Downregulating miR-183
- Circ_0075960 targets the miR-202-5p/CTNND1 axis to promote the growth and migration of endometrial carcinoma cells via regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling activity
- Retraction: Circ_0075960 targets the miR-202-5p/CTNND1 axis to promote the growth and migration of endometrial carcinoma cells via regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling activity
- Circular RNAs Regulate Cancer Onset and Progression via Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
- miR-34a Inhibitor May Effectively Protect against Sevoflurane-Induced Hippocampal Apoptosis through the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway by Targeting Wnt1