J Korean Acad Nurs Adm.
2016 Jun;22(3):292-302. 10.11111/jkana.2016.22.3.292.
A Structural Model of Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention: Focusing on Organizational Characteristics, Job Satisfaction, and Job Embeddedness
- Affiliations
-
- 1Dankook University Hospital, Korea.
- 2College of Nursing, Dankook University, Korea. jongkimk@dankook.ac.kr
- KMID: 2326657
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11111/jkana.2016.22.3.292
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was done to build and verify a model of clinical nurses' turnover intention using organizational characteristics, job satisfaction and job embeddedness.
METHODS
The study participants were 389 hospital nurses. SPSS and AMOS 22.0 program were used to analyze the data and the modeling of turnover intention.
RESULTS
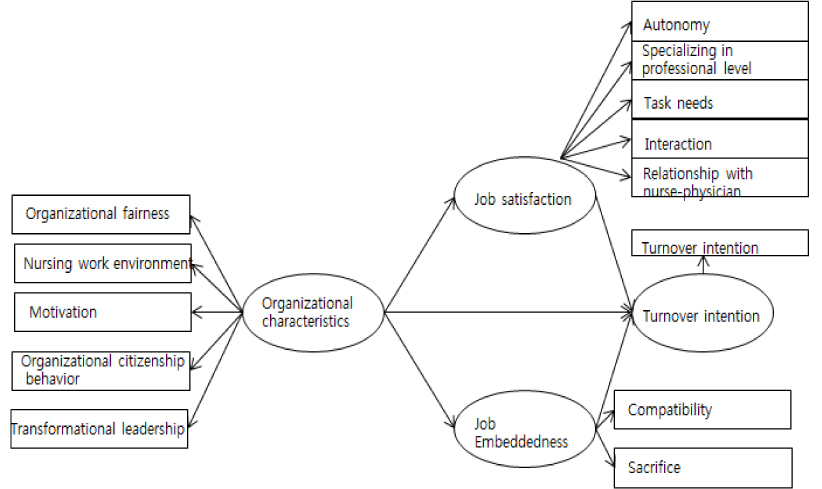
A total of 41% of turnover intention was explained by job satisfaction, job embeddedness and organizational characteristics. Nurses with higher job satisfaction and job embeddedness showed lower turnover intention, while organizational characteristics had an indirect effect on their turnover intention. It was found that organizational characteristics had positive effects on both job satisfaction and job embeddedness, and job embeddedness played a mediating role between organizational characteristics and turnover intention.
CONCLUSION
To reduce nurses' turnover intention, hospitals' organizational characteristics should be considered. Nurse managers should strive to increase nurses' job satisfaction and job embeddedness through an understanding of the factors of organizational characteristics such as organizational fairness, nursing work environment, motivation, organizational citizenship behavior, and transformational leadership.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Influence of Resilience and Job Embeddedness on Turnover Intention in General Hospital Nurses
Kyoung Ja Ko, Soo-Kyoung Lee
J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2019;25(4):362-372. doi: 10.11111/jkana.2019.25.4.362.Effects of Job Demand and Recovery Experience from Job Stress on Job Embeddedness among Workers in the Service Industry
So Yeun Jun, Youn Hyang Lee, Eun Kyung Choi
J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2018;29(2):143-154. doi: 10.12799/jkachn.2018.29.2.143.
