Ann Dermatol.
2014 Jun;26(3):308-313.
Comparative Analysis of Human Epidermal and Peripheral Blood gammadelta T Cell Cytokine Profiles
- Affiliations
-
- 1Laboratory of Immunology, College of Pharmacy, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea.
- 2Bioscience Research Institute, Amorepacific Corporation R&D Center, Yongin, Korea.
- 3Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Institute of Human-Environment Interface Biology, Medical Research Center, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. oskwon@snu.ac.kr
- 5Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Human epidermal gammadelta T cells are known to play crucial roles in the defense and homeostasis of the skin. However, their precise mechanism of action in skin inflammation remains less clear.
OBJECTIVE
In this study, we analyzed the cytokine expression profile of human epidermal gammadelta T cells and compared it to that of peripheral blood gammadelta T cells to investigate the specific activity of epidermal gammadelta T cells in modulating skin inflammation.
METHODS
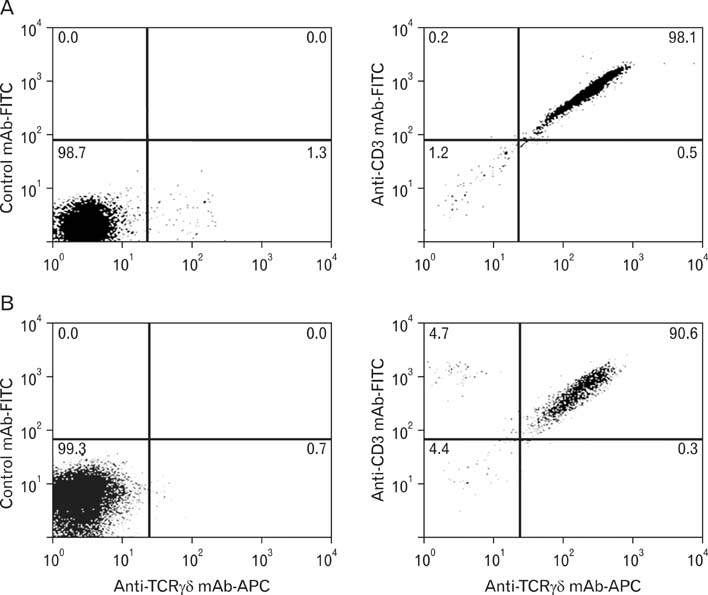
We isolated gammadelta T cells from epidermal tissue or peripheral blood obtained from healthy volunteers. Isolated gammadelta T cells were stimulated using immobilized anti-CD3 antibody and interleukin-2 plus phytohaemagglutinin, and were then analyzed using a cytokine array kit.
RESULTS
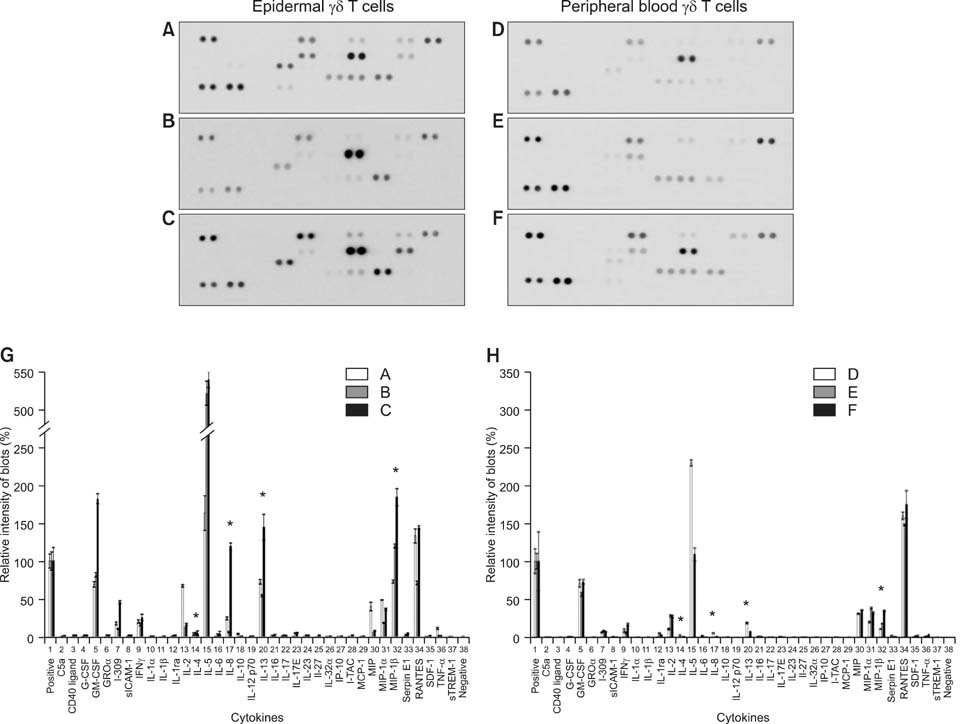
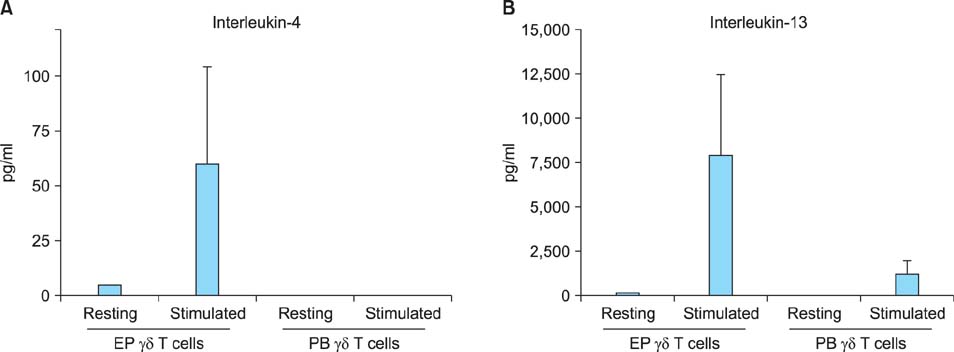
Both epidermal and peripheral blood gammadelta T cells produced comparable levels of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, I-309, interferon-gamma, macrophage migration inhibitory factor, macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha, and chemokine (C-C) ligand 5. The epidermal gammadelta T cells produced significantly higher levels of interleukin-4, -8, -13, and macrophage inflammatory protein-1beta than the peripheral blood gammadelta T cells did. Notably, the epidermal gammadelta T cells produced several hundred-fold higher levels of interleukin-13 than interleukin-4.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that the epidermal gammadelta T cells have a stronger potential to participate in the Th2-type response than the peripheral blood gammadelta T cells do. Furthermore, epidermal gammadelta T cells might play an important role in the pathogenesis of Th2-dominant skin diseases because of their active production of interleukin-13.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Epidermis
Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor
Healthy Volunteers
Homeostasis
Humans
Inflammation
Interferon-gamma
Interleukin-13
Interleukin-2
Interleukin-4
Macrophages
Skin
Skin Diseases
T-Lymphocytes
Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor
Interferon-gamma
Interleukin-13
Interleukin-2
Interleukin-4
Figure
Reference
-
1. Komori HK, Meehan TF, Havran WL. Epithelial and mucosal gamma delta T cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 2006; 18:534–538.2. Toulon A, Breton L, Taylor KR, Tenenhaus M, Bhavsar D, Lanigan C, et al. A role for human skin-resident T cells in wound healing. J Exp Med. 2009; 206:743–750.
Article3. Havran WL, Chien YH, Allison JP. Recognition of self antigens by skin-derived T cells with invariant gamma delta antigen receptors. Science. 1991; 252:1430–1432.
Article4. Ferrarini M, Ferrero E, Dagna L, Poggi A, Zocchi MR. Human gammadelta T cells: a nonredundant system in the immune-surveillance against cancer. Trends Immunol. 2002; 23:14–18.
Article5. Ebert LM, Meuter S, Moser B. Homing and function of human skin gammadelta T cells and NK cells: relevance for tumor surveillance. J Immunol. 2006; 176:4331–4336.
Article6. Macleod AS, Havran WL. Functions of skin-resident γδ T cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011; 68:2399–2408.
Article7. Jameson J, Havran WL. Skin gammadelta T-cell functions in homeostasis and wound healing. Immunol Rev. 2007; 215:114–122.
Article8. Nestle FO, Di Meglio P, Qin JZ, Nickoloff BJ. Skin immune sentinels in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009; 9:679–691.
Article9. Girardi M. Immunosurveillance and immunoregulation by gammadelta T cells. J Invest Dermatol. 2006; 126:25–31.10. Urban EM, Chapoval AI, Pauza CD. Repertoire development and the control of cytotoxic/effector function in human gammadelta T cells. Clin Dev Immunol. 2010; 2010:732893.11. Hayday AC. [gamma][delta] cells: a right time and a right place for a conserved third way of protection. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000; 18:975–1026.
