Ann Dermatol.
2014 Dec;26(6):675-680. 10.5021/ad.2014.26.6.675.
The Expression and Role of Kruppel-Like Factor 4 in Psoriasis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea. dermakkh@naver.com
- 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2264860
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2014.26.6.675
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) is a transcription factor that regulates a diverse array of cellular processes, including development, differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis. Although its function in keratinocytes has been widely studied, its exact role in psoriasis has not been elucidated.
OBJECTIVE
We designed this study to investigate epidermal expression levels of KLF4 and the change in KLF4 expression after treatment in patients with psoriasis.
METHODS
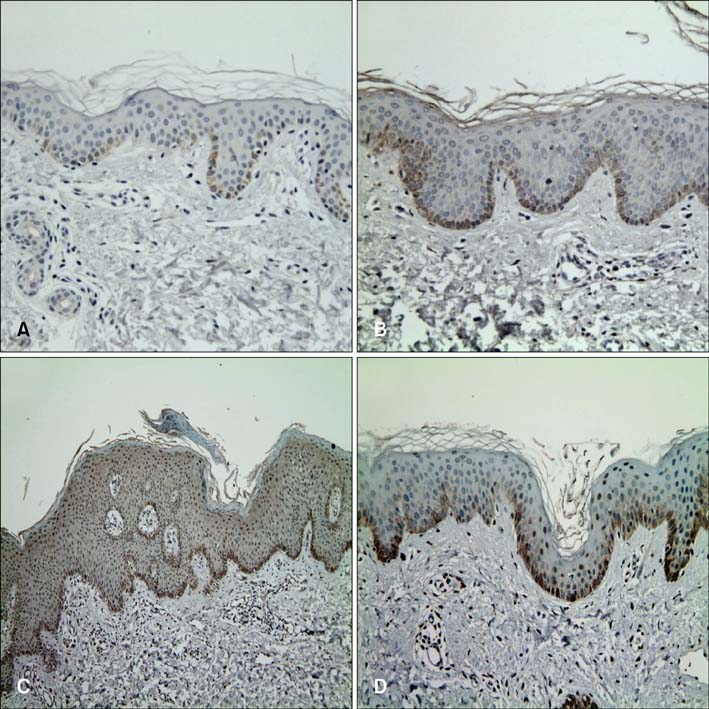
We compared the expression levels of KLF4 in the basal, suprabasal, and superficial epidermal layers, in psoriatic lesional, non-lesional, and normal skin, using an immunoreactivity intensity distribution index (IRIDI). In addition, we measured the change in KLF4 expression on the basis of the IRIDI and by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis after treatment.
RESULTS
The combined IRIDI scores in psoriatic lesional skin were significantly higher than the scores in both non-lesional and normal skin. The psoriatic epidermis, particularly the suprabasal layer, showed a significantly increased IRIDI score compared to that of non-lesional and normal skin, which was significantly decreased after treatment. RT-PCR analysis exhibited a slight increase in KLF4 mRNA expression level after treatment; however, this increase was not significant.
CONCLUSION
These data indicate that KLF4 could regulate epidermal proliferation and differentiation. Moreover, we believe that KLF4 may play an important role in the physiological reaction to counteract abnormal differentiation and proliferation of keratinocytes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kaczynski J, Cook T, Urrutia R. Sp1- and Krüppel-like transcription factors. Genome Biol. 2003; 4:206.2. McConnell BB, Ghaleb AM, Nandan MO, Yang VW. The diverse functions of Krüppel-like factors 4 and 5 in epithelial biology and pathobiology. Bioessays. 2007; 29:549–557.
Article3. Pearson R, Fleetwood J, Eaton S, Crossley M, Bao S. Krüppel-like transcription factors: a functional family. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008; 40:1996–2001.
Article4. Garrett-Sinha LA, Eberspaecher H, Seldin MF, de Crombrugghe B. A gene for a novel zinc-finger protein expressed in differentiated epithelial cells and transiently in certain mesenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 1996; 271:31384–31390.
Article5. Shields JM, Christy RJ, Yang VW. Identification and characterization of a gene encoding a gut-enriched Krüppellike factor expressed during growth arrest. J Biol Chem. 1996; 271:20009–20017.
Article6. Conkright MD, Wani MA, Anderson KP, Lingrel JB. A gene encoding an intestinal-enriched member of the Krüppel-like factor family expressed in intestinal epithelial cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999; 27:1263–1270.
Article7. Segre JA, Bauer C, Fuchs E. Klf4 is a transcription factor required for establishing the barrier function of the skin. Nat Genet. 1999; 22:356–360.
Article8. Tsoi LC, Spain SL, Knight J, Ellinghaus E, Stuart PE, Capon F, et al. Identification of 15 new psoriasis susceptibility loci highlights the role of innate immunity. Nat Genet. 2012; 44:1341–1348.
Article9. Madonna S, Scarponi C, Sestito R, Pallotta S, Cavani A, Albanesi C. The IFN-gamma-dependent suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 promoter activity is positively regulated by IFN regulatory factor-1 and Sp1 but repressed by growth factor independence-1b and Krüppel-like factor-4, and it is dysregulated in psoriatic keratinocytes. J Immunol. 2010; 185:2467–2481.
Article10. Chaiyarit P, Kafrawy AH, Miles DA, Zunt SL, Van Dis ML, Gregory RL. Oral lichen planus: an immunohistochemical study of heat shock proteins (HSPs) and cytokeratins (CKs) and a unifying hypothesis of pathogenesis. J Oral Pathol Med. 1999; 28:210–215.
Article11. Jaubert J, Cheng J, Segre JA. Ectopic expression of kruppel like factor 4 (Klf4) accelerates formation of the epidermal permeability barrier. Development. 2003; 130:2767–2777.
Article12. Chen X, Whitney EM, Gao SY, Yang VW. Transcriptional profiling of Krüppel-like factor 4 reveals a function in cell cycle regulation and epithelial differentiation. J Mol Biol. 2003; 326:665–677.
Article13. Chen X, Johns DC, Geiman DE, Marban E, Dang DT, Hamlin G, et al. Krüppel-like factor 4 (gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor) inhibits cell proliferation by blocking G1/S progression of the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:30423–30428.
Article14. Feinberg MW, Cao Z, Wara AK, Lebedeva MA, Senbanerjee S, Jain MK. Kruppel-like factor 4 is a mediator of proinflammatory signaling in macrophages. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280:38247–38258.
Article15. Yamada T, Park CS, Mamonkin M, Lacorazza HD. Transcription factor ELF4 controls the proliferation and homing of CD8+ T cells via the Krüppel-like factors KLF4 and KLF2. Nat Immunol. 2009; 10:618–626.
Article16. Rowland BD, Bernards R, Peeper DS. The KLF4 tumour suppressor is a transcriptional repressor of p53 that acts as a context-dependent oncogene. Nat Cell Biol. 2005; 7:1074–1082.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Coexistence of Bullous Pemphigoid and Psoriasis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Comparison of the Expression Profile of JunB, c-Jun, and S100A8 (Calgranulin A) in Psoriasis Vulgaris and Guttate Psoriasis
- Immunohistochemical studies of Interleukin-8 and Tumor necrosis factor-alpha on psoriatic lesions
- Potential Role of Cytosolic RNA Sensor MDA5 as an Inhibitor for Keratinocyte Differentiation in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis
- Infliximab: Effective Therapy for Pustular Psoriasis