Korean J Nutr.
2012 Apr;45(2):192-200. 10.4163/kjn.2012.45.2.192.
Sugar composition and glycemic indices of frequently consumed fruits in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medical Nutrition, Graduate School of East-West Medical Science, Kyung Hee University, Yongin 446-701, Korea. rwcho@khu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Food and Nutrition, College of Natural Sciences, Changwon National University, Changwon 641-773, Korea.
- 3Research Institute of Clinical Nutrition, Kyung Hee University, Seoul 130-701, Korea.
- 4Department of Endocrine and Metabolism, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul 130-872, Korea.
- 5Department of Food Science & Biotechnology and Institute of Life Sciences & Resources, Kyung Hee University, Seoul 130-701, Korea.
- KMID: 2268668
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4163/kjn.2012.45.2.192
Abstract
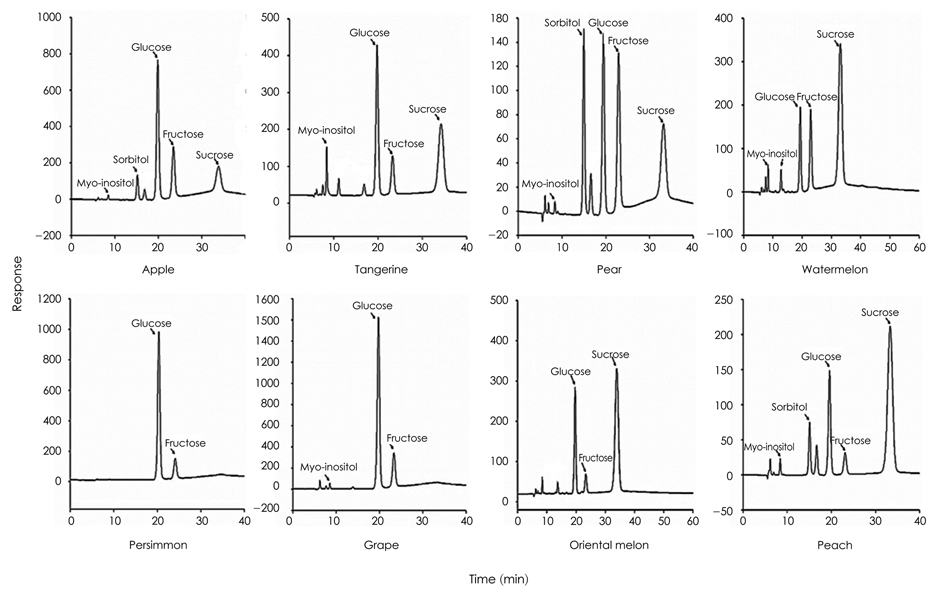
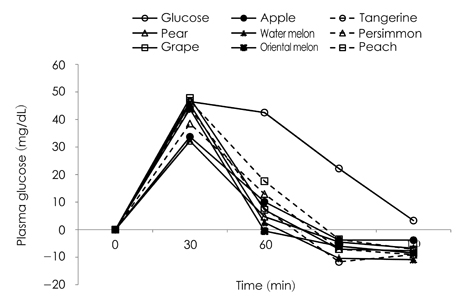
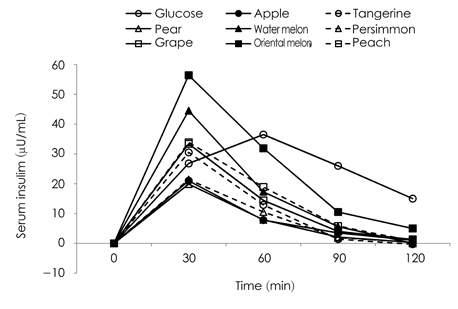
- Fruits are generally recommended for a balanced meal, as they are good sources of vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which may improve blood glucose control. However, fruits have simple sugars with a wide glycemic index (GI) range. The purpose of this study was to analyze the sugar content and composition and to determine the glycemic indices of the most frequently consumed fruits in Korea, including apple, tangerine, pear, water melon, persimmon, grape, oriental melon, and peach. The sugar content and composition of the fruits were analyzed by high performance anion-exchange chromatography (Dinonex model DX-600). The GI of the fruits was measured in 13 healthy subjects (seven females and six males) after permission was received from the University Hospital institutional review board (KHU-IRB 1114-06). The subjects consumed 50 g of glucose as a reference and carbohydrate portions of eight fruits. Blood samples were collected at 0, 30, 60, 90, and 120 min after consuming the fruits. The GI values for the fruits were calculated by expressing the increase in the area under the blood glucose response curve for each subject. As a result, the total sugar contents of 100 g fruits were: grape (13.9 g), apple (12.3 g), persimmon (11.9 g), oriental melon (11.2 g), watermelon (9.3 g), tangerine (8.9 g), peach (8.6 g), and pear (8.3 g). The GI values of the fruits were as follows: GI value of peach (56.5 +/- 14.17), watermelon (53.5 +/- 18.07), oriental melon (51.2 +/- 18.14), tangerine (50.4 +/- 15.16), grape (48.1 +/- 14.05), persimmon (42.9 +/- 18.92), pear (35.7 +/- 14.38), and apple (33.5 +/- 11.92). These findings will help individuals choose fruit for controlling blood sugar.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Development of a Food Exchange Table and Food Pattern for Nutritionally Balanced Menu Planning
Yun Ahn, Ikhyun Yeo, Sangyun Lee, Kisun Nam
Korean J Community Nutr. 2018;23(5):411-423. doi: 10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.5.411.Utility of the Glycemic Index in Practical Diabetes Management
Jung Hwa Lee
J Korean Diabetes. 2015;16(2):135-140. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2015.16.2.135.
