J Vet Sci.
2015 Sep;16(3):297-306. 10.4142/jvs.2015.16.3.297.
Cadmium induces apoptosis in primary rat osteoblasts through caspase and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Veterinary Medicine, Yangzhou University, and Jiangsu Co-innovation Center for Prevention and Control of Important Animal Infectious Diseases and Zoonoses, Yangzhou 225009, China. liuzongping@yzu.edu.cn
- KMID: 2344302
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2015.16.3.297
Abstract
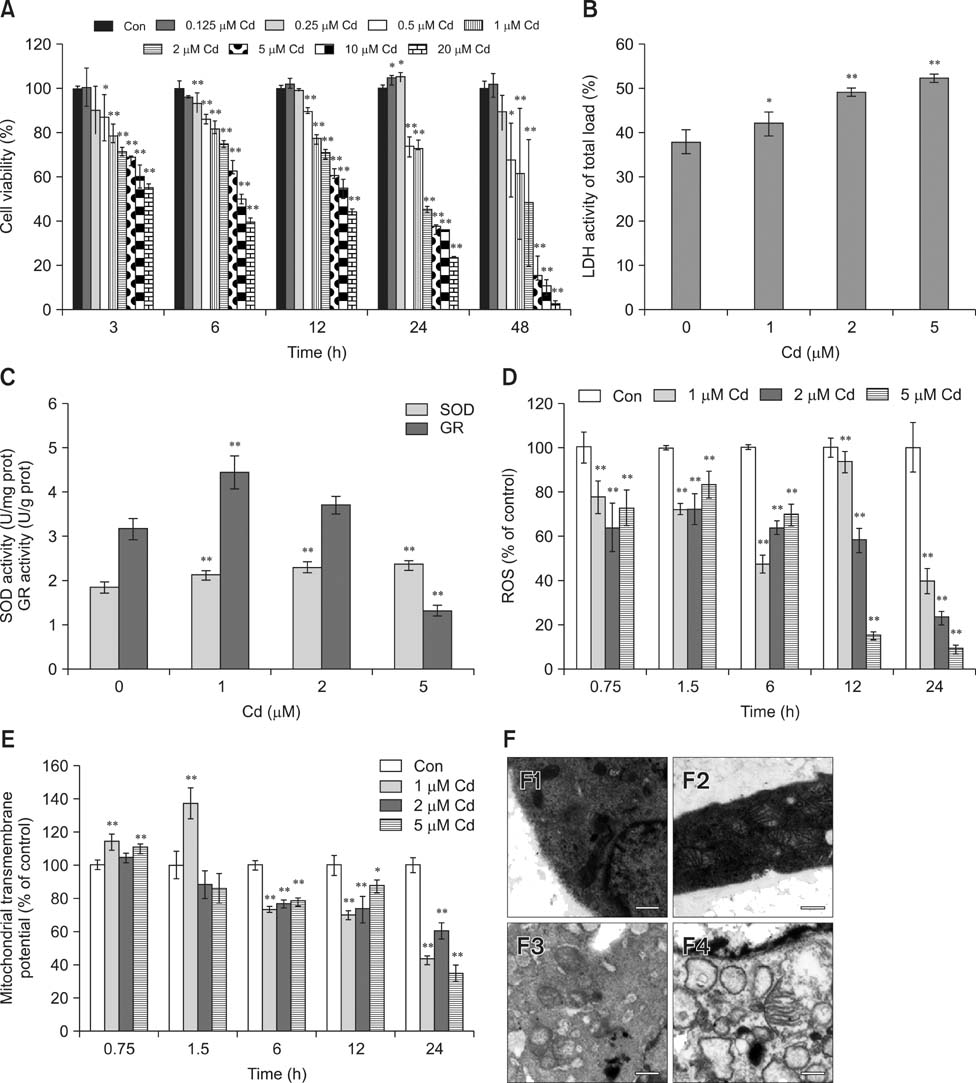
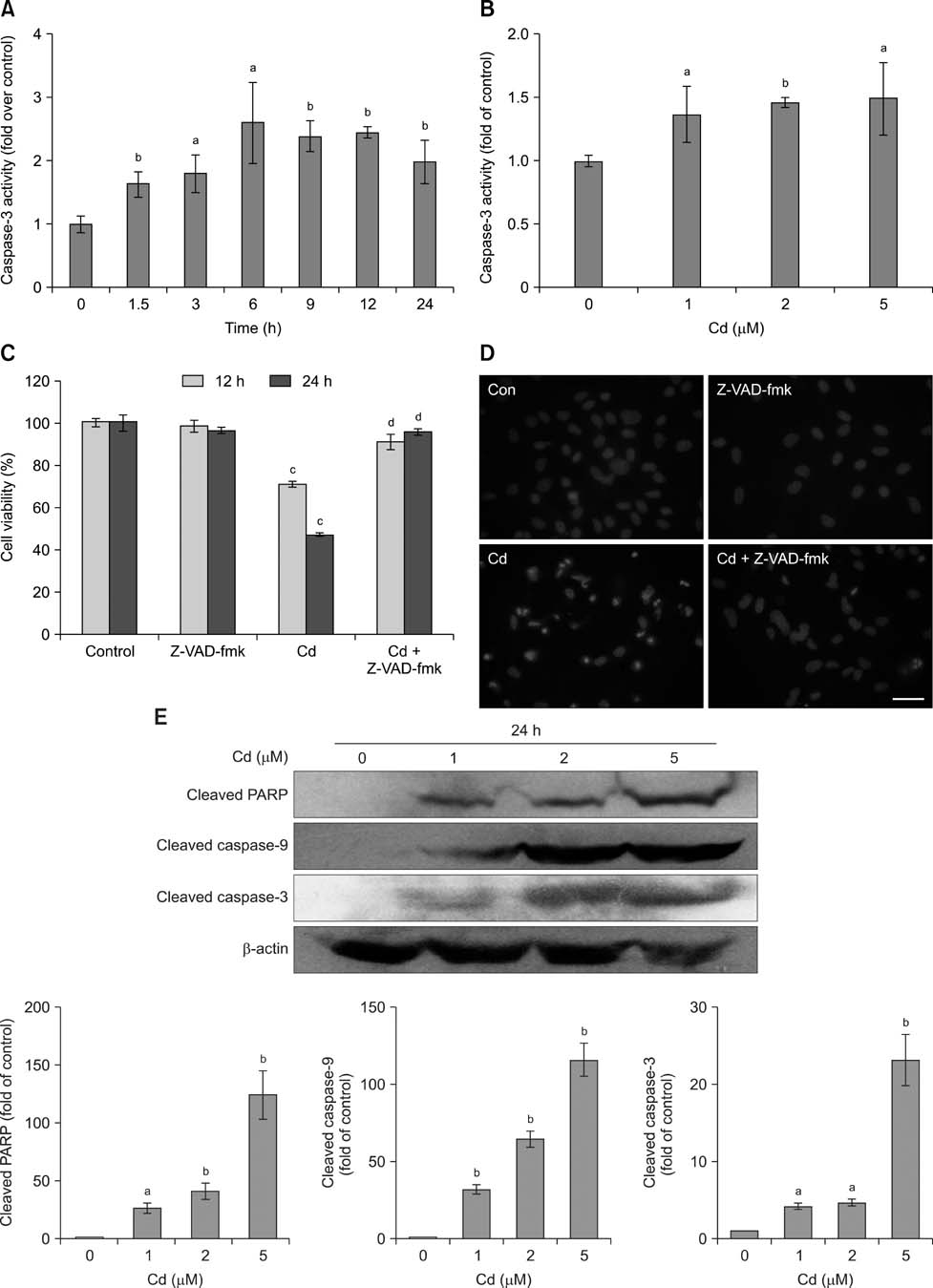
- Exposure to cadmium (Cd) induces apoptosis in osteoblasts (OBs); however, little information is available regarding the specific mechanisms of Cd-induced primary rat OB apoptosis. In this study, Cd reduced cell viability, damaged cell membranes and induced apoptosis in OBs. We observed decreased mitochondrial transmembrane potentials, ultrastructure collapse, enhanced caspase-3 activity, and increased concentrations of cleaved PARP, cleaved caspase-9 and cleaved caspase-3 following Cd treatment. Cd also increased the phosphorylation of p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK)1/2 and c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) in OBs. Pretreatment with the caspase inhibitor, N-benzyloxycarbonyl-Val-Ala-Asp-fluoromethylketone, ERK1/2 inhibitor (U0126), p38 inhibitor (SB203580) and JNK inhibitor (SP600125) abrogated Cd-induced cell apoptosis. Furthermore, Cd-treated OBs exhibited signs of oxidative stress protection, including increased antioxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase and glutathione reductase levels and decreased formation of reactive oxygen species. Taken together, the results of our study clarified that Cd has direct cytotoxic effects on OBs, which are mediated by caspase- and MAPK pathways in Cd-induced apoptosis of OBs.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Apoptosis/*drug effects
Cadmium/*toxicity
Caspases/metabolism
Environmental Pollutants/*toxicity
Osteoblasts/*drug effects/metabolism
Oxidative Stress/drug effects
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases/metabolism
Cadmium
Caspases
Environmental Pollutants
p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Figure
Reference
-
1. Agency for Toxic Substance and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological profile for Cadmium. Toxicological profile for Cadmium. Atlanta: Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service (US);2005.2. Angle CR, Thomas DJ, Swanson SA. Osteotoxicity of cadmium and lead in HOS TE 85 and ROS 17/2.8 cells: relation to metallothionein induction and mitochondrial binding. Biometals. 1993; 6:179–184.
