Nutr Res Pract.
2011 Oct;5(5):389-395.
Protective effect of methanol extract from citrus press cakes prepared by far-infrared radiation drying on H2O2-mediated oxidative damage in Vero cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Marine Biomedical Sciences, Jeju National University, 1, Ara 1-dong, 102 Jejudaehak-ro, Jeju 690-756, Korea. youjinj@jejunu.ac.kr
- 2Marine Bioprocess Research Center, Pukyong National University, Busan 608-737, Korea.
- 3Department of Food Science & Food Service Industry, Jeju International University, Jeju 690-714, Korea.
Abstract
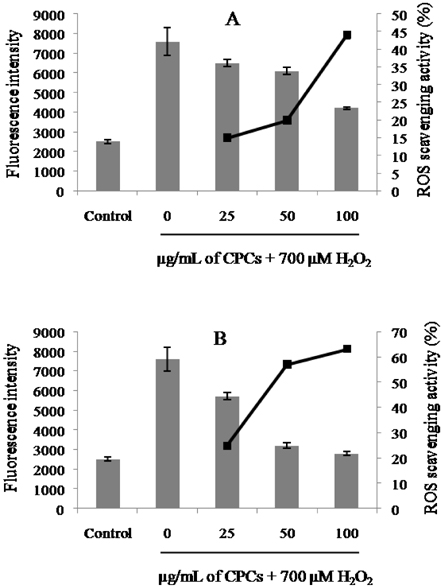
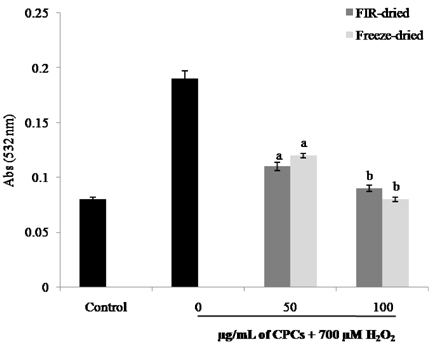
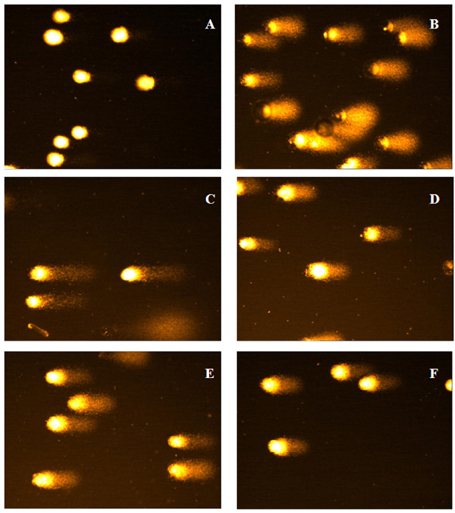
- In the present study, a suitable drying method was developed for citrus press cakes (CPCs), which are produced as a by-product in citrus juice plants, and the protective effect of methanol extract of CPCs prepared by far-infrared radiation (FIR) drying against H2O2-induced DNA damage was evaluated versus that of freeze-dried CPCs. Methanol extract of FIR-dried CPCs exhibited comparatively good ROS scavenging activity versus the freeze-dried CPCs at the concentration of 100 microg/mL. The extract strongly enhanced the cell viability against H2O2-induced oxidative damage in Vero cells. Lipid peroxidation inhibitory activity of the extract from FIR-dried CPCs was comparable to that of the extract from freeze-dried CPCs. This sample also exhibited good protective effects against H2O2-mediated cell apoptosis as demonstrated by decreased apoptotic body formation in the nuclear staining with Hoechst 33342. In the comet assay, the CPC extracts exhibited strong inhibitory effects against H2O2-mediated DNA damage in a dose-dependent manner. Thus, this study demonstrated that FIR drying effectively preserves CPC as a functionally important natural antioxidant source and the FIR drying can be adapted for drying CPCs and is more economical for massive production than freeze drying.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lohrasbi M, Pourbafrani M, Niklasson C, Taherzadeh MJ. Process design and economic analysis of a citrus waste biorefinery with biofuels and limonene as products. Bioresour Technol. 2010. 101:7382–7388.
Article2. Marín FR, Soler-Rivas C, Benavente-García O, Castillo J, Pérez-Alvarez JA. By-products from different citrus processes as a source of customized functional fibres. Food Chem. 2007. 100:736–741.
Article3. Sahraoui N, Vian MA, El Maataoui M, Boutekedjiret C, Chemat F. Valorization of citrus by-products using Microwave Steam Distillation (MSD). Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol. 2011. 12:163–170.
Article4. Manthey JA, Grohmann K. Concentrations of hesperidin and other orange peel flavonoids in citrus processing byproducts. J Agric Food Chem. 1996. 44:811–814.