Reference
-
1. Moon SJ, Han SS. A predictive model on turnover intention of nurses in Korea. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2011; 41(5):633–641. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2011.41.5.633.2. Yoo SJ, Choi YH. Predictive factors influencing turnover intention of nurses in small and medium-sized hospitals in Daegu city. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2009; 15(1):16–25.3. Kim JK, Kim MJ. A review of research on hospital nurses' turnover intention. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2011; 17(4):538–550. DOI: 10.11111/jkana.2011.17.4.538.4. Park SK, Cho KM, Jwa YK, Yi YJ. Survey of status on nursing activities. Osong: Korea Health Industry Development Institute;2014.5. Chang HT, Chi NW, Miao MC. Testing the relationship between three-component organizational/occupational commitment and organizational/occupational turnover intention using a non-recursive model. J Vocat Behav. 2007; 70(2):352–368. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvb.2006.10.001.6. Cho YK. A structural equation model on new graduate nurses' turnover intentions and turnover [dissertation]. Seoul: Ewha Womans University;2013.7. Price JL, Mueller CW. A causal model of turnover for nurses. Acad Manage J. 1981; 24(3):543–565. DOI: 10.2307/255574.8. Lee YJ, Kim SH, Lee TW. Effects of job characteristics, organizational culture on job satisfaction and turnover intention in public institution nurses. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2015; 21(4):354–365. DOI: 10.11111/jkana.2015.21.4.354.9. Lee SM. The impact of organizational and individual characteristics on outcome variables. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2007; 13(2):156–166.10. Yom YH. The effects of organizational justice and dispositional affectivity on job satisfaction and intent to leave among nurses. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2010; 16(3):276–285. DOI: 10.11111/jkana.2010.16.3.276.11. Ha HI. The influence of nursing manager's transformational leadership to the job satisfaction and turnover intentions of nurses: nursing unit characteristics [master's thesis]. Seoul: Konkuk University;2012.12. Lee YS, Park SH, Kim JK. A study on relationship among organizational fairness, motivation, job satisfaction, intention to stay of nurses. J Korea Contents Assoc. 2014; 14(10):596–609.13. Kim EH, Lee E, Choi HJ. Mediation effect of organizational citizenship behavior between job embeddedness and turnover intention in hospital nurses. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2012; 18(4):394–401. DOI: 10.11111/jkana.2012.18.4.394.14. Kwon JO, Kim EY. Impact of unit-level nurse practice environment on nurse turnover intention in the small and medium sized hospitals. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2012; 18(4):414–423. DOI: 10.11111/jkana.2012.18.4.414.15. Mitchell TR, Holtom BC, Lee TW, Sablynski CJ, Erez M. Why people stay: using job embeddedness to predict voluntary turnover. Acad Manage J. 2001; 44(6):1102–1121. DOI: 10.2307/3069391.16. Benner P. From novice to expert. Am J Nurs. 1982; 82(3):402–407.17. Anderson JC, Gerbing DW. Structural equation modeling in practice: A review and recommended two-step approach. Psychol Bull. 1988; 103(3):411–423. DOI: 10.1037/0033-2909.103.3.411.18. Lim JS. A study of influences of fairness perception on perceived organizational support, organizational commitment and organizational citizenship behavior: the emphasis on the comparison between profit and non-profit organizations [dissertation]. Gangneung: Kangnung National University;2008.19. Lake ET. Development of the practice environment scale of the Nursing Work Index. Res Nurs Health. 2002; 25(3):176–188. DOI: 10.1002/nur.10032.20. Cho E, Choi M, Kim EY, Yoo IY, Lee NJ. Construct validity and reliability of the Korean version of the practice environment scale of nursing work index for Korean nurses. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2011; 41(3):325–332. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2011.41.3.325.21. Kim IJ. Empirical study on the motivation of nurses: focusing on Herzberg's two factor theory [master's thesis]. Seoul: Hanyang University;1994.22. Lim JY. A study of the effects of motivation-hygiene factors on nurse's job satisfaction organizational commitment, and organizational identification. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2005; 11(3):1–19.23. Podsakoff PM, MacKenzie SB, Moorman RH, Fetter R. Transformational leader behaviors and their effects on followers' trust in leader, satisfaction, and organizational citizenship behaviors. Leadersh Q. 1990; 1(2):107–142. DOI: 10.1016/1048-9843(90)90009-7.24. Lee ES. The effects of perioperative nurse's personal & job characteristics on organizational citizenship behaviors [master's thesis]. Seoul: Hanyang University;2014.25. Bass BM, Avolio BJ. MLQ, Multifactor Leadership Questionnaire. Palo Alto, CA: Mind Garden;1995.26. Kim MJ. The effect of the transformational and transactional leadership on the organizational commitment: Mediating effect of emotional intelligence [master's thesis]. Seoul: Seoul National University;2014.27. Stamps PL, Piedmont EB, Slavitt DB, Haase AM. Measurement of work satisfaction among health professionals. Med Care. 1978; 16(4):337–352.28. Jang HS. Effect of communication satisfaction in relationship between job stress and job satisfaction among nurses in hospitals [master's thesis]. Gongju: Kongju National University;2009.29. Kim JS. The effect of job embeddedness on organizational citizenship behavior: moderating effect of authentic leadership and type of enterprise [dissertation]. Daejeon: Daejeon University;2014.30. Mobley WH. Employee turnover, causes, consequences, and control. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley;1982.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Self-efficacy, Career Plateau, Job Embeddedness, and Organizational Commitment on the Turnover Intention of Nurses
- Effect of Job Embeddedness and Job Satisfaction on Turnover Intention in Nurses
- Mediation Effect of Organizational Citizenship Behavior between Job Embeddedness and Turnover Intention in Hospital Nurses
- Relationships among Burnout, Job Satisfaction, Organizational Commitment and Turnover Intention to Resign in Hospital Nurses
- Influence of Job Embeddedness Factors on Turnover Intention of Nurses in Small and Medium Sized General Hospitals