Korean J Obstet Gynecol.
2011 Aug;54(8):441-447. 10.5468/KJOG.2011.54.8.441.
Expression of membrane type-2 and -3 matrix metalloproteinases in eutopic endometrium of women with advanced endometriosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hyewon@ewha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2274064
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5468/KJOG.2011.54.8.441
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the expression of messenger RNA (mRNA) for membrane type-2 matrix metalloproteinases (MT2-MMPs) and MT3-MMP and compare their expression pattern in women with severe endometriosis and normal controls.
METHODS
Quantitative competitive polymerase chain reaction was performed to evaluate the mRNA expression of MT2-MMP and MT3-MMP in endometrium from 36 women with severe endometriosis and 52 women without endometriosis throughout the menstrual cycle.
RESULTS
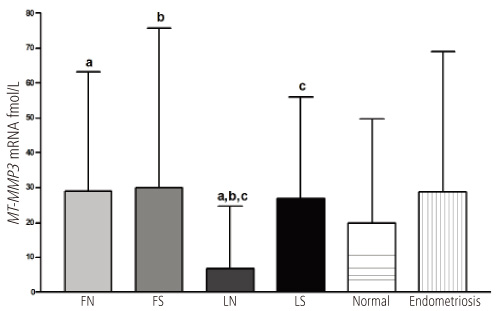
Eutopic endometrium from women with endometriosis expressed higher levels of MT3-MMP than that from normal women in secretory phase (P < 0.05). MT2-MMP expression from eutopic endometrium showed no significant differences between patients with endometriosis and controls.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that eutopic endometrium from patients with endometriosis may be more proteolytic, angiogenic and prone to growth because of greater MT3-MMP expression than endometrium from women without endometriosis. Thus, increased proteolytic and angiogenic activities may be one of the explanations of the pathogenesis of endometriosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lamb K, Hoffmann RG, Nichols TR. Family trait analysis: a case-control study of 43 women with endometriosis and their best friends. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986. 154:596–601.2. Cramer DW, Wilson E, Stillman RJ, Berger MJ, Belisle S, Schiff I, et al. The relation of endometriosis to menstrual characteristics, smoking, and exercise. JAMA. 1986. 255:1904–1908.3. Ramey JW, Archer DF. Peritoneal fluid: its relevance to the development of endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 1993. 60:1–14.4. Oosterlynck DJ, Meuleman C, Sobis H, Vandeputte M, Koninckx PR. Angiogenic activity of peritoneal fluid from women with endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 1993. 59:778–782.5. Sampson JA. Metastatic or Embolic Endometriosis, due to the Menstrual Dissemination of Endometrial Tissue into the Venous Circulation. Am J Pathol. 1927. 3:93–110.43.6. Heymans S, Luttun A, Nuyens D, Theilmeier G, Creemers E, Moons L, et al. Inhibition of plasminogen activators or matrix metalloproteinases prevents cardiac rupture but impairs therapeutic angiogenesis and causes cardiac failure. Nat Med. 1999. 5:1135–1142.7. Stetler-Stevenson WG. Matrix metalloproteinases in angiogenesis: a moving target for therapeutic intervention. J Clin Invest. 1999. 103:1237–1241.8. Pepper MS. Extracellular proteolysis and angiogenesis. Thromb Haemost. 2001. 86:346–355.9. MacDougall JR, Matrisian LM. Contributions of tumor and stromal matrix metalloproteinases to tumor progression, invasion and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1995. 14:351–362.10. Hotary K, Allen E, Punturieri A, Yana I, Weiss SJ. Regulation of cell invasion and morphogenesis in a three-dimensional type I collagen matrix by membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases 1, 2, and 3. J Cell Biol. 2000. 149:1309–1323.11. Visse R, Nagase H. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ Res. 2003. 92:827–839.12. Hotary KB, Yana I, Sabeh F, Li XY, Holmbeck K, Birkedal-Hansen H, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) regulate fibrin-invasive activity via MT1-MMP-dependent and -independent processes. J Exp Med. 2002. 195:295–308.13. Zhou Z, Apte SS, Soininen R, Cao R, Baaklini GY, Rauser RW, et al. Impaired endochondral ossification and angiogenesis in mice deficient in membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. 97:4052–4057.14. Sounni NE, Devy L, Hajitou A, Frankenne F, Munaut C, Gilles C, et al. MT1-MMP expression promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis through an up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression. FASEB J. 2002. 16:555–564.15. Seiki M, Yana I. Roles of pericellular proteolysis by membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase in cancer invasion and angiogenesis. Cancer Sci. 2003. 94:569–574.16. Chung HW, Lee JY, Moon HS, Hur SE, Park MH, Wen Y, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-2, membranous type 1 matrix metalloproteinase, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 expression in ectopic and eutopic endometrium. Fertil Steril. 2002. 78:787–795.17. Goffin F, Munaut C, Frankenne F, Perrier D'Hauterive S, Béliard A, Fridman V, et al. Expression pattern of metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of matrix-metalloproteinases in cycling human endometrium. Biol Reprod. 2003. 69:976–984.18. Määttä M, Soini Y, Liakka A, Autio-Harmainen H. Localization of MT1-MMP, TIMP-1, TIMP-2, and TIMP-3 messenger RNA in normal, hyperplastic, and neoplastic endometrium. Enhanced expression by endometrial adenocarcinomas is associated with low differentiation. Am J Clin Pathol. 