Ann Lab Med.
2018 Mar;38(2):125-131. 10.3343/alm.2018.38.2.125.
Serum Cytokine Profile in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyposis Infected by Aspergillus flavus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, University College of Medical Sciences (University of Delhi) & Guru Teg Bahadur Hospital, Delhi, India. shukladas_123@yahoo.com
- 2Research and Scientific Studies Unit, College of Nursing & Allied Health Sciences, University of Jazan, Jazan, Saudi Arabia.
- 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology, University College of Medical Sciences (University of Delhi) & Guru Teg Bahadur Hospital, Delhi, India.
- 4Department of Pathology, University College of Medical Sciences (University of Delhi) & Guru Teg Bahadur Hospital, Delhi, India.
- 5Department of Biosciences, Faculty of Natural Sciences, Jamia Millia Islamia (A Central University), New Delhi, India.
- 6Department of Medical Microbiology, Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education & Research, Chandigarh, India.
- KMID: 2403357
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2018.38.2.125
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Fungi, especially Aspergillus flavus, can cause chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis and modulate host innate immune components. The objective of this study was to examine the serum levels of T helper (Th) cell subset Th1, Th2, and Th17 cytokines and total IgE in patients having chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis and Aspergillus flavus infection.
METHODS
A case-control study including 40 patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis and 20 healthy controls was conducted. Aspergillus flavus infection was confirmed by standard potassium hydroxide (KOH) testing, culture, and PCR. Serum samples of all patients and controls were analyzed for various cytokines (interleukins [IL]-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-17, IL-21, IL-27, TGF-β) and total IgE by ELISA. Data from patients with Aspergillus flavus infection and healthy volunteers were compared using the independent t-test and non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test.
RESULTS
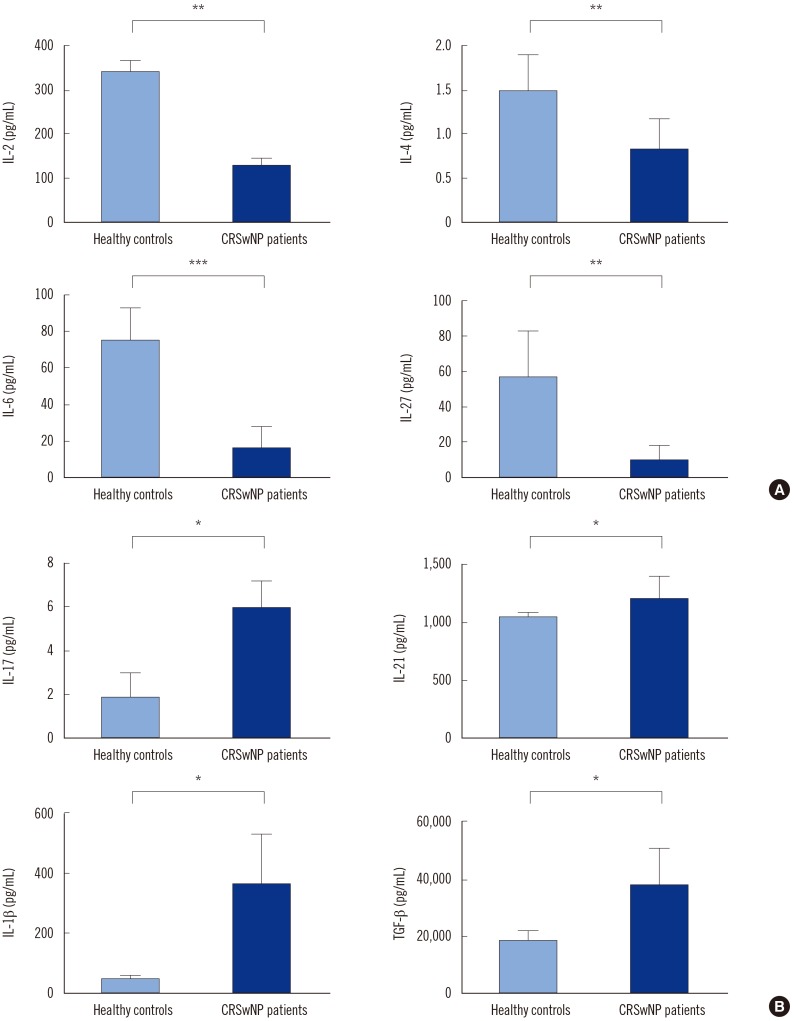
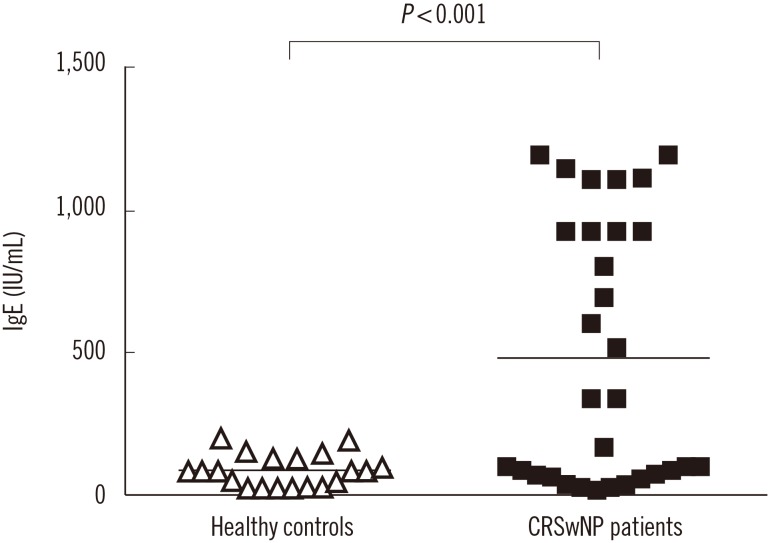
Aspergillus flavus infection was found in 31 (77.5%) patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. IL-1β, IL-17, IL-21, and TGF-β serum levels were significantly higher in these patients than in controls; however, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, and IL-27 levels were lower. Compared with nine (22.5%) patients without Aspergillus flavus infection, IL-17 level was higher while IL-2 level was lower in patients with Aspergillus flavus infection. Total IgE was significantly higher in patients with Aspergillus flavus infection than in controls.
CONCLUSIONS
High levels of IL-17 and its regulatory cytokines in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis infected by Aspergillus flavus raise a concern about effective disease management and therapeutic recovery. Surgical removal of the nasal polyp being the chief management option, the choice of post-operative drugs may differ in eosinophilic vs. non-eosinophilic nasal polyposis. The prognosis is likely poor, warranting extended care.
MeSH Terms
-
Aspergillus flavus*
Aspergillus*
Case-Control Studies
Cytokines
Disease Management
