Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2014 Jun;18(3):211-216. 10.4196/kjpp.2014.18.3.211.
Effect of Exercise Intensity on Unfolded Protein Response in Skeletal Muscle of Rat
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu 705-717, Korea. kodoh@ynu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu 705-717, Korea.
- KMID: 2285512
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2014.18.3.211
Abstract
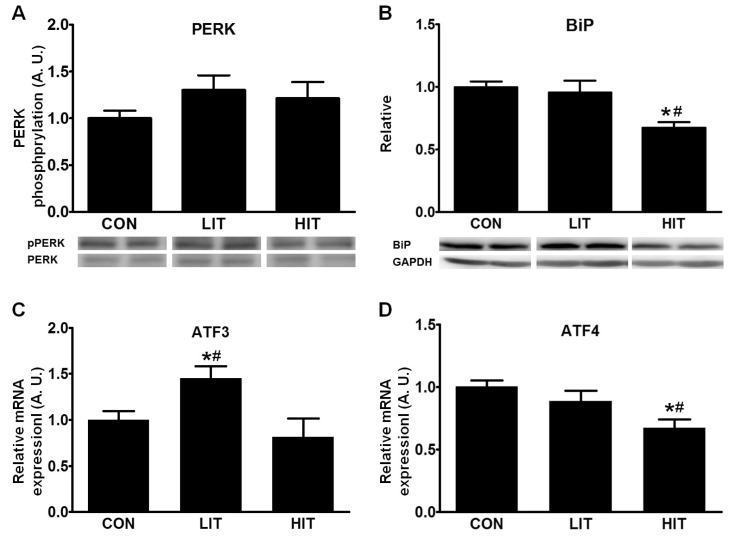
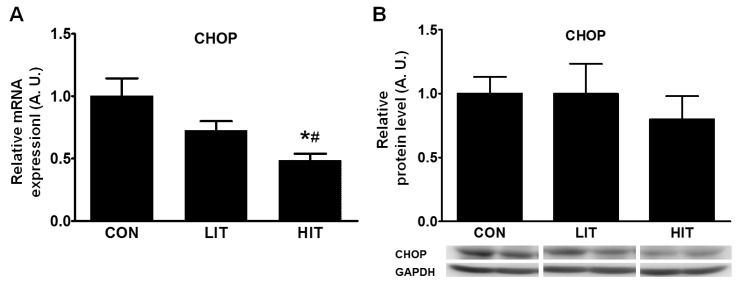
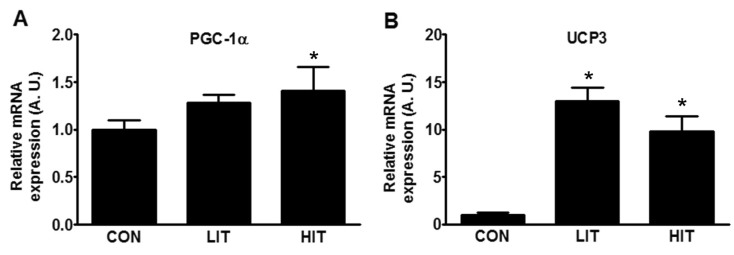
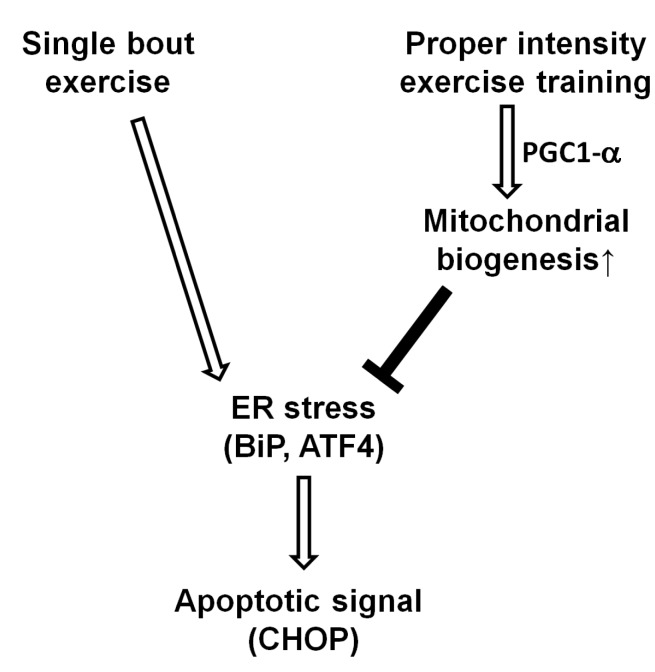
- Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, unfolded protein response (UPR), and mitochondrial biogenesis were assessed following varying intensities of exercise training. The animals were randomly assigned to receive either low- (LIT, n=7) or high intensity training (HIT, n=7), or were assigned to a control group (n=7). Over 5 weeks, the animals in the LIT were exercised on a treadmill with a 10degrees incline for 60 min at a speed of 20 m/min group, and in the HIT group at a speed of 34 m/min for 5 days a week. No statistically significant differences were found in the body weight, plasma triglyceride, and total cholesterol levels across the three groups, but fasting glucose and insulin levels were significantly lower in the exercise-trained groups. Additionally, no statistically significant differences were observed in the levels of PERK phosphorylation in skeletal muscles between the three groups. However, compared to the control and LIT groups, the level of BiP was lower in the HIT group. Compared to the control group, the levels of ATF4 in skeletal muscles and CHOP were significantly lower in the HIT group. The HIT group also showed increased PGC-1alpha mRNA expression in comparison with the control group. Furthermore, both of the trained groups showed higher levels of mitochondrial UCP3 than the control group. In summary, we found that a 5-week high-intensity exercise training routine resulted in increased mitochondrial biogenesis and decreased ER stress and apoptotic signaling in the skeletal muscle tissue of rats.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Ursolic Acid-Induced Elevation of Serum Irisin Augments Muscle Strength During Resistance Training in Men
Hyun Seok Bang, Dae Yun Seo, Yong Min Chung, Kyoung-Mo Oh, Jung Jun Park, Figueroa Arturo, Seung-Hun Jeong, Nari Kim, Jin Han
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014;18(5):441-446. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2014.18.5.441.
