J Breast Cancer.
2016 Dec;19(4):372-384. 10.4048/jbc.2016.19.4.372.
Lipid Raft Integrity Is Required for Survival of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Cancer Biology Lab, Department of Biochemistry, GIS, GITAM University, Visakhapatnam, India. dr.rrmalla@gmail.com
- 2Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Andhra Medical College, Visakhapatnam, India.
- 3Department of Biochemistry, GITAM Institute of Science, GITAM University, Visakhapatnam, India.
- KMID: 2362923
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2016.19.4.372
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Lipid rafts are cholesterol enriched microdomains that colocalize signaling pathways involved in cell proliferation, metastasis, and angiogenesis. We examined the effect of methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MβCD)-mediated cholesterol extraction on the proliferation, adhesion, invasion, and angiogenesis of triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells.
METHODS
We measured cholesterol and estimated cell toxicity. Detergent resistant membrane (DRM) and non-DRM fractions were separated using the OptiPrep gradient method. Cell cycles stages were analyzed by flow cytometry, apoptosis was assessed using the TdT-mediated dUTP nick end-labeling assay, and metastasis was determined using a Matrigel invasion assay. Neo-vessel pattern and levels of angiogenic modulators were determined using an in vitro angiogenesis assay and an angiogenesis array, respectively.
RESULTS
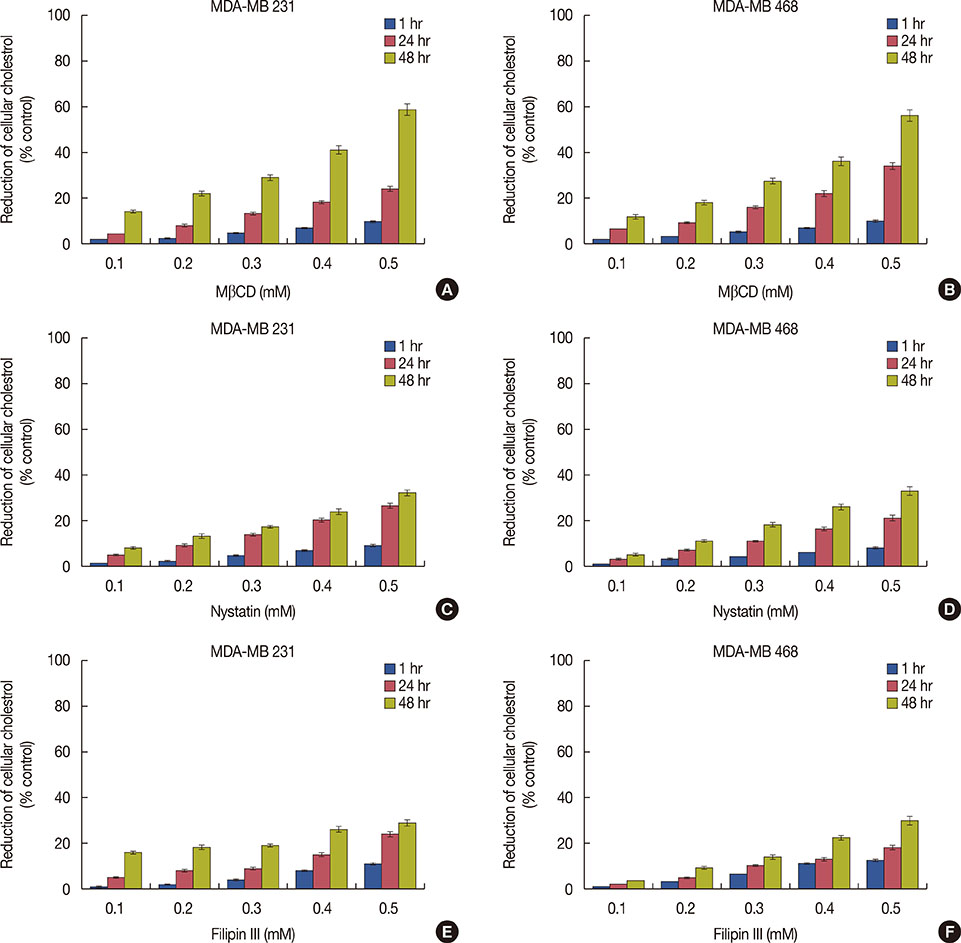
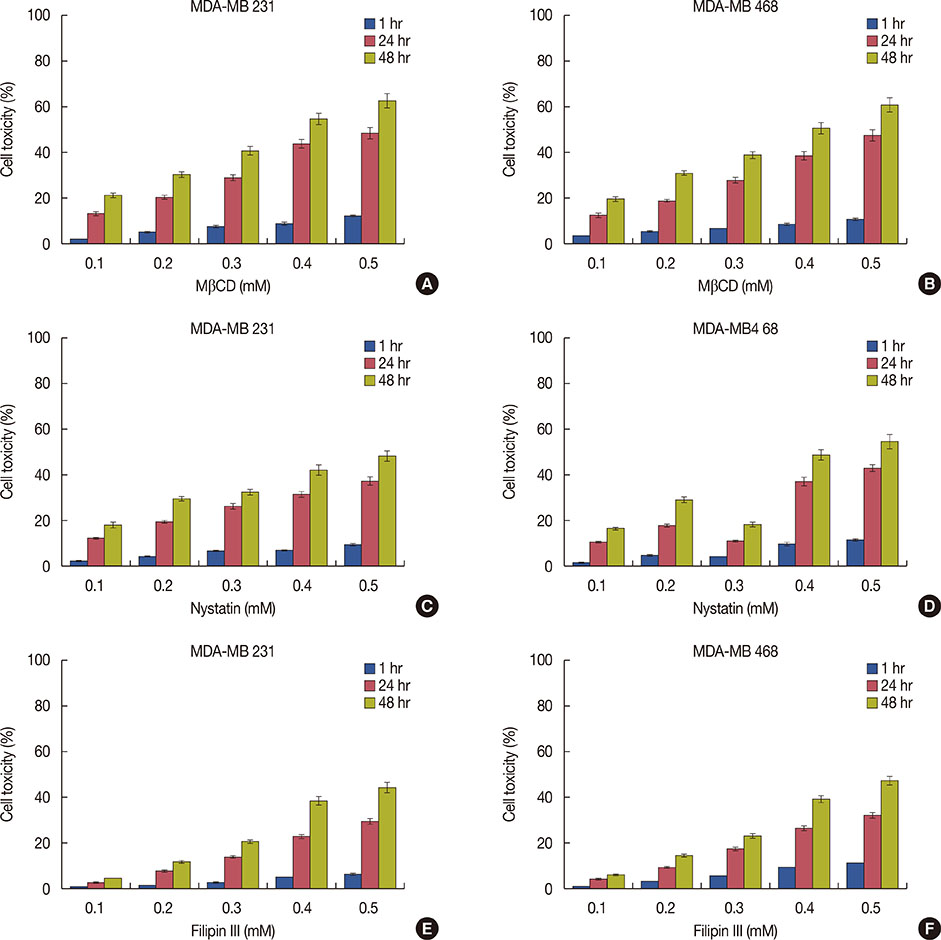
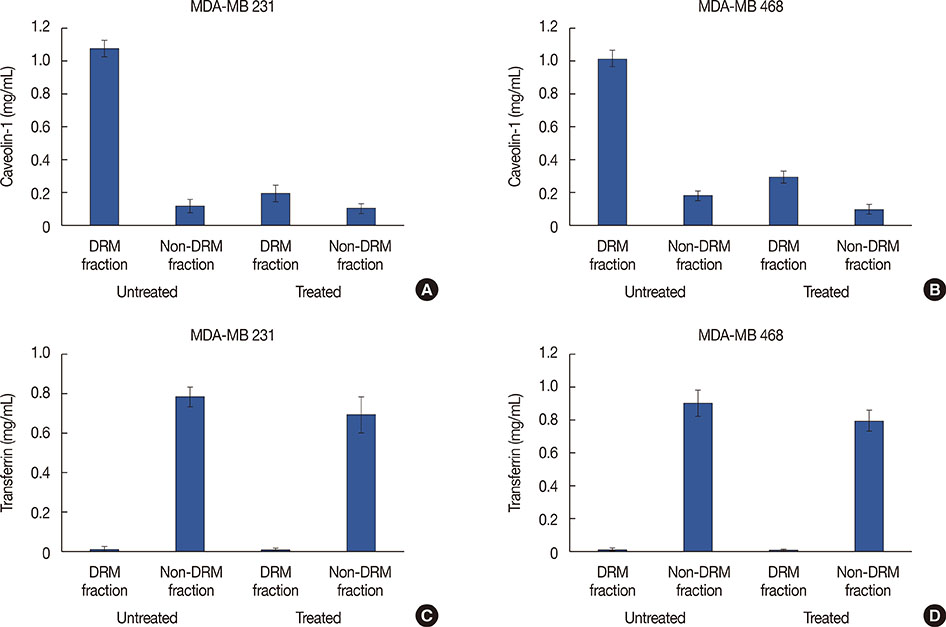
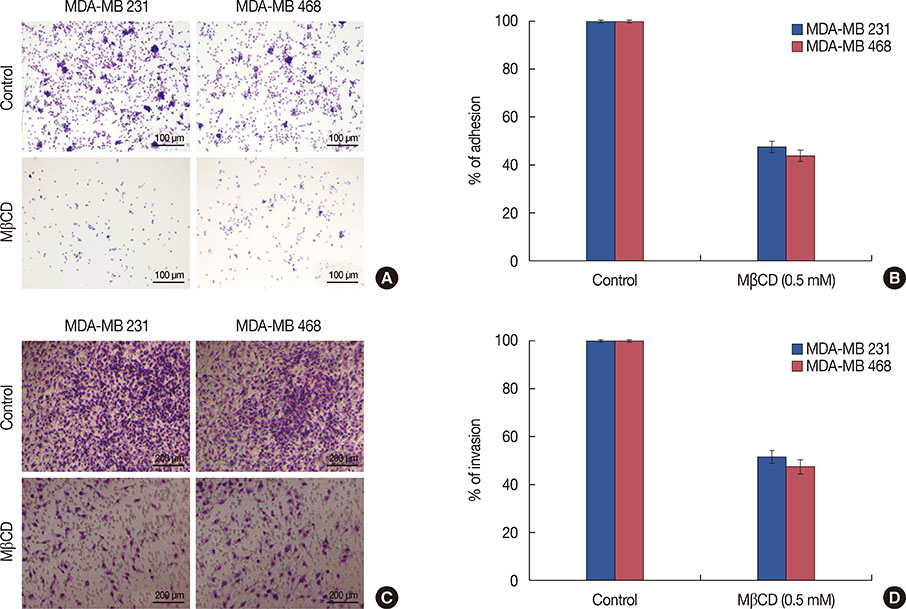
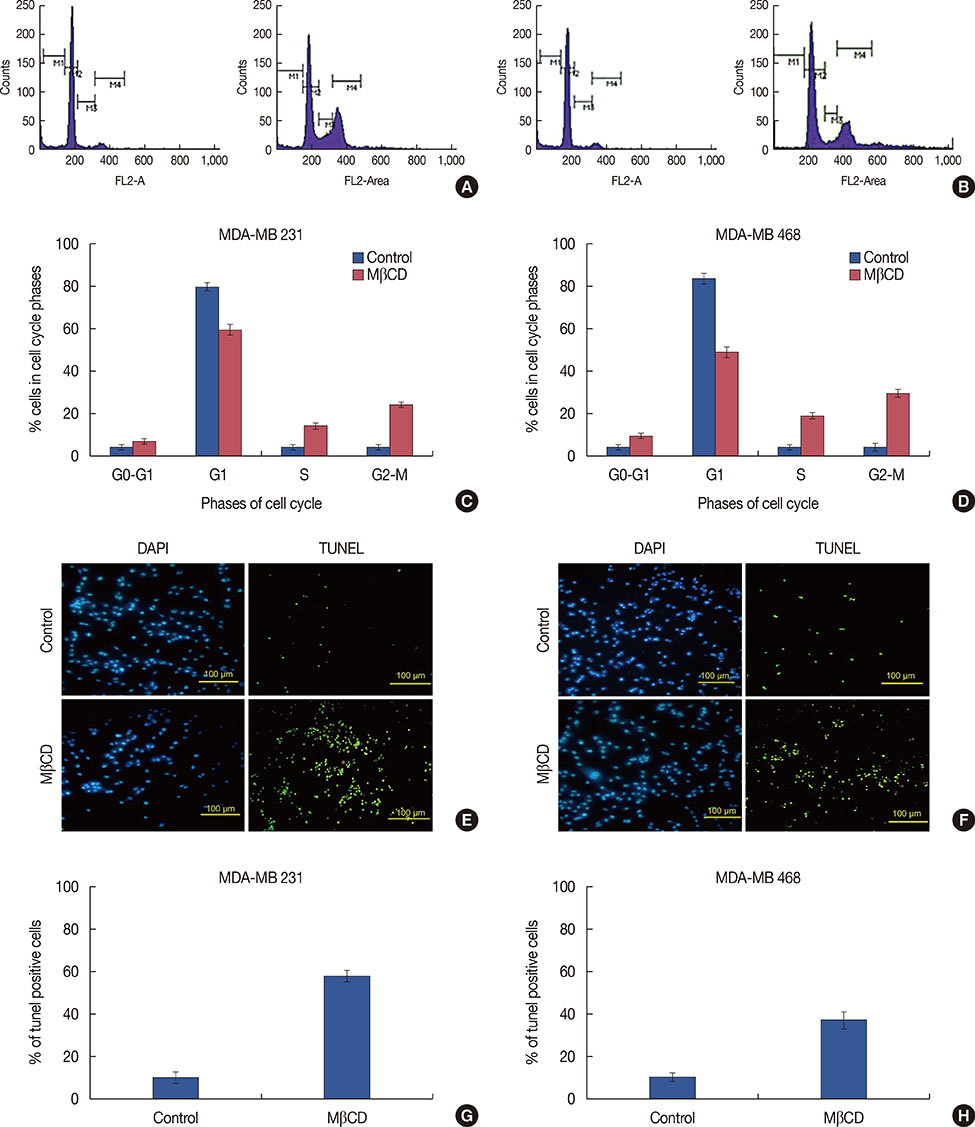
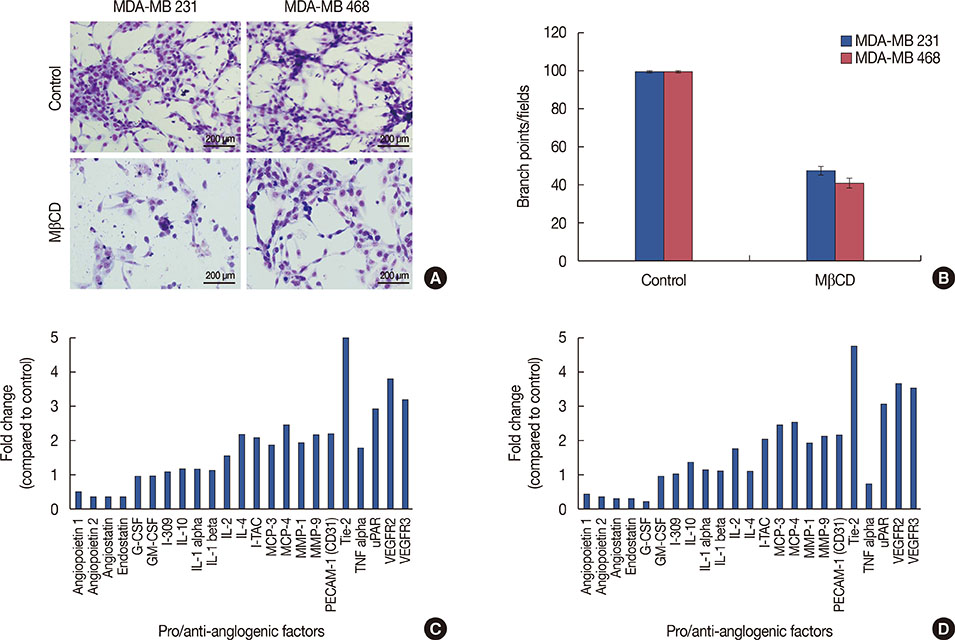
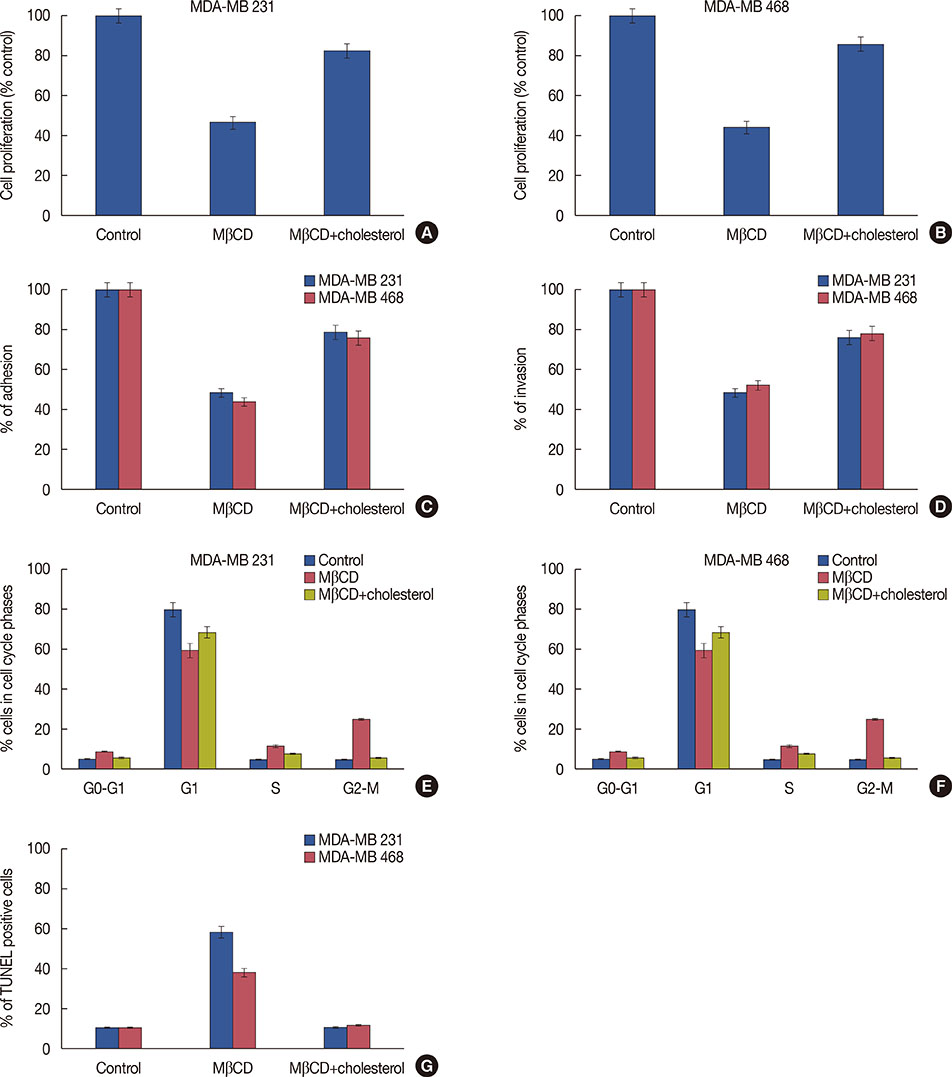
