Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2017 Mar;21(2):153-160. 10.4196/kjpp.2017.21.2.153.
Effect of subcutaneous treatment with human umbilical cord blood-derived multipotent stem cells on peripheral neuropathic pain in rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dental Anesthesiology and Dental Research Institute, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul 03080, Korea. dentane@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Konkuk University Medical Center, Research Institute of Medical Science, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul 05030, Korea.
- 3Adult Stem Cell Research Center, Laboratory of Stem Cell and Tumor Biology, Department of Veterinary Public Health, College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Korea. kangpub@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2371033
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2017.21.2.153
Abstract
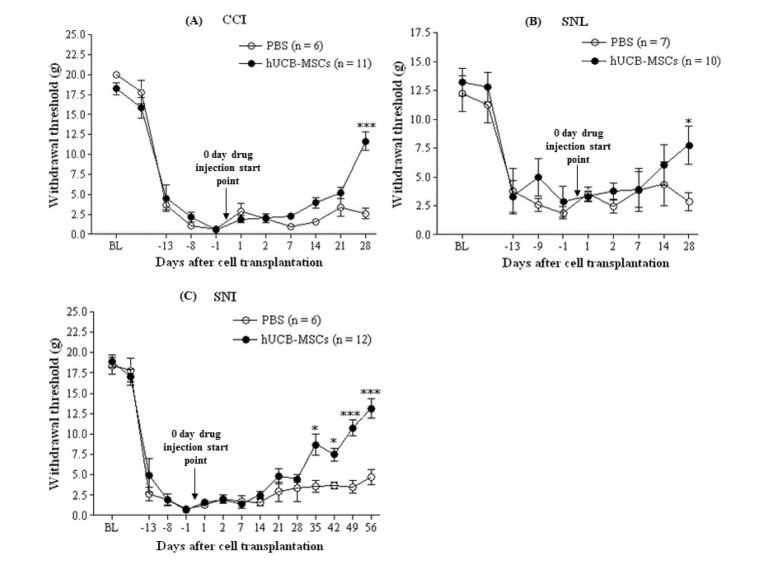
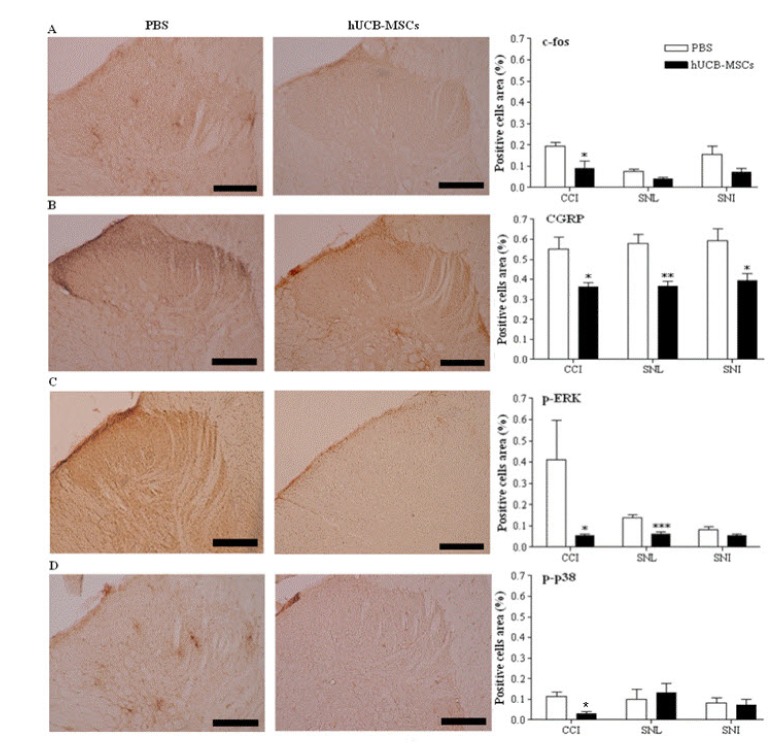
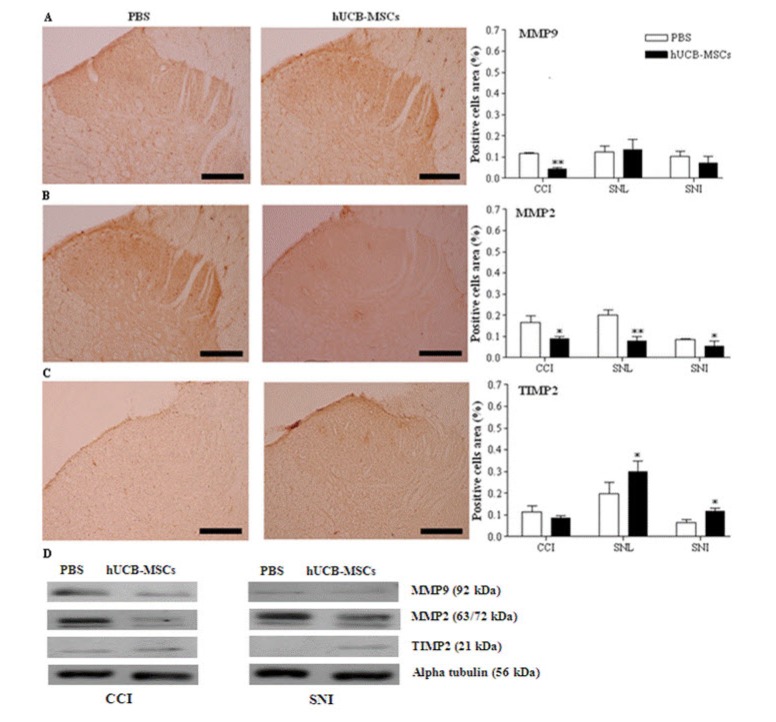
- In this study, we aim to determine the in vivo effect of human umbilical cord blood-derived multipotent stem cells (hUCB-MSCs) on neuropathic pain, using three, principal peripheral neuropathic pain models. Four weeks after hUCB-MSC transplantation, we observed significant antinociceptive effect in hUCB-MSC-transplanted rats compared to that in the vehicle-treated control. Spinal cord cells positive for c-fos, CGRP, p-ERK, p-p 38, MMP-9 and MMP 2 were significantly