Korean J Crit Care Med.
2015 Aug;30(3):151-157. 10.4266/kjccm.2015.30.3.151.
The Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Arginine-Vasopressin on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced IkappaBalpha/Nuclear Factor-kappaB Cascade
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Bundang CHA Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Respiratory Center, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. lungdrcho@gmail.com
- 3Division of Pulmonology and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Lung Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2227639
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/kjccm.2015.30.3.151
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Arginine vasopressin (AVP) is widely used as a vasopressor agent. Some recent studies have suggested that AVP may exert an immunomodulatory effect. However, the mechanism about the anti-inflammatory effect of AVP is not well known. We investigated the effect of AVP on the ihibitor of kappa B (IkappaBalpha)/nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB) pathway in RAW 264.7 cells.
METHODS
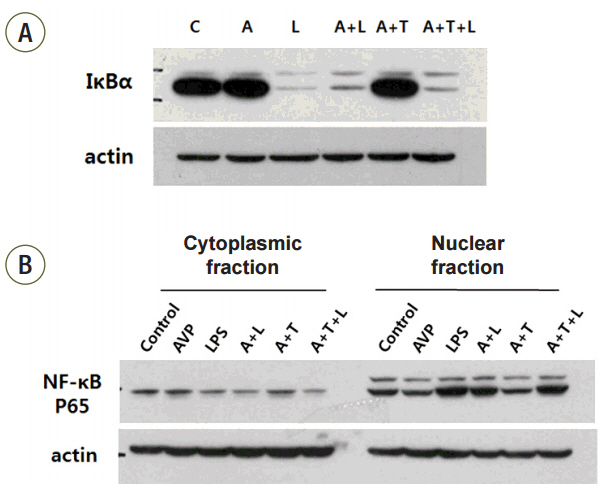
Cultured RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with AVP and stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). To evaluate the effect of AVP on inflammatory cytokines, the concentration of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) were assessed by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technique. The expression of IkappaBalpha and nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB p65 were measured by Western blotting, and IkappaB kinase (IKK) activity was analyzed by an in vitro immune complex kinase assay. To confirm the AVP effect on IkappaBalpha/NF-kappaB cascade and via V2 receptor, we added tolvaptan (V2 receptor antagonist) after AVP pretreatment.
RESULTS
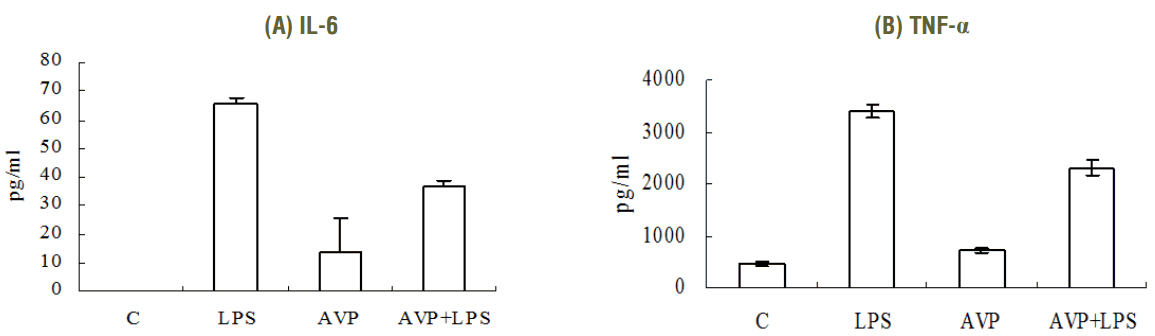
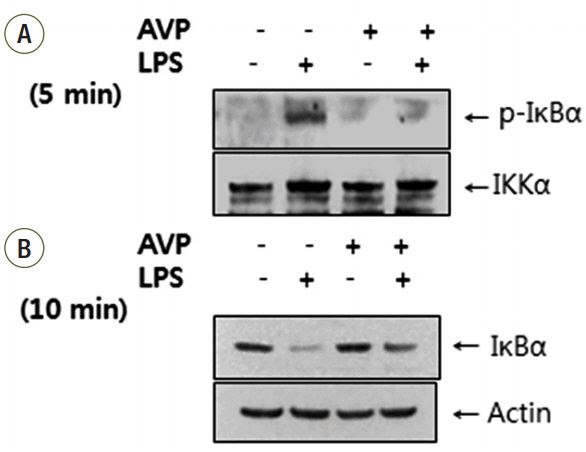
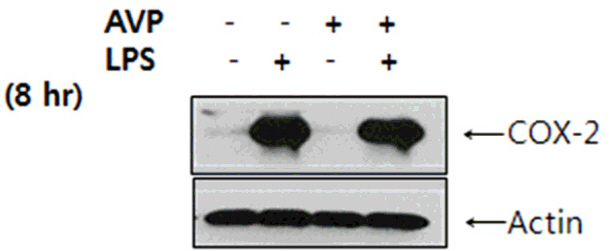
The increase of IL-6 and TNF-alpha in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells was suppressed by a treatment with AVP. Pretreatment of AVP inhibited increasing of IKK activity and IkappaBalpha degradation induced by LPS in RAW 264.7 cells. Furthermore, LPS induced and NF-kappaB transcription was inhibited by AVP pretreatment. The observed changes in IKK activity, IkappaBalpha degradation and NF-kappaB transcription by AVP was abolished by tolvaptan treatment.
CONCLUSIONS
Our results suggest that AVP showed anti-inflammatory effect on LPS-induced IkappaBalpha/NF-kappaB cascade in mouse macrophages via V2 receptors.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Antigen-Antibody Complex
Arginine Vasopressin
Blotting, Western
Cytokines
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
I-kappa B Kinase
Interleukin-6
Macrophages
Mice
NF-kappa B
Phosphotransferases
Receptors, Vasopressin
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Antigen-Antibody Complex
Arginine Vasopressin
Cytokines
I-kappa B Kinase
Interleukin-6
NF-kappa B
Phosphotransferases
Receptors, Vasopressin
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Yoon JY, Kwon JY. Inflammation and sepsis. Korean J Crit Care Med. 2010; 25:1–8.
Article2. Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit Care Med. 2013; 41:580–637.
Article3. Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, Pinsky MR. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 2001; 29:1303–10.
Article4. Vincent JL. EPIC II: sepsis around the world. Minerva Anestesiol. 2008; 74:293–6.5. Christman JW, Lancaster LH, Blackwell TS. Nuclear factor kappa B: a pivotal role in the systemic inflammatory response syndrome and new target for therapy. Intensive Care Med. 1998; 24:1131–8.6. Barnes PJ, Karin M. Nuclear factor-kappaB: a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med. 1997; 336:1066–71.7. Landry DW, Levin HR, Gallant EM, Seo S, D'Alessandro D, Oz MC, et al. Vasopressin pressor hypersensitivity in vasodilatory septic shock. Crit Care Med. 1997; 25:1279–82.
Article8. Landry DW, Levin HR, Gallant EM, Ashton RC Jr, Seo S, D'Alessandro D, et al. Vasopressin deficiency contributes to the vasodilation of septic shock. Circulation. 1997; 95:1122–25.
Article9. Holmes CL, Walley KR, Chittock DR, Lehman T, Russell JA. The effects of vasopressin on hemodynamics and renal function in severe septic shock: a case series. Intensive Care Med. 2001; 27:1416–21.
Article10. Patel BM, Chittock DR, Russell JA, Walley KR. Beneficial effects of short-term vasopressin infusion during severe septic shock. Anesthesiology. 2002; 96:576–82.
Article11. Dhingra VK, Uusaro A, Holmes CL, Walley KR. Attenuation of lung inflammation by adrenergic agonists in murine acute lung injury. Anesthesiology. 2001; 95:947–53.
Article12. Pastores SM, Hasko G, Vizi ES, Kvetan V. Cytokine production and its manipulation by vasoactive drugs. New Horiz. 1996; 4:252–64.13. Uusaro A, Russell JA. Could anti-inflammatory actions of catecholamines explain the possible beneficial effects of supranormal oxygen delivery in critically ill surgical patients? Intensive Care Med. 2000; 26:299–304.
Article14. Treschan TA, Peters J. The vasopressin system: physiology and clinical strategies. Anesthesiology. 2006; 105:599–612. quiz 639-40.15. Kampmeier TG, Rehberg S, Westphal M, Lange M. Vasopressin in sepsis and septic shock. Minerva Anestesiol. 2010; 76:844–50.16. Sharshar T, Blanchard A, Paillard M, Raphael JC, Gajdos P, Annane D. Circulating vasopressin levels in septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2003; 31:1752–8.
Article17. Lemmens-Gruber R, Kamyar M. Vasopressin antagonists. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006; 63:1766–79.
Article18. Holmes CL, Patel BM, Russell JA, Walley KR. Physiology of vasopressin relevant to management of septic shock. Chest. 2001; 120:989–1002.
Article19. Boyd JH, Holmes CL, Wang Y, Roberts H, Walley KR. Vasopressin decreases sepsis-induced pulmonary inflammation through the V2R. Resuscitation. 2008; 79:325–31.
Article20. Chassin C, Hornef MW, Bens M, Lotz M, Goujon JM, Vimont S, et al. Hormonal control of the renal immune response and antibacterial host defense by arginine vasopressin. J Exp Med. 2007; 204:2837–52.
Article21. Blackwell TS, Christman JW. The role of nuclear factor-kappa B in cytokine gene regulation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1997; 17:3–9.22. Siebenlist U, Franzoso G, Brown K. Structure, regulation and function of NF-kappa B. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1994; 10:405–55.23. Christman JW, Sadikot RT, Blackwell TS. The role of nuclear factor-kappa B in pulmonary diseases. Chest. 2000; 117:1482–7.24. Sarkar FH, Li Y, Wang Z, Kong D. NF-kappaB signaling pathway and its therapeutic implications in human diseases. Int Rev Immunol. 2008; 27:293–319.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Altered secretion of arginine vasopressin in children with CNS diseases
- (E)-3-(3-methoxyphenyl)-1-(2-pyrrolyl)-2-propenone displays suppression of inflammatory responses via inhibition of Src, Syk, and NF-kappaB
- Anti-inflammatory Mechanism of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in Lipopolysaccharide-stimulated HT-29 Cell
- Aromadendrin Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Nuclear Translocation of NF-kappaB and Phosphorylation of JNK in RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells
- Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Mangostenone F in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophages by Suppressing NF-kappaB and MAPK Activation