J Nutr Health.
2018 Oct;51(5):369-378. 10.4163/jnh.2018.51.5.369.
Alteration in plasma chemokine profile in a high-fat diet-induced obesity mouse model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Human Life Research Center, Dong-A University, Busan 49315, Korea. hrbae@dau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Plastic Surgery, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan 49201, Korea.
- 3Department of Emergency Medicine, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan 49201, Korea.
- 4Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan 49201, Korea.
- KMID: 2427760
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4163/jnh.2018.51.5.369
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Obesity is associated with a dysregulation of metabolic balance and is regarded as a low grade chronic inflammation. Western-style diet and physical inactivity are leading causes of obesity. This study examined the profiles of forty plasma cytokines and chemokines at the same time in the early stages of high-fat diet-induced obesity using a mouse model.
METHODS
A total of 30 male CD1 mice, 12 ~ 14 weeks of age, were enrolled. The mice were fed a high-fat diet for 6 weeks to induce obesity. The plasma glucose and triglyceride concentrations were measured using a hexokinase colorimetric assay kit and a serum triglyceride determination kit, respectively. The relative levels of multiple cytokines and chemokines in the plasma were determined using a mouse cytokine array kit.
RESULTS
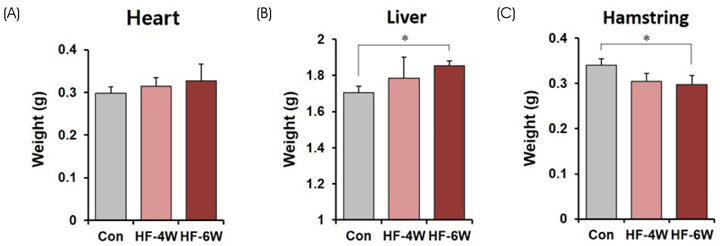
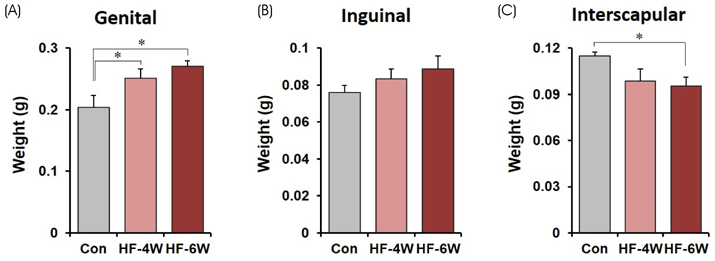
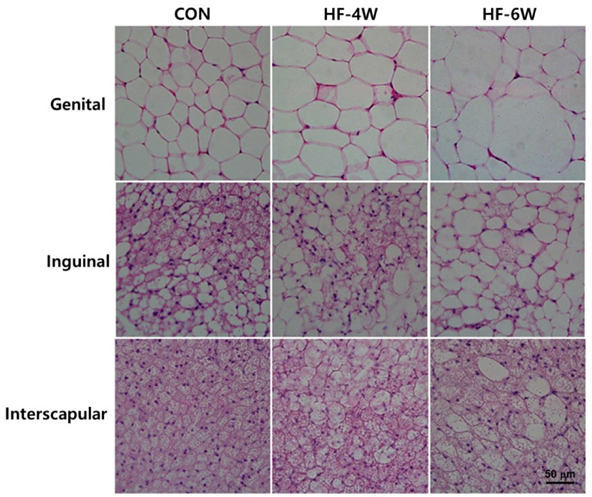
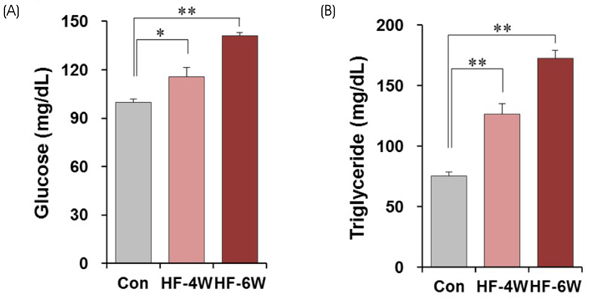
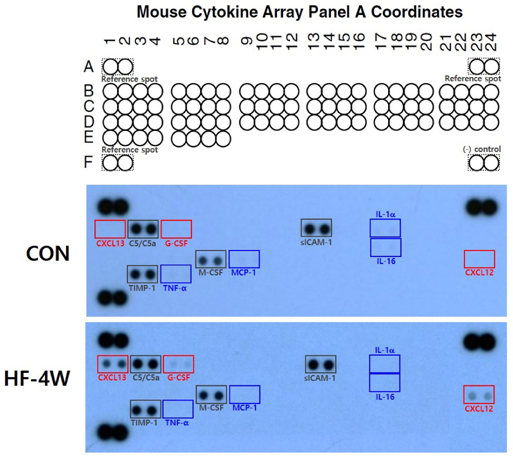
The mice exhibited significant weight gain after 6 weeks of a high-fat diet. The genital fat depot was enlarged along with an increase in the number and the mean size of white adipocytes as early as 4 weeks after a high-fat diet. In addition, the plasma glucose and triglyceride levels increased significantly after 4 weeks of a high-fat diet. Cytokine array analysis revealed a remarkable increase in the expression of both CXCL12 and CXCL13, whereas the proinflammatory cytokines remained low after 4 weeks of a high-fat diet.