decreased in only CCI model of hUCB-MSCs-grafted rats, while spinal cord cells positive for CGRP, p-ERK and MMP-2 significantly decreased in SNL model of hUCB-MSCs-grafted rats and spinal cord cells positive for CGRP and MMP-2 significantly decreased in SNI model of hUCB-MSCs-grafted rats, compared to the control 4 weeks or 8weeks after transplantation (p<0.05). However, cells positive for TIMP-2, an endogenous tissue inhibitor of MMP-2, were significantly increased in SNL and SNI models of hUCB-MSCs-grafted rats. Taken together, subcutaneous injection of hUCB-MSCs may have an antinociceptive effect via modulation of pain signaling during pain signal processing within the nervous system, especially for CCI model. Thus, subcutaneous administration of hUCB-MSCs might be beneficial for improving those patients suffering from neuropathic pain by decreasing neuropathic pain activation factors, while increasing neuropathic pain inhibition factor.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells engineered to overexpress growth factors accelerate outcomes in hair growth
Dong Ho Bak, Mi Ji Choi, Soon Re Kim, Byung Chul Lee, Jae Min Kim, Eun Su Jeon, Wonil Oh, Ee Seok Lim, Byung Cheol Park, Moo Joong Kim, Jungtae Na, Beom Joon Kim
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018;22(5):555-566. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2018.22.5.555.
Reference
-
1. Dworkin RH. An overview of neuropathic pain: syndromes, symptoms, signs, and several mechanisms. Clin J Pain. 2002; 18:343–349. PMID: 12441827.