The present study found that the cholesterol-depleting agent MβCD, efficiently depleted membrane cholesterol and caused concentration dependent (0.1-0.5 mM) cytotoxicity compared to nystatin and filipin III in TNBC cell lines, MDA-MB 231 and MDA-MB 468. A reduced proportion of caveolin-1 found in DRM fractions indicated a cholesterol extraction-induced disruption of lipid raft integrity. MβCD inhibited 52% of MDA-MB 231 cell adhesion on fibronectin and 56% of MDA-MB 468 cell adhesion on vitronectin, while invasiveness of these cells was decreased by 48% and 52% respectively, following MβCD treatment (48 hours). MβCD also caused cell cycle arrest at the G2M phase and apoptosis in MDA-MB 231 cells (25% and 58% cells, respectively) and in MDA-MB 468 cells (30% and 38% cells, respectively). We found that MβCD treated cells caused a 52% and 58% depletion of neovessel formation in both MDA-MB 231 and MDA-MB 468 cell lines, respectively. This study also demonstrated that MβCD treatment caused a respective 2.6- and 2.5-fold depletion of tyrosine protein kinase receptor (TEK) receptor tyrosine kinase levels in both TNBC cell lines.
CONCLUSION
MβCD-induced cholesterol removal enhances alterations in lipid raft integrity, which reduces TNBC cell survival.
MeSH Terms
-
Apoptosis
Caveolin 1
Cell Adhesion
Cell Cycle
Cell Cycle Checkpoints
Cell Line
Cell Proliferation
Cell Survival
Cholesterol
Detergents
Fibronectins
Filipin
Flow Cytometry
In Vitro Techniques
Membrane Microdomains
Membranes
Methods
Neoplasm Metastasis
Nystatin
Protein-Tyrosine Kinases
Triple Negative Breast Neoplasms*
Vitronectin
Caveolin 1
Cholesterol
Detergents
Fibronectins
Filipin
Nystatin
Protein-Tyrosine Kinases
Vitronectin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Singer SJ, Nicolson GL. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972; 175:720–731.
