Nutr Res Pract.
2011 Jun;5(3):219-223.
High fat diet-induced obesity leads to proinflammatory response associated with higher expression of NOD2 protein
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition, College of Human Ecology, Seoul National University, 599 Gwanak-ro, Gwanak-gu, Seoul 151-742, Korea. snhan@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Food Science and Nutrition, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 702-701, Korea.
- 3Human Ecology Research Institute, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742, Korea.
Abstract
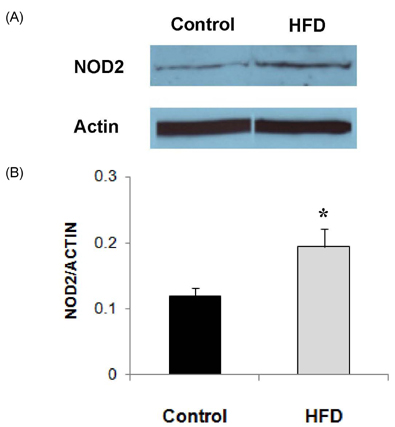
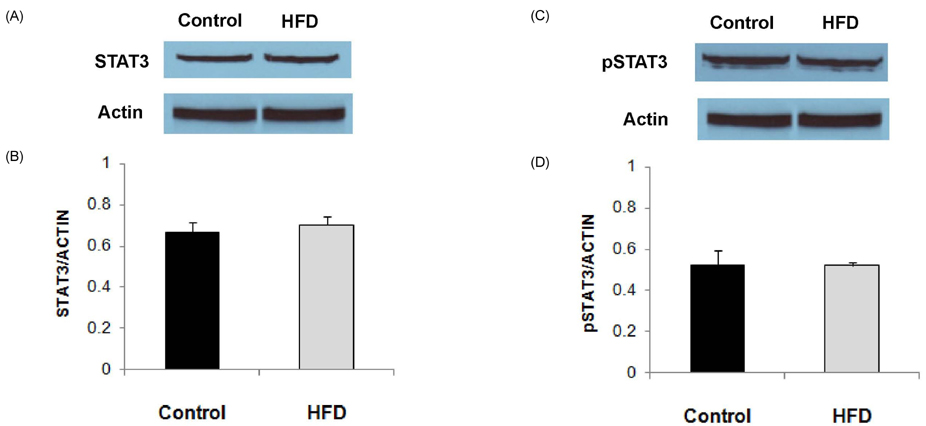
- Obesity has been reported to be associated with low grade inflammatory status. In this study, we investigated the inflammatory response as well as associated signaling molecules in immune cells from diet-induced obese mice. Four-week-old C57BL mice were fed diets containing 5% fat (control) or 20% fat and 1% cholesterol (HFD) for 24 weeks. Splenocytes (1 x 10(7) cells) were stimulated with 10 microg/mL of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for 6 or 24 hrs. Production of interleukin (IL)-1beta, IL-6, and TNF-alpha as well as protein expression levels of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD)2, signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)3, and pSTAT3 were determined. Mice fed HFD gained significantly more body weight compared to mice fed control diet (28.2 +/- 0.6 g in HFD and 15.4 +/- 0.8 g in control). After stimulation with LPS for 6 hrs, production of IL-1beta was significantly higher (P = 0.001) and production of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha tended to be higher (P < 0.064) in the HFD group. After 24 hrs of LPS stimulation, splenocytes from the HFD group produced significantly higher levels of IL-6 (10.02 +/- 0.66 ng/mL in HFD and 7.33 +/- 0.56 ng/mL in control, P = 0.005) and IL-1beta (121.34 +/- 12.72 pg/mL in HFD and 49.74 +/- 6.58 pg/mL in control, P < 0.001). There were no significant differences in the expression levels of STAT3 and pSTAT3 between the HFD and the control groups. However, the expression level of NOD2 protein as determined by Western blot analysis was 60% higher in the HFD group compared with the control group. NOD2 contributes to the induction of inflammation by activation of nuclear factor kappaB. These findings suggest that diet-induced obesity is associated with increased inflammatory response of immune cells, and higher expression of NOD2 may contribute to these changes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ferrante AW Jr. Obesity-induced inflammation: a metabolic dialogue in the language of inflammation. J Intern Med. 2007. 262:408–414.
Article2. Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, Tan G, Yang D, Chou CJ, Sole J, Nichols A, Ross JS, Tartaglia LA, Chen H. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2003. 112:1821–1830.
