Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2014 Oct;18(5):391-396. 10.4196/kjpp.2014.18.5.391.
Inhibition of the Interleukin-11-STAT3 Axis Attenuates Hypoxia-Induced Migration and Invasion in MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Chemistry, College of Biomedical & Health Science, Konkuk University, Chungju 380-701, Korea. jhlim@kku.ac.kr
- KMID: 2285537
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2014.18.5.391
Abstract
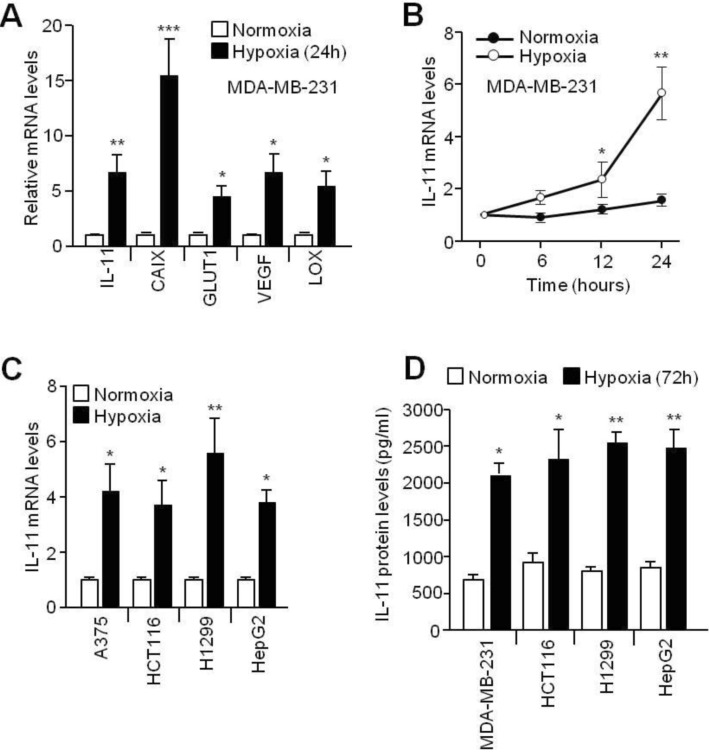
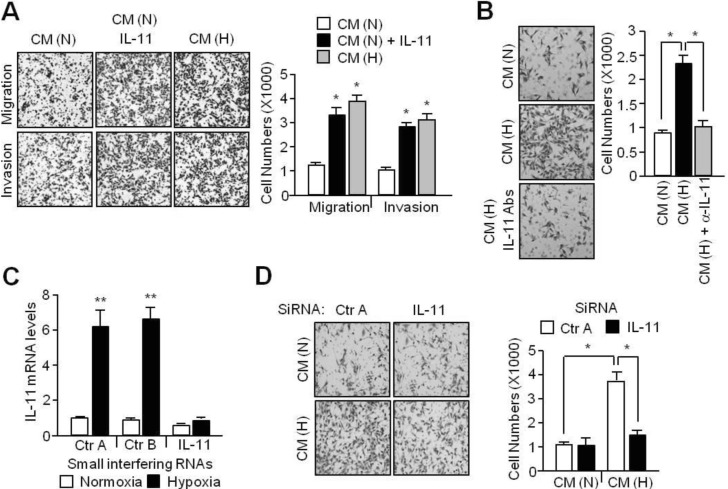
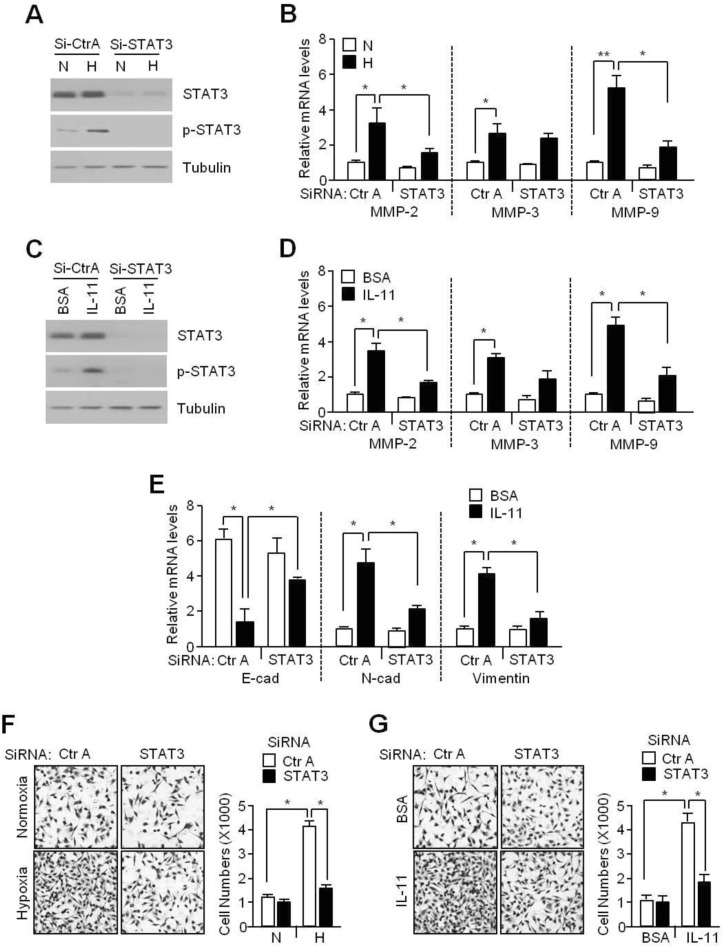
- Although interleukin-11 (IL-11) has been reported to be elevated in hypoxic tumors and has been associated with a poor prognosis in various cancers, little is known about its precise role in promoting metastasis in hypoxic tumors. In the present study, the molecular mechanism underlying the effects of IL-11 on MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells migration and invasion in relation to metastasis under hypoxic conditions has been defined. Inhibition of IL-11 expression or function using small interfering RNA (siRNA) or a neutralizing antibody attenuated hypoxic MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell migration and invasion through down-regulation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and activation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) related gene expression. In addition, hypoxia-induced IL-11 increased STAT3 phosphorylation and STAT3 knockdown suppressed hypoxic MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell invasion due to reduced MMP levels and reprogrammed EMT-related gene expression. These results suggest that one of the hypoxic metastasis pathways and the regulation of this pathway could be a potential target for novel cancer therapeutics.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Anoxia
Antibodies, Neutralizing
Axis, Cervical Vertebra*