CONCLUSION
A significant increase in plasma levels of CXCL12 and CXCL13 was observed after 4 weeks of a high-fat diet, which might induce the migration of B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes, and monocytes from the blood to expanding adipose tissue or fat associated lymphoid clusters, playing a key role in adipose tissue remodeling and local immunity during the early stages of high-fat diet-induced obesity.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kahn BB, Flier JS. Obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2000; 106(4):473–481.
Article2. Landsberg L, Aronne LJ, Beilin LJ, Burke V, Igel LI, Lloyd-Jones D, Sowers J. Obesity-related hypertension: pathogenesis, cardiovascular risk, and treatment: a position paper of The Obesity Society and the American Society of Hypertension. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2013; 15(1):14–33.3. De Pergola G, Silvestris F. Obesity as a major risk factor for cancer. J Obes. 2013; 2013:291546.
Article4. Lumeng CN, Saltiel AR. Inflammatory links between obesity and metabolic disease. J Clin Invest. 2011; 121(6):2111–2117.
Article5. Kershaw EE, Flier JS. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004; 89(6):2548–2556.
Article6. Makki K, Froguel P, Wolowczuk I. Adipose tissue in obesityrelated inflammation and insulin resistance: cells, cytokines, and chemokines. ISRN Inflamm. 2013; 2013:139239.
Article7. Kanneganti TD, Dixit VD. Immunological complications of obesity. Nat Immunol. 2012; 13(8):707–712.
Article8. Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL, Ferrante AW Jr. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest. 2003; 112(12):1796–1808.
Article9. Suganami T, Ogawa Y. Adipose tissue macrophages: their role in adipose tissue remodeling. J Leukoc Biol. 2010; 88(1):33–39.
Article10. Lumeng CN, Bodzin JL, Saltiel AR. Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J Clin Invest. 2007; 117(1):175–184.
Article11. Ito A, Suganami T, Yamauchi A, Degawa-Yamauchi M, Tanaka M, Kouyama R, Kobayashi Y, Nitta N, Yasuda K, Hirata Y, Kuziel WA, Takeya M, Kanegasaki S, Kamei Y, Ogawa Y. Role of CC chemokine receptor 2 in bone marrow cells in the recruitment of macrophages into obese adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 2008; 283(51):35715–35723.
Article12. Shi C, Pamer EG. Monocyte recruitment during infection and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011; 11(11):762–774.
Article13. Surmi BK, Hasty AH. Macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue: initiation, propagation and remodeling. Future Lipidol. 2008; 3(5):545–556.
Article14. Kanda H, Tateya S, Tamori Y, Kotani K, Hiasa K, Kitazawa R, Kitazawa S, Miyachi H, Maeda S, Egashira K, Kasuga M. MCP-1 contributes to macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis in obesity. J Clin Invest. 2006; 116(6):1494–1505.
Article15. Takahashi K, Mizuarai S, Araki H, Mashiko S, Ishihara A, Kanatani A, Itadani H, Kotani H. Adiposity elevates plasma MCP-1 levels leading to the increased CD11b-positive monocytes in mice. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278(47):46654–46660.
Article16. Heydemann A. An overview of murine high fat diet as a model for type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Res. 2016; 2016:2902351.
Article17. Wang CY, Liao JK. A mouse model of diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. Methods Mol Biol. 2012; 821:421–433.
Article18. Comerford I, McColl SR. Mini-review series: focus on chemokines. Immunol Cell Biol. 2011; 89(2):183–184.
Article19. Bunting MD, Comerford I, McColl SR. Finding their niche: chemokines directing cell migration in the thymus. Immunol Cell Biol. 2011; 89(2):185–196.
Article20. Gerard C, Rollins BJ. Chemokines and disease. Nat Immunol. 2001; 2(2):108–115.
Article21. Balkwill F. Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004; 4(7):540–550.
Article22. Nagasawa T, Kikutani H, Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning and structure of a pre-B-cell growth-stimulating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994; 91(6):2305–2309.
Article23. Nagasawa T. CXCL12/SDF-1 and CXCR4. Front Immunol. 2015; 6:301.
Article24. Sun X, Cheng G, Hao M, Zheng J, Zhou X, Zhang J, Taichman RS, Pienta KJ, Wang J. CXCL12 / CXCR4 / CXCR7 chemokine axis and cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010; 29(4):709–722.
Article25. Nagasawa T, Omatsu Y, Sugiyama T. Control of hematopoietic stem cells by the bone marrow stromal niche: the role of reticular cells. Trends Immunol. 2011; 32(7):315–320.
Article26. Sengenès C, Miranville A, Maumus M, de Barros S, Busse R, Bouloumié A. Chemotaxis and differentiation of human adipose tissue CD34+/CD31− progenitor cells: role of stromal derived factor-1 released by adipose tissue capillary endothelial cells. Stem Cells. 2007; 25(9):2269–2276.