2000. 114:402–411.19. Zhang J, Hampton AL, Nie G, Salamonsen LA. Progesterone inhibits activation of latent matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 by membrane-type 1 MMP: enzymes coordinately expressed in human endometrium. Biol Reprod. 2000. 62:85–94.20. Plaisier M, Koolwijk P, Hanemaaijer R, Verwey RA, van der Weiden RM, Risse EK, et al. Membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases and vascularization in human endometrium during the menstrual cycle. Mol Hum Reprod. 2006. 12:11–18.21. Collette T, Bellehumeur C, Kats R, Maheux R, Mailloux J, Villeneuve M, et al. Evidence for an increased release of proteolytic activity by the eutopic endometrial tissue in women with endometriosis and for involvement of matrix metalloproteinase-9. Hum Reprod. 2004. 19:1257–1264.22. Revised American Fertility Society classification of endometriosis: 1985. Fertil Steril. 1985. 43:351–352.23. Noyes RW, Hertig AT, Rock J. Dating the endometrial biopsy. Fertil Steril. 1950. 1:3–25.24. Sato H, Takino T, Okada Y, Cao J, Shinagawa A, Yamamoto E, et al. A matrix metalloproteinase expressed on the surface of invasive tumour cells. Nature. 1994. 370:61–65.25. Takino T, Sato H, Shinagawa A, Seiki M. Identification of the second membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase (MT-MMP-2) gene from a human placenta cDNA library. MT-MMPs form a unique membrane-type subclass in the MMP family. J Biol Chem. 1995. 270:23013–23020.26. Will H, Hinzmann B. cDNA sequence and mRNA tissue distribution of a novel human matrix metalloproteinase with a potential transmembrane segment. Eur J Biochem. 1995. 231:602–608.27. Puente XS, Pendás AM, Llano E, Velasco G, López-Otín C. Molecular cloning of a novel membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase from a human breast carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1996. 56:944–949.28. Pei D. Identification and characterization of the fifth membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase MT5-MMP. J Biol Chem. 1999. 274:8925–8932.29. Kolkenbrock H, Hecker-Kia A, Orgel D, Ulbrich N, Will H. Activation of progelatinase A and progelatinase A/TIMP-2 complex by membrane type 2-matrix metalloproteinase. Biol Chem. 1997. 378:71–76.30. Atkinson SJ, Crabbe T, Cowell S, Ward RV, Butler MJ, Sato H, et al. Intermolecular autolytic cleavage can contribute to the activation of progelatinase A by cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1995. 270:30479–30485.31. Knäuper V, Will H, López-Otin C, Smith B, Atkinson SJ, Stanton H, et al. Cellular mechanisms for human procollagenase-3 (MMP-13) activation. Evidence that MT1-MMP (MMP-14) and gelatinase a (MMP-2) are able to generate active enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1996. 271:17124–17131.32. Okada A, Bellocq JP, Rouyer N, Chenard MP, Rio MC, Chambon P, et al. Membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase (MT-MMP) gene is expressed in stromal cells of human colon, breast, and head and neck carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995. 92:2730–2734.33. Velasco G, Cal S, Merlos-Suárez A, Ferrando AA, Alvarez S, Nakano A, et al. Human MT6-matrix metalloproteinase: identification, progelatinase A activation, and expression in brain tumors. Cancer Res. 2000. 60:877–882.34. Crawford HC, Matrisian LM. Tumor and stromal expression of matrix metalloproteinases and their role in tumor progression. Invasion Metastasis. 1994. 14:234–245.35. Ueno H, Nakamura H, Inoue M, Imai K, Noguchi M, Sato H, et al. Expression and tissue localization of membrane-types 1, 2, and 3 matrix metalloproteinases in human invasive breast carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1997. 57:2055–2060.36. Gilles C, Polette M, Piette J, Munaut C, Thompson EW, Birembaut P, et al. High level of MT-MMP expression is associated with invasiveness of cervical cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 1996. 65:209–213.37. Kitagawa Y, Kunimi K, Ito H, Sato H, Uchibayashi T, Okada Y, et al. Expression and tissue localization of membrane-types 1, 2, and 3 matrix metalloproteinases in human urothelial carcinomas. J Urol. 1998. 160:1540–1545.38. Pap T, Shigeyama Y, Kuchen S, Fernihough JK, Simmen B, Gay RE, et al. Differential expression pattern of membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000. 43:1226–1232.39. Davidson B, Goldberg I, Berner A, Nesland JM, Givant-Horwitz V, Bryne M, et al. Expression of membrane-type 1, 2, and 3 matrix metalloproteinases messenger RNA in ovarian carcinoma cells in serous effusions. Am J Clin Pathol. 2001. 115:517–524.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- mRNA Expression Differences of uPA, uPAR in Eutopic Endometrium of Advanced Stage Endometriosis Patients
- Survivin and Bcl-2 expression in eutopic endometrium with and without endometriosis
- mRNA Expression of Thrombospondin-1 and -2 in Severe Endometriosis Patients in Korean Women
- Increased Proliferating Activity of Endometrium in Endometriosis
- Detection of nerve fibers in the eutopic endometrium of women with endometriosis, uterine fibroids and adenomyosis