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Eosinophils
Fungi
Healthy Volunteers
Humans
Immunoglobulin E
Interleukin-17
Interleukin-2
Interleukin-27
Interleukin-4
Interleukin-6
Nasal Polyps
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Potassium
Prognosis
Cytokines
Immunoglobulin E
Interleukin-17
Interleukin-2
Interleukin-4
Interleukin-6
Potassium
Figure
Reference
-
1. Polzehl D, Moeller P, Riechelmann H, Perner S. Distinct features of chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyps. Allergy. 2006; 61:1275–1279. PMID: 17002702.2. Bachert C, Wagenmann M, Rudack C, Hopken K, Hiltebrandt M, Wang D, et al. The role of cytokines in infectious sinusitis and nasal polyposis. Allergy. 1998; 53:2–13. PMID: 9491223.3. Meltzer EO, Hamilos DL, Hadley JA, Lanza DC, Marple BF, Nicklas RA, et al. Rhinosinusitis: establishing definitions for clinical research and patient care. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 114:155–212. PMID: 15577865.4. Wynn R. Recurrence rates after endoscopic sinus surgery for massive sinus polyposis. Laryngoscope. 2004; 114:811–813. PMID: 15126735.5. Soler ZM, Sauer DA, Mace J, Smith TL. Relationship between clinical measures and histopathologic findings in chronic rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009; 141:454–461. PMID: 19786212.6. Zelante T, De Luca A, Bonifazi P, Montagnoli C, Bozza S, Moretti S, et al. IL-23 and the Th17 path way promote inflammation and impair antifungal immune resistance. Eur J Immunol. 2007; 37:2695–2706. PMID: 17899546.7. Bozza S, Zelante T, Moretti S, Bonifazi P, DeLuca A, D’Angelo C, et al. Lack of toll IL-1R8 exacerbates Th17 cell responses in fungal infection. J Immunol. 2008; 180:4022–4031. PMID: 18322211.8. Cao PP, Li HB, Wang BF, Wang SB, You XJ, Cui YH, et al. Distinct immunopathologic characteristics of various types of chronic rhinosinusitis in adult Chinese. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124:478–484. PMID: 19541359.9. Zhang N, Holtappels G, Claeys C, Huang G, van Cauwenberge P, Bachert C. Pattern of inflammation and impact of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins in nasal polyps from southern China. Am J Rhinol. 2006; 20:445–450.10. Zhang N, Van Zele T, Perez-Novo C, Van Bruaene N, Holtappels G, DeRuyck N, et al. Different types of T-effector cells orchestrate mucosal inflammation in chronic sinus disease. JAllergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 122:961–968. PMID: 18804271.11. Bettelli E, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK. T(H)-17 cells in the circle of immunity and autoimmunity. Nat Immunol. 2007; 8:345–350. PMID: 17375096.12. Park H, Li Z, Yang XO, Chang SH, Nurieva R, Wang YH, et al. A distinct lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing interleukin 17. Nat Immunol. 2005; 6:1133–1141. PMID: 16200068.13. Laurence A, Tato CM, Davidson TS, Kanno Y, Chen Z, Yao Z, et al. Interleukin-2 signaling via STAT5 constrains T helper 17 cell generation. Immunity. 2007; 26:371–381. PMID: 17363300.14. Lund VJ, Holmstrom M, Scadding GK. Functional endoscopic sinus surgery in the management of chronic rhino sinusitis. An objective assessment. J Laryngol Otol. 1991; 105:832–835. PMID: 1753193.15. Lund VJ, Kennedy DW. Staging for rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997; 117:S35–S40. PMID: 9334786.16. Leck A. Preparation of Lactophenol Cotton Blue Slide Mounts. Community Eye Health. 