Article27. Shin J, Fukuhara A, Onodera T, Kita S, Yokoyama C, Otsuki M, Shimomura I. SDF-1 is an autocrine insulin-desensitizing factor in adipocytes. Diabetes. 2018; 67(6):1068–1078.
Article28. Peng H, Zhang H, Zhu H. Blocking CXCR7-mediated adipose tissue macrophages chemotaxis attenuates insulin resistance and inflammation in obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016; 479(4):649–655.
Article29. Kim D, Kim J, Yoon JH, Ghim J, Yea K, Song P, Park S, Lee A, Hong CP, Jang MS, Kwon Y, Park S, Jang MH, Berggren PO, Suh PG, Ryu SH. CXCL12 secreted from adipose tissue recruits macrophages and induces insulin resistance in mice. Diabetologia. 2014; 57(7):1456–1465.
Article30. Legler DF, Loetscher M, Roos RS, Clark-Lewis I, Baggiolini M, Moser B. B cell-attracting chemokine 1, a human CXC chemokine expressed in lymphoid tissues, selectively attracts B lymphocytes via BLR1/CXCR5. J Exp Med. 1998; 187(4):655–660.
Article31. Schiffer L, Worthmann K, Haller H, Schiffer M. CXCL13 as a new biomarker of systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis - from bench to bedside? Clin Exp Immunol. 2015; 179(1):85–89.
Article32. Klimatcheva E, Pandina T, Reilly C, Torno S, Bussler H, Scrivens M, Jonason A, Mallow C, Doherty M, Paris M, Smith ES, Zauderer M. CXCL13 antibody for the treatment of autoimmune disorders. BMC Immunol. 2015; 16:6.
Article33. Fletcher AL, Acton SE, Knoblich K. Lymph node fibroblastic reticular cells in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015; 15(6):350–361.
Article34. Förster R, Emrich T, Kremmer E, Lipp M. Expression of the G-protein-coupled receptor BLR1 defines mature, recirculating B cells and a subset of T-helper memory cells. Blood. 1994; 84(3):830–840.35. Förster R, Mattis AE, Kremmer E, Wolf E, Brem G, Lipp M. A putative chemokine receptor, BLR1, directs B cell migration to defined lymphoid organs and specific anatomic compartments of the spleen. Cell. 1996; 87(6):1037–1047.
Article36. Moro K, Yamada T, Tanabe M, Takeuchi T, Ikawa T, Kawamoto H, Furusawa J, Ohtani M, Fujii H, Koyasu S. Innate production of TH2 cytokines by adipose tissue-associated c-Kit+Sca-1+ lymphoid cells. Nature. 2010; 463(7280):540–544.37. Bénézech C, Luu NT, Walker JA, Kruglov AA, Loo Y, Nakamura K, Zhang Y, Nayar S, Jones LH, Flores-Langarica A, McIntosh A, Marshall J, Barone F, Besra G, Miles K, Allen JE, Gray M, Kollias G, Cunningham AF, Withers DR, Toellner KM, Jones ND, Veldhoen M, Nedospasov SA, McKenzie AN, Caamaño JH. Inflammation-induced formation of fat-associated lymphoid clusters. Nat Immunol. 2015; 16(8):819–828.
Article38. Shaikh SR, Haas KM, Beck MA, Teague H. The effects of diet-induced obesity on B cell function. Clin Exp Immunol. 2015; 179(1):90–99.
Article39. Winer DA, Winer S, Chng MH, Shen L, Engleman EG. B Lymphocytes in obesity-related adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014; 71(6):1033–1043.
Article40. Shen P, Fillatreau S. Antibody-independent functions of B cells: a focus on cytokines. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015; 15(7):441–451.
Article41. do Carmo LS, Rogero MM, Paredes-Gamero EJ, Nogueira-Pedro A, Xavier JG, Cortez M, Borges MC, Fujii TM, Borelli P, Fock RA. A high-fat diet increases interleukin-3 and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor production by bone marrow cells and triggers bone marrow hyperplasia and neutrophilia in Wistar rats. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2013; 238(4):375–384.
Article42. Yang H, Youm YH, Vandanmagsar B, Ravussin A, Gimble JM, Greenway F, Stephens JM, Mynatt RL, Dixit VD. Obesity increases the production of proinflammatory mediators from adipose tissue T cells and compromises TCR repertoire diversity: implications for systemic inflammation and insulin resistance. J Immunol. 2010; 185(3):1836–1845.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Impact of High Fat Diet-induced Obesity on the Plasma Levels of Monoamine Neurotransmitters in C57BL/6 Mice
- High fat diet confers vascular hyper-contractility against angiotensin II through upregulation of MLCK and CPI-17
- Obesity and binge alcohol intake are deadly combination to induce steatohepatitis: A model of high-fat diet and binge ethanol intake
- Effects of Calcium and Genistein on Body Fat and Lipid Metabolism in High Fat-induced Obese Mice
- A ketogenic diet reduces body weight gain and alters insulin sensitivity and gut microbiota in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity