Late-term healing in an augmented sinus with different ratios of biphasic calcium phosphate: a pilot study using a rabbit sinus model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Periodontology, Kyung Hee University School of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Periodontology, Research Institute for Periodontal Regeneration, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea. shchoi726@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2391730
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2016.46.1.57
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this pilot study was to determine the osteoconductivity and dimensional stability of augmented sinuses using different ratios of biphasic calcium phosphate (BCP) in a rabbit sinus model.
METHODS
Each sinus of New Zealand white rabbits (2.5-3.5 kg) was assigned to one of two groups: BCP with a hydroxyapatite to beta-tricalcium phosphate (HA:beta-TCP) ratio of 70:30 (group TCP30) and BCP with an HA:beta-TCP ratio of 30:70 (group TCP70). After preparing a window in the antral wall of a sinus, the Schneiderian membrane was elevated, and the applicable material was grafted. A fluorochrome calcein green was injected five days before euthanizing the animals at four months post-surgery. The specimens were analyzed histologically, histomorphometrically, and by using micro-computed tomography (micro-CT).
RESULTS
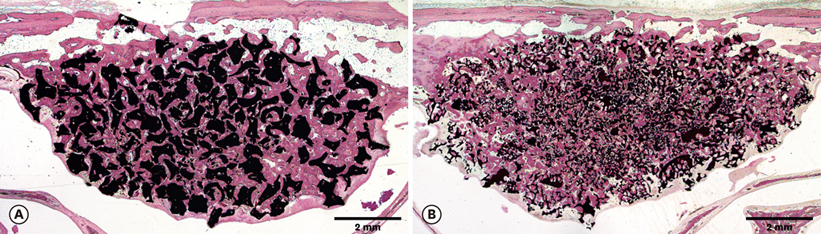
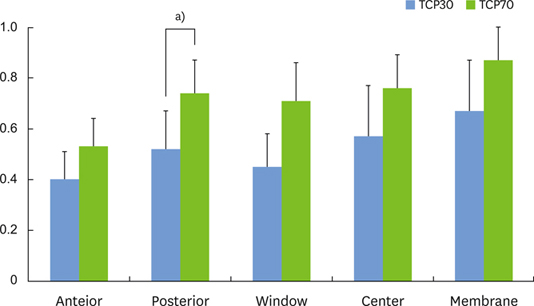
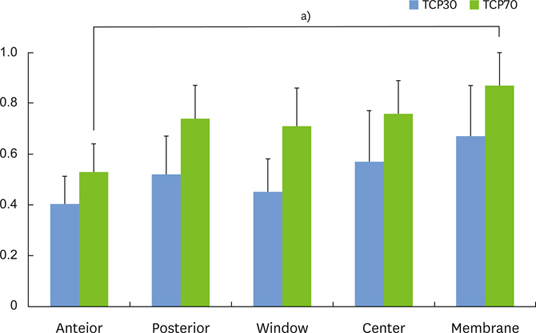
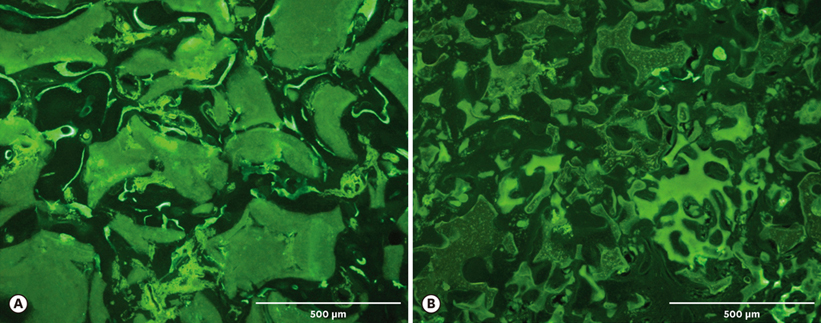
Micro-CT analysis revealed that the total augmented volume and the new bone volume did not differ significantly between the two groups whereas the resorption of materials was greater in the TCP70 group. The trabecular thickness, number, and separation also did not differ significantly between the two groups. Histomorphometrically, the areas of total augmentation, new bone, and residual material, as well as the ratio of new-bone-material contact did not differ significantly between the groups. Histologically, the residual particles were more scattered in the TCP70 group than in the TCP30 group. The fluorescence of the calcein green did not differ notably between the two groups.