Article2. Simons K, Ikonen E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature. 1997; 387:569–572.
Article3. Mollinedo F, Gajate C. Lipid rafts as major platforms for signaling regulation in cancer. Adv Biol Regul. 2015; 57:130–146.
Article4. Staubach S, Hanisch FG. Lipid rafts: signaling and sorting platforms of cells and their roles in cancer. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2011; 8:263–277.
Article5. Maxfield FR. Plasma membrane microdomains. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002; 14:483–487.
Article6. Simons K, Toomre D. Lipid rafts and signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000; 1:31–39.
Article7. Pike LJ. Lipid rafts: bringing order to chaos. J Lipid Res. 2003; 44:655–667.
Article8. Li YC, Park MJ, Ye SK, Kim CW, Kim YN. Elevated levels of cholesterol-rich lipid rafts in cancer cells are correlated with apoptosis sensitivity induced by cholesterol-depleting agents. Am J Pathol. 2006; 168:1107–1118.
Article9. Zhang Q, Wakelam MJ. Lipidomics in the analysis of malignancy. Adv Biol Regul. 2014; 54:93–98.
Article10. Caliceti C, Zambonin L, Rizzo B, Fiorentini D, Vieceli Dalla Sega F, Hrelia S, et al. Role of plasma membrane caveolae/lipid rafts in VEGF-induced redox signaling in human leukemia cells. Biomed Res Int. 2014; 2014:857504.
Article11. Zhuang L, Lin J, Lu ML, Solomon KR, Freeman MR. Cholesterol-rich lipid rafts mediate akt-regulated survival in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2002; 62:2227–2231.12. Marcella SW, David A, Ohman-Strickland PA, Carson J, Rhoads GG. Statin use and fatal prostate cancer: a matched case-control study. Cancer. 2012; 118:4046–4052.13. Fang L, Miller YI. Targeted cholesterol efflux. Cell Cycle. 2013; 12:3345–3346.