Reference
-
1. Korea Agro-Fisheries & Food Trade Corporation. Consumption patterns of the main fruits 2005. 2006. Seoul:2. Korea Rural Economic Institute (KREI). Food balance sheet. 2008. Seoul:3. World Cancer Research Fund. American Institute for Cancer Research. Food, nutrition, physical activity, and the prevention of cancer: a global perspective. 2007. 9.4. Ibiebele TI, van der Pols JC, Hughes MC, Marks GC, Williams GM, Green AC. Dietary pattern in association with squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: a prospective study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007. 85(5):1401–1408.
Article5. Lichtenstein AH, Appel LJ, Brands M, Carnethon M, Daniels S, Franch HA, Franklin B, Kris-Etherton P, Harris WS, Howard B, Karanja N, Lefevre M, Rudel L, Sacks F, Van Horn L, Winston M, Wylie-Rosett J. Diet and lifestyle recommendations revision 2006: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Nutrition Committee. Circulation. 2006. 114(1):82–96.6. Kushi LH, Byers T, Doyle C, Bandera EV, McCullough M, McTiernan A, Gansler T, Andrews KS, Thun MJ. American Cancer Society 2006 Nutrition and Physical Activity Guidelines Advisory Committee. American Cancer Society Guidelines on Nutrition and Physical Activity for cancer prevention: reducing the risk of cancer with healthy food choices and physical activity. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006. 56(5):254–281.
Article7. Liu S, Manson JE, Lee IM, Cole SR, Hennekens CH, Willett WC, Buring JE. Fruit and vegetable intake and risk of cardiovascular disease: the Women's Health Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000. 72(4):922–928.
Article8. Sesso HD, Buring JE, Christen WG, Kurth T, Belanger C, MacFadyen J, Bubes V, Manson JE, Glynn RJ, Gaziano JM. Vitamins E and C in the prevention of cardiovascular disease in men: the Physicians' Health Study II randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2008. 300(18):2123–2133.9. Huxley RR, Neil HA. The relation between dietary flavonol intake and coronary heart disease mortality: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2003. 57(8):904–908.
Article10. Hertog MG, Feskens EJ, Hollman PC, Katan MB, Kromhout D. Dietary antioxidant flavonoids and risk of coronary heart disease: the Zutphen Elderly Study. Lancet. 1993. 342(8878):1007–1011.
Article11. Jenkins DJ, Wolever TM, Taylor RH, Barker H, Fielden H, Baldwin JM, Bowling AC, Newman HC, Jenkins AL, Goff DV. Glycemic index of foods: a physiological basis for carbohydrate exchange. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981. 34(3):362–366.
Article12. Carbohydrates in human nutrition. Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation. FAO Food Nutr Pap. 1998. 66:1–140.13. Bahadori B, Yazdani-Biuki B, Krippl P, Brath H, Uitz E, Wascher TC. Low-fat, high-carbohydrate (low-glycaemic index) diet induces weight loss and preserves lean body mass in obese heal-thy subjects: results of a 24-week study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2005. 7(3):290–293.
Article14. Dumesnil JG, Turgeon J, Tremblay A, Poirier P, Gilbert M, Gagnon L, St-Pierre S, Garneau C, Lemieux I, Pascot A, Bergeron J, Després JP. Effect of a low-glycaemic index--low-fat--high protein diet on the atherogenic metabolic risk profile of abdominally obese men. Br J Nutr. 2001. 86(5):557–568.