Article2. Bennett GJ, Xie YK. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain. 1988; 33:87–107. PMID: 2837713.
Article3. Kim SH, Chung JM. An experimental model for peripheral neuropathy produced by segmental spinal nerve ligation in the rat. Pain. 1992; 50:355–363. PMID: 1333581.4. Decosterd I, Woolf CJ. Spared nerve injury: an animal model of persistent peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain. 2000; 87:149–158. PMID: 10924808.
Article5. Mukhida K, Mendez I, McLeod M, Kobayashi N, Haughn C, Milne B, Baghbaderani B, Sen A, Behie LA, Hong M. Spinal GABAergic transplants attenuate mechanical allodynia in a rat model of neuro-pathic pain. Stem Cells. 2007; 25:2874–2885. PMID: 17702982.
Article6. Dellemijn P. Are opioids effective in relieving neuropathic pain? Pain. 1999; 80:453–462. PMID: 10342407.
Article7. Jackson KC 2nd. Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain. Pain Pract. 2006; 6:27–33. PMID: 17309706.
Article8. McQuay H, Carroll D, Jadad AR, Wiffen P, Moore A. Anticonvulsant drugs for management of pain: a systematic review. BMJ. 1995; 311:1047–1052. PMID: 7580659.
Article9. Gang EJ, Hong SH, Jeong JA, Hwang SH, Kim SW, Yang IH, Ahn C, Han H, Kim H. In vitro mesengenic potential of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004; 321:102–108. PMID: 15358221.
Article10. Kuh SU, Cho YE, Yoon DH, Kim KN, Ha Y. Functional recovery after human umbilical cord blood cells transplantation with brain-derived neutrophic factor into the spinal cord injured rat. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2005; 147:985–992. PMID: 16010451.
Article11. Lim JH, Byeon YE, Ryu HH, Jeong YH, Lee YW, Kim WH, Kang KS, Kweon OK. Transplantation of canine umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in experimentally induced spinal cord injured dogs. J Vet Sci. 2007; 8:275–282. PMID: 17679775.
Article12. Seo KW, Lee SR, Bhandari DR, Roh KH, Park SB, So AY, Jung JW, Seo MS, Kang SK, Lee YS, Kang KS. OCT4A contributes to the stemness and multi-potency of human umbilical cord blood-derived multipotent stem cells (hUCB-MSCs). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009; 384:120–125. PMID: 19394308.
Article13. Sun B, Roh KH, Park JR, Lee SR, Park SB, Jung JW, Kang SK, Lee YS, Kang KS. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stromal cells in a mouse breast cancer metastasis model. Cytotherapy. 2009; 11:289–298. PMID: 19308770.
Article14. Kim SW, Han H, Chae GT, Lee SH, Bo S, Yoon JH, Lee YS, Lee KS, Park HK, Kang KS. Successful stem cell therapy using umbilical cord blood-derived multipotent stem cells for Buerger's disease and ischemic limb disease animal model. Stem Cells. 2006; 24:1620–1626. PMID: 16497946.
Article15. Chattopadhyay S, Myers RR, Janes J, Shubayev V. Cytokine regulation of MMP-9 in peripheral glia: implications for pathological processes and pain in injured nerve. Brain Behav Immun. 2007; 21:561–568. PMID: 17189680.
Article16. Parks WC, Wilson CL, López-Boado YS. Matrix metalloproteinases as modulators of inflammation and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004; 4:617–629. PMID: 15286728.
Article17. Rosenberg GA. Matrix metalloproteinases in neuroinflammation. Glia. 2002; 39:279–291. PMID: 12203394.
Article18. Wang X, Jung J, Asahi M, Chwang W, Russo L, Moskowitz MA, Dixon CE, Fini ME, Lo EH. Effects of matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene knock-out on morphological and motor outcomes after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci. 2000; 20:7037–7042. PMID: 10995849.
