Tuberc Respir Dis.
2018 Apr;81(2):148-155. 10.4046/trd.2017.0090.
Pemetrexed Continuation Maintenance versus Conventional Platinum-Based Doublet Chemotherapy in EGFR-Negative Lung Adenocarcinoma: Retrospective Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Dongnam Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Busan, Korea.
- 2Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. humanmd04@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2420603
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2017.0090
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Although targeted therapy and immuno-oncology have shifted the treatment paradigm for lung cancer, platinum-based combination is still the standard of care for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Pemetrexed continuation maintenance therapy has been approved and increasingly used for patients with nonsquamous NSCLC. However, the efficacy of this strategy has not been proven in patients without driving mutations. The objective of this study was to compare the clinical benefit of pemetrexed continuation maintenance to conventional platinum-based doublet in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-negative lung adenocarcinoma.
METHODS
A total of 114 patients with EGFR-negative lung adenocarcinoma who were treated with platinum doublet were retrospectively enrolled. We compared the survival rates between patients received pemetrexed maintenance after four-cycled pemetrexed/cisplatin and those received at least four-cycled platinum doublet without maintenance chemotherapy as a first-line treatment.
RESULTS
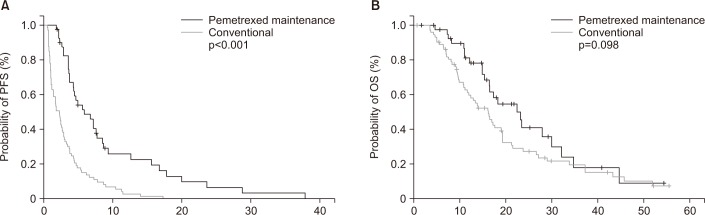
Forty-one patients received pemetrexed maintenance and 73 received conventional platinum doublet. Median progression-free survival (PFS), which was defined as the time from the day of response evaluation after four cycles of chemotherapy to disease progression or death, was significantly higher in the pemetrexed maintenance group compared to conventional group (5.8 months vs. 2.2 months, p<0.001). Median overall survival showed an increasing trend in the pemetrexed maintenance group (22.3 months vs. 16.1 months, p=0.098). Multivariate analyses showed that pemetrexed maintenance chemotherapy was associated with better PFS (hazard ratio, 0.73; 95% confidence interval, 0.15-0.87).
CONCLUSION
Compared to conventional platinum-based chemotherapy, premetrexed continuation maintenance treatment is associated with better clinical outcome for the patients with EGFR wild-type lung adenocarcinoma.
MeSH Terms
-
Adenocarcinoma*
Carcinoma, Non-Small-Cell Lung
Disease Progression
Disease-Free Survival
Drug Therapy*
Humans
Lung Neoplasms
Lung*
Maintenance Chemotherapy
Multivariate Analysis
Pemetrexed*
Platinum
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Retrospective Studies*
Standard of Care
Survival Rate
Pemetrexed
Platinum
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
What is Currently the Best for Adenocarcinoma without Driver Mutation?
Cheol-Kyu Park, In-Jae Oh, Young-Chul Kim
Tuberc Respir Dis. 2018;81(3):258-259. doi: 10.4046/trd.2018.0024.Chemotherapy for Lung Cancer in the Era of Personalized Medicine
Seung Hyeun Lee
Tuberc Respir Dis. 2019;82(3):179-189. doi: 10.4046/trd.2018.0068.
Reference
-
1. Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015; 65:87–108. PMID: 25651787.
Article2. Park JY, Jang SH. Epidemiology of Lung Cancer in Korea: Recent Trends. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2016; 79:58–69. PMID: 27064578.
Article3. Bansal P, Osman D, Gan GN, Simon GR, Boumber Y. Recent advances in targetable therapeutics in metastatic non-squamous NSCLC. Front Oncol. 2016; 6:112. PMID: 27200298.
Article4. Reck M, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG, Hui R, Csoszi T, Fulop A, et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:1823–1833. PMID: 27718847.
Article5. Peters S, Gettinger S, Johnson ML, Janne PA, Garassino MC, Christoph D, et al. Phase II trial of atezolizumab as first-line or subsequent therapy for patients with programmed death-ligand 1-selected advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (BIRCH). J Clin Oncol. 2017; 35:2781–2789. PMID: 28609226.6. Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L, Spigel DR, Steins M, Ready NE, et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:1627–1639. PMID: 26412456.
Article7. Chang YS, Choi CM, Lee JC. Mechanisms of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance and Strategies to Overcome Resistance in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2016; 79:248–256. PMID: 27790276.
Article8. National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines [Internet]. Fort Washington: National Comprehensive Cancer Network;2017. cited 2017 Jul 15. Available from: http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf.9. Masters GA, Temin S, Azzoli CG, Giaccone G, Baker S Jr, Brahmer JR, et al. Systemic therapy for stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2015; 33:3488–3515. PMID: 26324367.10. Joerger M, Omlin A, Cerny T, Fruh M. The role of pemetrexed in advanced non small-cell lung cancer: special focus on pharmacology and mechanism of action. Curr Drug Targets. 2010; 11:37–47. PMID: 19839929.
Article11. Scagliotti GV, Parikh P, von Pawel J, Biesma B, Vansteenkiste J, Manegold C, et al. Phase III study comparing cisplatin plus gemcitabine with cisplatin plus pemetrexed in chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:3543–3551. PMID: 18506025.
Article12. Wu YL, Lu S, Cheng Y, Zhou C, Wang M, Qin S, et al. Efficacy and safety of pemetrexed/cisplatin versus gemcitabine/cisplatin as first-line treatment in Chinese patients with advanced nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2014; 85:401–407. PMID: 25082564.
Article13. Yang CH, Simms L, Park K, Lee JS, Scagliotti G, Orlando M. Efficacy and safety of cisplatin/pemetrexed versus cisplatin/gemcitabine as first-line treatment in East Asian patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: results of an exploratory subgroup analysis of a phase III trial. J Thorac Oncol. 2010; 5:688–695. PMID: 20150825.
Article14. Belani CP, Brodowicz T, Ciuleanu TE, Krzakowski M, Yang SH, Franke F, et al. Quality of life in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer given maintenance treatment with pemetrexed versus placebo (H3E-MC-JMEN): results from a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2012; 13:292–299. PMID: 22336221.
Article15. Paz-Ares LG, de Marinis F, Dediu M, Thomas M, Pujol JL, Bidoli P, et al. PARAMOUNT: Final overall survival results of the phase III study of maintenance pemetrexed versus placebo immediately after induction treatment with pemetrexed plus cisplatin for advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31:2895–2902. PMID: 23835707.
Article16. Belani CP, Wu YL, Chen YM, Kim JH, Yang SH, Zhang L, et al. Efficacy and safety of pemetrexed maintenance therapy versus best supportive care in patients from East Asia with advanced, nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer: an exploratory subgroup analysis of a global, randomized, phase 3 clinical trial. J Thorac Oncol. 2012; 7:567–573. PMID: 22157370.
Article17. Park S, Kim HJ, Choi CM, Lee DH, Kim SW, Lee JS, et al. Predictive factors for a long-term response duration in non-squamous cell lung cancer patients treated with pemetrexed. BMC Cancer. 2016; 16:417. PMID: 27388008.
Article18. Park S, Park TS, Choi CM, Lee DH, Kim SW, Lee JS, et al. Survival benefit of pemetrexed in lung adenocarcinoma patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene rearrangements. Clin Lung Cancer. 2015; 16:e83–e89. PMID: 25682546.
Article19. Goldstraw P. The 7th edition of TNM in lung cancer: what now? J Thorac Oncol. 2009; 4:671–673. PMID: 19461399.
Article20. Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 2009; 45:228–247. PMID: 19097774.
Article21. Hwang KE, Kim HR. Response Evaluation of Chemotherapy for Lung Cancer. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2017; 80:136–142. PMID: 28416953.
Article22. Gerber DE, Rasco DW, Le P, Yan J, Dowell JE, Xie Y. Predictors and impact of second-line chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer in the United States: real-world considerations for maintenance therapy. J Thorac Oncol. 2011; 6:365–371. PMID: 21173713.
Article23. Ciuleanu T, Brodowicz T, Zielinski C, Kim JH, Krzakowski M, Laack E, et al. Maintenance pemetrexed plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care for non-small-cell lung cancer: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2009; 374:1432–1440. PMID: 19767093.
Article24. Cappuzzo F, Ciuleanu T, Stelmakh L, Cicenas S, Szczesna A, Juhasz E, et al. Erlotinib as maintenance treatment in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2010; 11:521–529. PMID: 20493771.
Article25. Mubarak N, Gaafar R, Shehata S, Hashem T, Abigeres D, Azim HA, et al. A randomized, phase 2 study comparing pemetrexed plus best supportive care versus best supportive care as maintenance therapy after first-line treatment with pemetrexed and cisplatin for advanced, non-squamous, non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer. 2012; 12:423. PMID: 23006447.
Article26. Paz-Ares L, de Marinis F, Dediu M, Thomas M, Pujol JL, Bidoli P, et al. Maintenance therapy with pemetrexed plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care after induction therapy with pemetrexed plus cisplatin for advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (PARAMOUNT): a double-blind, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012; 13:247–255. PMID: 22341744.
Article27. Jiang X, Yang B, Lu J, Zhan Z, Li K, Ren X. Pemetrexed-based chemotherapy in advanced lung adenocarcinoma patients with different EGFR genotypes. Tumour Biol. 2015; 36:861–869. PMID: 25301443.
Article28. Hanna N, Shepherd FA, Fossella FV, Pereira JR, De Marinis F, von Pawel J, et al. Randomized phase III trial of pemetrexed versus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:1589–1597. PMID: 15117980.
Article29. Yoh K, Goto Y, Naito Y, Kishi K, Mori K, Hotta K, et al. Impact of maintenance therapy for patients with non-small cell lung cancer in a real-world setting. Anticancer Res. 2017; 37:1507–1513. PMID: 28314326.30. Lee JK, Hahn S, Kim DW, Suh KJ, Keam B, Kim TM, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors vs conventional chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer harboring wild-type epidermal growth factor receptor: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2014; 311:1430–1437. PMID: 24715074.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pemetrexed Singlet Versus Nonpemetrexed-Based Platinum Doublet as Second-Line Chemotherapy after First-Line Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Failure in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with EGFR Mutations
- Lenvatinib and pembrolizumab versus platinum doublet chemotherapy as second-line therapy for advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer
- Interstitial Pneumonitis after Treatment with Pemetrexed for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- Clinical outcomes of erlotinib, gefitinib, or pemetrexed in patients with non-squamous, non-small-cell lung cancer
- Safety and efficacy of pemetrexed for the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma in patients with various stages of chronic kidney disease