1999; 12:24.17. Logotheti M, Kotsovili-Tseleni A, Arsenis G, Legakis NI. Multiplex PCR for the Discrimination of A. fumigatus, A. flavus, A. niger and A. terreus. J Microbiol Methods. 2009; 76:209–211. PMID: 18992777.18. Mazumdar A, Das S, Saha R, Ramachandran VG, Gupta N, Sharma S, et al. Correlation of nucleic acid amplification based detection and conventional methods of identification of Aspergillus flavus species in chronic rhinosinusitis. Research & Reviews: J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013; 2:61–66.19. Ricchetti A, Landis BN, Maffioli A, Giger R, Zeng C, Lacroix JS. Effect of anti-fungal nasal lavage with amphotericin B on nasal polyposis. J Laryngol Otol. 2002; 116:261–263. PMID: 11945184.20. Garín L, Armengot M, Alba JR, Carda C. Correlations between clinical and histological aspects in nasal polyposis. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp. 2008; 59:315–320. PMID: 18817712.21. Shen Y, Tang XY, Yang YC, Ke X, Kou W, Pan CK, et al. Impaired balance of Th17/Treg in patients with nasal polyposis. Scand J Immunol. 2011; 74:176–185. PMID: 21375554.22. Bent JP 3rd, Kuhn FA. Diagnosis of allergic fungal sinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1994; 111:580–588. PMID: 7970796.23. Ferguson BJ. Eosinophilic mucin rhinosinusitis: a distinct clinicopathological entity. Laryngoscope. 2000; 110:799–813. PMID: 10807359.24. Chakrabarti A, Denning DW, Ferguson BJ, Ponikau J, Buzina W, Kita H, et al. Fungal rhinosinusitis: a categorization and definitional schema addressing current controversies. Laryngoscope. 2009; 119:1809–1818. PMID: 19544383.25. Bozza S, Gaziano >R, Spreca A, Bacci A, Montagnoli C, di Francesco P, et al. Dendritic cells transport conidia and hyphae of Aspergillus fumigatus from the airways to the draining lymph nodes and initiate disparate Th responses to the fungus. J Immunol. 2002; 168:1362–1371. PMID: 11801677.26. Korn T, Bettelli E, Gao W, Awasthi A, Jäger A, Strom TB, et al. IL-21 initiates an alternative pathway to induce proinflammatory T(H)17 cells. Nature. 2007; 448:484–487. PMID: 17581588.27. Murdock BJ, Shreiner AB, McDonald RA, Osterholzer JJ, White ES, Toews GB, et al. Co-evolution of TH1, TH2, and TH17 responses during repeated pulmonary exposure to Aspergillus fumigatus conidia. Infect Immun. 2011; 79:125–135. PMID: 21041495.28. Van Beelen AJ, Zelinkova Z, Taanman-Kueter EW, Muller FJ, Hommes DW, Zaat SA, et al. Stimulation of the intracellular bacterial sensor NOD2 programs dendritic cells to promote interleukin-17 production in human memory T cells. Immunity. 2007; 27:660–669. PMID: 17919942.29. Radhakrishnan S, Cabrera R, Schenk EL, Nava-Parada P, Bell MP, Van Keulen VP, et al. Reprogrammed FoxP3+ T regulatory cells become IL-17 antigen-specific autoimmune effectors in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol. 2008; 181:3137–3147. PMID: 18713984.30. Osorio F, Leibund Gut-Landmann S, Lochner M, Lahl K, Sparwasser T, Eberl G, et al. DC activated via dectin-1 convert Treg into IL-17 producers. Eur J Immunol. 2008; 38:3274–3281. PMID: 19039774.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Role of Superantigen in Nasal Polypogenesis
- Medical treatment according to phenotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis
- The role of cytokines in rhinosinusitis
- Expression of Cytokines in Nasal Polyps with Chronic Sinusitis and Asthma
- The Impact of Nasal Polyposis on Olfactory Dysfunction in Chronic Rhinosinusitis