Article19. Yong VW. Metalloproteinases: mediators of pathology and regeneration in the CNS. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005; 6:931–944. PMID: 16288297.
Article20. Zhao BQ, Wang S, Kim HY, Storrie H, Rosen BR, Mooney DJ, Wang X, Lo EH. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in delayed cortical responses after stroke. Nat Med. 2006; 12:441–445. PMID: 16565723.
Article21. Kawasaki Y, Xu ZZ, Wang X, Park JY, Zhuang ZY, Tan PH, Gao YJ, Roy K, Corfas G, Lo EH, Ji RR. Distinct roles of matrix metalloproteases in the early- and late-phase development of neuropathic pain. Nat Med. 2008; 14:331–336. PMID: 18264108.
Article22. Conlee KM, Stephens ML, Rowan AN, King LA. Carbon dioxide for euthanasia: concerns regarding pain and distress, with special reference to mice and rats. Lab Anim. 2005; 39:137–161. PMID: 15901358.
Article23. Zimmermann M. Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain. 1983; 16:109–110. PMID: 6877845.
Article24. Tal M, Bennett GJ. Extra-territorial pain in rats with a peripheral mononeuropathy: mechano-hyperalgesia and mechano-allodynia in the territory of an uninjured nerve. Pain. 1994; 57:375–382. PMID: 7936715.
Article25. Ahn SN, Guu JJ, Tobin AJ, Edgerton VR, Tillakaratne NJ. Use of c-fos to identify activity-dependent spinal neurons after stepping in intact adult rats. Spinal Cord. 2006; 44:547–559. PMID: 16344852.
Article26. Lin YR, Chen HH, Ko CH, Chan MH. Effects of honokiol and magnolol on acute and inflammatory pain models in mice. Life Sci. 2007; 81:1071–1078. PMID: 17826802.
Article27. Tsuda M, Tozaki-Saitoh H, Masuda T, Toyomitsu E, Tezuka T, Yamamoto T, Inoue K. Lyn tyrosine kinase is required for P2X(4) receptor upregulation and neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury. Glia. 2008; 56:50–58. PMID: 17918263.
Article28. Blackburn-Munro G. Pain-like behaviours in animals - how human are they? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2004; 25:299–305. PMID: 15165744.
Article29. Bridges D, Thompson SW, Rice AS. Mechanisms of neuropathic pain. Br J Anaesth. 2001; 87:12–26. PMID: 11460801.
Article30. Bettoni I, Comelli F, Rossini C, Granucci F, Giagnoni G, Peri F, Costa B. Glial TLR4 receptor as new target to treat neuropathic pain: efficacy of a new receptor antagonist in a model of peripheral nerve injury in mice. Glia. 2008; 56:1312–1319. PMID: 18615568.
Article31. Stubley LA, Martinez MA, Karmally S, Lopez T, Cejas P, Eaton MJ. Only early intervention with gamma-aminobutyric acid cell therapy is able to reverse neuropathic pain after partial nerve injury. J Neurotrauma. 2001; 18:471–477. PMID: 11336447.
Article32. Cejas PJ, Martinez M, Karmally S, McKillop M, McKillop J, Plunkett JA, Oudega M, Eaton MJ. Lumbar transplant of neurons genetically modified to secrete brain-derived neurotrophic factor attenuates allodynia and hyperalgesia after sciatic nerve constriction. Pain. 2000; 86:195–210. PMID: 10779676.
Article33. Décosterd I, Buchser E, Gilliard N, Saydoff J, Zurn AD, Aebischer P. Intrathecal implants of bovine chromaffin cells alleviate mechanical allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Pain. 1998; 76:159–166. PMID: 9696469.
Article34. Eaton MJ, Martinez M, Karmally S, Lopez T, Sagen J. Initial characterization of the transplant of immortalized chromaffin cells for the attenuation of chronic neuropathic pain. Cell Transplant. 2000; 9:637–656. PMID: 11144961.