Article15. Pi-Sunyer X. Do glycemic index, glycemic load, and fiber play a role in insulin sensitivity, disposition index, and type 2 diabetes? Diabetes Care. 2005. 28(12):2978–2979.
Article16. Riccardi G, Rivellese AA, Giacco R. Role of glycemic index and glycemic load in the healthy state, in prediabetes, and in diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008. 87(1):269S–274S.
Article17. Atkinson FS, Foster-Powell K, Brand-Miller JC. International tables of glycemic index and glycemic load values: 2008. Diabetes Care. 2008. 31(12):2281–2283.
Article18. Jenkins DJ, Srichaikul K, Kendall CW, Sievenpiper JL, Abdulnour S, Mirrahimi A, Meneses C, Nishi S, He X, Lee S, So YT, Esfahani A, Mitchell S, Parker TL, Vidgen E, Josse RG, Leiter LA. The relation of low glycaemic index fruit consumption to glycaemic control and risk factors for coronary heart disease in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2011. 54(2):271–279.
Article19. Wolever TM, Miller JB. Sugars and blood glucose control. Am J Clin Nutr. 1995. 62(1 Suppl):212S–221S.
Article20. Crapo PA. Theory vs. fact: The glycemic response to foods. Nutr Today. 1984. 19(2):6–11.21. Mani UV, Bhatt S, Mehta NC, Pradhan SN, Shah V, Mani I. Glycemic index of traditional Indian carbohydrate foods. J Am Coll Nutr. 1990. 9(6):573–577.
Article22. Guevarra MTB, Panlasigui LN. Blood glucose responses of diabetes mellitus type II patients to some local fruits. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2000. 9(4):303–308.
Article23. Wolever TMS, Vuksan V, Relle LK, Jenkins AL, Josse RG, Wong GS, Jenkins DJA. Glycaemic index of fruits and fruit products in patients with diabetes. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 1993. 43(4):205–212.
Article24. Ha MA, Mann JI, Melton LD, Lewis-Barned NJ. Relationship between the glycaemic index and sugar content of fruits. Diabetes Nutr Metab. 1992. 5(3):199–203.25. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The Third Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHA-NES IV). 2009. Cheongwon:26. Jeong JS, Kwon HJ, Lee YM, Yoon HR, Hong SP. Determination of sugar phosphates by high-performance anion-exchange chromatography coupled with pulsed amperometric detection. J Chromatogr A. 2007. 1164(1-2):167–173.
Article27. Wolever TM, Jenkins DJ, Jenkins AL, Josse RG. The glycemic index: methodology and clinical implications. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991. 54(5):846–854.
Article28. Kim MJ, Kim JH, Oh HK, Chang MJ, Kim SH. Seasonal variations of nutrients in Korean fruits and vegetables: Examining water, protein, lipid, ascorbic acid, and β-carotene contents. Korean J Food Cookery Sci. 2007. 23(4):423–432.29. Lunetta M, Di Mauro M, Crimi S, Mughini L. No important differences in glycaemic responses to common fruits in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabet Med. 1995. 12(8):674–678.
Article30. Foster-Powell K, Holt SH, Brand-Miller JC. International table of glycemic index and glycemic load values: 2002. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002. 76(1):5–56.
Article31. Holub BJ. Metabolism and function of myo-inositol and inositol phospholipids. Annu Rev Nutr. 1986. 6:563–597.
Article32. Foster-Powell K, Miller JB. International tables of glycemic index. Am J Clin Nutr. 1995. 62(4):871S–890S.
Article33. Sydney University Glycemic Index Research Service (SUGiRS). 1995-2007. Australia: The University of Sydney, Human Nutrition Unit.34. Collier G, McLean A, O'Dea K. Effect of co-ingestion of fat on the metabolic responses to slowly and rapidly absorbed carbohydrates. Diabetologia. 1984. 26(1):50–54.
Article35. Nuttall FQ, Mooradian AD, Gannon MC, Billington C, Krezowski P. Effect of protein ingestion on the glucose and insulin response to a standardized oral glucose load. Diabetes Care. 1984. 7(5):465–470.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Short-term impact of sugar consumption on hunger and ad libitum food intake in young women
- Intake of Fruits for Diabetics: Why and How Much?
- Composition of Food Groups Appropriate for Evaluation of Diet Quality of Korean Adolescents: Based on Kant's Minimum Amount
- A study of dietary intake of total sugars by elementary students in Jeju province
- Glycemic Variability and Diabetes Mellitus