Article14. George KS, Wu S. Lipid raft: a floating island of death or survival. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012; 259:311–319.
Article15. Ohtani Y, Irie T, Uekama K, Fukunaga K, Pitha J. Differential effects of alpha-, beta- and gamma-cyclodextrins on human erythrocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1989; 186:17–22.
Article16. Zidovetzki R, Levitan I. Use of cyclodextrins to manipulate plasma membrane cholesterol content: evidence, misconceptions and control strategies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007; 1768:1311–1324.
Article17. Bang B, Gniadecki R, Gajkowska B. Disruption of lipid rafts causes apoptotic cell death in HaCaT keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol. 2005; 14:266–272.
Article18. Pucadyil TJ, Shrivastava S, Chattopadhyay A. The sterol-binding antibiotic nystatin differentially modulates ligand binding of the bovine hippocampal serotonin1A receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004; 320:557–562.
Article19. Raghu H, Sodadasu PK, Malla RR, Gondi CS, Estes N, Rao JS. Localization of uPAR and MMP-9 in lipid rafts is critical for migration, invasion and angiogenesis in human breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 2010; 10:647.
Article20. Malla R, Gopinath S, Alapati K, Gondi CS, Gujrati M, Dinh DH, et al. Downregulation of uPAR and cathepsin B induces apoptosis via regulation of Bcl-2 and Bax and inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway in gliomas. PLoS One. 2010; 5:e13731.
Article21. Rao Malla R, Gopinath S, Alapati K, Gorantla B, Gondi CS, Rao JS. Knockdown of cathepsin B and uPAR inhibits CD151 and α3β1 integrin-mediated cell adhesion and invasion in glioma. Mol Carcinog. 2013; 52:777–790.
Article22. Malla RR, Gopinath S, Gondi CS, Alapati K, Dinh DH, Gujrati M, et al. Cathepsin B and uPAR knockdown inhibits tumor-induced angiogenesis by modulating VEGF expression in glioma. Cancer Gene Ther. 2011; 18:419–434.
Article23. Rao Malla R, Raghu H, Rao JS. Regulation of NADPH oxidase (Nox2) by lipid rafts in breast carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 2010; 37:1483–1493.
Article24. Mohammad N, Malvi P, Meena AS, Singh SV, Chaube B, Vannuruswamy G, et al. Cholesterol depletion by methyl-β-cyclodextrin augments tamoxifen induced cell death by enhancing its uptake in melanoma. Mol Cancer. 2014; 13:204.
Article25. Grossmann J. Molecular mechanisms of “detachment-induced apoptosis: Anoikis”. Apoptosis. 2002; 7:247–260.26. Ghibelli L, Grzanka A. Organelle cross-talk in apoptotic and survival pathways. Int J Cell Biol. 2012; 2012:968586.
Article27. Cheung KJ, Gabrielson E, Werb Z, Ewald AJ. Collective invasion in breast cancer requires a conserved basal epithelial program. Cell. 2013; 155:1639–1651.
Article28. Longatto Filho A, Lopes JM, Schmitt FC. Angiogenesis and breast cancer. J Oncol. 2010; 2010:576384.
Article29. Peters KG, Coogan A, Berry D, Marks J, Iglehart JD, Kontos CD, et al. Expression of Tie2/Tek in breast tumour vasculature provides a new marker for evaluation of tumour angiogenesis. Br J Cancer. 1998; 77:51–56.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis of Early Stage Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Comparison with Non-triple Negative Group
- Treatment Outcomes of Weakly Positive Hormone Receptor Breast Cancer and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Fear of Cancer Recurrence and Unmet Needs in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Survivors
- Bilateral Triple-Negative Invasive Breast Cancer with a BRCA2 Mutation, and Glioblastoma: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Overexpression of Cell Cycle Progression Inhibitor Geminin is Associated with Tumor Stem-Like Phenotype of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer