World J Mens Health.
2013 Dec;31(3):239-246.
The Effect of Anthocyanin on the Prostate in an Andropause Animal Model: Rapid Prostatic Cell Death by Apoptosis Is Partially Prevented by Anthocyanin Supplementation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ksw1227@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Health Promotion Center, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Korea BioMedical Science Institute, Seoul, Korea.
- 4The Catholic Agro-Medical Center, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Urology, Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the anti-apoptotic effect of the antioxidant reaction of anthocyanin on the prostate in an andropause animal model.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
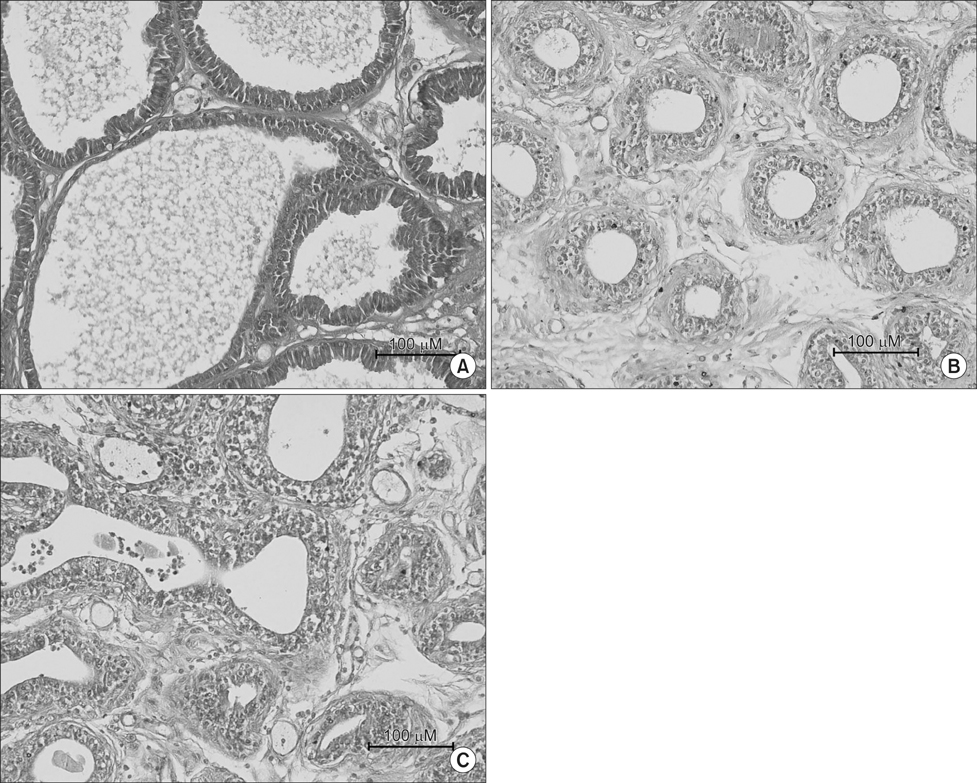
Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into three groups (n=12 in each): control (Group I), andropause (Group II), andropause treated with anthocyanin (Group III). For induction of andropause, Group II and III underwent bilateral orchiectomy. Group III was treated with daily oral anthocyanin (160 mg/kg) for 8 weeks. After 8 weeks, the rats were sacrificed and their blood and prostates were examined pathohistologically and evaluated for oxidative stress and apoptosis. Oxidative stress was assessed by the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and apoptosis in the prostate was identified by terminal deoxyribonucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-digoxigenin nick end-labelling assay.
RESULTS
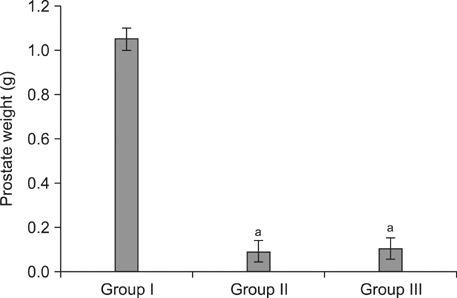
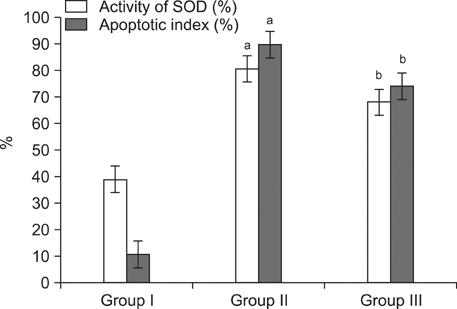
Group II showed markedly increased activity of SOD in serum over that observed in Group I, whereas the rats in Group III showed reduced oxidative stress compared to Group II. Despite no significant differences in prostate weight between Group II and III (p=0.078), the apoptotic index was significantly greater in Group II than Group I, and was significantly lesser in Group III than Group II.
CONCLUSIONS
We suggest that the oxidative stress caused by low testosterone may be another inducer of apoptosis, and this apoptosis may partly contribute to the overall apoptosis of the prostate in the andropause animal model. Therefore, anthocyanin supplementation may contribute to preventing excessively rapid cell death by apoptosis in the prostate in an animal model of andropause.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Arias E. United States life tables, 2007. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2011; 59:1–60.2. Schubert M, Jockenhövel F. Late-onset hypogonadism in the aging male (LOH): definition, diagnostic and clinical aspects. J Endocrinol Invest. 2005; 28:23–27.3. Morales A. Andropause (or symptomatic late-onset hypogonadism): facts, fiction and controversies. Aging Male. 2004; 7:297–303.
