The Neuroprotective Potential of Cyanidin-3-glucoside Fraction Extracted from Mulberry Following Oxygen-glucose Deprivation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacology, Cell Death Disease Research Center, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 137-701, Korea. kocho@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Rural Development Administration, Suwon 441-707, Korea.
- KMID: 2285422
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2011.15.6.353
Abstract
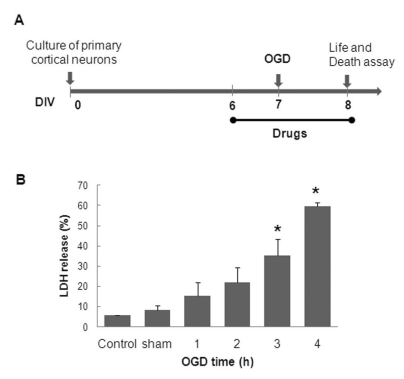
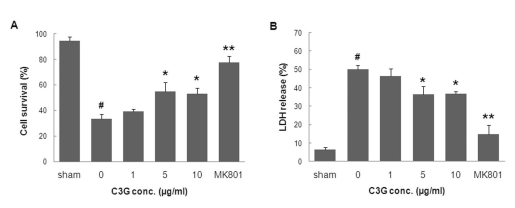
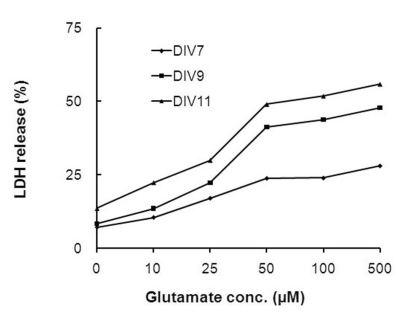
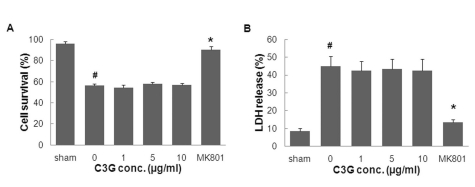
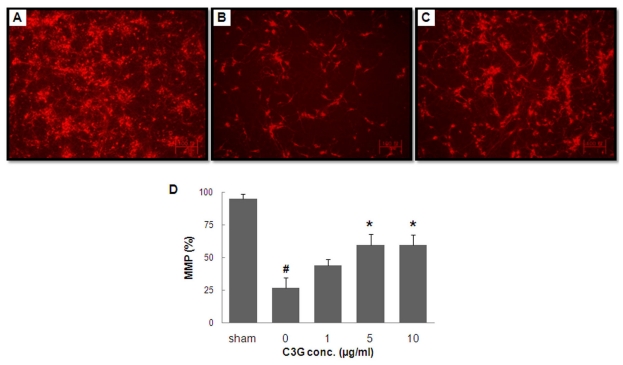
- In this study, cyanidin-3-glucoside (C3G) fraction extracted from the mulberry fruit (Morus alba L.) was investigated for its neuroprotective effects against oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) and glutamate-induced cell death in rat primary cortical neurons. Cell membrane damage and mitochondrial function were assessed by LDH release and MTT reduction assays, respectively. A time-course study of OGD-induced cell death of primary cortical neurons at 7 days in vitro (DIV) indicated that neuronal death was OGD duration-dependent. It was also demonstrated that OGD for 3.5 h resulted in approximately 50% cell death, as determined by the LDH release assay. Treatments with mulberry C3G fraction prevented membrane damage and preserved the mitochondrial function of the primary cortical neurons exposed to OGD for 3.5 h in a concentration-dependent manner. Glutamate-induced cell death was more pronounced in DIV-9 and DIV-11 cells than that in DIV-7 neurons, and an application of 50microM glutamate was shown to induce approximately 40% cell death in DIV-9 neurons. Interestingly, treatment with mulberry C3G fraction did not provide a protective effect against glutamate-induced cell death in primary cortical neurons. On the other hand, treatment with mulberry C3G fraction maintained the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) in primary cortical neurons exposed to OGD as assessed by the intensity of rhodamine-123 fluorescence. These results therefore suggest that the neuroprotective effects of mulberry C3G fraction are mediated by the maintenance of the MMP and mitochondrial function but not by attenuating glutamate-induced excitotoxicity in rat primary cortical neurons.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Expression and Activity of the Na-K ATPase in Ischemic Injury of Primary Cultured Astrocytes
Mi Jung Kim, Jinyoung Hur, In-Hye Ham, Hye Jin Yang, Younghoon Kim, Seungjoon Park, Young-Wuk Cho
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013;17(4):275-281. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.4.275.Cyanidin-3-glucoside Inhibits ATP-induced Intracellular Free Ca2+ Concentration, ROS Formation and Mitochondrial Depolarization in PC12 Cells
Shazia Perveen, Ji Seon Yang, Tae Joung Ha, Shin Hee Yoon
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014;18(4):297-305. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2014.18.4.297.Cyanidin-3-glucoside inhibits amyloid β25–35-induced neuronal cell death in cultured rat hippocampal neurons
Ji Seon Yang, Sujeong Jeon, Kee Dong Yoon, Shin Hee Yoon
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018;22(6):689-696. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2018.22.6.689.
Reference
-
1. American Heart Association. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2008 update. 2008. Dallas, Texas:2. O'Collins VE, Macleod MR, Donnan GA, Horky LL, van der Worp BH, Howells DW. 1,026 experimental treatments in acute stroke. Ann Neurol. 2006; 59:467–477. PMID: 16453316.3. Lee KE, Kim SK, Cho KO, Kim SY. Pre-ischemic treatment with ampicillin reduces neuronal damage in the mouse hippocampus and neostriatum after transient forebrain ischemia. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008; 12:287–291. PMID: 19967069.
Article4. Cho KO, Kim SK, Cho YJ, Sung KW, Kim SY. Regional differences in the neuroprotective effect of minocycline in a mouse model of global forebrain ischemia. Life Sci. 2007; 80:2030–2035. PMID: 17408699.
Article5. Coyle JT, Puttfarcken P. Oxidative stress, glutamate, and neurodegenerative disorders. Science. 1993; 262:689–695. PMID: 7901908.
Article6. Tan S, Wood M, Maher P. Oxidative stress induces a form of programmed cell death with characteristics of both apoptosis and necrosis in neuronal cells. J Neurochem. 1998; 71:95–105. PMID: 9648855.
Article7. Lipton P. Ischemic cell death in brain neurons. Physiol Rev. 1999; 79:1431–1568. PMID: 10508238.
Article8. Choi DW, Rothman SM. The role of glutamate neurotoxicity in hypoxic-ischemic neuronal death. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1990; 13:171–182. PMID: 1970230.
Article9. Kontos HA. Oxygen radicals in cerebral ischemia: the 2001 Willis lecture. Stroke. 2001; 32:2712–2716. PMID: 11692043.
Article10. Warner DS, Sheng H, Batinić-Haberle I. Oxidants, antioxidants and the ischemic brain. J Exp Biol. 2004; 207:3221–3231. PMID: 15299043.
Article11. Niizuma K, Endo H, Chan PH. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction as determinants of ischemic neuronal death and survival. J Neurochem. 2009; 109(Suppl 1):133–138. PMID: 19393019.
Article12. Cherubini A, Ruggiero C, Morand C, Lattanzio F, Dell'aquila G, Zuliani G, Di Iorio A, Andres-Lacueva C. Dietary antioxidants as potential pharmacological agents for ischemic stroke. Curr Med Chem. 2008; 15:1236–1248. PMID: 18473816.
Article13. Slemmer JE, Shacka JJ, Sweeney MI, Weber JT. Antioxidants and free radical scavengers for the treatment of stroke, traumatic brain injury and aging. Curr Med Chem. 2008; 15:404–414. PMID: 18288995.14. Andres-Lacueva C, Shukitt-Hale B, Galli RL, Jauregui O, Lamuela-Raventos RM, Joseph JA. Anthocyanins in aged blueberry-fed rats are found centrally and may enhance memory. Nutr Neurosci. 2005; 8:111–120. PMID: 16053243.
Article15. Margaill I, Plotkine M, Lerouet D. Antioxidant strategies in the treatment of stroke. Free Radic Biol Med. 2005; 39:429–443. PMID: 16043015.
Article16. Vokó Z, Hollander M, Hofman A, Koudstaal PJ, Breteler MM. Dietary antioxidants and the risk of ischemic stroke: the Rotterdam Study. Neurology. 2003; 61:1273–1275. PMID: 14610137.
Article17. Amorini AM, Lazzarino G, Galvano F, Fazzina G, Tavazzi B, Galvano G. Cyanidin-3-O-beta-glucopyranoside protects myocardium and erythrocytes from oxygen radical-mediated damages. Free Radic Res. 2003; 37:453–460. PMID: 12747740.18. Tsuda T, Horio F, Kitoh J, Osawa T. Protective effects of dietary cyanidin 3-O-beta-D-glucoside on liver ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1999; 368:361–366. PMID: 10441388.19. Kang TH, Hur JY, Kim HB, Ryu JH, Kim SY. Neuroprotective effects of the cyanidin-3-O-beta-d-glucopyranoside isolated from mulberry fruit against cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Lett. 2006; 391:122–126. PMID: 16181734.20. Kim KT, Nam TK, Park YS, Kim YB, Park SW. Neuroprotective effect of anthocyanin on experimental traumatic spinal cord injury. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2011; 49:205–211. PMID: 21607177.
Article21. Heo HJ, Lee CY. Strawberry and its anthocyanins reduce oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. J Agric Food Chem. 2005; 53:1984–1989. PMID: 15769124.
Article22. Kim HB, Kim SL. Identification of C3G (cyanidin-3-glucoside) from mulberry fruits and quantification with different varieties. Korean J Sericult Sci. 2003; 45:90–95.23. Kim HB, Kim SL, Koh SH, Seok YS, Kim YS, Sung GB, Kang PD. The development of natural pigment with mulberry fruit as a food additive. Korean J Crop Sci. 2011; 56:18–22.
Article24. Bhuiyan MI, Islam MN, Jung SY, Yoo HH, Lee YS, Jin C. Involvement of ceramide in ischemic tolerance induced by preconditioning with sublethal oxygen-glucose deprivation in primary cultured cortical neurons of rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010; 33:11–17. PMID: 20045928.
Article25. Bhuiyan MI, Jung SY, Kim HJ, Lee YS, Jin C. Major role of the PI3K/Akt pathway in ischemic tolerance induced by sublethal oxygen-glucose deprivation in cortical neurons in vitro. Arch Pharm Res. 2011; 34:1023–1034. PMID: 21725824.
Article26. Brewer GJ, Torricelli JR, Evege EK, Price PJ. Optimized survival of hippocampal neurons in B27-supplemented Neurobasal, a new serum-free medium combination. J Neurosci Res. 1993; 35:567–576. PMID: 8377226.
Article27. Lesuisse C, Martin LJ. Immature and mature cortical neurons engage different apoptotic mechanisms involving caspase-3 and the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2002; 22:935–950. PMID: 12172379.
Article28. Serraino I, Dugo L, Dugo P, Mondello L, Mazzon E, Dugo G, Caputi AP, Cuzzocrea S. Protective effects of cyanidin-3-O-glucoside from blackberry extract against peroxynitrite-induced endothelial dysfunction and vascular failure. Life Sci. 2003; 73:1097–1114. PMID: 12818719.
Article29. Mitcheva M, Astroug H, Drenska D, Popov A, Kassarova M. Biochemical and morphological studies on the effects of anthocyans and vitamin E on carbon tetrachloride induced liver injury. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 1993; 39:443–448. PMID: 8329983.30. Matsunaga N, Imai S, Inokuchi Y, Shimazawa M, Yokota S, Araki Y, Hara H. Bilberry and its main constituents have neuroprotective effects against retinal neuronal damage in vitro and in vivo. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2009; 53:869–877. PMID: 19415665.
Article31. Tarozzi A, Morroni F, Merlicco A, Bolondi C, Teti G, Falconi M, Cantelli-Forti G, Hrelia P. Neuroprotective effects of cyanidin 3-O-glucopyranoside on amyloid beta (25-35) oligomer-induced toxicity. Neurosci Lett. 2010; 473:72–76. PMID: 20152881.
Article32. Kapinya KJ, Löwl D, Fütterer C, Maurer M, Waschke KF, Isaev NK, Dirnagl U. Tolerance against ischemic neuronal injury can be induced by volatile anesthetics and is inducible NO synthase dependent. Stroke. 2002; 33:1889–1898. PMID: 12105371.33. Pérez-Pinzón MA, Tao L, Nicholson C. Extracellular potassium, volume fraction, and tortuosity in rat hippocampal CA1, CA3, and cortical slices during ischemia. J Neurophysiol. 1995; 74:565–573. PMID: 7472364.34. Goldberg MP, Choi DW. Combined oxygen and glucose deprivation in cortical cell culture: calcium-dependent and calcium-independent mechanisms of neuronal injury. J Neurosci. 1993; 13:3510–3524. PMID: 8101871.
Article35. Aizenman Y, de Vellis J. Brain neurons develop in a serum and glial free environment: effects of transferrin, insulin, insulin-like growth factor-I and thyroid hormone on neuronal survival, growth and differentiation. Brain Res. 1987; 406:32–42. PMID: 3105814.
Article36. Lindsay RM. Adult rat brain astrocytes support survival of both NGF-dependent and NGF-insensitive neurones. Nature. 1979; 282:80–82. PMID: 503191.
Article37. Jones PA, May GR, McLuckie JA, Iwashita A, Sharkey J. Apoptosis is not an invariable component of in vitro models of cortical cerebral ischaemia. Cell Res. 2004; 14:241–250. PMID: 15225418.
Article38. Andjelković M, Jakubowicz T, Cron P, Ming XF, Han JW, Hemmings BA. Activation and phosphorylation of a pleckstrin homology domain containing protein kinase (RAC-PK/PKB) promoted by serum and protein phosphatase inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996; 93:5699–5704. PMID: 8650155.39. Benveniste H, Drejer J, Schousboe A, Diemer NH. Elevation of the extracellular concentrations of glutamate and aspartate in rat hippocampus during transient cerebral ischemia monitored by intracerebral microdialysis. J Neurochem. 1984; 43:1369–1374. PMID: 6149259.
Article40. Park CK, Nehls DG, Graham DI, Teasdale GM, McCulloch J. The glutamate antagonist MK-801 reduces focal ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol. 1988; 24:543–551. PMID: 2853604.
Article41. Alix JJ, Fern R. Glutamate receptor-mediated ischemic injury of premyelinated central axons. Ann Neurol. 2009; 66:682–693. PMID: 19938170.
Article42. Khkönen MP, Heinmki J, Ollilainen V, Heinonen M. Berry anthocyanins: isolation, identification and antioxidant activities. J Sci Food Agric. 2003; 83:1403–1411.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cyanidin-3-glucoside Inhibits ATP-induced Intracellular Free Ca2+ Concentration, ROS Formation and Mitochondrial Depolarization in PC12 Cells
- Isolation And Development Of Quantification Method For Cyanidin-3-glucoside And Cyanidin-3-rutinoside In Mulberry Fruit By High-performance Countercurrent Chromatography And High-performance Liquid Chromatography
- Neuregulin 1/ErbB4 signaling attenuates neuronal cell damage under oxygen-glucose deprivation in primary hippocampal neurons
- Cyanidin-3-glucoside inhibits amyloid β₂₅₋₃₅-induced neuronal cell death in cultured rat hippocampal neurons
- The individual and combined neuroprotective effects of propofol and ketamine on rat mixed cortical cultures exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation-reperfusion injury