Article35. Yu W, Hao JX, Xu XJ, Saydoff J, Haegerstrand A, Hökfelt T, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z. Long-term alleviation of allodynia-like behaviors by intrathecal implantation of bovine chromaffin cells in rats with spinal cord injury. Pain. 1998; 74:115–122. PMID: 9520225.
Article36. Zhuang ZY, Gerner P, Woolf CJ, Ji RR. ERK is sequentially activated in neurons, microglia, and astrocytes by spinal nerve ligation and contributes to mechanical allodynia in this neuropathic pain model. Pain. 2005; 114:149–159. PMID: 15733640.
Article37. Ji RR, Baba H, Brenner GJ, Woolf CJ. Nociceptive-specific activation of ERK in spinal neurons contributes to pain hypersensitivity. Nat Neurosci. 1999; 2:1114–1119. PMID: 10570489.
Article38. Impey S, Obrietan K, Storm DR. Making new connections: role of ERK/MAP kinase signaling in neuronal plasticity. Neuron. 1999; 23:11–14. PMID: 10402188.39. Herdegen T, Leah JD. Inducible and constitutive transcription factors in the mammalian nervous system: control of gene expression by Jun, Fos and Krox, and CREB/ATF proteins. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1998; 28:370–490. PMID: 9858769.
Article40. Ji RR, Xu ZZ, Wang X, Lo EH. Matrix metalloprotease regulation of neuropathic pain. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009; 30:336–340. PMID: 19523695.
Article41. Jin SX, Zhuang ZY, Woolf CJ, Ji RR. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is activated after a spinal nerve ligation in spinal cord microglia and dorsal root ganglion neurons and contributes to the generation of neuropathic pain. J Neurosci. 2003; 23:4017–4022. PMID: 12764087.
Article42. Hu J, Van den Steen PE, Sang QX, Opdenakker G. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors as therapy for inflammatory and vascular diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007; 6:480–498. PMID: 17541420.
Article43. Jeffery N, McLean MH, El-Omar EM, Murray GI. The matrix metalloproteinase/tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase profile in colorectal polyp cancers. Histopathology. 2009; 54:820–828. PMID: 19635101.
Article44. Saporta S, Kim JJ, Willing AE, Fu ES, Davis CD, Sanberg PR. Human umbilical cord blood stem cells infusion in spinal cord injury: engraftment and beneficial influence on behavior. J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 2003; 12:271–278. PMID: 12857368.
Article45. Veeravalli KK, Dasari VR, Tsung AJ, Dinh DH, Gujrati M, Fassett D, Rao JS. Human umbilical cord blood stem cells upregulate matrix metalloproteinase-2 in rats after spinal cord injury. Neurobiol Dis. 2009; 36:200–212. PMID: 19631747.
Article46. Renn CL, Dorsey SG. The physiology and processing of pain: a review. AACN Clin Issues. 2005; 16:277–290. quiz 413-415. PMID: 16082231.47. Han F, Zhang YF, Li YQ. Fos expression in tyrosine hydroxylase-containing neurons in rat brainstem after visceral noxious stimulation: an immunohistochemical study. World J Gastroenterol. 2003; 9:1045–1050. PMID: 12717853.
Article48. Hentall ID, Mesigil R, Pinzon A, Noga BR. Temporal and spatial profiles of pontine-evoked monoamine release in the rat's spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 2003; 89:2943–2951. PMID: 12612020.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Simple Method to Isolate and Expand Human Umbilical Cord Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Using Explant Method and Umbilical Cord Blood Serum
- Percutaneous transplantation of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a dog suspected to have fibrocartilaginous embolic myelopathy
- Differentiation of Osteoblast Progenitor Cells from Human Umbilical Cord Blood
- Stem Cell Transplantation in Umbilical Cord Blood(I) Expansion Effects of Stem Cells in Umbilical Cord Blood with Various Hematopoietic Growth Factors
- Stem Cell Properties of Therapeutic Potential