Article3. Shoelson SE, Herrero L, Naaz A. Obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Gastroenterology. 2007. 132:2169–2180.
Article4. Karalis KP, Giannogonas P, Kodela E, Koutmani Y, Zoumakis M, Teli T. Mechanisms of obesity and related pathology: linking immune responses to metabolic stress. FEBS J. 2009. 276:5747–5754.
Article5. Strandberg L, Verdrengh M, Enge M, Andersson N, Amu S, Onnheim K, Benrick A, Brisslert M, Bylund J, Bokarewa M, Nilsson S, Jansson JO. Mice chronically fed high-fat diet have increased mortality and disturbed immune response in sepsis. PLoS One. 2009. 4:e7605.
Article6. Shapiro NI, Khankin EV, Van Meurs M, Shih SC, Lu S, Yano M, Castro PR, Maratos-Flier E, Parikh SM, Karumanchi SA, Yano K. Leptin exacerbates sepsis-mediated morbidity and mortality. J Immunol. 2010. 185:517–524.
Article7. Lago R, Gómez R, Lago F, Gómez-Reino J, Gualillo O. Leptin beyond body weight regulation-current concepts concerning its role in immune function and inflammation. Cell Immunol. 2008. 252:139–145.
Article8. Amar S, Zhou Q, Shaik-Dasthagirisaheb Y, Leeman S. Diet-induced obesity in mice causes changes in immune responses and bone loss manifested by bacterial challenge. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. 104:20466–20471.
Article9. Inohara N, Ogura Y, Nuñez G. Nods: a family of cytosolic proteins that regulate the host response to pathogens. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2002. 5:76–80.
Article10. Gutierrez O, Pipaon C, Inohara N, Fontalba A, Ogura Y, Prosper F, Nunez G, Fernandez-Luna JL. Induction of Nod2 in myelomonocytic and intestinal epithelial cells via nuclear factor-kappa B activation. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:41701–41705.
Article11. Inohara N, Nuñez G. NODs: intracellular proteins involved in inflammation and apoptosis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003. 3:371–382.
Article12. Myers MG, Cowley MA, Münzberg H. Mechanisms of leptin action and leptin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol. 2008. 70:537–556.
Article13. Stepkowski SM, Chen W, Ross JA, Nagy ZS, Kirken RA. STAT3: an important regulator of multiple cytokine functions. Transplantation. 2008. 85:1372–1377.
Article14. Greenhill CJ, Rose-John S, Lissilaa R, Ferlin W, Ernst M, Hertzog PJ, Mansell A, Jenkins BJ. IL-6 trans-signaling modulates TLR4-dependent inflammatory responses via STAT3. J Immunol. 2011. 186:1199–1208.
Article15. Park EJ, Lee JH, Yu GY, He G, Ali SR, Holzer RG, Osterreicher CH, Takahashi H, Karin M. Dietary and genetic obesity promote liver inflammation and tumorigenesis by enhancing IL-6 and TNF expression. Cell. 2010. 140:197–208.
Article16. Mito N, Hosoda T, Kato C, Sato K. Change of cytokine balance in diet-induced obese mice. Metabolism. 2000. 49:1295–1300.
Article17. Liu SF, Malik AB. NF-κB activation as a pathological mechanism of septic shock and inflammation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006. 290:L622–L645.
Article18. Vandanmagsar B, Youm YH, Ravussin A, Galgani JE, Stadler K, Mynatt RL, Ravussin E, Stephens JM, Dixit VD. The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat Med. 2011. 17:179–188.
Article19. Lamkanfi M, Kanneganti TD. Nlrp3: an immune sensor of cellular stress and infection. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010. 42:792–795.
Article20. Hanada T, Yoshimura A. Regulation of cytokine signaling and inflammation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002. 13:413–421.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Exercise and a High-Fat, High-Sucrose Restriction Diet on Metabolic Indicators, Nr4a3, and Mitochondria-Associated Protein Expression in the Gastrocnemius Muscles of Mice with Diet-Induced Obesity
- Alteration in plasma chemokine profile in a high-fat diet-induced obesity mouse model
- Effect of vegetable oils with different fatty acid composition on high-fat dietinduced obesity and colon inflammation
- High-fat Intake is Associated with Alteration of Peripheral Circadian Clock Gene Expression
- Dietary glucosinolates inhibit splenic inflammation in high fat/cholesterol diet-fed C57BL/6 mice