Breast Neoplasms*
Cell Movement
Down-Regulation
Gene Expression
Interleukin-11
Matrix Metalloproteinases
Neoplasm Metastasis
Phosphorylation
Prognosis
RNA, Small Interfering
Antibodies, Neutralizing
Interleukin-11
Matrix Metalloproteinases
RNA, Small Interfering
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011; 144:646–674. PMID: 21376230.
Article2. Tsai YP, Wu KJ. Hypoxia-regulated target genes implicated in tumor metastasis. J Biomed Sci. 2012; 19:102. PMID: 23241400.
Article3. Semenza GL. Hypoxia-inducible factors: mediators of cancer progression and targets for cancer therapy. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2012; 33:207–214. PMID: 22398146.
Article4. Chan DA, Giaccia AJ. Hypoxia, gene expression, and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007; 26:333–339. PMID: 17458506.
Article5. Bertout JA, Patel SA, Simon MC. The impact of O2 availability on human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008; 8:967–975. PMID: 18987634.
Article6. Taniguchi K, Karin M. IL-6 and related cytokines as the critical lynchpins between inflammation and cancer. Semin Immunol. 2014; 26:54–74. PMID: 24552665.
Article7. Ren L, Wang X, Dong Z, Liu J, Zhang S. Bone metastasis from breast cancer involves elevated IL-11 expression and the gp130/STAT3 pathway. Med Oncol. 2013; 30:634. PMID: 23813018.
Article8. Kang Y, He W, Tulley S, Gupta GP, Serganova I, Chen CR, Manova-Todorova K, Blasberg R, Gerald WL, Massagué J. Breast cancer bone metastasis mediated by the Smad tumor suppressor pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102:13909–13914. PMID: 16172383.
Article9. Tsai CY, Wang CS, Tsai MM, Chi HC, Cheng WL, Tseng YH, Chen CY, Lin CD, Wu JI, Wang LH, Lin KH. Interleukin-32 increases human gastric cancer cell invasion associated with tumor progression and metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 2014; 20:2276–2288. PMID: 24602839.