Article12. Carding SR, Egan PJ. Gammadelta T cells: functional plasticity and heterogeneity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002; 2:336–345.13. Groh V, Steinle A, Bauer S, Spies T. Recognition of stress-induced MHC molecules by intestinal epithelial gammadelta T cells. Science. 1998; 279:1737–1740.
Article14. Ferrarini M, Ferrero E, Dagna L, Poggi A, Zocchi MR. Human gammadelta T cells: a nonredundant system in the immune-surveillance against cancer. Trends Immunol. 2002; 23:14–18.
Article15. Matsue H, Cruz PD Jr, Bergstresser PR, Takashima A. Profiles of cytokine mRNA expressed by dendritic epidermal T cells in mice. J Invest Dermatol. 1993; 101:537–542.
Article16. Boismenu R, Feng L, Xia YY, Chang JC, Havran WL. Chemokine expression by intraepithelial gamma delta T cells. Implications for the recruitment of inflammatory cells to damaged epithelia. J Immunol. 1996; 157:985–992.17. Romagnani S. Regulation of the T cell response. Clin Exp Allergy. 2006; 36:1357–1366.
Article18. Taub D. Cytokine, growth factor, and chemokine ligand database. Current Protocols in Immunology. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.;2004. p. 6.29.1–6.29.89.19. Yang Y, Yoo HM, Choi I, Pyun KH, Byun SM, Ha H. Interleukin 4-induced proliferation in normal human keratinocytes is associated with c-myc gene expression and inhibited by genistein. J Invest Dermatol. 1996; 107:367–372.
Article20. Heinzmann A, Mao XQ, Akaiwa M, Kreomer RT, Gao PS, Ohshima K, et al. Genetic variants of IL-13 signalling and human asthma and atopy. Hum Mol Genet. 2000; 9:549–559.
Article21. Oh MH, Oh SY, Yu J, Myers AC, Leonard WJ, Liu YJ, et al. IL-13 induces skin fibrosis in atopic dermatitis by thymic stromal lymphopoietin. J Immunol. 2011; 186:7232–7242.
Article22. Novak N, Kruse S, Kraft S, Geiger E, Klüken H, Fimmers R, et al. Dichotomic nature of atopic dermatitis reflected by combined analysis of monocyte immunophenotyping and single nucleotide polymorphisms of the interleukin-4/interleukin-13 receptor gene: the dichotomy of extrinsic and intrinsic atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 2002; 119:870–875.
Article23. Hamid Q, Naseer T, Minshall EM, Song YL, Boguniewicz M, Leung DY. In vivo expression of IL-12 and IL-13 in atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996; 98:225–231.
Article24. Tazawa T, Sugiura H, Sugiura Y, Uehara M. Relative importance of IL-4 and IL-13 in lesional skin of atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol Res. 2004; 295:459–464.
Article25. Wańkowicz-Kalińska A, van den Wijngaard RM, Tigges BJ, Westerhof W, Ogg GS, Cerundolo V, et al. Immunopolarization of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells to Type-1-like is associated with melanocyte loss in human vitiligo. Lab Invest. 2003; 83:683–695.
Article26. Hamid Q, Boguniewicz M, Leung DY. Differential in situ cytokine gene expression in acute versus chronic atopic dermatitis. J Clin Invest. 1994; 94:870–876.
Article27. Hamid Q, Naseer T, Minshall EM, Song YL, Boguniewicz M, Leung DY. In vivo expression of IL-12 and IL-13 in atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996; 98:225–231.
Article28. Novak N, Kraft S, Bieber T. Unraveling the mission of FcepsilonRI on antigen-presenting cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 111:38–44.29. Akdis M, Akdis CA, Weigl L, Disch R, Blaser K. Skin-homing, CLA+ memory T cells are activated in atopic dermatitis and regulate IgE by an IL-13-dominated cytokine pattern: IgG4 counter-regulation by CLA-memory T cells. J Immunol. 1997; 159:4611–4619.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Corrigendum: Comparative Analysis of Human Epidermal and Peripheral Blood gammadelta T Cell Cytokine Profiles
- The Clinical Significance of gamma delta T lymphocytes with pleural tuberculosis
- Phenotypic and functional analysis of bovine gammadelta lymphocytes.
- Cloning a new allele form of bovine TNF-alpha
- Analysis of Cytokine Gene Expression in Thyroid Aspirates and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell and in vitro Production of Interferon - Gamma by Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell Culture