Article5. Senevirathne M, Kim SH, Kim YD, Oh CK, Oh MC, Ahn CB, Je JY, Lee WW, Jeon YJ. Effect of far-infrared radiation drying of citrus press-cakes on free radical scavenging and antioxidant activities. J Food Eng. 2010. 97:168–176.
Article6. Senevirathne M, Jeon YJ, Ha JH, Kim SH. Effective drying of citrus by-products by high speed drying: a novel drying technique and their antioxidant activity. J Food Eng. 2009. 92:157–163.
Article7. Nowak D, Lewicki PP. Infrared drying of apple slices. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol. 2004. 5:353–360.
Article8. Choi CS, Chung HK, Choi MK, Kang MH. Effects of grape pomace on the antioxidant defense system in diet-induced hypercholesterolemic rabbits. Nutr Res Pract. 2010. 4:114–120.
Article9. Juan MY, Chou CC. Enhancement of antioxidant activity, total phenolic and flavonoid content of black soybeans by solid state fermentation with Bacillus subtilis BCRC 14715. Food Microbiol. 2010. 27:586–591.
Article10. Cao Y, Cao R. Angiogenesis inhibited by drinking tea. Nature. 1999. 398:381.
Article11. Madsen HL, Bertelsen G. Spices as antioxidants. Trends Food Sci Technol. 1995. 6:271–277.
Article12. Shahidi F, Janitha PK, Wanasundara PD. Phenolic antioxidants. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 1992. 32:67–103.
Article13. Song WY, Ku KH, Choi JH. Effect of ethanol extracts from red pepper seeds on antioxidative defense system and oxidative stress in rats fed high-fat high-cholesterol diet. Nutr Res Pract. 2010. 4:11–15.
Article14. Senevirathne M, Jeon YJ, Ha JH, Kim SH. Effect of far-infrared radiation for drying citrus by-products and their radical scavenging activities and protective effects against H2O2-induced DNA damage. J Food Sci Nutr. 2008. 13:313–320.
Article15. Engelmann J, Volk J, Leyhausen G, Geurtsen W. ROS formation and glutathione levels in human oral fibroblasts exposed to TEGDMA and camphorquinone. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2005. 75:272–276.
Article16. Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983. 65:55–63.
Article17. Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem. 1979. 95:351–358.
Article18. Gschwind M, Huber G. Apoptotic cell death induced by beta-amyloid 1-42 peptide is cell type dependent. J Neurochem. 1995. 65:292–300.
Article19. Lizard G, Fournel S, Genestier L, Dhedin N, Chaput C, Flacher M, Mutin M, Panaye G, Revillard JP. Kinetics of plasma membrane and mitochondrial alterations in cells undergoing apoptosis. Cytometry. 1995. 21:275–283.
Article20. Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL. A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res. 1988. 175:184–191.
Article21. Mahro B, Timm M. Potential of biowaste from the food industry as a biomass resource. Eng Life Sci. 2007. 7:457–468.
Article22. Jeong SM, Kim SY, Park HR, Lee SC. Effect of far-infrared radiation on the on the antioxidant activity of extracts from citrus unshiu peels. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2004. 33:1580–1583.23. LeBel CP, Ischiropoulos H, Bondy SC. Evaluation of the probe 2', 7'-dichlorofluorescin as an indicator of reactive oxygen species formation and oxidative stress. Chem Res Toxicol. 1992. 5:227–231.
Article24. Zhang R, Kang KA, Piao MJ, Maeng YH, Lee KH, Chang WY, You HJ, Kim JS, Kang SS, Hyun JW. Cellular protection of morin against the oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide. Chem Biol Interact. 2009. 177:21–27.
Article25. Halliwell B, Chirico S. Lipid peroxidation: its mechanism, measurement, and significance. Am J Clin Nutr. 1993. 57:715S–724S.
Article26. Halliwell B, Gutteridge JM, Cross CE. Free radicals, antioxidants, and human disease: where are we now? J Lab Clin Med. 1992. 119:598–620.27. Luo W, Zhao M, Yang B, Shen G, Rao G. Identification of bioactive compounds in Phyllenthus emblica L. fruit and their free radical scavenging activity. Food Chem. 2009. 114:499–504.
Article28. Wang AY, Zhou MY, Lin WC. Antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties of Citrus sulcata extracts. Food Chem. 2011. 124:958–963.
Article29. Dizdaroglu M, Jaruga P, Birincioglu M, Rodriguez H. Free radical-induced damage to DNA: mechanisms and measurement. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002. 32:1102–1115.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Antibacterial effect of citrus press-cakes dried by high speed and far-infrared radiation drying methods
- The Neuro-Protective Effect of the Methanolic Extract of Perilla frutescens var. japonica and Rosmarinic Acid against H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress in C6 Glial Cells
- Protective Effects of Alpinia katsumadai Extract Against Oxidative Stress
- Antioxidant Activity of Xanthium Strumarium L. Extracted F ractions in Lens Epithelial Cells
- The protective effects of trace elements against side effects induced by ionizing radiation