CONCLUSIONS
The osteoconductivity and dimensional stability of the two BCPs with different ratios tested in this study were comparable after four months of healing. Therefore, we conclude that both BCPs show promise as a bone substitute for sinus augmentation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 5 articles
-
Increased osteoinductivity and mineralization by minimal concentration of bone morphogenetic protein-2 loaded onto biphasic calcium phosphate in a rabbit sinus
Jae-Shin Kim, Jae-Kook Cha, Jung-Seok Lee, Seong-Ho Choi, Kyoo-Sung Cho
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2016;46(5):350-359. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2016.46.5.350.Increased osteoinductivity and mineralization by minimal concentration of bone morphogenetic protein-2 loaded onto biphasic calcium phosphate in a rabbit sinus
Jae-Shin Kim, Jae-Kook Cha, Jung-Seok Lee, Seong-Ho Choi, Kyoo-Sung Cho
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2016;46(5):350-359. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2016.46.5.350.Comparative preclinical assessment of the use of dehydrated human amnion/chorion membrane to repair perforated sinus membranes
Yun-Young Chang, Su-Hwan Kim, Mi-Seon Goh, Jeong-Ho Yun
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2019;49(5):330-343. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2019.49.5.330.Maxillary sinus augmentation using biphasic calcium phosphate: dimensional stability results after 3–6 years
Jae-Kook Cha, Chingu Kim, Hyung-Chul Pae, Jung-Seok Lee, Ui-Won Jung, Seong-Ho Choi
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2019;49(1):47-57. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2019.49.1.47.Dental alloplastic bone substitutes currently available in Korea
Jeong-Kui Ku, Inseok Hong, Bu-Kyu Lee, Pil-Young Yun, Jeong Keun Lee
J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019;45(2):51-67. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2019.45.2.51.
Reference
-
1. Uchida Y, Goto M, Katsuki T, Soejima Y. Measurement of maxillary sinus volume using computerized tomographic images. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1998; 13:811–818.2. Sbordone C, Toti P, Guidetti F, Califano L, Bufo P, Sbordone L. Volume changes of autogenous bone after sinus lifting and grafting procedures: a 6-year computerized tomographic follow-up. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2013; 41:235–241.
Article3. Pjetursson BE, Tan WC, Zwahlen M, Lang NP. A systematic review of the success of sinus floor elevation and survival of implants inserted in combination with sinus floor elevation. J Clin Periodontol. 2008; 35:Suppl. 216–240.
Article4. Nkenke E, Stelzle F. Clinical outcomes of sinus floor augmentation for implant placement using autogenous bone or bone substitutes: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009; 20:Suppl 4. 124–133.
Article5. Bae JH, Kim YK, Kim SG, Yun PY, Kim JS. Sinus bone graft using new alloplastic bone graft material (Osteon)-II: clinical evaluation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010; 109:e14–e20.
Article6. Favato MN, Vidigal BC, Cosso MG, Manzi FR, Shibli JA, Zenóbio EG. Impact of human maxillary sinus volume on grafts dimensional changes used in maxillary sinus augmentation: a multislice tomographic study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015; 26:1450–1455.
Article7. Kim YK, Yun PY, Lim SC, Kim SG, Lee HJ, Ong JL. Clinical evaluations of OSTEON as a new alloplastic material in sinus bone grafting and its effect on bone healing. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008; 86:270–277.
Article8. Ohayon L. Maxillary sinus floor augmentation using biphasic calcium phosphate: a histologic and histomorphometric study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014; 29:1143–1148.
Article9. LeGeros RZ, Lin S, Rohanizadeh R, Mijares D, LeGeros JP. Biphasic calcium phosphate bioceramics: preparation, properties and applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2003; 14:201–209.10. Jensen SS, Broggini N, Hjørting-Hansen E, Schenk R, Buser D. Bone healing and graft resorption of autograft, anorganic bovine bone and beta-tricalcium phosphate. A histologic and histomorphometric study in the mandibles of minipigs. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006; 17:237–243.
Article11. von Arx T, Cochran DL, Hermann JS, Schenk RK, Higginbottom FL, Buser D. Lateral ridge augmentation and implant placement: an experimental study evaluating implant osseointegration in different augmentation materials in the canine mandible. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2001; 16:343–354.12. Zijderveld SA, Schulten EA, Aartman IH, ten Bruggenkate CM. Long-term changes in graft height after maxillary sinus floor elevation with different grafting materials: radiographic evaluation with a minimum follow-up of 4.5 years. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009; 20:691–700.