Article3. Arbon KS, Christensen CM, Harvey WA, Heggland SJ. Cadmium exposure activates the ERK signaling pathway leading to altered osteoblast gene expression and apoptotic death in Saos-2 cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 2012; 50:198–205.
Article4. Bertin G, Averbeck D. Cadmium: cellular effects, modifications of biomolecules, modulation of DNA repair and genotoxic consequences (a review). Biochimie. 2006; 88:1549–1559.
Article5. Boutros T, Chevet E, Metrakos P. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase/MAP kinase phosphatase regulation: roles in cell growth, death, and cancer. Pharmacol Rev. 2008; 60:261–310.
Article6. Brama M, Politi L, Santini P, Migliaccio S, Scandurra R. Cadmium-induced apoptosis and necrosis in human osteoblasts: role of caspases and mitogen-activated protein kinases pathways. J Endocrinol Invest. 2012; 35:198–208.7. Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X, Wang X. Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1999; 15:269–290.
Article8. Chang KC, Hsu CC, Liu SH, Su CC, Yen CC, Lee MJ, Chen KL, Ho TJ, Hung DZ, Wu CC, Lu TH, Su YC, Chen YW, Huang CF. Cadmium induces apoptosis in pancreatic β-cells through a mitochondria-dependent pathway: the role of oxidative stress-mediated c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation. PLoS One. 2013; 8:54374.
Article9. Chen L, Liu L, Huang S. Cadmium activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway via induction of reactive oxygen species and inhibition of protein phosphatases 2A and 5. Free Radic Biol Med. 2008; 45:1035–1044.
Article10. Chen X, Zhu G, Gu S, Jin T, Shao C. Effects of cadmium on osteoblasts and osteoclasts in vitro. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2009; 28:232–236.11. Chen X, Zhu G, Jin T, Zhou Z, Gu S, Qiu J, Xiao H. Cadmium stimulates the osteoclastic differentiation of RAW264.7 cells in presence of osteoblasts. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2012; 146:349–353.
Article12. Coonse KG, Coonts AJ, Morrison EV, Heggland SJ. Cadmium induces apoptosis in the human osteoblast-like cell line Saos-2. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2007; 70:575–581.
Article13. Cuypers A, Plusquin M, Remans T, Jozefczak M, Keunen E, Gielen H, Opdenakker K, Nair AR, Munters E, Artois TJ, Nawrot T, Vangronsveld J, Smeets K. Cadmium stress: an oxidative challenge. Biometals. 2010; 23:927–940.
Article14. Ikediobi CO, Badisa VL, Ayuk-Takem LT, Latinwo LM, West J. Response of antioxidant enzymes and redox metabolites to cadmium-induced oxidative stress in CRL-1439 normal rat liver cells. Int J Mol Med. 2004; 14:87–92.
Article15. Iryo Y, Matsuoka M, Wispriyono B, Sugiura T, Igisu H. Involvement of the extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) pathway in the induction of apoptosis by cadmium chloride in CCRF-CEM cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000; 60:1875–1882.
Article16. Junttila MR, Li SP, Westermarck J. Phosphatase-mediated crosstalk between MAPK signaling pathways in the regulation of cell survival. FASEB J. 2008; 22:954–965.
Article17. Kjellström T. Mechanism and epidemiology of bone effects of cadmium. IARC Sci Publ. 1992; 301–310.18. Låg M, Refsnes M, Lilleaas EM, Holme JA, Becher R, Schwarze PE. Role of mitogen activated protein kinases and protein kinase C in cadmium-induced apoptosis of primary epithelial lung cells. Toxicology. 2005; 211:253–264.
Article19. Liu J, Kadiiska MB, Corton JC, Qu W, Waalkes MP, Mason RP, Liu Y, Klaassen CD. Acute cadmium exposure induces stress-related gene expression in wild-type and metallothionein-I/II-null mice. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002; 32:525–535.
Article20. Liu J, Qu W, Kadiiska MB. Role of oxidative stress in cadmium toxicity and carcinogenesis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009; 238:209–214.
Article21. Liu Y, Templeton DM. Initiation of caspase-independent death in mouse mesangial cells by Cd2+: involvement of p38 kinase and CaMK-II. J Cell Physiol. 2008; 217:307–318.