Reference
-
1. Ron D, Walter P. Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007; 8:519–529. PMID: 17565364.
Article2. Hetz C. The unfolded protein response: controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012; 13:89–102. PMID: 22251901.
Article3. Lee GH, Oh HW, Lim HD, Lee W, Chae HJ, Kim HR. 4-phenylbutyric acid regulates collagen synthesis and secretion induced by high concentrations of glucose in human gingival fibroblasts. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011; 15:345–351. PMID: 22359472.
Article4. Hetz C, Martinon F, Rodriguez D, Glimcher LH. The unfolded protein response: integrating stress signals through the stress sensor IRE1α. Physiol Rev. 2011; 91:1219–1243. PMID: 22013210.
Article5. Hotamisligil GS. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell. 2010; 140:900–917. PMID: 20303879.
Article6. Peter A, Weigert C, Staiger H, Machicao F, Schick F, Machann J, Stefan N, Thamer C, Häring HU, Schleicher E. Individual stearoyl-coa desaturase 1 expression modulates endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation in human myotubes and is associated with skeletal muscle lipid storage and insulin sensitivity in vivo. Diabetes. 2009; 58:1757–1765. PMID: 19478146.
Article7. Cash JG, Kuhel DG, Basford JE, Jaeschke A, Chatterjee TK, Weintraub NL, Hui DY. Apolipoprotein E4 impairs macrophage efferocytosis and potentiates apoptosis by accelerating endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Biol Chem. 2012; 287:27876–27884. PMID: 22730380.
Article8. Ozcan U, Cao Q, Yilmaz E, Lee AH, Iwakoshi NN, Ozdelen E, Tuncman G, Görgün C, Glimcher LH, Hotamisligil GS. Endoplasmic reticulum stress links obesity, insulin action, and type 2 diabetes. Science. 2004; 306:457–461. PMID: 15486293.
Article9. Huang CJ, Haataja L, Gurlo T, Butler AE, Wu X, Soeller WC, Butler PC. Induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced beta-cell apoptosis and accumulation of polyubiquitinated proteins by human islet amyloid polypeptide. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 293:E1656–E1662. PMID: 17911343.10. Lindström J, Ilanne-Parikka P, Peltonen M, Aunola S, Eriksson JG, Hemiö K, Hämäläinen H, Härkönen P, Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi S, Laakso M, Louheranta A, Mannelin M, Paturi M, Sundvall J, Valle TT, Uusitupa M, Tuomilehto J. Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study Group. Sustained reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes by lifestyle intervention: follow-up of the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study. Lancet. 2006; 368:1673–1679. PMID: 17098085.
Article11. Sherman WM, Friedman JE, Gao JP, Reed MJ, Elton CW, Dohm GL. Glycemia and exercise training alter glucose transport and GLUT4 in the Zucker rat. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1993; 25:341–348. PMID: 8455449.
Article12. Powers SK, Criswell D, Lawler J, Martin D, Lieu FK, Ji LL, Herb RA. Rigorous exercise training increases superoxide dismutase activity in ventricular myocardium. Am J Physiol. 1993; 265:H2094–H2098. PMID: 8285249.
Article13. Jong-Yeon K, Hickner RC, Dohm GL, Houmard JA. Long- and medium-chain fatty acid oxidation is increased in exercisetrained human skeletal muscle. Metabolism. 2002; 51:460–464. PMID: 11912554.
Article14. McArdle A, Pattwell D, Vasilaki A, Griffiths RD, Jackson MJ. Contractile activity-induced oxidative stress: cellular origin and adaptive responses. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001; 280:C621–C627. PMID: 11171582.
Article15. Yuzefovych LV, Musiyenko SI, Wilson GL, Rachek LI. Mitochondrial DNA damage and dysfunction, and oxidative stress are associated with endoplasmic reticulum stress, protein degradation and apoptosis in high fat diet-induced insulin resistance mice. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e54059. PMID: 23342074.
