Korean J Urol.
2006 Feb;47(2):189-194. 10.4111/kju.2006.47.2.189.
The Protein Expressions of Apoptosis-associated Genes in the Obstructed Ureters of Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Konkuk University College of Medicine, Korea.
- 2Department of Urology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hhkim@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2294200
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2006.47.2.189
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: The role of apoptosis in the pathogenesis of ureteral damage from obstructive uropathy has rarely been studied. This study was performed to determine the protein expression of the apoptosis-associated genes in the pathogenesis of ureteral damage during the course of obstructive uropathy in ligated rat ureters.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
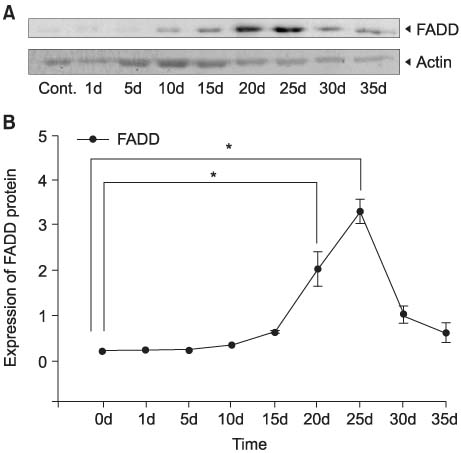
After unilateral ligation of the ureter, each group of five Sprague-Dawley rats was sacrificed and examined at 1, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 and 35 days after ligation: five rats with normal ureters were also examined as controls. The protein expressions of the fas-associated death domain (FADD), Bax, Bcl-xL and cyclooxygenases (COX)-2 genes in obstructed ureters were assessed by performing Western blotting.
RESULTS
The expressions of FADD protein in the 20 and 25 day-obstructed ureters (DOUs) were significantly higher than that in control ureters and the peak was reached in the 25 DOUs. The expressions of Bcl-xL protein in the 20, 25 and 30 DOUs were significantly higher than that in the control ureters and the peak was reached in the 25 DOUs. The expression of COX-2 protein in the 5, 10, 15, 25 DOUs were significantly higher than that in the control ureters and the peak was reached in the 10 DOUs.
CONCLUSIONS
The FADD and Bcl-xL genes were involved in apoptosis of the obstructed ureter. The peaks of their expressions were at 25 DOUs. The expression of the COX-2 gene may be related with apoptosis in the obstructed ureter.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gobe GC, Axelsen RA. Genesis of renal tubular atrophy in experimental hydronephrosis in the rat. Role of apoptosis. Lab Invest. 1987. 56:273–281.2. Nagle RB, Bulger RE. Unilateral obstructive nephropathy in the rabbit. II. Late morphologic changes. Lab Invest. 1978. 38:270–278.3. Truong LD, Sheikh-Hamad D, Chakraborty S, Suki WN. Cell apoptosis and proliferation in obstructive uropathy. Semin Nephrol. 1998. 18:641–651.4. Choi YJ, Baranowska-Daca E, Nguyen V, Koji T, Ballantyne CM, Sheikh-Hamad D, et al. Mechanism of chronic obstructive uropathy: increased expression of apoptosis-promoting molecules. Kidney Int. 2000. 58:1481–1491.5. Truong LD, Petrusevska G, Yang G, Gurpinar T, Shappell S, Lechago J, et al. Cell apoptosis and proliferation in experimental chronic obstructive uropathy. Kidney Int. 1996. 50:200–207.6. Truong LD, Choi YJ, Tsao CC, Ayala G, Sheikh-Hamad D, Nassar G, et al. Renal cell apoptosis in chronic obstructive uropathy: the roles of caspases. Kidney Int. 2001. 60:924–934.7. Kim HG, Kwak C, Kim HH, Paick SH, Lho YS, Lee JW, et al. The serial microscopic changes of cell proliferative and apoptotic phenomenon in obstructed ureters in the rat. Korean J Urol. 2005. 46:495–501.8. Chuang YH, Chuang WL, Huang CH. Myocyte apoptosis in the pathogenesis of ureteral damage in rats with obstructive uropathy. Urology. 2001. 58:463–470.9. Chuang YH, Chuang WL, Huang SP, Huang CH. Over-expression of apoptosis-related proteins contributes to muscular damage in the obstructed ureter of the rat. BJU Int. 2002. 89:106–112.10. Chuang YH, Chuang WL, Huang SP, Huang CH. Release of cytochrome c and activation of caspases related to myocyte apoptosis in obstructed ureters in a rat model of obstructive uropathy. BJU Int. 2003. 92:113–118.11. Steller H. Mechanisms and genes of cellular suicide. Science. 1995. 267:1445–1449.12. Hu Y, Benedict MA, Ding L, Nunez G. Role of cytochrome c and dATP/ATP hydrolysis in Apaf-1-mediated caspase-9 activation and apoptosis. EMBO J. 1999. 18:3586–3595.13. Shimizu S, Narita M, Tsujimoto Y. Bcl-2 family proteins regulate the release of apoptogenic cytochrome c by the mitochondrial channel VDAC. Nature. 1999. 399:483–487.14. Li H, Yuan J. Deciphering the pathways of life and death. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999. 11:261–266.15. Cao Y, Prescott SM. Many actions of cyclooxygenase-2 in cellular dynamics and in cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2002. 190:279–286.16. Trifan OC, Hla T. Cyclooxygenase-2 modulates cellular growth and promotes tumorigenesis. J Cell Mol Med. 2003. 7:207–222.17. Kismet K, Akay MT, Abbasoglu O, Ercan A. Celecoxib: a potent cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor in cancer prevention. Cancer Detect Prev. 2004. 28:127–142.18. Ding H, Han C, Zhu J, Chen CS, D'Ambrosio SM. Celecoxib derivertives induce apoptosis via the disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential and activation of caspase 9. Int J Cancer. 2005. 113:803–810.19. Chuang YH, Chuang WL, Huang SP, Liu KM, Huang CH. The temporal relationship between the severity of hydroureter and the dynamic changes of obstructed ureters in a rat model. Br J Urol. 1995. 76:303–310.20. Chinnaiyan AM, Tepper CG, Seldin MF, O'Rourke K, Kischkel FC, Hellbardt S, et al. FADD/MORT1 is a common mediator of CD95 (Fas/APO-1) and tumor necrosis factor receptor-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1996. 271:4961–4965.21. Kim PK, Dutra AS, Chandrasekharappa SC, Puck JM. Genomic structure and mapping of human FADD, an intracellular mediator of lymphocyte apoptosis. J Immunol. 1996. 157:5461–5466.22. Strasser A, Newton K. FADD/MORT1, a signal transducer that can promote cell death or cell growth. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999. 31:533–537.23. Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Green DR, Newmeyer DD. The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: a primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science. 1997. 275:1132–1136.24. Oltvai ZN, Korsmeyer SJ. Checkpoints of dueling dimers foil death wishes. Cell. 1994. 79:189–192.25. Kujubu DA, Fletcher BS, Varnum BC, Lim RW, Herschman HR. TIS10, a phorbol ester tumor promoter-inducible mRNA from Swiss 3T3 cell, encodes a novel prostaglandin synthase/cyclooxygenase homologue. J Biol Chem. 1991. 266:12866–12872.26. Pruthi RS, Derksen E, Gaston K. Cyclooxygenase-2 as a potential target in the prevention and treatment of genitourinary tumors: a review. J Urol. 2003. 169:2352–2359.27. Tsujii M, Kawano S, Tsuji S, Sawaoka H, Hori M, DuBois RN. Cyclooxygenase regulates angiogenesis induced by colon cancer cells. Cell. 1998. 93:705–716.28. Fosslien E. Review: molecular pathology of cyclooxygenase-2 in cancer-induced angiogenesis. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2001. 31:325–348.29. Sheng H, Shao J, Morrow JD, Beauchamp RD, DuBois RN. Modulation of apoptosis and Bcl-2 expression by prostaglandin E2 in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1998. 58:362–366.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Serial Microscopic Changes of Cell Proliferative and Apoptotic Phenomenon in Obstructed Ureters in the Rat
- Increased Phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR in the Obstructed Kidney of Rats with Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction
- Apoptosis, P53, bax and Bcl-2 Protein Expressions in Neonatal rat Hippocampus by Kainic Acid-induced Seizure
- A Study of Apoptosis, and bcl-2 and p53 Expressions in Breast Cancer
- Primary Obstructed Megaureter: A Clinical Review of 17 Ureters in 13 Patients