Article10. Calon A, Espinet E, Palomo-Ponce S, Tauriello DV, Iglesias M, Céspedes MV, Sevillano M, Nadal C, Jung P, Zhang XH, Byrom D, Riera A, Rossell D, Mangues R, Massagué J, Sancho E, Batlle E. Dependency of colorectal cancer on a TGF-β-driven program in stromal cells for metastasis initiation. Cancer Cell. 2012; 22:571–584. PMID: 23153532.
Article11. Shin SY, Choi C, Lee HG, Lim Y, Lee YH. Transcriptional regulation of the interleukin-11 gene by oncogenic Ras. Carcinogenesis. 2012; 33:2467–2476. PMID: 23027619.
Article12. Onnis B, Fer N, Rapisarda A, Perez VS, Melillo G. Autocrine production of IL-11 mediates tumorigenicity in hypoxic cancer cells. J Clin Invest. 2013; 123:1615–1629. PMID: 23549086.
Article13. Gao YB, Xiang ZL, Zhou LY, Wu ZF, Fan J, Zeng HY, Zeng ZC. Enhanced production of CTGF and IL-11 from highly metastatic hepatoma cells under hypoxic conditions: an implication of hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis to bone. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013; 139:669–679. PMID: 23307318.
Article14. Huang S. Regulation of metastases by signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling pathway: clinical implications. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13:1362–1366. PMID: 17332277.15. Bromberg J. Stat proteins and oncogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2002; 109:1139–1142. PMID: 11994401.
Article16. Seo IA, Lee HK, Shin YK, Lee SH, Seo SY, Park JW, Park HT. Janus Kinase 2 Inhibitor AG490 inhibits the STAT3 signaling pathway by suppressing protein translation of gp130. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009; 13:131–138. PMID: 19885008.
Article17. Rokavec M, Öner MG, Li H, Jackstadt R, Jiang L, Lodygin D, Kaller M, Horst D, Ziegler PK, Schwitalla S, Slotta-Huspenina J, Bader FG, Greten FR, Hermeking H. IL-6R/STAT3/miR-34a feedback loop promotes EMT-mediated colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis. J Clin Invest. 2014; 124:1853–1867. PMID: 24642471.
Article18. Ito N, Eto M, Nakamura E, Takahashi A, Tsukamoto T, Toma H, Nakazawa H, Hirao Y, Uemura H, Kagawa S, Kanayama H, Nose Y, Kinukawa N, Nakamura T, Jinnai N, Seki T, Takamatsu M, Masui Y, Naito S, Ogawa O. STAT3 polymorphism predicts interferon-alfa response in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:2785–2791. PMID: 17602083.19. Fang Z, Tang Y, Fang J, Zhou Z, Xing Z, Guo Z, Guo X, Wang W, Jiao W, Xu Z, Liu Z. Simvastatin inhibits renal cancer cell growth and metastasis via AKT/mTOR, ERK and JAK2/STAT3 pathway. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e62823. PMID: 23690956.
Article20. Steder M, Alla V, Meier C, Spitschak A, Pahnke J, Fürst K, Kowtharapu BS, Engelmann D, Petigk J, Egberts F, Schäd-Trcka SG, Gross G, Nettelbeck DM, Niemetz A, Pützer BM. DNp73 exerts function in metastasis initiation by disconnecting the inhibitory role of EPLIN on IGF1R-AKT/STAT3 signaling. Cancer Cell. 2013; 24:512–527. PMID: 24135282.
Article21. Pawlus MR, Wang L, Hu CJ. STAT3 and HIF1α cooperatively activate HIF1 target genes in MDA-MB-231 and RCC4 cells. Oncogene. 2014; 33:1670–1679. PMID: 23604114.
Article22. Mamlouk S, Wielockx B. Hypoxia-inducible factors as key regulators of tumor inflammation. Int J Cancer. 2013; 132:2721–2729. PMID: 23055435.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Novel Suppressive Effects of Ketotifen on Migration and Invasion of MDA-MB-231 and HT-1080 Cancer Cells
- Action and Signaling of Lysophosphatidylethanolamine in MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells
- Effect of corosolic acid on apoptosis and angiogenesis in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells
- Effect of Curcumin on Cancer Invasion and Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Activity in MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cell
- The anti-cancer effect of pomegranate-derived nanovesicles on MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells