Sensitization rates to inhalant allergens in children and adolescents of Incheon and Asan area and the relationship between polysensitization and prevalence of allergic diseases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Korea Cancer Center Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sjhong@amc.seoul.kr
- 4Childhood Asthma Atopy Center, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Preventive Medicine, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- 6Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- 7Department of Information Statistics, Korean National Open University, College of Natural Science, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Statistics, Bukyong National University, College of Natural Science, Busan, Korea.
- 9Institute for Environmental Research, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- 10Institute of Environmental Safety and Protection, Neo Environmental Business Co., Bucheon, Korea.
- 11Department of Adolescent Psychiatry, National Center for Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Seoul National Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 12Department of Preventive Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, School of Dentistry, Daegu, Korea.
- 13Department of Pediatrics, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- 14Cancer Epidemiology Branch, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- 15Department of Environmental Health Research, National Institute of Environmental Research, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2263058
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2013.1.1.41
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Sensitization to allergens is considered as major mechanism of allergy and related to the development of allergic diseases. The objective of this study was to evaluate overall sensitization rates of inhalant allergens and the relationship between polysensitization and prevalence of allergic diseases in children and adolescents.
METHODS
A cross-sectional pilot study of 122 elementary school students, 114 middle school students, and 115 high school students from Incheon and Asan was conducted by using the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISSAC) questionnaire. The skin prick tests were performed with 14 common inhalant allergens on 339 students.
RESULTS
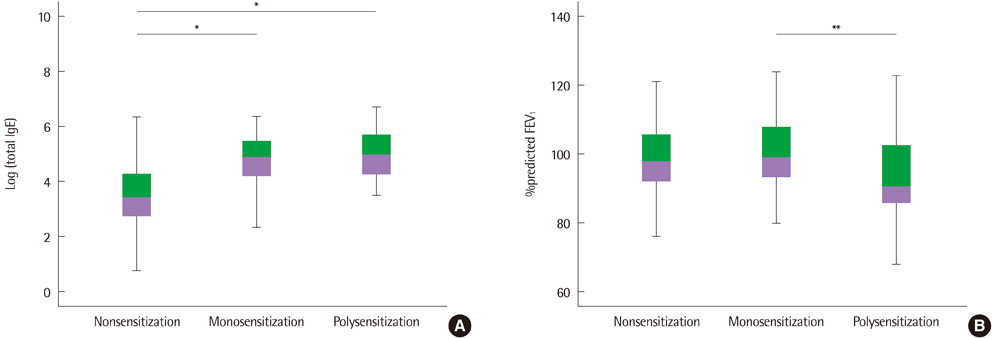
The inhalant allergen that has a significantly different sensitization rate according to age was Dermatophagoides farinae. And the inhalant allergen that has significantly different sensitization rate according to region was Japanese hop. In addition, girls have higher sensitization rate to any mold allergens than boys. In case of having sensitization more than two allergens, the risks of diagnosis of asthma and allergic rhinitis on questionnaire were increased. Asthma is related to sensitization of dog or cat and allergic rhinitis is related to sensitization of house dust mites. However, atopic dermatitis is not related to sensitization of any inhalant allergens.
CONCLUSION
The sensitization rates of inhalant allergens may differ among age, gender, and region in children and adolescents of Incheon and Asan area. The polysensitized children and adolescents with inhalant allergens showed higher prevalences of allergic diseases such as asthma and allergic rhinitis on questionnaire than monosensitized group.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 6 articles
-
The prevalence and risk factors of allergic rhinitis from a nationwide study of Korean elementary, middle, and high school students
Yeongho Kim, Ju-Hee Seo, Ji-Won Kwon, Eun Lee, Song-I Yang, Hyun-Ju Cho, Mina Ha, Eunae Burm, Kee-Jae Lee, Hwan-Cheol Kim, Sinye Lim, Hee-Tae Kang, Mia Son, Soo-Young Kim, Hae-Kwan Cheong, Yu-Mi Kim, Gyung-Jae Oh, Joon Sakong, Chul-Gab Lee, Sue Jin Kim, Yong-Wook Beak, Soo-Jong Hong
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015;3(4):272-280. doi: 10.4168/aard.2015.3.4.272.Prevalence of atopic dermatitis and its associated factors for elementary school children in Gyeonggi-do province
Eunji Kim, Soohyun Ri, Sung Chul Seo, Ji Tae Choung, Young Yoo
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2016;4(5):346-353. doi: 10.4168/aard.2016.4.5.346.Research on pediatric allergic rhinitis in Korea
Kyung Suk Lee, Yeong Ho Rha
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(Suppl 1):S58-S65. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.S1.S58.Parental burden of food-allergic children's parents and influencing factors
EunSun Lee, KyooSang Kim
J Nutr Health. 2018;51(2):140-152. doi: 10.4163/jnh.2018.51.2.140.Proper allergen selection for serum specific IgE test in children
Yong Ju Lee, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Jong-Seo Yoon, Man-Yong Han, Chang Keun Kim, Jin Tack Kim
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(5):237-240. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.5.237.Environmental Factors Affecting Prevalence of Allergic Diseases in Elementary School Children in a Province
Hyun Kim
Korean J Health Promot. 2022;22(1):10-17. doi: 10.15384/kjhp.2022.22.1.10.
Reference
-
1. Downs SH, Marks GB, Sporik R, Belosouva EG, Car NG, Peat JK. Continued increase in the prevalence of asthma and atopy. Arch Dis Child. 2001. 84:20–23.
Article2. Johnson CC, Ownby DR, Zoratti EM, Alford SH, Williams LK, Joseph CL. Environmental epidemiology of pediatric asthma and allergy. Epidemiol Rev. 2002. 24:154–175.
Article3. Kwon JW, Kim BJ, Song Y, Seo JH, Kim TH, Yu J, et al. Changes in the prevalence of childhood asthma in seoul from 1995 to 2008 and its risk factors. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2011. 3:27–33.
Article4. Suh M, Kim HH, Sohn MH, Kim KE, Kim C, Shin DC. Prevalence of allergic diseases among Korean school-age children: a nationwide cross-sectional questionnaire study. J Korean Med Sci. 2011. 26:332–338.
Article5. Dean T, Venter C, Pereira B, Arshad SH, Grundy J, Clayton CB, et al. Patterns of sensitization to food and aeroallergens in the first 3 years of life. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007. 120:1166–1171.
Article6. Arbes SJ Jr, Gergen PJ, Vaughn B, Zeldin DC. Asthma cases attributable to atopy: results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007. 120:1139–1145.
Article7. Chan-Yeung M, Hegele RG, Dimich-Ward H, Ferguson A, Schulzer M, Chan H, et al. Early environmental determinants of asthma risk in a high-risk birth cohort. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2008. 19:482–489.
Article8. Kim SH, Kang HR, Kim KM, Kim TB, Kim SS, Chang YS, et al. The sensitization rates of food allergens in a Korean population: a multi-center study. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. 23:502–514.9. Kim YJ, Han JE, Kang IJ. Change of inhalant allergen sensitization in children with allergic respiratory diseases during recent 10 years. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004. 24:241–246.10. Choi BS, Lee YJ, Baek JY, Kim KW, Sohn MH, Kim KE. Prevalence of sensitization to tyrophagus putrescentiae in children with allegic diseases. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2010. 20:107–113.11. Lee JW, Choi GS, Kim JE, Jin HJ, Kim JH, Ye YM, et al. Changes in sensitization rates to pollen allergens in allergic patients in the southern part of gyeonggi province over the last 10 years. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011. 31:33–40.12. Jeon BH, Lee J, Kim JH, Kim JW, Lee HS, Lee KH. Atopy and sensitization rates to aeroallergens in children and teenagers in Jeju, Korea. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. 30:14–20.13. Jung HH, Kwon JW, Lee SY, Seo JH, Song YH, Kim BJ, et al. Correlation between demographic characteristics and indoor allergen sensitization among Jeongeup countryside, Jeongeup city, and Seoul city in Korea. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. 30:277–284.14. Kim J, Hahm MI, Lee SY, Kim WK, Chae Y, Park YM, et al. Sensitization to aeroallergens in Korean children: a population-based study in 2010. J Korean Med Sci. 2011. 26:1165–1172.
Article15. Park SH, Lim DH, Son BK, Kim JH, Song YE, Oh IB, et al. Sensitization rates of airborne pollen and mold in children. Korean J Pediatr. 2012. 55:322–329.
Article16. Kim JH, Oh JW, Lee HB, Kim SW, Kang IJ, Kook MH, et al. Changes in sensitization rate to weed allergens in children with increased weeds pollen counts in Seoul metropolitan area. J Korean Med Sci. 2012. 27:350–355.
Article17. Croner S, Kjellman NI. Development of atopic disease in relation to family history and cord blood IgE levels. Eleven-year follow-up in 1654 children. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 1990. 1:14–20.
Article18. Silvestri M, Oddera S, Rossi GA, Crimi P. Sensitization to airborne allergens in children with respiratory symptoms. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1996. 76:239–244.
Article19. Kim KW, Kim EA, Kwon BC, Kim ES, Song TW, Sohn MH, et al. Comparison of allergic indices in monosensitized and polysensitized patients with childhood asthma. J Korean Med Sci. 2006. 21:1012–1016.
Article20. Lee JH, Kim JH, Yun SW, Han YS, Ahn K, Chae SA, et al. Differences of the clinical manifestations and laboratory tests between monosensitized and polysensitized children: a single center study. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2011. 21:277–284.
Article21. Kim KH, Kim KT, Lee SK, Park HS, Lee YM, Nahm DH, et al. Sensitization rates for inhalant allergens in patients with respiratory allergy in Busan. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005. 25:59–63.22. Park HS, Nahm DH, Kim HY, Suh YJ, Cho JW, Kim SS, et al. Clinical and immunologic changes after allergen immunotherapy with Hop Japanese pollen. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001. 86:444–448.
Article23. Roberts G, Peckitt C, Northstone K, Strachan D, Lack G, Henderson J, et al. Relationship between aeroallergen and food allergen sensitization in childhood. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005. 35:933–940.
Article24. Kim BS, Jin HS, Kim HB, Lee SY, Kim JH, Kwon JW, et al. Airway hyperresponsiveness is associated with total serum immunoglobulin E and sensitization to aeroallergens in Korean adolescents. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2010. 45:1220–1227.
Article25. McGrath JA, Uitto J. The filaggrin story: novel insights into skin-barrier function and disease. Trends Mol Med. 2008. 14:20–27.
Article26. Palmer CN, Irvine AD, Terron-Kwiatkowski A, Zhao Y, Liao H, Lee SP, et al. Common loss-of-function variants of the epidermal barrier protein filaggrin are a major predisposing factor for atopic dermatitis. Nat Genet. 2006. 38:441–446.
Article27. Baurecht H, Irvine AD, Novak N, Illig T, Buhler B, Ring J, et al. Toward a major risk factor for atopic eczema: meta-analysis of filaggrin polymorphism data. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007. 120:1406–1412.
Article28. Elias PM, Hatano Y, Williams ML. Basis for the barrier abnormality in atopic dermatitis: outside-inside-outside pathogenic mechanisms. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008. 121:1337–1343.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Determinants of sensitization to allergen in infants and young children
- Comparison of inhalant allergen sensitization between children, adolescents, and adults with asthma and allergic rhinitis
- Sensitization to Inhalant Allergens and Its Association with Allergic Diseases in Preschool Children
- Change of Inhalant Allergen Sensitization in Children with Allergic Respiratory Diseases during Recent 10 Years
- A comparison of Sensitization to Major Indoor & Outdoor Inhalant Allergens in Children with Respiratory Allergic Diseases