Article4. Staerman F, Léon P. Andropause (androgen deficiency of the aging male): diagnosis and management. Minerva Med. 2012; 103:333–342.5. Mahmoud A, Comhaire FH. Mechanisms of disease: late-onset hypogonadism. Nat Clin Pract Urol. 2006; 3:430–438.
Article6. Nieschlag E, Swerdloff R, Behre HM, Gooren LJ, Kaufman JM, Legros JJ, et al. Investigation, treatment and monitoring of late-onset hypogonadism in males. Aging Male. 2005; 8:56–58.
Article7. Lunenfeld B, Saad F, Hoesl CE. ISA, ISSAM and EAU recommendations for the investigation, treatment and monitoring of late-onset hypogonadism in males: scientific background and rationale. Aging Male. 2005; 8:59–74.
Article8. English HF, Drago JR, Santen RJ. Cellular response to androgen depletion and repletion in the rat ventral prostate: autoradiography and morphometric analysis. Prostate. 1985; 7:41–51.
Article9. Sandford NL, Searle JW, Kerr JF. Successive waves of apoptosis in the rat prostate after repeated withdrawal of testosterone stimulation. Pathology. 1984; 16:406–410.
Article10. Berges RR, Furuya Y, Remington L, English HF, Jacks T, Isaacs JT. Cell proliferation, DNA repair, and p53 function are not required for programmed death of prostatic glandular cells induced by androgen ablation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993; 90:8910–8914.
Article11. Buttyan R, Shabsigh A, Perlman H, Colombel M. Regulation of apoptosis in the prostate gland by androgenic steroids. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1999; 10:47–54.
Article12. Mancini A, Leone E, Festa R, Grande G, Silvestrini A, de Marinis L, et al. Effects of testosterone on antioxidant systems in male secondary hypogonadism. J Androl. 2008; 29:622–629.
Article13. Kerr JF, Winterford CM, Harmon BV. Apoptosis. Its significance in cancer and cancer therapy. Cancer. 1994; 73:2013–2026.
Article14. Thompson CB. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science. 1995; 267:1456–1462.
Article15. Buttke TM, Sandstrom PA. Oxidative stress as a mediator of apoptosis. Immunol Today. 1994; 15:7–10.
Article16. Francis FJ. Food colorants: anthocyanins. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 1989; 28:273–314.
Article17. Harborne JB, Williams CA. Advances in flavonoid research since 1992. Phytochemistry. 2000; 55:481–504.
Article18. Jang H, Ha US, Kim SJ, Yoon BI, Han DS, Yuk SM, et al. Anthocyanin extracted from black soybean reduces prostate weight and promotes apoptosis in the prostatic hyperplasia-induced rat model. J Agric Food Chem. 2010; 58:12686–12691.
Article19. Kumar VL, Majumder PK. Prostate gland: structure, functions and regulation. Int Urol Nephrol. 1995; 27:231–243.
Article20. Lee C, Sensibar JA, Dudek SM, Hiipakka RA, Liao ST. Prostatic ductal system in rats: regional variation in morphological and functional activities. Biol Reprod. 1990; 43:1079–1086.21. Ward GR, Abdel-Rahman AA. Effect of testosterone replacement or duration of castration on baroreflex bradycardia in conscious rats. BMC Pharmacol. 2005; 5:9.22. Sastre J, Pallardó FV, García de la Asunción J, Viña J. Mitochondria, oxidative stress and aging. Free Radic Res. 2000; 32:189–198.
Article23. Rahman K. Studies on free radicals, antioxidants, and co-factors. Clin Interv Aging. 2007; 2:219–236.24. Shih PH, Yeh CT, Yen GC. Effects of anthocyanidin on the inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis in human gastric adenocarcinoma cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 2005; 43:1557–1566.
Article25. Schwartzman RA, Cidlowski JA. Apoptosis: the biochemistry and molecular biology of programmed cell death. Endocr Rev. 1993; 14:133–151.
Article26. Buttyan R, Zakeri Z, Lockshin R, Wolgemuth D. Cascade induction of c-fos, c-myc, and heat shock 70K transcripts during regression of the rat ventral prostate gland. Mol Endocrinol. 1988; 2:650–657.
Article27. Marti A, Jehn B, Costello E, Keon N, Ke G, Martin F, et al. Protein kinase A and AP-1 (c-Fos/JunD)are induced during apoptosis of mouse mammary epithelial cells. Oncogene. 1994; 9:1213–1223.28. Suzuki A, Matsuzawa A, Iguchi T. Down regulation of Bcl-2 is the first step on Fas-mediated apoptosis of male reproductive tract. Oncogene. 1996; 13:31–37.29. Perlman H, Zhang X, Chen MW, Walsh K, Buttyan R. An elevated bax/bcl-2 ratio corresponds with the onset of prostate epithelial cell apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1999; 6:48–54.
Article30. Colombel M, Radvanyi F, Blanche M, Abbou C, Buttyan R, Donehower LA, et al. Androgen suppressed apoptosis is modified in p53 deficient mice. Oncogene. 1995; 10:1269–1274.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of Anthocyanin Extracted from Black Soybean on a Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia-induced Rat Model
- The Changes of Testis and the Effects of Anthocyanin on Spermatogenesis in Rat Induced Varicocele
- Anthocyanin Induces Apoptosis of DU-145 Cells In Vitro and Inhibits Xenograft Growth of Prostate Cancer
- The Effect of A Potent Calcium Channel Blocker, Nifedipine, on the Castration-induced Apoptosis of the Rat Ventral Prostate
- Identification and quantification of anthocyanin pigments in colored rice