Article13. Hatano N, Shimizu Y, Ooya K. A clinical long-term radiographic evaluation of graft height changes after maxillary sinus floor augmentation with a 2:1 autogenous bone/xenograft mixture and simultaneous placement of dental implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004; 15:339–345.
Article14. Chang SH, Lin CL, Lin YS, Hsue SS, Huang SR. Biomechanical comparison of a single short and wide implant with monocortical or bicortical engagement in the atrophic posterior maxilla and a long implant in the augmented sinus. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012; 27:e102–e111.15. Kim HR, Choi BH, Xuan F, Jeong SM. The use of autologous venous blood for maxillary sinus floor augmentation in conjunction with sinus membrane elevation: an experimental study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010; 21:346–349.
Article16. Lim HC, Zhang ML, Lee JS, Jung UW, Choi SH. Effect of different hydroxyapatite:β-tricalcium phosphate ratios on the osteoconductivity of biphasic calcium phosphate in the rabbit sinus model. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2015; 30:65–72.
Article17. Kühl S, Payer M, Kirmeier R, Wildburger A, Acham S, Jakse N. The influence of particulated autogenous bone on the early volume stability of maxillary sinus grafts with biphasic calcium phosphate: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2015; 17:173–178.
Article18. Shanbhag S, Shanbhag V, Stavropoulos A. Volume changes of maxillary sinus augmentations over time: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014; 29:881–892.
Article19. Scharf KE, Lawson W, Shapiro JM, Gannon PJ. Pressure measurements in the normal and occluded rabbit maxillary sinus. Laryngoscope. 1995; 105:570–574.
Article20. Roberts WE, Turley PK, Brezniak N, Fielder PJ. Implants: Bone physiology and metabolism. CDA J. 1987; 15:54–61.21. Artzi Z, Weinreb M, Givol N, Rohrer MD, Nemcovsky CE, Prasad HS, et al. Biomaterial resorption rate and healing site morphology of inorganic bovine bone and beta-tricalcium phosphate in the canine: a 24-month longitudinal histologic study and morphometric analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004; 19:357–368.22. Cha JK, Park JC, Jung UW, Kim CS, Cho KS, Choi SH. Case series of maxillary sinus augmentation with biphasic calcium phosphate: a clinical and radiographic study. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2011; 41:98–104.
Article23. Arasawa M, Oda Y, Kobayashi T, Uoshima K, Nishiyama H, Hoshina H, et al. Evaluation of bone volume changes after sinus floor augmentation with autogenous bone grafts. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 41:853–857.
Article24. Kirmeier R, Payer M, Wehrschuetz M, Jakse N, Platzer S, Lorenzoni M. Evaluation of three-dimensional changes after sinus floor augmentation with different grafting materials. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008; 19:366–372.
Article25. Klijn RJ, van den Beucken JJ, Bronkhorst EM, Berge SJ, Meijer GJ, Jansen JA. Predictive value of ridge dimensions on autologous bone graft resorption in staged maxillary sinus augmentation surgery using Cone-Beam CT. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012; 23:409–415.
Article26. Umanjec-Korac S, Wu G, Hassan B, Liu Y, Wismeijer D. A retrospective analysis of the resorption rate of deproteinized bovine bone as maxillary sinus graft material on cone beam computed tomography. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2014; 25:781–785.
Article27. Wanschitz F, Figl M, Wagner A, Rolf E. Measurement of volume changes after sinus floor augmentation with a phycogenic hydroxyapatite. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2006; 21:433–438.28. Yang C, Unursaikhan O, Lee JS, Jung UW, Kim CS, Choi SH. Osteoconductivity and biodegradation of synthetic bone substitutes with different tricalcium phosphate contents in rabbits. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2014; 102:80–88.
Article29. Lim HC, Song KH, You H, Lee JS, Jung UW, Kim SY, et al. Effectiveness of biphasic calcium phosphate block bone substitutes processed using a modified extrusion method in rabbit calvarial defects. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2015; 45:46–55.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Increased osteoinductivity and mineralization by minimal concentration of bone morphogenetic protein-2 loaded onto biphasic calcium phosphate in a rabbit sinus
- Maxillary sinus augmentation using biphasic calcium phosphate: dimensional stability results after 3–6 years
- Improvement of osteogenic potential of biphasic calcium phosphate bone substitute coated with synthetic cell binding peptide sequences
- Case series of maxillary sinus augmentation with biphasic calcium phosphate: a clinical and radiographic study
- Improvement of the osteogenic potential of ErhBMP-2-/EGCG-coated biphasic calcium phosphate bone substitute: in vitro and in vivo activity