Article22. Martin P, Poggi MC, Chambard JC, Boulukos KE, Pognonec P. Low dose cadmium poisoning results in sustained ERK phosphorylation and caspase activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006; 350:803–807.
Article23. Oda N, Sogawa CA, Sogawa N, Onodera K, Furuta H, Yamamoto T. Metallothionein expression and localization in rat bone tissue after cadmium injection. Toxicol Lett. 2001; 123:143–150.
Article24. Ola MS, Nawaz M, Ahsan H. Role of Bcl-2 family proteins and caspases in the regulation of apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011; 351:41–58.
Article25. Papadakis ES, Finegan KG, Wang X, Robinson AC, Guo C, Kayahara M, Tournier C. The regulation of Bax by c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase (JNK) is a prerequisite to the mitochondrial-induced apoptotic pathway. FEBS Lett. 2006; 580:1320–1326.
Article26. Pathak N, Mitra S, Khandelwal S. Cadmium induces thymocyte apoptosis via caspase-dependent and caspase-independent pathways. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2013; 27:193–203.
Article27. Petanidis S, Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M, Salifoglou A. Cadmium modulates H-ras expression and caspase-3 apoptotic cell death in breast cancer epithelial MCF-7 cells. J Inorg Biochem. 2013; 121:100–107.
Article28. Porter AG, Jänicke RU. Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1999; 6:99–104.
Article29. Pourahmad J, O'Brien PJ, Jokar F, Daraei B. Carcinogenic metal induced sites of reactive oxygen species formation in hepatocytes. Toxicol In Vitro. 2003; 17:803–810.
Article30. Regunathan A, Glesne DA, Wilson AK, Song J, Nicolae D, Flores T, Bhattacharyya MH. Microarray analysis of changes in bone cell gene expression early after cadmium gavage in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2003; 191:272–293.
Article31. Stinson LJ, Darmon AJ, Dagnino L, D'Souza SJ. Delayed apoptosis post-cadmium injury in renal proximal tubule epithelial cells. Am J Nephrol. 2003; 23:27–37.
Article32. Thévenod F. Cadmium and cellular signaling cascades: to be or not to be? Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009; 238:221–239.
Article33. Thijssen S, Cuypers A, Maringwa J, Smeets K, Horemans N, Lambrichts I, Van Kerkhove E. Low cadmium exposure triggers a biphasic oxidative stress response in mice kidneys. Toxicology. 2007; 236:29–41.
Article34. Vander Heiden MG, Chandel NS, Li XX, Schumacker PT, Colombini M, Thompson CB. Outer mitochondrial membrane permeability can regulate coupled respiration and cell survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000; 97:4666–4671.
Article35. Weber LP, Kiparissis Y, Hwang GS, Niimi AJ, Janz DM, Metcalfe CD. Increased cellular apoptosis after chronic aqueous exposure to nonylphenol and quercetin in adult medaka (Oryzias latipes). Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2002; 131:51–59.
Article36. Xing L, Boyce BF. Regulation of apoptosis in osteoclasts and osteoblastic cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005; 328:709–720.
Article37. Xu J, Zhou M, Ouyang J, Wang J, Zhang Q, Xu Y, Xu Y, Zhang Q, Xu X, Zeng H. Gambogic acid induces mitochondria-dependent apoptosis by modulation of Bcl-2 and Bax in mantle cell lymphoma JeKo-1 cells. Chin J Cancer Res. 2013; 25:183–191.38. Yamamoto T, Hsu S, Lewis J, Wataha J, Dickinson D, Singh B, Bollag WB, Lockwood P, Ueta E, Osaki T, Schuster G. Green tea polyphenol causes differential oxidative environments in tumor versus normal epithelial cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003; 307:230–236.
Article39. Yang LY, Wu KH, Chiu WT, Wang SH, Shih CM. The cadmium-induced death of mesangial cells results in nephrotoxicity. Autophagy. 2009; 5:571–572.
Article40. Zhang Y, Jiang C, Wang J, Yuan Y, Gu J, Bian J, Liu X, Liu Z. Oxidative stress and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways involved in cadmium-induced BRL 3A cell apoptosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013; 2013:516051.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of p-38 MAP Kinase in apoptosis of hypoxia-induced osteoblasts
- Induction of Apoptosis by Heavy Metals in HL-60 Cells
- Cadmium-induced Apoptosis in HL-60 Cells Via Signal Transduction
- Dexamethasone Induces Apoptosis of Nasal Polyp-Derived Tissue Cultures Through JNK and p38 MAPK Activation
- PDTC Inhibits TNF-alpha-Induced Apoptosis in MC3T3E1 Cells