Endocrinol Metab.
2015 Sep;30(3):361-370. 10.3803/EnM.2015.30.3.361.
Effect of Mefloquine, a Gap Junction Blocker, on Circadian Period2 Gene Oscillation in the Mouse Suprachiasmatic Nucleus Ex Vivo
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biological Sciences and Brain Research Center for 21st Frontier Program in Neuroscience, Seoul National University College of Natural Sciences, Seoul, Korea. kyungjin@dgist.ac.kr
- 2Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Seoul National University College of Natural Sciences, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Legal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2407088
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.3.361
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
In mammals, the master circadian pacemaker is localized in an area of the ventral hypothalamus known as the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN). Previous studies have shown that pacemaker neurons in the SCN are highly coupled to one another, and this coupling is crucial for intrinsic self-sustainability of the SCN central clock, which is distinguished from peripheral oscillators. One plausible mechanism underlying the intercellular communication may involve direct electrical connections mediated by gap junctions.
METHODS
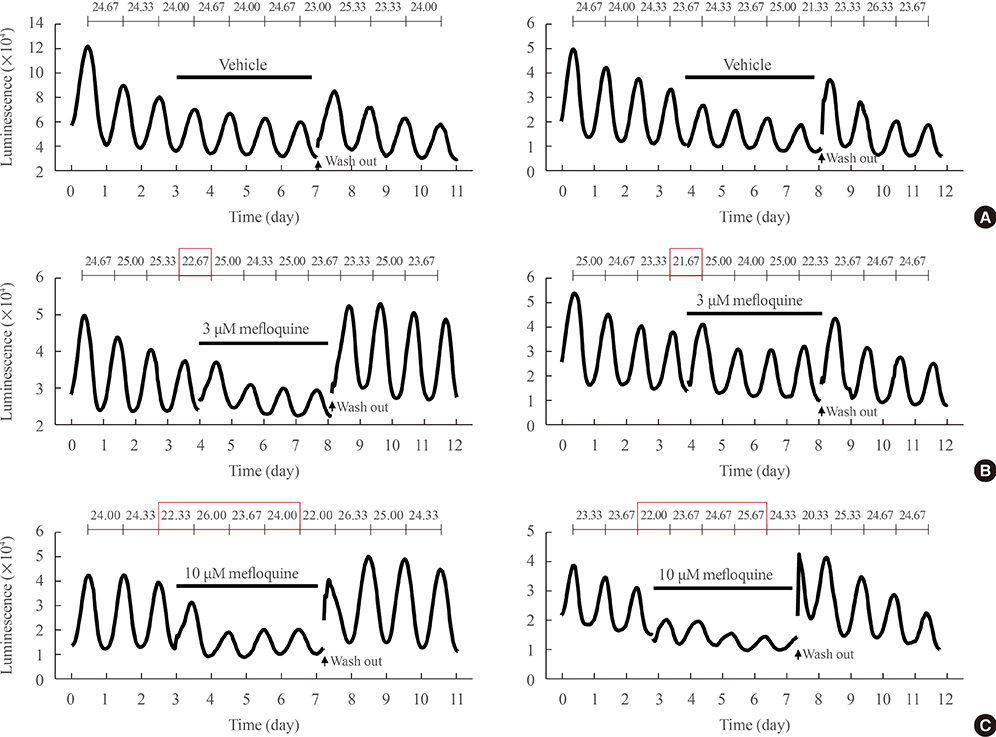
We examined the effect of mefloquine, a neuronal gap junction blocker, on circadian Period 2 (Per2) gene oscillation in SCN slice cultures prepared from Per2::luciferase (PER2::LUC) knock-in mice using a real-time bioluminescence measurement system.
RESULTS
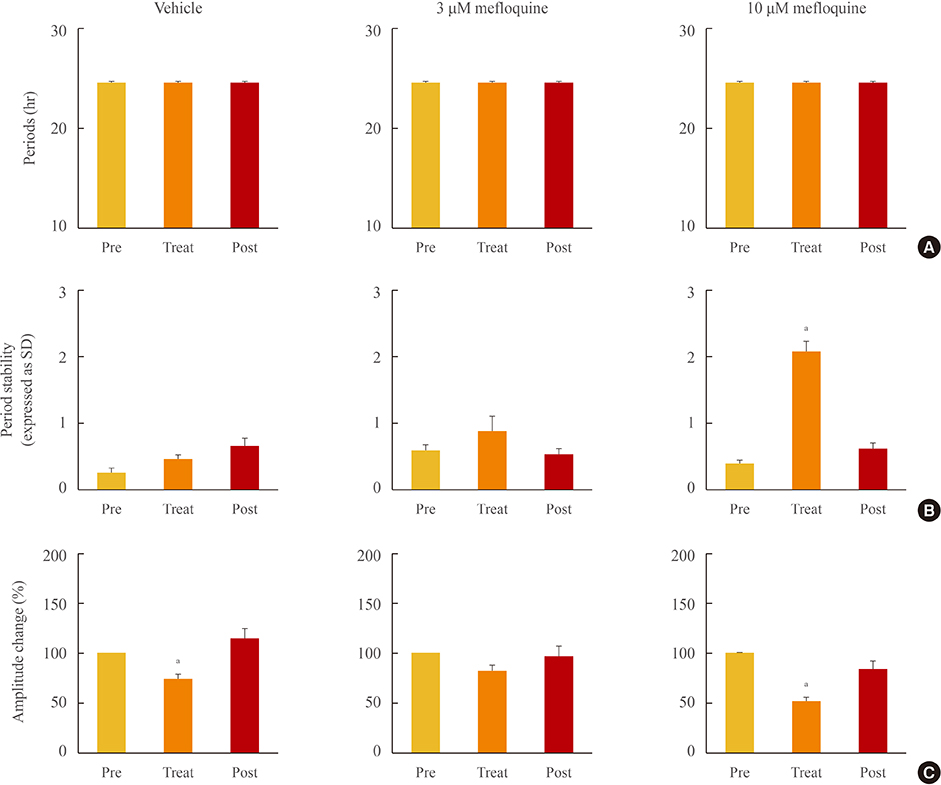
Administration of mefloquine causes instability in the pulse period and a slight reduction of amplitude in cyclic PER2::LUC expression. Blockade of gap junctions uncouples PER2::LUC-expressing cells, in terms of phase transition, which weakens synchrony among individual cellular rhythms.
CONCLUSION
These findings suggest that neuronal gap junctions play an important role in synchronizing the central pacemaker neurons and contribute to the distinct self-sustainability of the SCN master clock.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dibner C, Schibler U, Albrecht U. The mammalian circadian timing system: organization and coordination of central and peripheral clocks. Annu Rev Physiol. 2010; 72:517–549.2. Son GH, Chung S, Kim K. Biological rhythms and neuroendocrine systems. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2010; 25:249–257.3. Mohawk JA, Green CB, Takahashi JS. Central and peripheral circadian clocks in mammals. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2012; 35:445–462.4. Girardet C, Becquet D, Blanchard MP, Francois-Bellan AM, Bosler O. Neuroglial and synaptic rearrangements associated with photic entrainment of the circadian clock in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Eur J Neurosci. 2010; 32:2133–2142.5. Colwell CS. Rhythmic coupling among cells in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. J Neurobiol. 2000; 43:379–388.6. Welsh DK, Takahashi JS, Kay SA. Suprachiasmatic nucleus: cell autonomy and network properties. Annu Rev Physiol. 2010; 72:551–577.7. Herzog ED, Aton SJ, Numano R, Sakaki Y, Tei H. Temporal precision in the mammalian circadian system: a reliable clock from less reliable neurons. J Biol Rhythms. 2004; 19:35–46.8. Long MA, Jutras MJ, Connors BW, Burwell RD. Electrical synapses coordinate activity in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Nat Neurosci. 2005; 8:61–66.9. Shinohara K, Funabashi T, Mitushima D, Kimura F. Effects of gap junction blocker on vasopressin and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide rhythms in the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus in vitro. Neurosci Res. 2000; 38:43–47.10. Wang MH, Chen N, Wang JH. The coupling features of electrical synapses modulate neuronal synchrony in hypothalamic superachiasmatic nucleus. Brain Res. 2014; 1550:9–17.11. McCracken CB, Roberts DC. Neuronal gap junctions: expression, function, and implications for behavior. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2006; 73:125–151.12. Rash JE, Olson CO, Pouliot WA, Davidson KG, Yasumura T, Furman CS, et al. Connexin36 vs. connexin32, "miniature" neuronal gap junctions, and limited electrotonic coupling in rodent suprachiasmatic nucleus. Neuroscience. 2007; 149:350–371.13. Juszczak GR, Swiergiel AH. Properties of gap junction blockers and their behavioural, cognitive and electrophysiological effects: animal and human studies. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2009; 33:181–198.14. Cruikshank SJ, Hopperstad M, Younger M, Connors BW, Spray DC, Srinivas M. Potent block of Cx36 and Cx50 gap junction channels by mefloquine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101:12364–12369.15. Yoo SH, Yamazaki S, Lowrey PL, Shimomura K, Ko CH, Buhr ED, et al. PERIOD2::LUCIFERASE real-time reporting of circadian dynamics reveals persistent circadian oscillations in mouse peripheral tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101:5339–5346.16. Choe HK, Kim HD, Park SH, Lee HW, Park JY, Seong JY, et al. Synchronous activation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene transcription and secretion by pulsatile kisspeptin stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013; 110:5677–5682.17. Asai M, Yamaguchi S, Isejima H, Jonouchi M, Moriya T, Shibata S, et al. Visualization of mPer1 transcription in vitro: NMDA induces a rapid phase shift of mPer1 gene in cultured SCN. Curr Biol. 2001; 11:1524–1527.18. Abe M, Herzog ED, Yamazaki S, Straume M, Tei H, Sakaki Y, et al. Circadian rhythms in isolated brain regions. J Neurosci. 2002; 22:350–356.19. Aton SJ, Colwell CS, Harmar AJ, Waschek J, Herzog ED. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide mediates circadian rhythmicity and synchrony in mammalian clock neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2005; 8:476–483.20. Irwin RP, Allen CN. Neuropeptide-mediated calcium signaling in the suprachiasmatic nucleus network. Eur J Neurosci. 2010; 32:1497–1506.21. Maywood ES, Chesham JE, O'Brien JA, Hastings MH. A diversity of paracrine signals sustains molecular circadian cycling in suprachiasmatic nucleus circuits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011; 108:14306–14311.22. Sohl G, Willecke K. An update on connexin genes and their nomenclature in mouse and man. Cell Commun Adhes. 2003; 10:173–180.23. Mizoro Y, Yamaguchi Y, Kitazawa R, Yamada H, Matsuo M, Fustin JM, et al. Activation of AMPA receptors in the suprachiasmatic nucleus phase-shifts the mouse circadian clock in vivo and in vitro. PLoS One. 2010; 5:e10951.24. O'Neill JS, Maywood ES, Chesham JE, Takahashi JS, Hastings MH. cAMP-dependent signaling as a core component of the mammalian circadian pacemaker. Science. 2008; 320:949–953.25. Ciarleglio CM, Resuehr HE, McMahon DG. Interactions of the serotonin and circadian systems: nature and nurture in rhythms and blues. Neuroscience. 2011; 197:8–16.26. Balsalobre A, Brown SA, Marcacci L, Tronche F, Kellendonk C, Reichardt HM, et al. Resetting of circadian time in peripheral tissues by glucocorticoid signaling. Science. 2000; 289:2344–2347.27. Buhr ED, Yoo SH, Takahashi JS. Temperature as a universal resetting cue for mammalian circadian oscillators. Science. 2010; 330:379–385.28. Kiessling S, Eichele G, Oster H. Adrenal glucocorticoids have a key role in circadian resynchronization in a mouse model of jet lag. J Clin Invest. 2010; 120:2600–2609.29. Ko CH, Yamada YR, Welsh DK, Buhr ED, Liu AC, Zhang EE, et al. Emergence of noise-induced oscillations in the central circadian pacemaker. PLoS Biol. 2010; 8:e1000513.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Neurobiological Functions of the Period Circadian Clock 2 Gene, Per2
- A study on the expression of immediate-early genes by light stimuli in the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus using differential display
- Mammalian Molecular Clocks
- Dopaminergic Neurons in the Diencephalon of Striped Field Mouse[Apodemus agrarius coreae]
- Diabetes and Circadian Rhythm