Article16. Wu J, Ruas JL, Estall JL, Rasbach KA, Choi JH, Ye L, Boström P, Tyra HM, Crawford RW, Campbell KP, Rutkowski DT, Kaufman RJ, Spiegelman BM. The unfolded protein response mediates adaptation to exercise in skeletal muscle through a PGC-1α/ATF6α complex. Cell Metab. 2011; 13:160–169. PMID: 21284983.
Article17. Kim HJ, Jamart C, Deldicque L, An GL, Lee YH, Kim CK, Raymackers JM, Francaux M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress markers and ubiquitin-proteasome pathway activity in response to a 200-km run. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011; 43:18–25. PMID: 20473228.
Article18. Rayavarapu S, Coley W, Nagaraju K. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in skeletal muscle homeostasis and disease. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2012; 14:238–243. PMID: 22410828.
Article19. Hansen D, Dendale P, van Loon LJ, Meeusen R. The impact of training modalities on the clinical benefits of exercise intervention in patients with cardiovascular disease risk or type 2 diabetes mellitus. Sports Med. 2010; 40:921–940. PMID: 20942509.
Article20. Garekani ET, Mohebbi H, Kraemer RR, Fathi R. Exercise training intensity/volume affects plasma and tissue adiponectin concentrations in the male rat. Peptides. 2011; 32:1008–1012. PMID: 21291933.
Article21. Norheim F, Langleite TM, Hjorth M, Holen T, Kielland A, Stadheim HK, Gulseth HL, Birkeland KI, Jensen J, Drevon CA. The effects of acute and chronic exercise on PGC-1α, irisin and browning of subcutaneous adipose tissue in humans. FEBS J. 2014; 281:739–749. PMID: 24237962.
Article22. Deldicque L, Cani PD, Delzenne NM, Baar K, Francaux M. Endurance training in mice increases the unfolded protein response induced by a high-fat diet. J Physiol Biochem. 2013; 69:215–225. PMID: 23011781.
Article23. Ogata T, Machida S, Oishi Y, Higuchi M, Muraoka I. Differential cell death regulation between adult-unloaded and aged rat soleus muscle. Mech Ageing Dev. 2009; 130:328–336. PMID: 19428451.
Article24. Schröder M, Kaufman RJ. The mammalian unfolded protein response. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005; 74:739–789. PMID: 15952902.
Article25. Lin JH, Li H, Zhang Y, Ron D, Walter P. Divergent effects of PERK and IRE1 signaling on cell viability. PLoS One. 2009; 4:e4170. PMID: 19137072.
Article26. Deldicque L, Hespel P, Francaux M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in skeletal muscle: origin and metabolic consequences. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2012; 40:43–49. PMID: 21918459.27. Sou SN, Ilieva KM, Polizzi KM. Binding of human BiP to the ER stress transducers IRE1 and PERK requires ATP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012; 420:473–478. PMID: 22446326.
Article28. Harding HP, Zhang Y, Zeng H, Novoa I, Lu PD, Calfon M, Sadri N, Yun C, Popko B, Paules R, Stojdl DF, Bell JC, Hettmann T, Leiden JM, Ron D. An integrated stress response regulates amino acid metabolism and resistance to oxidative stress. Mol Cell. 2003; 11:619–633. PMID: 12667446.
Article29. Rutkowski DT, Arnold SM, Miller CN, Wu J, Li J, Gunnison KM, Mori K, Sadighi Akha AA, Raden D, Kaufman RJ. Adaptation to ER stress is mediated by differential stabilities of pro-survival and pro-apoptotic mRNAs and proteins. PLoS Biol. 2006; 4:e374. PMID: 17090218.
Article30. Xu L, Su L, Liu X. PKCδ regulates death receptor 5 expression induced by PS-341 through ATF4-ATF3/CHOP axis in human lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012; 11:2174–2182. PMID: 22848091.
Article31. Rao J, Qin J, Qian X, Lu L, Wang P, Wu Z, Zhai Y, Zhang F, Li G, Wang X. Lipopolysaccharide preconditioning protects hepatocytes from ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI) through inhibiting ATF4-CHOP pathway in mice. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e65568. PMID: 23750267.
Article32. Csordás G, Hajnóczky G. SR/ER-mitochondrial local communication: calcium and ROS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009; 1787:1352–1362. PMID: 19527680.
Article33. Irrcher I, Ljubicic V, Hood DA. Interactions between ROS and AMP kinase activity in the regulation of PGC-1alpha transcription in skeletal muscle cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009; 296:C116–C123. PMID: 19005163.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Regulation of exercise-stimulated glucose uptake in skeletal muscle
- Effect of Resistance Exercise Training on Mustn1 mRNA Expression in Rat Skeletal Muscle
- Aerobic Exercise Ameliorates Muscle Atrophy Induced by Methylglyoxal via Increasing Gastrocnemius and Extensor Digitorum Longus Muscle Sensitivity
- Exercise Training Attenuates Ovariectomy-Induced Alterations in Skeletal Muscle Remodeling, Apoptotic Signaling, and Atrophy Signaling in Rat Skeletal Muscle
- Efficient Exercise Volume Analysis through Number of Repetitions and EMG Response of Agonist Muscle During the Bench Press